Theory of karst dynamics and development of modern karst science
-
摘要:
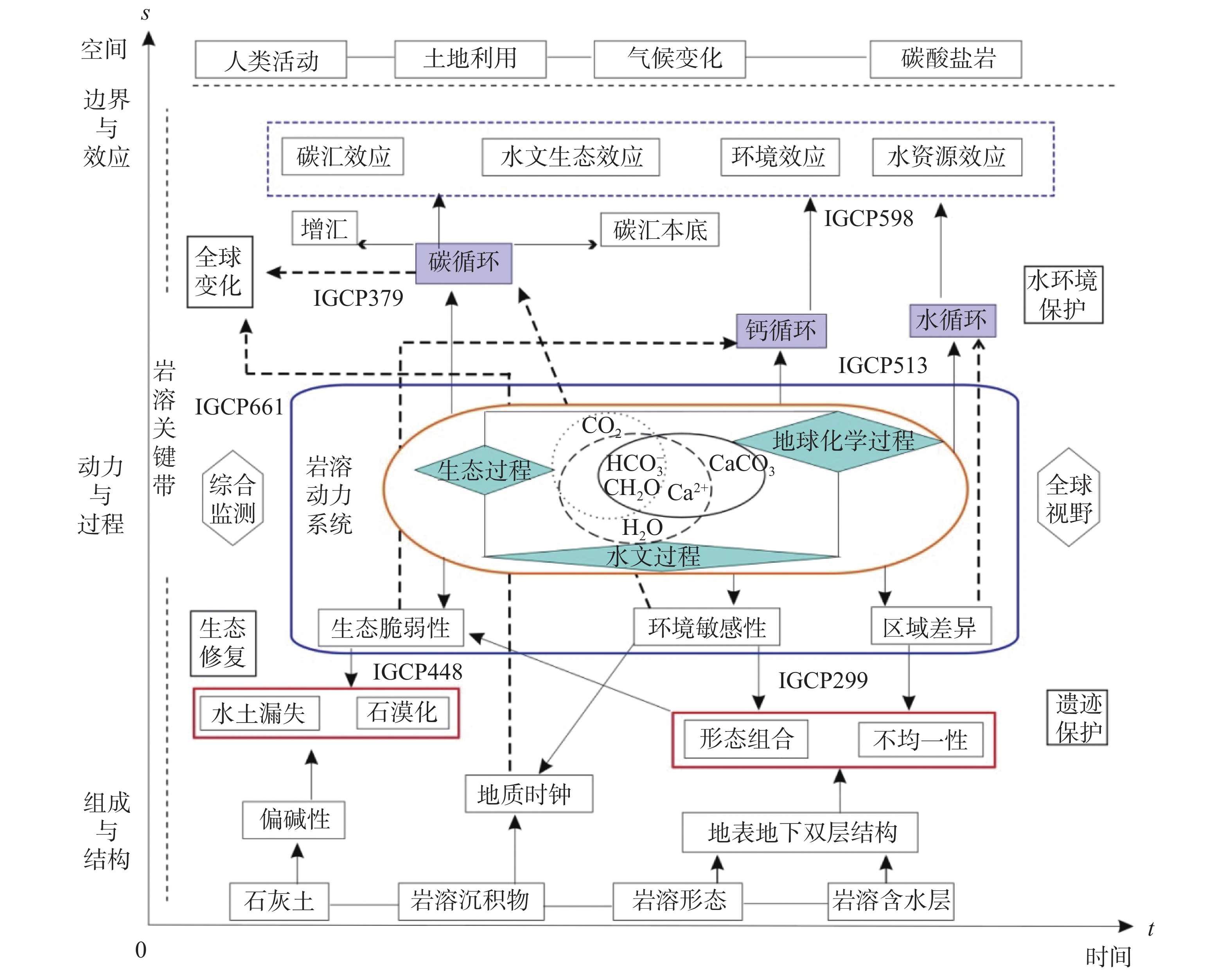
岩溶动力学理论的核心是碳水钙循环,强调系统思维和全球视野观,提出了岩溶动力系统概念模型、结构与功能。岩溶动力学研究产生的新的学科生长点,对现代岩溶学形成与发展具有里程碑式的意义。“岩溶形态组合”概念的提出为岩溶不均一性研究、岩溶类型与形成环境划分奠定了完整的方法体系;将岩溶学研究成功引入全球变化领域,由此开辟了岩溶碳循环与碳汇效应研究,为重新认识岩溶作用在全球碳循环中的地位打开了窗口;将岩溶地球化学研究延伸至无机与有机过程的融合研究,为脆弱岩溶环境修复与保护提供了更加清晰的思路与方法。岩溶IGCP项目的执行,体现了岩溶动力学理论为建立联合国教科文组织国际岩溶研究中心的指导意义,同时,岩溶动力学理论为我们自觉融入国家“一带一路”倡议、生态文明发展战略和“双碳”目标等奠定了坚实的理论与方法基础。
Abstract:The core of the theory of karst dynamics is the carbon-water-calcium cycle, which emphasizes the systematic thinking and global view, and puts forward the conceptual model, structure and function of the karst dynamic system. The new growing point of discipline resulted from karst dynamics research has a milestone significance for the formation and development of modern karst science. The concept of "karst feature complex" has laid a complete method system for the study of karst heterogeneity, classification of karst types and formation environment. The initiation study of karst carbon cycle and carbon sink effects has successfully introduced karstology study into the field of global change, which opens a window for recognizing the role of karst processes in the global carbon cycle. Moreover, extending the study of karst geochemistry to the integration of inorganic and organic processes provides a clearer idea and method for the restoration and protection of fragile karst environment. The implementation of karst IGCP project reflects the guiding significance of karst dynamics theory for the establishment of International Karst Research Center under the auspices of UNESCO, meanwhile, karst dynamics theory has laid a solid theoretical and method foundation for us to consciously integrate into the national "Belt and Road" initiative, ecological civilization development strategy and the goals of "double carbon".
-

-
[1] White W B. Geomorphology and hydrology of karst terains[M]. New York: Oxford University Press, 1988: 1-464.
[2] 袁道先, 蔡桂鸿. 岩溶环境学[M]. 重庆: 重庆出版社, 1988: 1-332.
YUAN Daoxian, CAI Guihong. Karst environment[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing Publishing House, 1988: 1-332.
[3] 朱学稳, 汪训一, 朱德浩, 等. 桂林岩溶地貌与洞穴研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1988: 1-249.
ZHU Xueweng, WANG Xunyi, ZHU Dehao, et al. Guilin karst geomorphology and cave study[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1988: 1-249.
[4] Ford D C, Williams P W. Karst geomorphology and hydrology[M]. London: Unwin Hyman, 1989: 1-601.
[5] Yuan D, Zhu D, Weng J, et al. Karst of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1991, 224 p.
[6] Ford D C, Williams P. Karst hydrogeology and geomorphology[M]. London: John Wiley and Sons Ltd. 2007: 1-562.
[7] Goldscheider N, Drew D (Eds). Methods in karst hydrogeology[M]. Leiden: Taylor & Francis, 2007, 264 p.
[8] 袁道先. 现代岩溶学和全球变化研究[J]. 地学前缘( 中国地质大学,北京), 1997, 4(1-2):17-25. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1997.01.003
[9] 袁道先. 碳循环与全球岩溶[J]. 第四纪研究. 1993a, 13(1): 1-6.
YUAN Daoxian. Carbon cycle and global karst[J].Quaternary Sciences,1993a,13(1):1-6.
[10] Yuan Daoxian. IGCP448, World correlation of karst ecosystem (2000–2004)[J]. Episodes, 2000, 23(4):285-286.
[11] 袁道先, 蒋勇军, 沈立成, 等. 现代岩溶学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 1-363.
YUAN Daoxian, JIANG Yongjun, SHEN Licheng, et al. Modern karstology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 1-363.
[12] Yuan Daoxian, On the karst ecosystem [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2001, 75(3): 336- 338.
[13] Yuan Daoxian, Liu Zaihua (Eds). Global karst correlation [M]. Utrecht, Netherlands/Beijing, New York: Science Press. 1998, 308 pages.
[14] Yuan D, Summary of IGC P379“ Karst Processes and the Carbon Cycle” (1995-1999) [A] . In: Yuan D, Zhang C (Eds), Karst processes and the carbon cycle-final report of IGCP379 [C]. Beijing: Geological Publishing Hous e. 2002: 1- 32.
[15] 袁道先, 章程. 岩溶动力学的理论探索与实践[J]. 地球学报, 2008, 29(3):355-365. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.03.009
YUAN Daoxian, ZHANG Cheng. Karst dynamics theory in China and its practice[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2008, 29(3):355-365. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.03.009
[16] National Research Council. Basic research opportunities in earth science [M]. Washington D C: National Academy Press, 2001, Chapter 2: 35-45.
[17] Brantley S L, White T S, White A F. Frontiers in exploration of the critical zone [R]. USA, 2005.
[18] Chris Groves, Yuan Daoxian, Zhang Cheng. IGCP 299, 379, 448, 513, 598: Global efforts to understand the nature of karst systems: over two decades with the IGCP[A]. In: Derbyshire E(Editor). Tales Set in Stone–40 years of the International Geoscience Programme. Paris: UNESCO, 2012: 80-87.
[19] Yuan Daoxian. Sensitivity of karst process to environmental change alone the PEP II Transect[J]. Quaternary International, 1997, 37: 105-113.
[20] Regnier P, Friedlingstein P, Ciais P, et al. Anthropogenic perturbation of the carbon fluxes from land to ocean[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6(8): 597-607.
[21] Ciais P, Sabine C, Bala G, et al. Carbon and other biogeochemical cycles//Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis[A]. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014: 465-570.
[22] Zhang Cheng, Yuan Daoxian. New development of IGCP 448 “World Correlation of Karst Ecosystem (2000–2004)”[J]. Episodes, 2001, 24(4):279-280.
[23] Zhang Cheng, Chris Groves, Yuan Daoxian. New development of IGCP/SIDA 598 “Environmental Change and Sustainability in Karst Systems (2011-2015)”[J]. Episodes, 2015, 38(3): 219-221.
[24] Yuan DX. Contribution of IGCP379 “Karst Processes and Carbon Cycle” to Global Change[J]. Episodes, 1998, 21(3): 198.
[25] 袁道先, 蒋忠诚. IGCP379“岩溶作用与碳循环”在中国的研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2000, 27(1): 49-51.
YUAN Daoxian, JIANG Zhongcheng. Progress of IGCP379 “Karst Processes and Carbon Cycle” in China. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2000, 27(1): 49-51.
[26] Yuan D X, Zhang C(Eds). Karst Processes and the carbon cycle-Final Report of IGCP379. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. 2002, 1-220.
[27] Merkel B J, Planer-Friedrich B. Groundwater geochemistry[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2005, 1-200.
[28] Zhang C, Yuan D X, Cao J H. Analysis of the environmental sensitivities of a typical dynamic epikarst system at the Nongla monitoring site, Guangxi, China[J]. Environmental Geology, 2005, 47: 615–619.
[29] Zhang C. Carbonate rock dissolution rates in different landuses and their carbon sink effect[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(35): 3759-3765.
[30] Liu Z, Liu X, Liao C. Daytime deposition and nighttime dissolution of calcium carbonate controlled by submerged plants in a karst spring-fed pool: insights from high time-resolution monitoring of physico-chemistry of water[J]. Environmental Geology. 2008, 55, 1159-1168.
[31] Zhang C, Wang J L, Pu J B, et al. Bicarbonate daily variations in a karst river: the carbon sink effect of subaquatic vegetation photosynthesis[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2012, 86(4): 973-979.
[32] 肖琼, 赵海娟, 章程, 贺秋芳,吴夏. 岩溶区地表水体惰性有机碳研究[J]. 第四纪研究. 2020, 40(4): 1058-1069.
XIAO Qiong, ZHAO Haijuan, ZHANG Cheng, HE Qiufang,WU Xia. Study of the recalcitrant dissolved organic carbon in karst surface water[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2020, 40(4): 1058-1069.
[33] He Q F, Xiao Q, Fan J X, et al. The impact of heterotrophic bacteria on recalcitrant dissolved organic carbon formation in a typical karstic river[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 815 152576.
[34] 刘再华, Dreybrodt W, 王海静. 一种由全球水循环产生的可能重要的CO2汇[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(20): 2418-2422.
LIU Zaihua, Dreybrodt W, WANG Haijing. A potentially important CO2 sink caused by the global water cycle. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(20): 2418-2422.
[35] Yuan D X. Foreword for the special topic “Geological Processes in Carbon Cycle”[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(35): 3741-3742.
[36] Andrews J A, Schlesinger W H. Soil CO2 dynamics, acidification, and chemical weathering in a temperate forest with experimental CO2 enrichment[J]. Global Biogeochemical cycles, 2001, 15(1): 149-162.
[37] Schindlbacher A, Borken W, Djukic I, et al. Contribution of carbonate weathering to the CO2 efflux from temperate forest soils[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2015, 124:273-290. doi: 10.1007/s10533-015-0097-0
[38] Zhang C, Xiao Q, Wu Z, et al. Ecosystem-driven karst carbon cycle and carbon sink effects[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 2022, 10(2): 99-112.
[39] http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-10/26/content_5644984.htm.
[40] 袁道先, 刘再华, 林玉石, 等. 中国岩溶动力系统[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002: 1-275.
YUAN Daoxian, LIU Zaihua, LIN Yushi, et al. Karst dynamic systems in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2002:1-275.
-



 下载:
下载: