Remediation of polluted sites in the typical area of karst underground river based on "Three-Source Model": A case study in the Pingqiao underground river system, Zunyi, China
-
摘要:
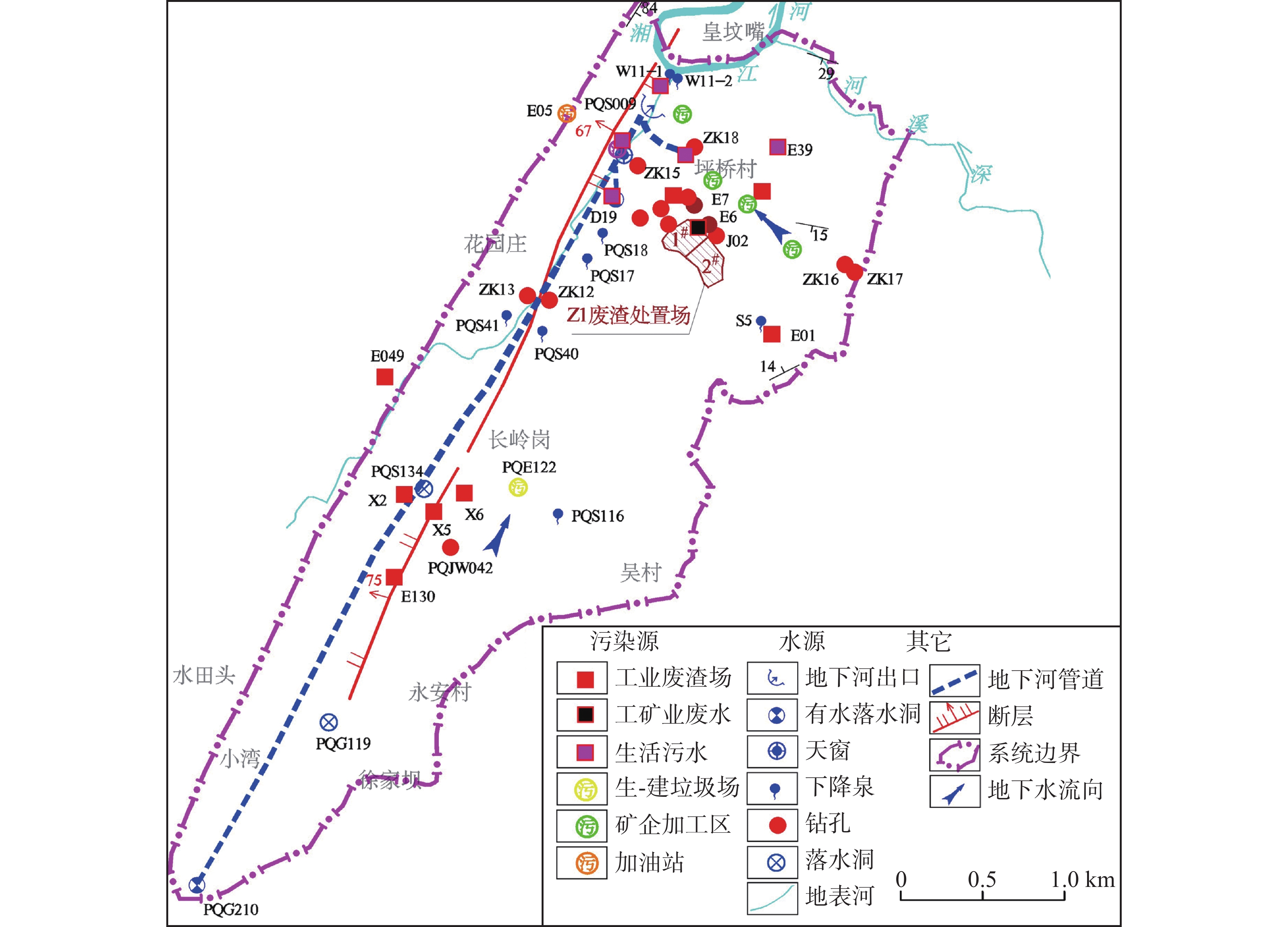
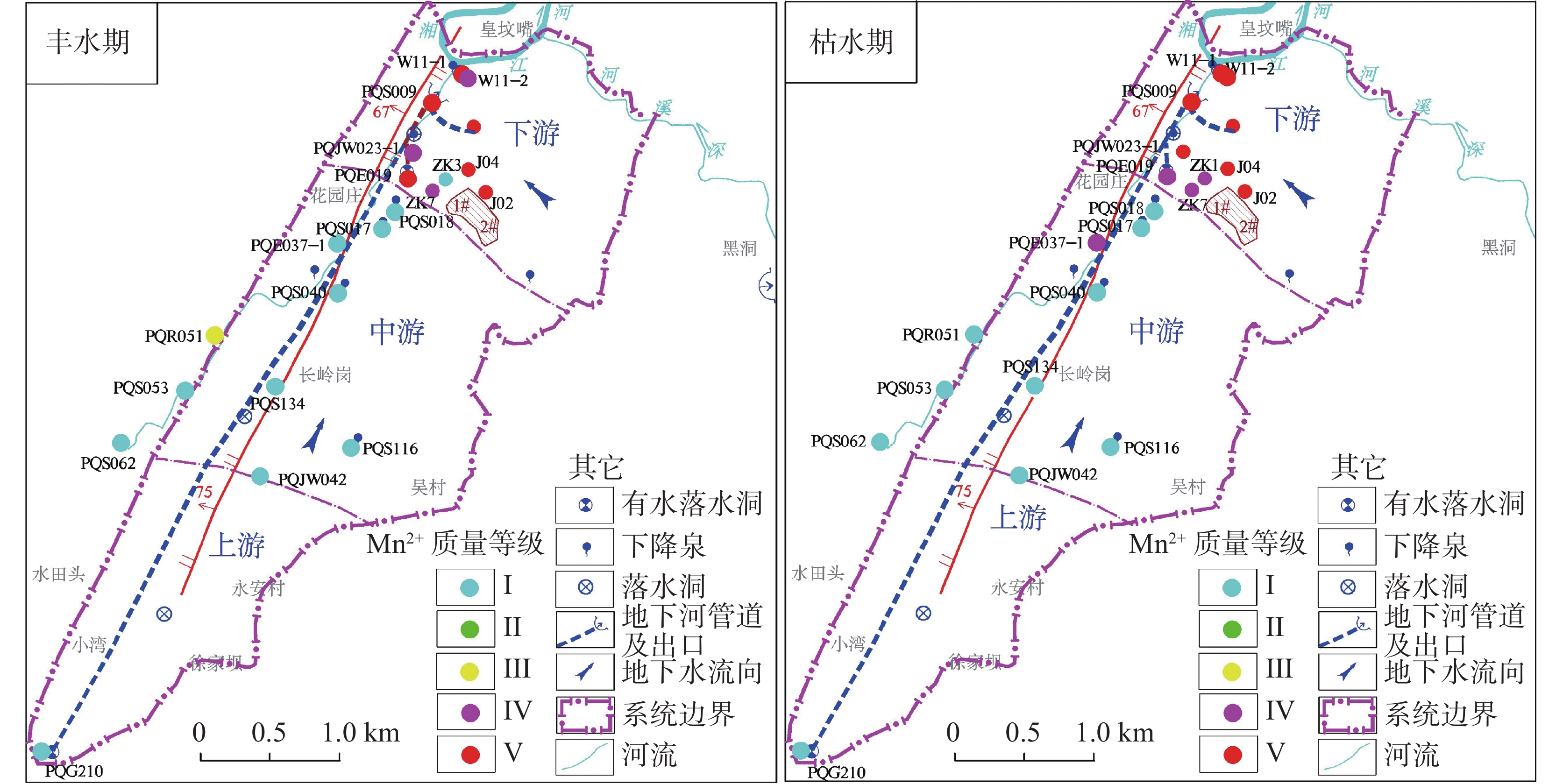
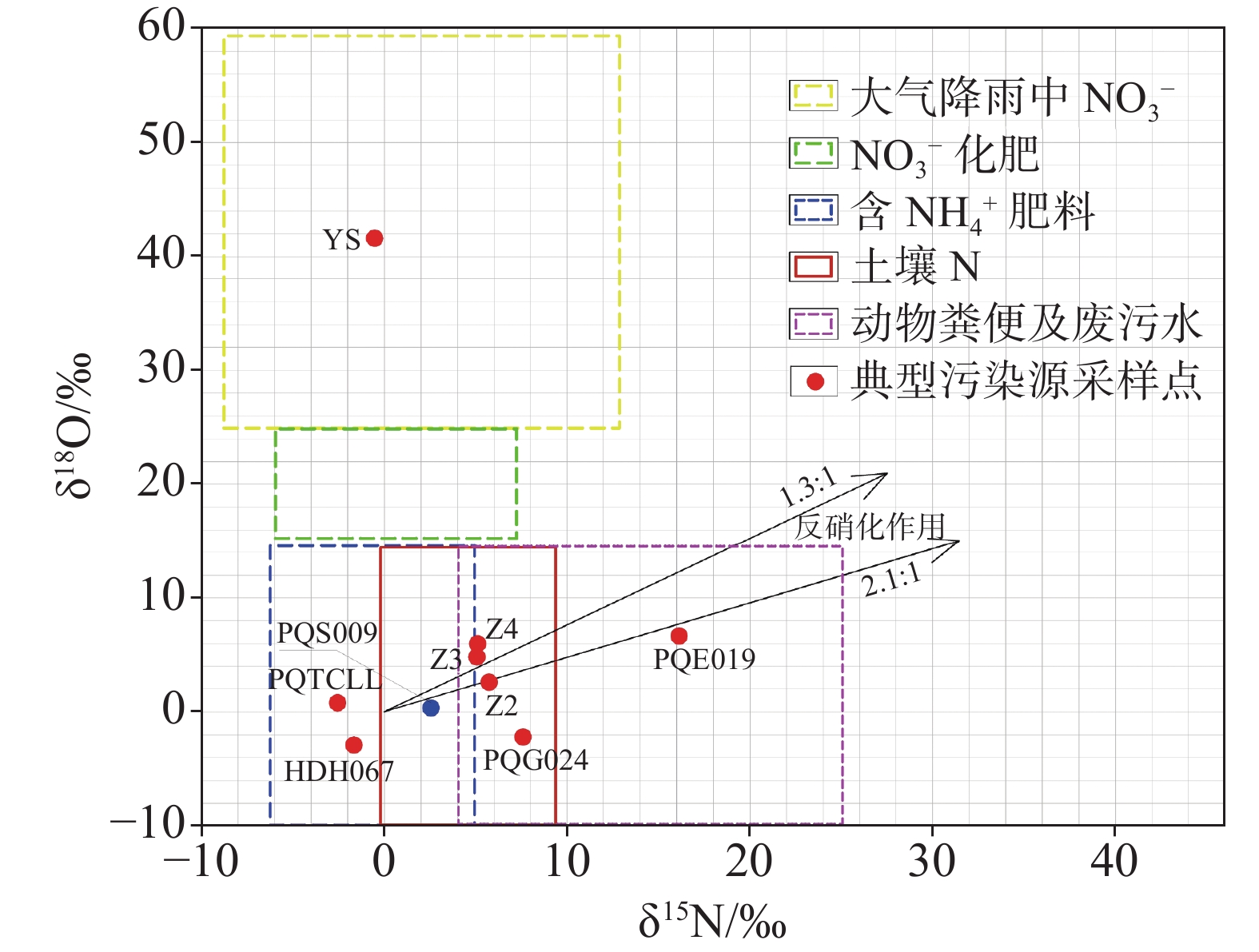
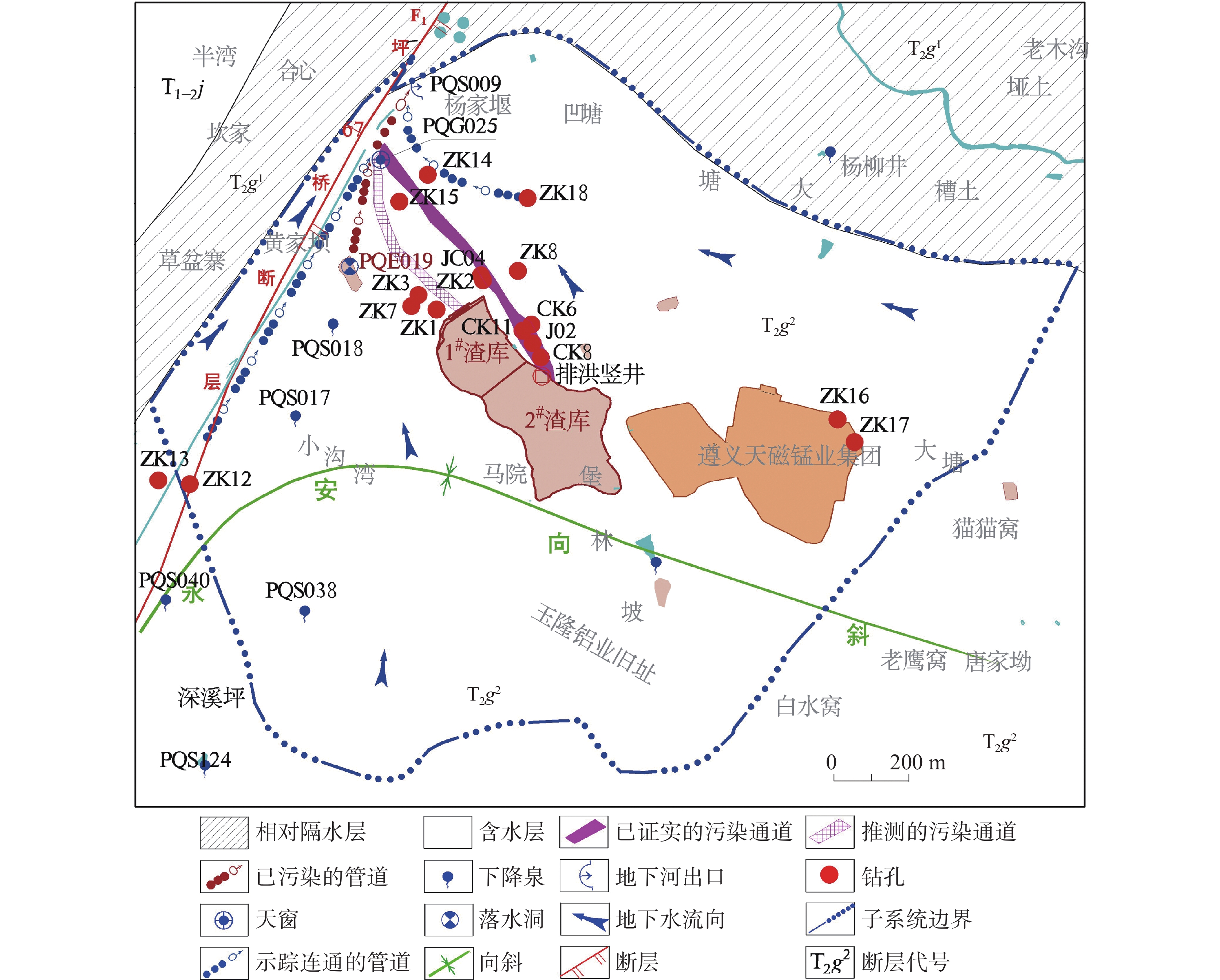
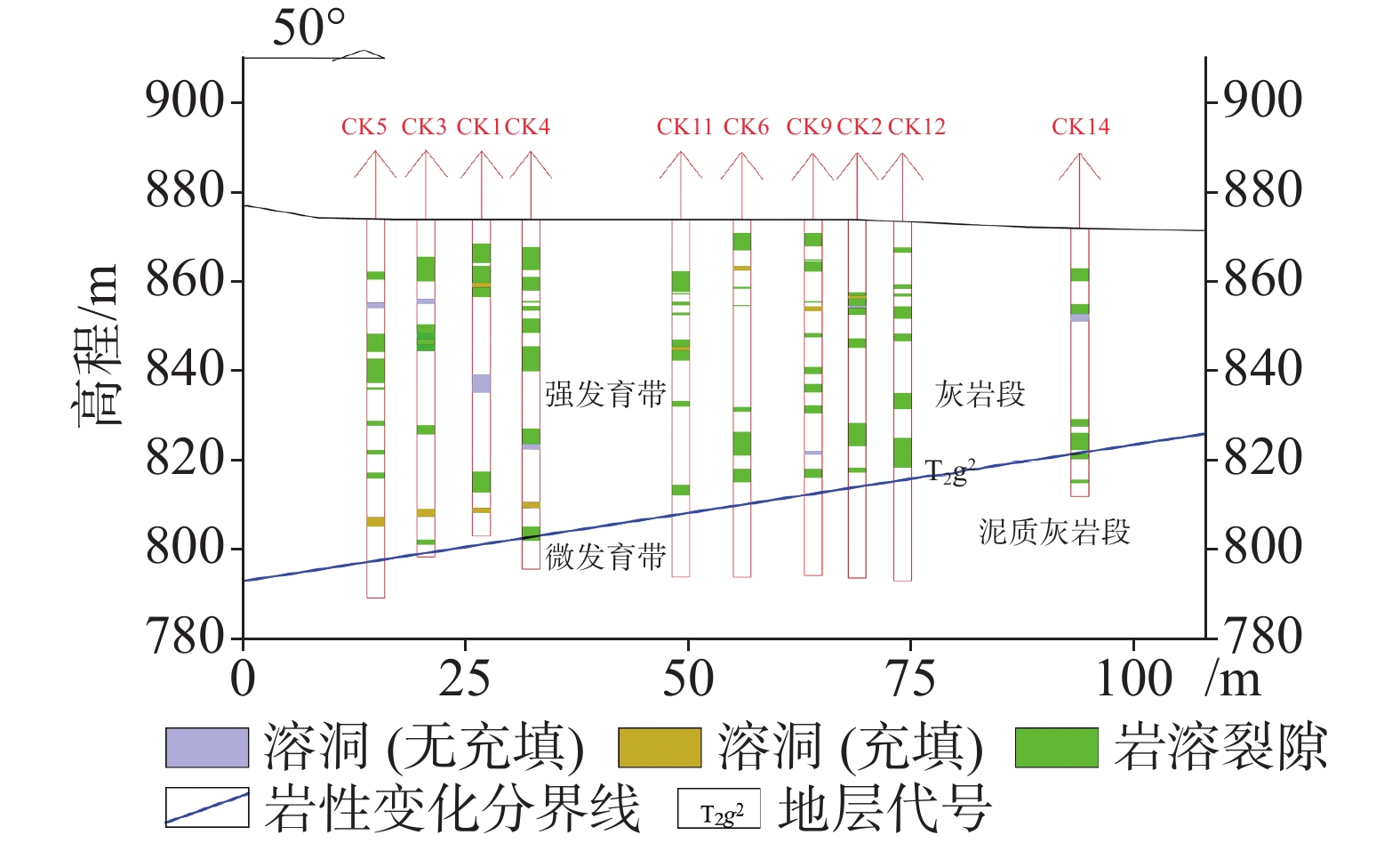
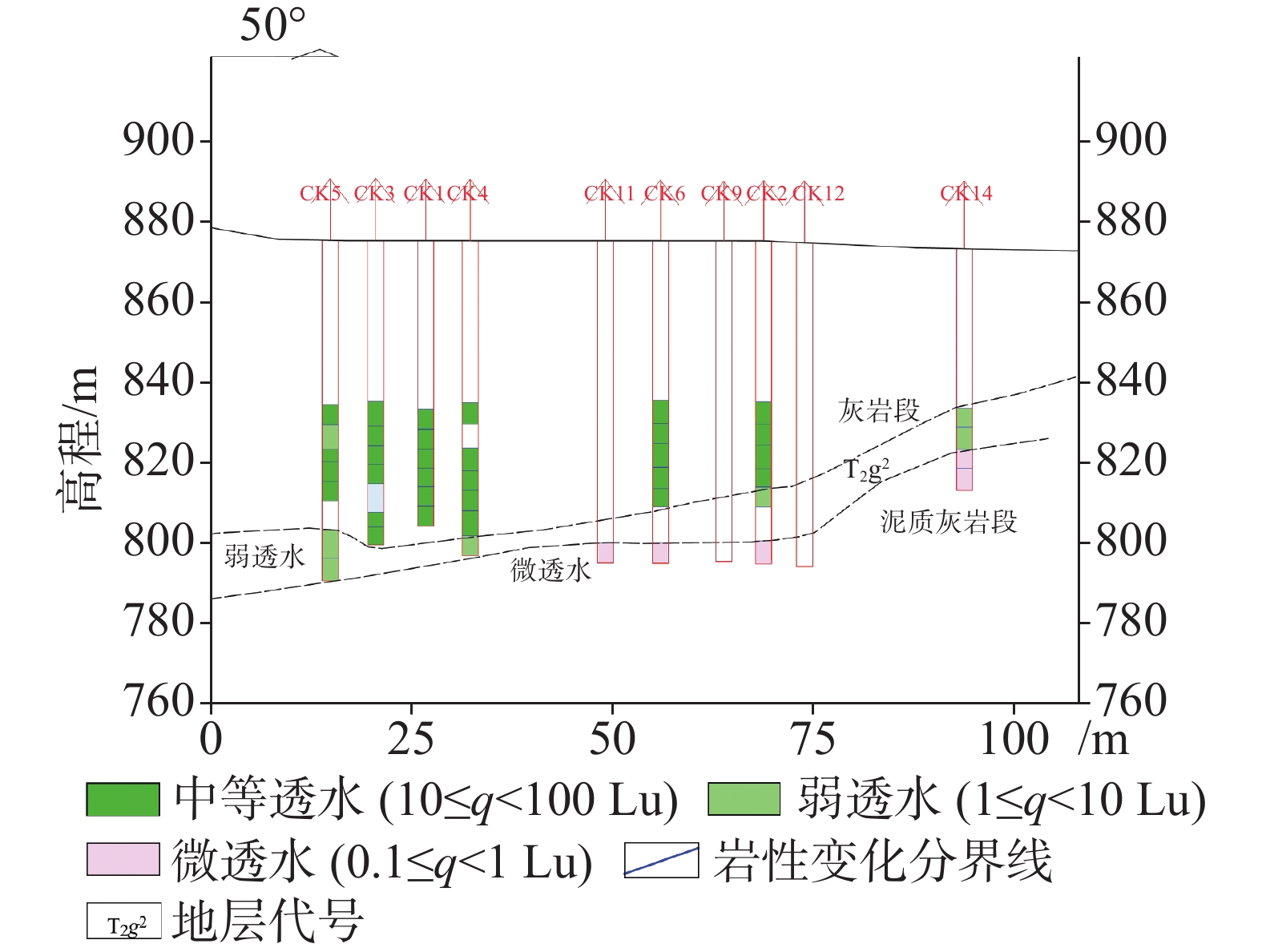
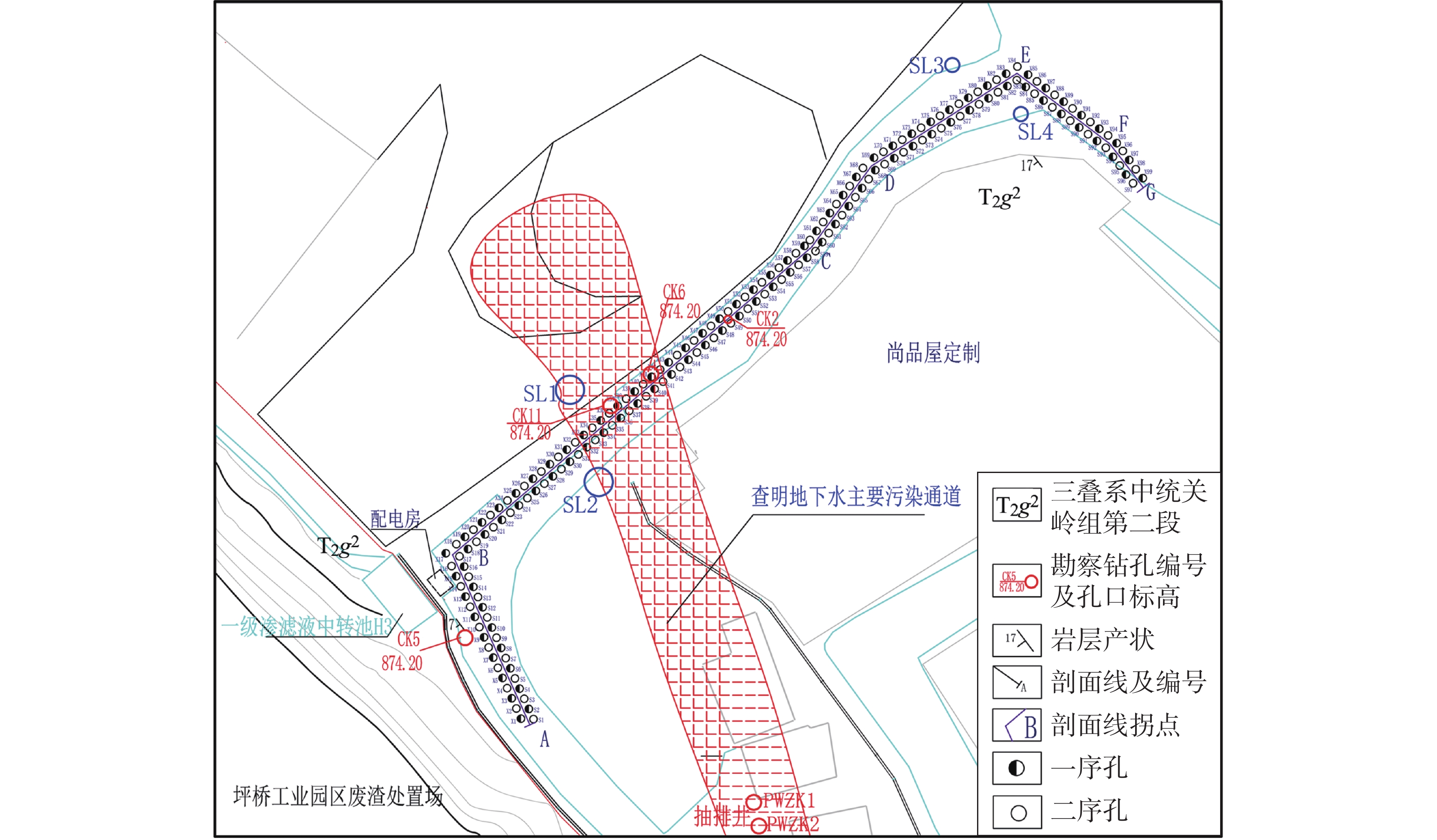
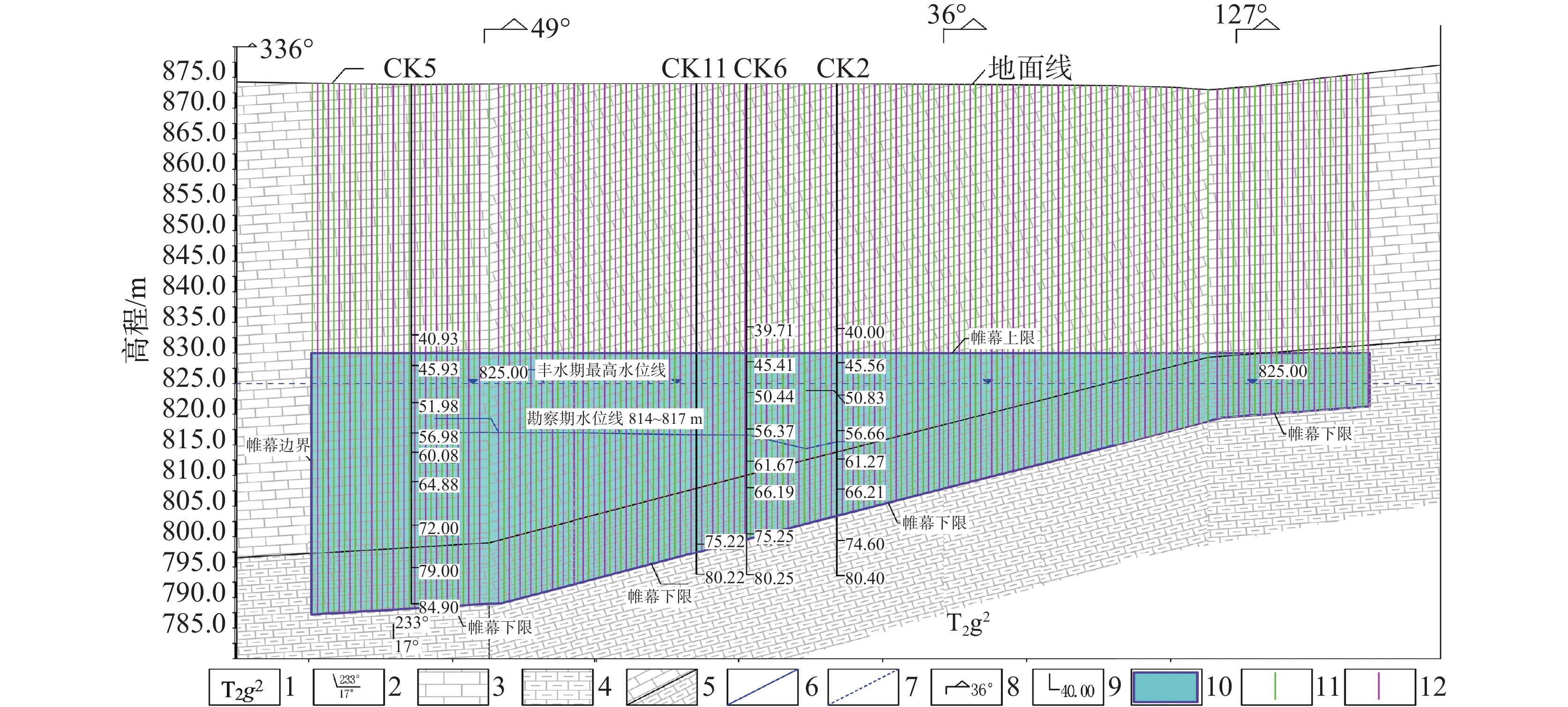
在分析岩溶地下河系统范围内水源、污染源特性的基础上,建立了双源调查、源汇追踪和源头阻控为主要内容的岩溶地下河污染修复治理模式——三源模式。以遵义市坪桥地下河系统为例,利用三源模式对该地下河污染进行修复治理实践。结果表明:研究区分布有各类水点25处,以钻孔、岩溶泉点、地下河出口为主,特征污染物为以NH
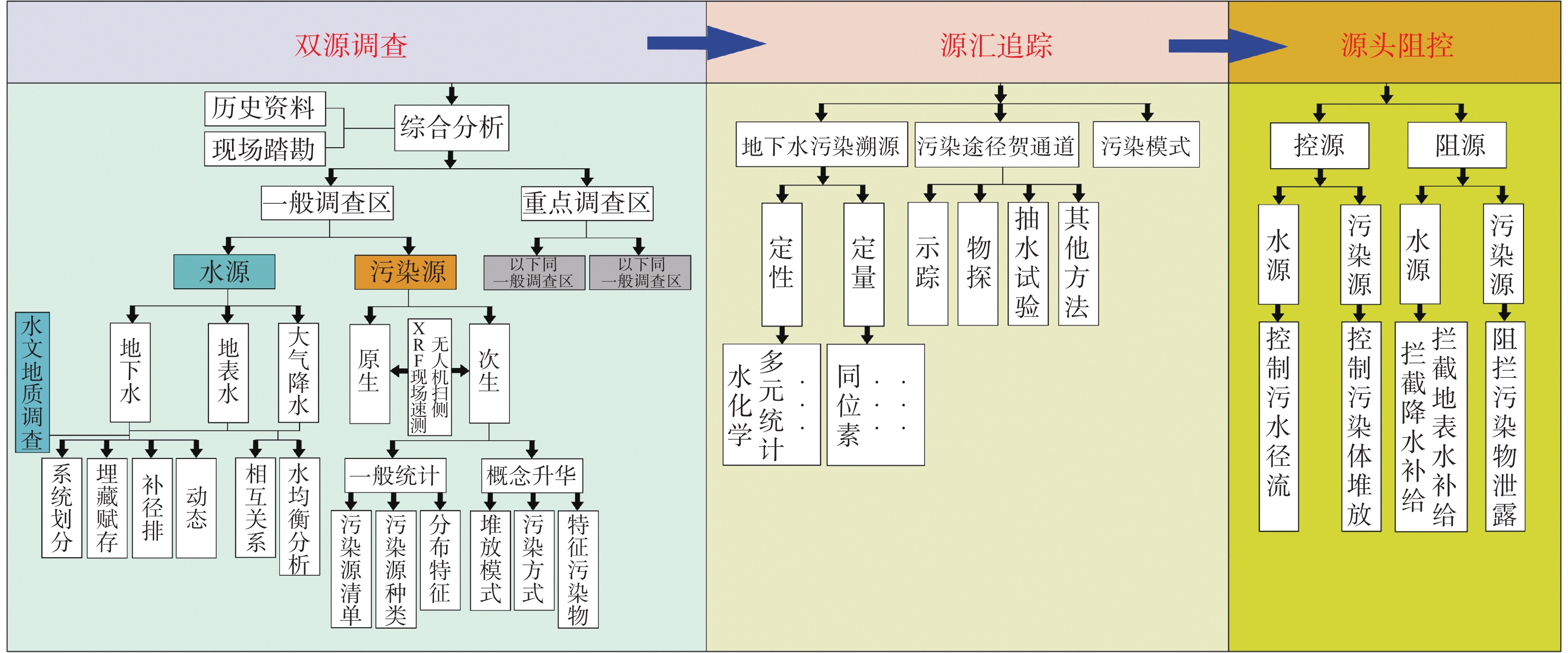
$_4^{+}$ ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ $_4^{+}$ ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ $_4^{+}$ $_4^{+}$ Abstract:Karst groundwater is an important water resource in karst areas of China and even the world, playing a crucial role in residents' daily life and industrial and agricultural production. The soil layer in karst areas is generally thin, with a double-layer structure between the surface and underground. Pollutants can directly enter the underground aquifer through thin soil layers, sinkholes, skylights, and karst cracks, making the karst groundwater extremely susceptible to pollution. In recent years, human's industrial and agricultural activities and domestic pollution have caused a large number of various types of organic and inorganic pollutants to continuously enter the underground river, posing a huge threat to the safety of drinking water and ecological agriculture development of local residents. Therefore, pollution remediation of underground rivers is of great significance for the protection of karst underground water resources. Focusing on water sources and pollution sources, this study conducts a systematic analysis of the investigation, evaluation, and remediation process of underground river pollution. It establishes a pollution remediation and control model of karst underground rivers—the "Three Source Model". This model mainly includes dual-source investigation, source tracking, and source control.
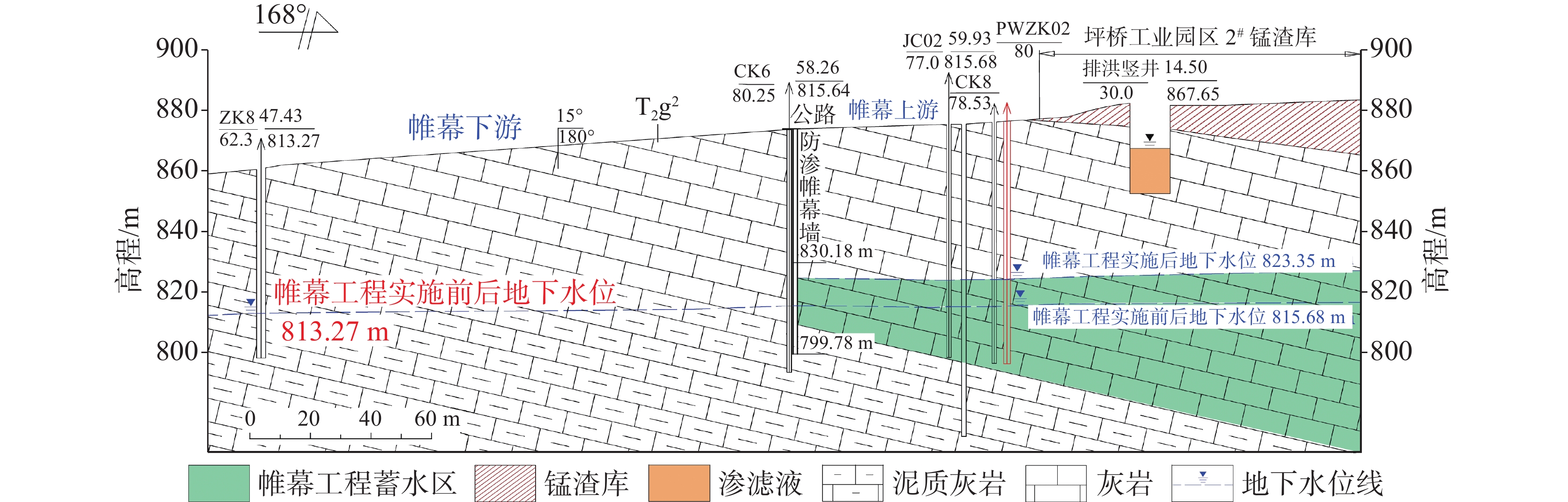
As a typical dendritic underground river in the exposed karst area of Southwest China with a pollution history of nearly 20 years, the Pingqiao underground river in Zunyi City, was selected as the study area for remediation and control of the pollution in the underground river with the use of "Three-Source Model". The results show: (1) There are 25 water points in the study area, mainly boreholes, karst springs and underground river outlets, and the characteristic pollutants are mainly NH
$_4^{+}$ ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ $_4^{+}$ ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ $_4^{+}$ $_4^{+}$ $_4^{+}$ $_4^{+}$ $_4^{+}$ $_4^{+}$ $_4^{+}$ $_4^{+}$ -
Key words:
- underground rivers /
- pollution /
- remediation /
- dual-source /
- near-source interception /
- curtain engineering
-

-
[1] Weedon C M. Compact vertical flow constructed wetland systems first two years performance[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2003, 48(5):15-23. doi: 10.2166/wst.2003.0269
[2] 李娜. 香溪河流域岩溶热水成因模式及水文地质参数反演研究: 以湖北省兴山县南阳温泉为例[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2020.
LI Na. The formation mechanism and hydrogeological parameters of karst thermal water: A case study of Nanyang thermal spring in Xingshan county of Hubei Province, Xiangxi river basin[J]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2020.
[3] 李玉辉, 章程, 庄晓东, 丁文荣, 俞筱押. 中国岩溶研究进展的哲学认知与展望[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(3):401-413.
LI Yuhui, ZHANG Cheng, ZHUANG Xiaodong, DING Wenrong, YU Xiaoya. Philosophical cognition and prospect of karst research in China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(3):401-413.
[4] 章程, 蒋忠诚, Chris Groves, 袁道先. 岩溶IGCP国际合作30年与岩溶关键带研究展望[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(3):301-306.
ZHANG Cheng, JIANG Zhongcheng, GROVES Chris, YUAN Daoxian. 30 years international cooperation with IGCP and perspectives of karst critical zone research[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(3):301-306.
[5] 李耕, 韩志伟, 申春华, 曾祥颖. 曾祥颖典型岩溶小流域水体中硝酸盐分布特征及成因:以普定后寨河流域为例[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(9):2899-2908.
LI Geng, HAN Zhiwei, SHEN Chunhua, ZENG Xiangying. Distribution characteristics and causes of nitrate in waters of typical small karst catchment: A case of the Houzhai river catchment[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(9):2899-2908.
[6] 李军, 邹胜章, 赵一, 赵瑞科, 党志文, 潘民强, 朱丹尼, 周长松. 会仙岩溶湿地地下水主要离子特征及成因分析[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(4):1750-1760.
LI Jun, ZOU Shengzhang, ZHAO Yi, ZHAO Ruike, DANG Zhiwen, PAN Minqiang, ZHU Danni, ZHOU Changsong. Major ionic characteristics and factors of karst groundwater at Huixian karst wetland, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(4):1750-1760.
[7] 任坤, 杨平恒, 江泽利, 王尊波, 师阳, 王凤康, 李晓春. 降雨期间岩溶城镇区地下河水重金属变化特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(4):1270-1276. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.04.018
REN Kun, YANG Pingheng, JIANG Zeli, WANG Zunbo, SHI Yang, WANG Fengkang, LI Xiaochun. Variation characteristics and sources of heavy metals in an urban karst groundwater system during rainfall event[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(4):1270-1276. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.04.018
[8] Vukosav Petra, Mlakar Marina, Cukrov Neven, Kwokal Željko, Pižeta Ivanka, Pavlus Natalija, Špoljarić Ivanka, Vurnek Maja, Brozinčević Andrijana, Omanović Dario. Heavy metal contents in water, sediment and fish in a karst aquatic ecosystem of the Plitvice Lakes National Park (Croatia)[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2014, 21(5):3826-3839. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-2377-3
[9] Dautovic Jelena, Fiket Zeljka, Baresic Jadranka, Ahel Marijan, Mikac Nevenka. Sources, distribution and behavior of major and trace elements in a complex karst lake system[J]. Aquatic Geochemistry, 2014, 20(1):19-38. doi: 10.1007/s10498-013-9204-9
[10] Zhou Changsong, Zou Shengzhang, Zhu Danni, XIE Hao, CHEN Hongfeng, WANG Jia. Pollution pattern of underground river in karst area of the Southwest China[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 2018, 6(2):71-83.
[11] 陈俭友, 易世友, 顾和孝. 坪桥工业矿废渣影响下的典型裸露型岩溶水文地球化学特征与控制因素研究[J]. 地下水, 2021, 43(5):43-49. doi: 10.19807/j.cnki.DXS.2021-05-014
CHEN Jianyou, YI Shiyou, GU Hexiao. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and concrol factors of typical exposed karst affected by Ping bridge industrial mine waste[J]. Ground Water, 2021, 43(5):43-49. doi: 10.19807/j.cnki.DXS.2021-05-014
[12] 曹玉婷. 建设用地土壤污染风险管控制度完善研究[D]. 武汉: 中南财经政法大学, 2021.
CAO Yuting. Study on the improvement of soil pollution risk control system of construction land[D]. Wuhan: Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, 2021.
[13] 王雨旸, 杨平恒, 张洁茹. 重庆市老龙洞地下河流域硝酸盐来源和生物地球化学过程的识别[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(10):4470-4479.
WANG Yuyang, YANG Pingheng, ZHANG Jieru. Sources and biogeochemical processes of nitrate in the Laolongdong karst underground river basin, Chongqing[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(10):4470-4479.
[14] Nestler Angelika, Berglund Michael, Accoe Frederik, Duta Steluta, Xue Dongmei, Boeckx Pascal, Taylor Philip. Isotopes for improved management of nitrate pollution in aqueous resources: Review of surface water field studies[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2011, 18(4):519-533. doi: 10.1007/s11356-010-0422-z
[15] 盛婷. 基于氮氧同位素和IsoSource模型的农业区地下河硝酸盐来源研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2019.
SHENG Ting. Nitrate-nitrogen pollution sources of an underground river in karst agricultural area uing 15N and 18O isotope technique and isosource model[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2019.
[16] 申春华. 喀斯特地下暗河流域水体中硝酸盐的来源、运移过程及转化机制研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2019.
SHEN Chunhua. Study on the source, migration and transformation mechanism of Nitrate in karst underground river catchment[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2019.
[17] 易世友, 周长松, 朱丹尼, 等. 长江经济带西南裸露型岩溶山区遵义市坪桥地下河系统污染防治试点项目(一期)水文地质详细调查报告[R]. 遵义: 贵州省地矿局第二工程勘察院有限公司, 2021.
[18] 冯海明. 压水试验在岩溶路基注浆效果评价中的应用研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(2):243-250. doi: 10.11932/karst20200214
FENG Haiming. Application of pressure water tests to evaluation of grouting effects on the karst roadbed[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(2):243-250. doi: 10.11932/karst20200214
[19] 汤振, 蒋小珍, 陈立根, 雷明堂, 马骁, 吴晟堂. 龙门县某石灰岩采石场帷幕止水工程及注浆效果评价[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(1):47-58.
TANG Zhen, JIANG Xiaozhen, CHEN Ligen, LEI Mingtang, MA Xiao, WU Shengtang. Groundwater sealing by grouting curtain technique and its grouting effect evaluation of a limestone quarry in Longmen county[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(1):47-58.
[20] 樊科峰. 城镇污水厂雨季截流污水强化二级处理消纳能力研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2020.
FAN Kefeng. Study on the capacity of secondary treatment of intercepted sewage in urban sewage plant in rainy season[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2020.
-



 下载:
下载: