Characteristics and influencing factors of heavy metal accumulation in soil-crop system in the karst area with high geological background of Chongqing
-
摘要:
为了揭示重庆岩溶地质高背景区土壤-农作物系统中重金属的迁移累积特征,选择在重庆市南部典型岩溶区,系统地采集大宗农作物(水稻、玉米和红薯)及其耕层土壤84组,分析测定农作物及耕层土壤中重金属砷(As)、镉(Cd)、铬(Cr)、铜(Cu)、汞(Hg)、镍(Ni)、锌(Zn)含量及理化性质,采用地统计、生物富集因子及皮尔逊相关系数分析等方法,开展重金属元素在重庆岩溶地质高背景地区土壤−农作物系统中累积特征及影响因素。结果表明,研究区水稻田、玉米地和红薯地耕层土壤重金属平均含量均高于重庆市和全国表层土壤背景值,呈现不同程度的积累,其中Cd元素富集现象较为突出。依据GB 15618-2018和GB 2762-2017,耕层土壤种Cd超标率达41.59%,水稻、玉米和红薯中Cd超标率分别为5.89%、6.25%和5.56%,显示出岩溶地质高背景区虽然土壤中重金属含量总量高,但生物有效性较低。相关分析显示,土壤-农作物系统Cd等重金属含量主要受土壤pH、土壤质地和土壤中铁锰氧化物影响。
Abstract:Heavy metal pollution in agricultural soil has been attracted worldwide attention for its negative effects on food safety and soil environmental quality, particularly in developing countries, e.g., China. Numerous studies investigated concentrations of heavy metals in soil in relation to different factors, such as high geological background, agricultural activities, industrial activities, mining and transportation. Generally, two different sources of heavy metal accumulated in soil have been put forward, (i) heavy metals from human activities, such as agricultural production, mining and industrial activities, urban life, and from other pollution, such as sewage irrigation, atmospheric sedimentation and incineration, and landfill of domestic waste, and (ii) heavy metals from geological background primarily due to the high content of heavy metals in the parent material itself, which leads to their accumulation in soils. According to China’s National Survey of Soil Pollution, the soil in the southwestern area of China has been heavily polluted by heavy metals, especially cadmium (Cd), and the high geological background is an important factor leading to excessive heavy metals in soil. The heavy metals contained in soil is mainly derived from the primary minerals of rock. In Southwest China, karst areas are widely distributed where trace elements are rich in soil, hence presenting typical characteristics of high geochemical background. Therefore, soil ecological risk has gradually attracted extensive attention. Heavy metals migrate into soil in various forms and then are transported through the food chain, threatening food safety and human health. In order to investigate the effects of heavy metals in soil-crop systems in the karst areas with high geological background of Chongqing, 84 sets of major crops (rice, corn and sweet potato) and the top soil were collected from the south of Chongqing, and the concentrations of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni and Zn and physical and chemical properties of soil were analyzed and determined. Accumulation characteristics and influencing factors of heavy metals in soil and crops were analyzed and determined by geostatistics, bioenrichment factor and pearson correlation coefficient analysis.
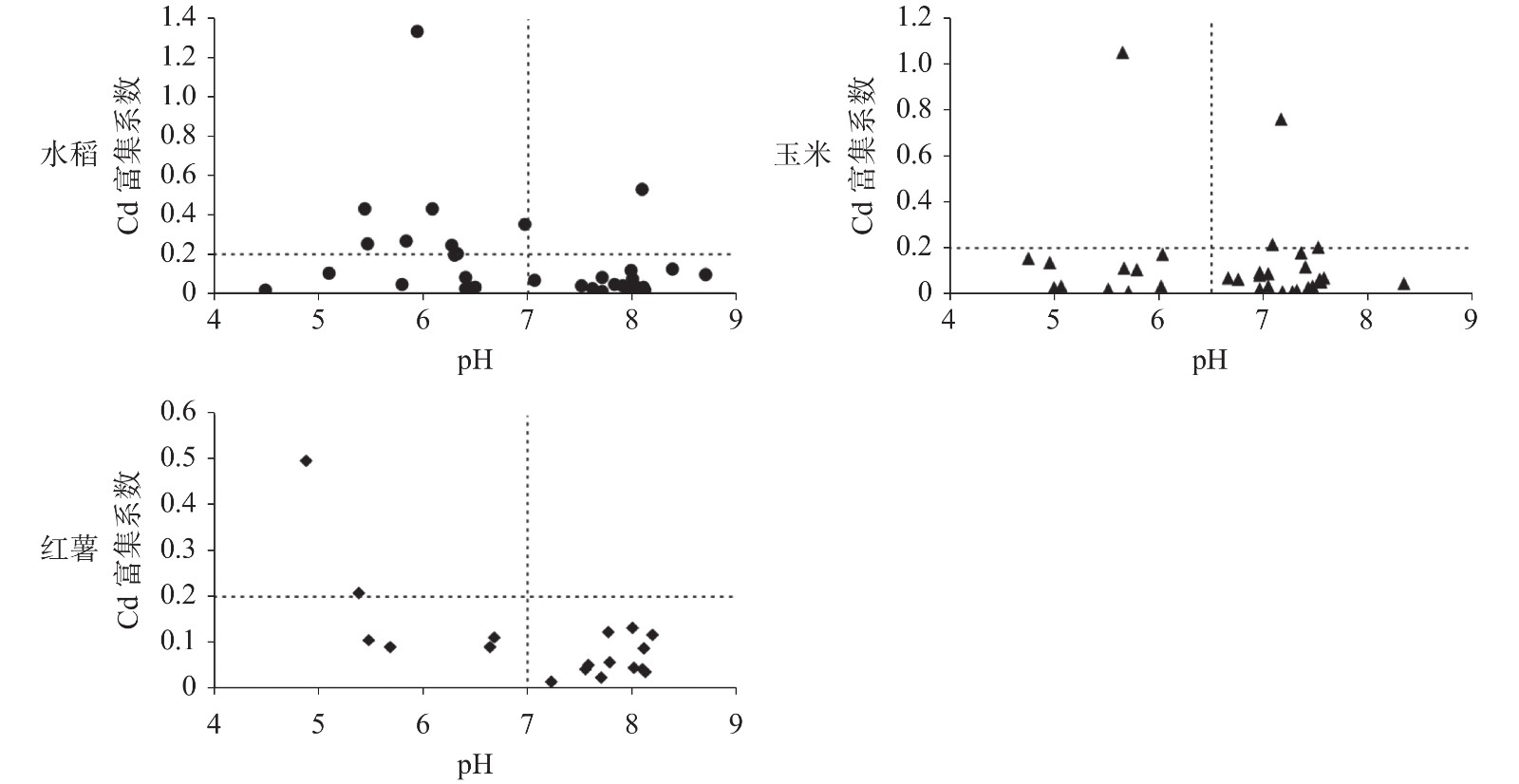
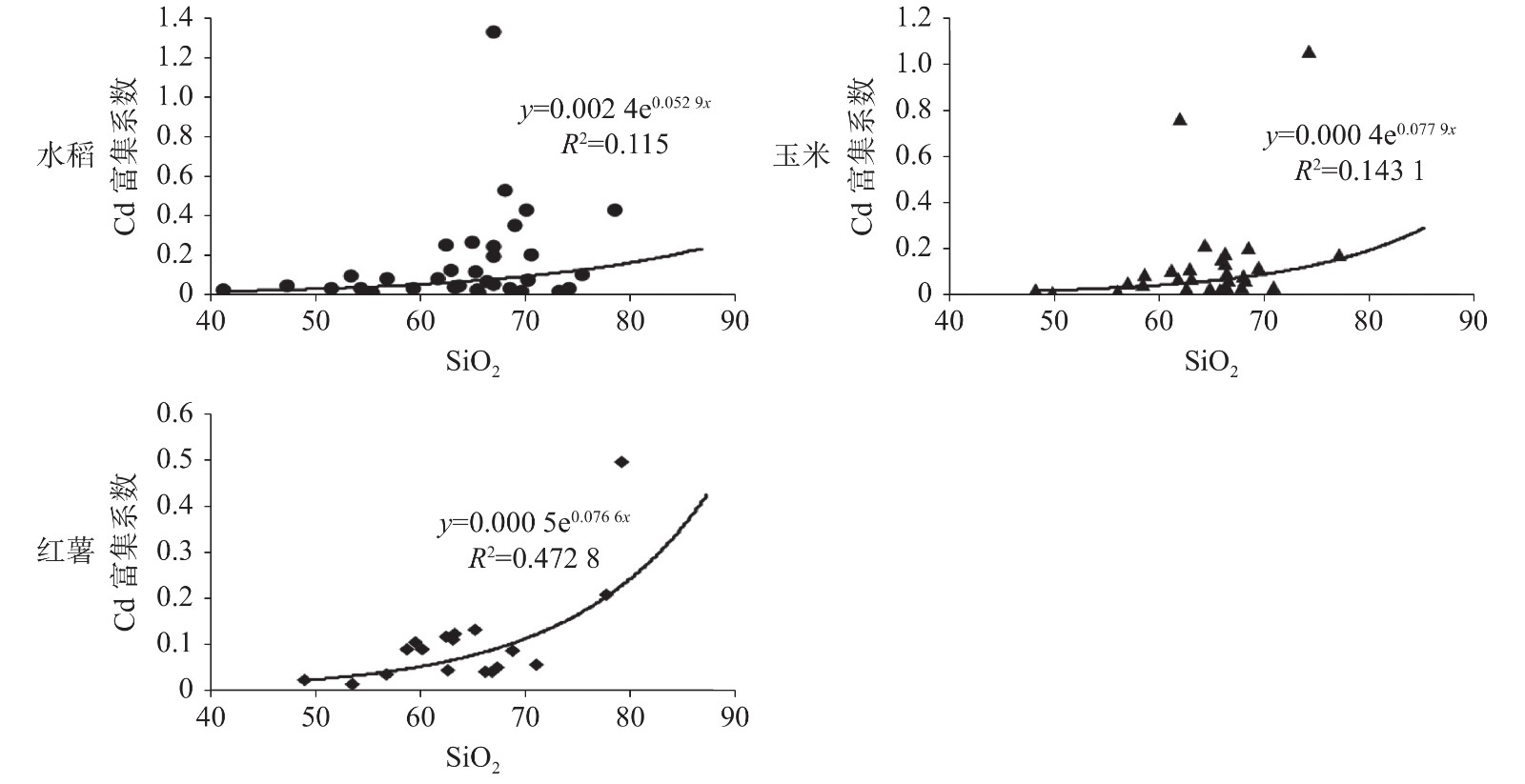
Results show that the average values of heavy metals in the top soil of karst area, which present different degree of accumulation, are higher than those of top soil in Chongqing and China. Concentrations of Cd significantly exceed the risk screening values for soil contamination of agricultural land, with the over-standard rate of 41.59%. According to Chinese Food Safety Standard (GB 2762-2017), the contents of As, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Zn in crop samples do not exceed the national food safety standards, and the exceeding rates of Cd in rice, maize and sweet potato are 5.89%, 6.25% and 5.56%, respectively. Meanwhile, the bioenrichment factors of heavy metals in soil-crop system are all smaller than 1, which does not indicate obvious enrichment. This result illustrates that despite high levels of heavy metal elements in the surface soil in the high geological background of karst area, the levels of bioavailable heavy metals that can be absorbed and utilized by crop are low. The pearson correlation coefficient analysis shows that the accumulation of heavy metals in the soil-crop system is mainly affected by soil pH, soil texture and soil Fe and Mn oxides. The migration of heavy metals from soil to crops is inhibited by higher pH, lower SiO2 content and more iron and manganese oxides in soil.
-

-
表 1 土壤元素分析方法与检出限
Table 1. Element analysis method and detection limit of soil
指标 测定方法 检出限/mg·kg−1 指标 测定方法 检出限/mg·kg−1 Al2O3 X射线荧光光谱法 0.05 Se 原子荧光光谱法 0.01 CaO X射线荧光光谱法 0.05 As 原子荧光光谱法 0.2 K2O X射线荧光光谱法 0.05 Hg 原子荧光光谱法 0.000 5 MgO X射线荧光光谱法 0.05 Mn 等离子体光量计法 10 Na2O X射线荧光光谱法 0.1 Cu 等离子体发射光谱法 1 TFe2O3 X射线荧光光谱法 0.05 Ni 等离子体发射光谱法 1 SiO2 X射线荧光光谱法 0.1 Cd 等离子体质谱法 0.02 Cr X射线荧光光谱法 3 pH pH计电极法 0.1 Zn X射线荧光光谱法 1 表 2 农作物元素分析方法与检出限
Table 2. Element analysis method and detection limit of crop
指标 测定方法 检出限/mg·kg−1 指标 测定方法 检出限/mg·kg−1 As 等离子体质谱法 0.03 Hg 等离子体质谱法 0.000 5 Cd 等离子体质谱法 0.000 1 Ni 等离子体质谱法 0.2 Cr 等离子体质谱法 0.2 Zn 等离子体光谱法 0.05 Cu 等离子体质谱法 1 表 3 研究区不同农作物耕层土壤重金属含量特征(mg·kg−1)
Table 3. Concentrations of heavy metals in the top soil of different crops in the study area (mg·kg−1)
耕层土类型 统计值 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Zn pH 水稻耕层土 最小值 3.33 0.10 52.7 15.8 0.03 17.1 46.5 4.51 最大值 22.53 2.45 131.8 88.1 0.25 54.4 149.1 8.72 平均值 9.72 0.54 79.6 34.7 0.11 33.6 96.1 7.03 变异系数 0.51 0.78 0.23 0.35 0.48 0.27 0.24 0.16 玉米耕层土 最小值 3.47 0.07 61.9 20.1 0.04 13.7 51.9 4.90 最大值 26.52 3.78 272.0 120.2 0.68 119.5 180.5 9.20 平均值 11.35 0.52 88.8 38.4 0.12 38.5 101.6 7.18 变异系数 0.43 0.14 0.33 0.32 0.17 0.32 0.56 0.78 红薯耕层土 最小值 3.13 0.11 41.7 14.7 0.04 13.0 45.5 4.88 最大值 20.53 1.14 119.9 86.5 0.33 62.7 179.2 8.20 平均值 11.11 0.48 80.9 35.0 0.12 35.8 98.4 7.16 变异系数 0.41 0.52 0.27 0.45 0.56 0.34 0.30 0.15 研究区耕层土壤平均值 11.53 0.51 84.83 37.62 0.11 36.62 99.99 7.06 重庆表层土壤背景值[14] 6.62 0.28 74.4 24.6 0.069 31.6 81.9 — 中国表层土壤背景值[15] 9.1 0.15 63 23 0.05 26 67 — 广西岩溶地区平均值[17] 26.3 1.004 147 31 0.185 38 130 — 重庆黑色岩系区平均值[18] — 9.16 344 33.2 — 93.9 193 — 表 4 研究区不同农作物重金属含量特征(mg·kg−1)
Table 4. Concentrations of heavy metals in different crops in the study area(mg·kg−1)
农作物 元素 极小值 极大值 均值 标准差 富集系数 GB 2762-2017 超标率/% 水稻 As 0.05 0.26 0.13 0.05 0.015 0.5 0 Cd 0.01 0.27 0.05 0.06 0.157 0.2 5.88 Cr 0.10 0.14 0.12 0.01 0.002 1 0 Cu 0.60 4.57 2.30 0.91 0.071 — — Hg 0.002 0.008 0.005 0.002 0.051 0.02 0 Ni 0.09 1.40 0.24 0.24 0.008 — — Zn 16.0 31.9 21.1 3.64 0.234 — — 玉米 As 0.03 0.07 0.04 0.01 0.004 0.5 0 Cd 0.002 0.30 0.04 0.06 0.125 0.1 6.25 Cr 0.09 0.14 0.11 0.01 0.001 1 0 Cu 1.47 10.09 2.67 1.55 0.080 — — Hg 0.001 0.005 0.002 0.001 0.023 0.02 0 Ni 0.12 1.05 0.25 0.18 0.007 — — Zn 15.0 43.5 25.4 6.13 0.270 — — 红薯 As 0.04 0.13 0.09 0.02 0.010 0.5 0 Cd 0.01 0.10 0.04 0.02 0.102 0.1 5.56 Cr 0.23 0.41 0.27 0.04 0.004 0.5 0 Cu 4.51 11.99 7.93 2.00 0.255 — — Hg 0.001 0.004 0.002 0.001 0.026 0.01 0 Ni 0.29 1.71 0.59 0.40 0.019 — — Zn 7.65 14.6 10.8 2.08 0.120 — — 表 5 研究区土壤重金属与pH、氧化物含量的Pearson相关系数表(n=113)
Table 5. Pearson correlation of soil heavy metals with pH and oxide contents in the study area (n=113)
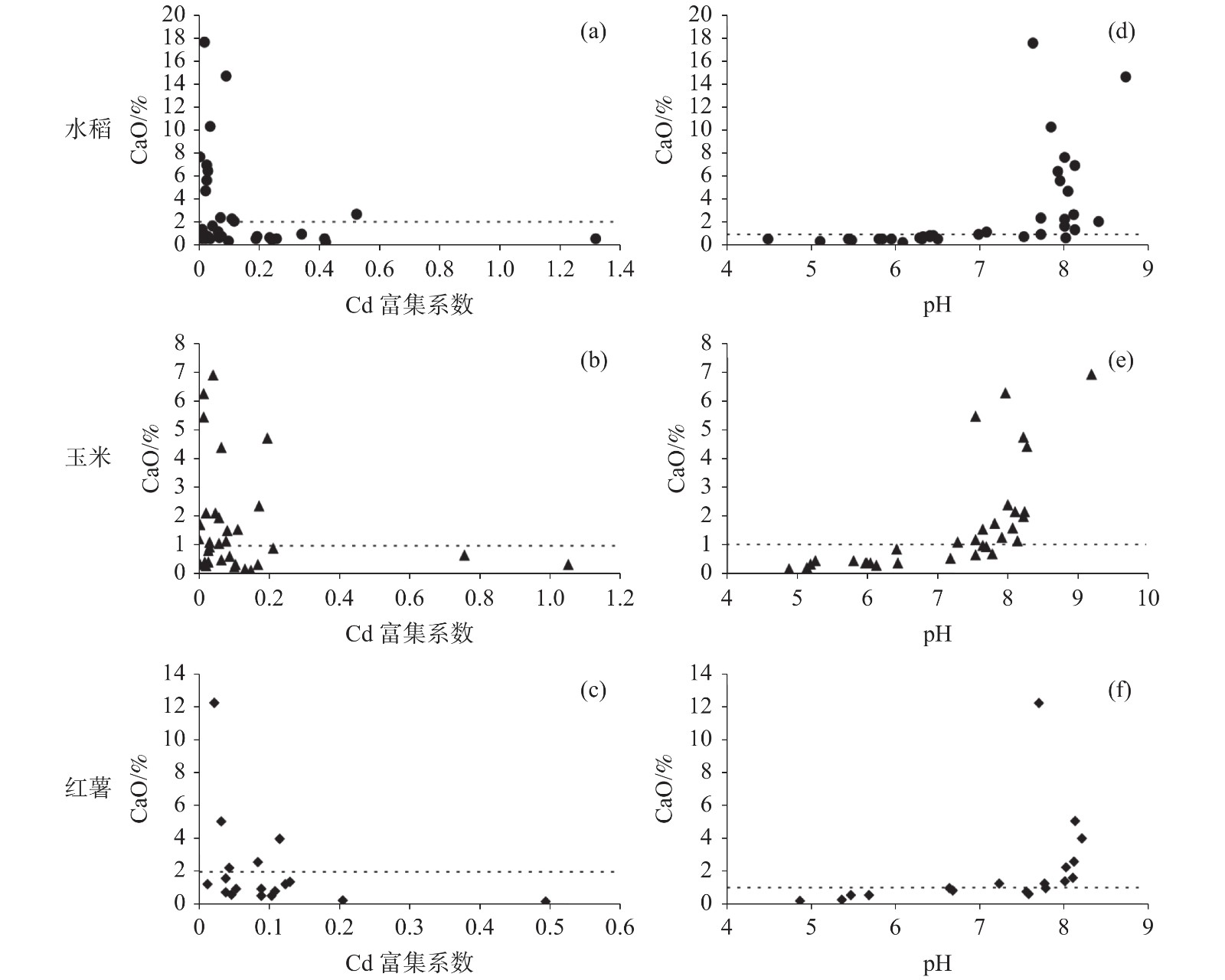
元素 pH Na20 MgO Al2O3 SiO2 K2O CaO Mn TFe2O3 Se As 0.135 −.285** −0.087 0.175 −0.127 −0.209* −0.070 0.290** 0.382** 0.191* Cd 0.162 −0.066 0.086 0.190* −0.305** −0.117 0.117 0.006 0.296** 0.396** Cr 0.219* −0.092 0.140 0.478** −0.427** −0.148 −0.016 0.123 0.671** 0.320** Cu 0.056 −0.055 0.024 0.224* −0.391** −0.158 0.030 0.065 0.743** 0.509** Hg 0.142 −0.189* −0.039 0.159 −0.243** −0.297** 0.121 0.052 0.245** 0.311** Ni 0.128 0.055 0.012 0.602** −0.503** 0.078 −0.021 0.240* 0.775** 0.289** Zn 0.158 0.116 −0.061 0.499** −0.494** 0.258** −0.021 0.303** 0.756** 0.426** **: P<0.01, 在0.01水平上显著相关; *: P<0.05, 在0.05水平上显著相关。 表 6 研究区Cd富集系数与pH、氧化物含量的Pearson相关系数表
Table 6. Pearson correlation of Cd enrichment coefficient with pH and oxide contents in the study area
农作物 pH Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 K2O CaO Mn TFe2O3 Se 水稻 −0.291 0.026 −0.129 0.062 0.264 0.189 −0.236 −0.258 −0.097 −0.307 玉米 −0.111 −0.138 0.001 −0.139 0.284 −0.039 −0.192 −0.174 −0.153 −0.201 红薯 −0.653** 0.008 −0.280 −0.398 0.659** −0.320 −0.306 −0.553* −0.209 −0.455 **: P<0.01, 在0.01水平上显著相关; *: P<0.05, 在0.05水平上显著相关。 -
[1] 陈能场, 郑煜基, 何晓峰, 李小飞, 张晓霞. 《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》探析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(9):1689-1692. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1220
CHEN Nengchang, ZHENG Yuji, HE Xiaofeng, LI Xiaofei, ZHANG Xiaoxia. Analysis of the report on the national general survey of soil contamination[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(9):1689-1692. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1220
[2] 赵方杰, 谢婉滢, 汪鹏. 土壤与人体健康[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(1):1-11. doi: 10.11766/trxb201907200376
ZHAO Fangjie, XIE Wanying, WANG Peng. Soil and human health[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(1):1-11. doi: 10.11766/trxb201907200376
[3] 张广映, 吴琳娜, 欧阳坤长, 吴攀. 都柳江上游沿岸喀斯特地区土壤重金属污染特征及风险评价[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(3):495-503.
ZHANG Guangying, WU Linna, OUYANG Kunchang, WU Pan. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils along the upper reaches of the Duliu river[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(3):495-503.
[4] 王锐, 邓海, 贾中民, 严明书, 周皎, 董金秀, 王佳彬, 余飞. 典型喀斯特地区土壤-作物系统镉的富集特征与污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(2):941-951.
WANG Rui, DENG Hai, JIA Zhongmin, YAN Mingshu, ZHOU Jiao, DONG Jinxiu, WANG Jiabin, YU Fei. Characteristics of cadmium enrichment and pollution evaluation of a soil-crop system in a typical karst area[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(2):941-951.
[5] Yubo Wen, Wei Li, Zhongfang Yang, Qizuan Zhang, Junfeng Ji. Enrichment and source identification of Cd and other heavy metals in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 245:125620.
[6] Cai Limei, Wang Qiushuang, Wen Hanhui, Luo Jie, Wang Shuo. Heavy metals in agricultural soils from a typical township in Guangdong Province, China: Occurrences and spatial distribution[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 168:184-191.
[7] 罗慧, 刘秀明, 王世杰, 刘方, 李颖. 中国南方喀斯特集中分布区土壤Cd污染特征及来源[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(5):1538-1544.
LUO Hui, LIU Xiuming, WANG Shijie, LIU Fang, LI Ying. Pollution characteristics and sources of cadmium in soils of the karst area in South China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(5):1538-1544.
[8] 刘意章, 肖唐付, 熊燕, 宁增平, 双燕, 李航, 马良, 陈海燕. 西南高Cd 地质背景区农田土壤与农作物的重金属富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(6):2877-2884.
LIU Yizhang, XIAO Tangfu, XIONG Yan, NING Zengping, SHUANG Yan, LI Hang, MA Liang, CHEN Haiyan. Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops from an area with a high geochemical background of cadmium, Southwestern China[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(6):2877-2884.
[9] 李一蒙, 马建华, 刘德新, 孙艳丽, 陈彦芳. 开封城市土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(3):1037-1044.
LI Yimeng, MA Jianhua, LIU Dexin, SUN Yanli, CHEN Yanfang. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of urban soils in Kaifeng City, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(3):1037-1044.
[10] 陈凤, 董泽琴, 王程程, 韦雪花, 胡宇, 张丽娟. 锌冶炼区耕地土壤和农作物重金属污染状况及风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(10):4360-4369.
CHEN Feng, DONG Zeqin, WANG Chengcheng, WEI Xuehua, HU Yu, ZHANG Lijuan. Heavy metal contamination of soils and crops near a zinc smelter[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(10):4360-4369.
[11] 余飞, 张永文, 严明书, 王锐, 张风雷, 钟克强, 朱海山, 罗凯. 重庆汞矿区耕地土壤和农作物重金属污染状况及健康风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(2):536-548.
YU Fei, ZHANG Yongwen, YAN Mingshu, WANG Rui, ZHANG Fenglei, ZHONG Keqiang, ZHU Haishan, LUO Kai. Heavy metal pollution and human health risks assessment of soil and crops near the mercury ore in Chongqing[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(2):536-548.
[12] 马宏宏, 彭敏, 郭飞, 刘飞, 唐世琪, 杨峥, 张富贵, 周亚龙, 杨柯, 李括, 刘秀金. 广西典型岩溶区农田土壤-作物系统Cd迁移富集影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(3):1514-1522.
MA Honghong, PENG Min, GUO Fei, LIU Fei, TANG Shiqi, YANG Zheng, ZHANG Fugui, ZHOU Yalong, YANG Ke, LI Kuo, LIU Xiujin. Factors affecting translocation and accumulation of cadmium in soil-crop system from a typical karst area in Guangxi Province, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3):1514-1522.
[13] 杨阳, 彭叶棉, 王莹, 李芳柏, 刘同旭. 稻田土壤镉的表面络合模型及其生物有效性验证[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(33):3449-3457.
YANG Yang, PENG Yemian, WANG Ying, LI Fangbai, LIU Tongxu. Surface complexation model of Cd in paddy soil and its validation with bioavailability[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(33):3449-3457.
[14] Chaosheng Zhang, Gerald Lalor. Multivariate relationships and spatial distribution of geochemical features of soils in Jamaica[J]. Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability, 2003, 14(SI):57-65.
[15] Grant C N , Dennis H T , Antoine J M R , Hoo Fung L A , Lalor G C. Agglomerative hierarchical clustering analysis of twenty-six rice samples analysed by instrumental neutron activation analysis and other techniques[J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2013, 297(2):233-239.
[16] 杨琼, 杨忠芳, 张起钻, 刘旭, 卓小雄, 吴天生, 王磊, 韦雪姬, 季峻峰. 中国广西岩溶地质高背景区土壤-水稻系统Cd等重金属生态风险评价[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2021, 51(8):1317-1331.
YANG Qiong, YANG Zhongfang, ZHANG Qizuan, LIU Xu, ZHUO Xiaoxiong, WU Tiansheng, WANG Lei, WEI Xueji, JI Junfeng. Ecological risk assessment of Cd and other heavy metals in soil-rice system in the karst areas with high geochemical background of Guangxi, China[J]. Scientia Sinica(Terrae), 2021, 51(8):1317-1331.
[17] 李杰, 战明国, 钟晓宇, 王新宇, 欧阳鑫东, 赵辛金. 广西典型岩溶地区重金属在土壤-农作物系统中累积特征及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(2):597-606.
LI Jie, ZHAN Mingguo, ZHONG Xiaoyu, WANG Xinju, OUYANG Xindong, ZHAO Xinjin. Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in soil-crop systems from a typical carbonate rocks in Guangxi[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(2):597-606.
[18] 唐世琪, 杨峥, 马宏宏, 郭飞, 杨柯, 刘飞, 彭敏, 李括, 刘秀金. 岩溶区土壤镉生物有效性影响因素研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(6):1221-1229. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1370
TANG Shiqi, YANG Zheng, MA Honghong, GUO Fei, YANG Ke, LIU Fei, PENG Min, LI Kuo, LIU Xiujin. Study on factors affecting soil cadmium bioavailability in soil in karst area[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(6):1221-1229. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1370
[19] 余飞, 张风雷, 张永文, 王锐, 王佳彬. 重庆典型农业区土壤硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4):830-838.
YU Fei, ZHANG Fenglei, ZHANG Yongwen, WANG Rui, WANG Jiabin. Geochemical characteristics and influential factors of soil selenium in typical agricultural area, Chongqing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4):830-838.
[20] 姚成斌, 周明忠, 熊康宁, 杨桦, 张迪, 杨连升, 王贵云. 撒拉溪石漠化治理示范区土壤-作物系统中重金属含量特征[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(6):1256-1267. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1267
YAO Chengbin, ZHOU Mingzhong, XIONG Kangning, YANG Hua, ZHANG Di, YANG Liansheng, WANG Guiyun. Characteristics analysis of heavy metal content in the soil-crop system in the rocky desertification control demonstration area in Salaxi, Guizhou Province, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(6):1256-1267. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1267
[21] 鲍丽然, 邓海, 贾中民, 李瑜, 董金秀, 严明书, 张风雷. 重庆秀山西北部农田土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6):1625-1636. doi: 10.12029/gc20200602
BAO Liran, DENG Hai, JIA Zhongmin, LI Yu, DONG Jinxiu, YAN Mingshu, ZHANG Fenglei. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil in northwest Xiushan, Chongqing[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6):1625-1636. doi: 10.12029/gc20200602
[22] 国家环境保护局. 中国土壤环境背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990
State Burean of Environmental Conservation. Soil environmental background values in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990.
[23] 李杰, 朱立新, 康志强. 南宁市郊周边农田土壤–农作物系统重金属元素迁移特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(1):43-52.
LI Jie, ZHU Lixin, KANG Zhiqiang. Characteristics of transfer and their influencing factors of heavy metals in soil-crop system of periurban agricultural soils of Nanning, South China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1):43-52.
[24] 王锐, 胡小兰, 张永文, 余飞, 朱海山, 李瑜. 重庆市主要农耕区土壤Cd生物有效性及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(4):1864-1870.
WANG Rui, HU Xiaolan, ZHANG Yongwen, YU Fei, ZHU Haishan, LI Yu. Bioavailability and influencing factors of soil cd in the major farming areas of Chongqing[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(4):1864-1870.
[25] Li Cheng, Yang Zhongfang, Yu Tao, Hou Qingye, Liu Xu, Wang Jue, Zhang Qizuan, Wu Tiansheng. Study on safe usage of agricultural land in karst and non-karst areas based on soil Cd and prediction of cd in rice: A case study of Heng county, Guangxi[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 208:111505.
[26] Lina Cao, Chenlu Lin, Yufu Gao, Caiyun Sun, Liang Xu, Liang Zheng, Zhenxing Zhang. Health risk assessment of trace elements exposure through the soil-plant (maize)-human contamination pathway near a petrochemical industry complex, Northeast China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 263(Part A):114414.
[27] 唐豆豆, 袁旭音, 汪宜敏, 季峻峰, 文宇博, 赵万伏. 地质高背景农田土壤中水稻对重金属的富集特征及风险预测[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(1):18-26. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-0801
TANG Doudou, YUAN Xuyin, WANG Yimin, JI Junfeng, WEN Yubo, ZHAO Wanfu. Enrichment characteristics and risk prediction of heavy metals for rice grains growing in paddy soils with a high geological background[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(1):18-26. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-0801
[28] Chen Hongyan, Yuan Xuyin, Li Tianyuan, Hu Sun, Ji Junfeng, Wang Cheng. Characteristics of heavy metal transfer and their influencing factors in different soil-crop systems of the industrialization region, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2016, 126:193-201.
[29] MAKABE Shuhei, KAKUDA Ken-ichi, SASAKI Yuka, ANDO Tadashi, FUJII Hiroshi, ANDO Ho. Relationship between mineral composition or soil texture and available silicon in alluvial paddy soils on the Shounai Plain, Japan[J]. Soil Science & Plant Nutrition (Wiley-Blackwell), 2009, 55(2):300-308.
[30] 刘旭, 顾秋蓓, 杨琼, 余涛, 张起钻. 广西象州与横县碳酸盐岩分布区土壤中Cd 形态分布特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(2):374-385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.02.016
LIU Xu, GU Qiubei, YANG Qiong, YU Tao, ZHANG Qizuan. Distribution and influencing factors of cadmium geochemical fractions of soils at carbonate covering area in Hengxian and Xiangzhou of Guangxi[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(2):374-385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.02.016
[31] LI Tianyuan, CHANG Qing, YUAN Xuyin, LI Jizhou, AYOKO Godwin A, FROST Ray L, CHEN Hongyan, ZHANG Xinjian, SONG Yinxian, SONG Wenzhi. Cadmium transfer from contaminated soils to the human body through rice consumption in southern Jiangsu Province, China[J]. Environmental Science: Processes Impacts, 2017, 19(6):843-850.
[32] Mao Changping, Song Yinxian, Chen Lingxiao, Ji Junfeng, Li Jizhou, Yuan Xuyin, Yang Zhongfang, Ayoko Godwin A, Frost Ray L, Theiss Frederick. Human health risks of heavy metals in paddy rice based on transfer characteristics of heavy metals from soil to rice[J]. Catena, 2019, 175:339-348.
[33] 郭超, 文宇博, 杨忠芳, 李伟, 管冬兴, 季峻峰. 典型岩溶地质高背景土壤Cd生物有效性及其控制因素研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2019, 55(4):678-687.
GUO Chao, WEN Yubo, YANG Zhongfang, LI Wei, GUAN Dongxing, JI Junfeng. Factors controlling the bioavailability of soil cadmium in typical karst areas with high geogenic background[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Scinece), 2019, 55(4):678-687.
[34] Sebei Abdelaziz, Helali Mohamed Amine, Oueslati Walid, Abdelmalek-Babbou Chiraz, Chaabani Fredj. Bioavailability of Pb, Zn, Cu, Cd, Ni and Cr in the sediments of the Tessa River: A mining area in the North-West Tunisia[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2018, 137:1-8.
[35] Han Lanfang, Zhao Xingjuan, Jin Jie, Gao Bo, Yang Yan, Sun Ke, Li Fangbai. Using sequential extraction and DGT techniques to assess the efficacy of plant-and manurederived hydrochar and pyrochar for alleviating the bioavailability of Cd in soils[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 678:543-550.
[36] 韩伟, 王成文, 彭敏, 王乔林, 杨帆, 徐仁廷. 川南山区土壤与农作物重金属特征及成因[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(5):2480-2489.
HAN Wei, WANG Chengwen, PENG Min, WANG Qiaolin, YANG Fan, XU Renting. Characteristics and origins of heavy metals in soil and crops in mountain area of southern Sichuan[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(5):2480-2489.
[37] 王锐, 余涛, 杨忠芳, 侯青叶, 曾庆良, 马宏宏. 富硒土壤硒生物有效性及影响因素研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2018, 27(7):1647-1654.
WANG Rui, YU Tao, YANG Zhongfang, HOU Qingye, ZENG Qingliang, MA Honghong. Bioavailability of soil selenium and its influencing factors in selenium-enriched soil[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2018, 27(7):1647-1654.
[38] 陈小华, 沈根祥, 白玉杰, 郭春霞, 钱晓雍, 顾海蓉, 胡双庆, 赵庆节, 王振旗, 付侃. 不同作物对土壤中Cd 的富集特征及低累积品种筛选[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(10):4647-4653.
CHEN Xiaohua, SHEN Genxiang, BAI Yujie, GUO Chunxia, QIAN Xiaoyong, GU Hairong, HU Shuangqing, ZHAO Qingjie, WANG Zhenqi, FU Kan. Accumulation of Cd in different crops and screening of low-Cd accumulation cultivars[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(10):4647-4653.
-




 下载:
下载: