Distribution characteristics of iodine in karst groundwater in Xintian county, Hunan Province and the analysis on the causes of high iodine
-
摘要:
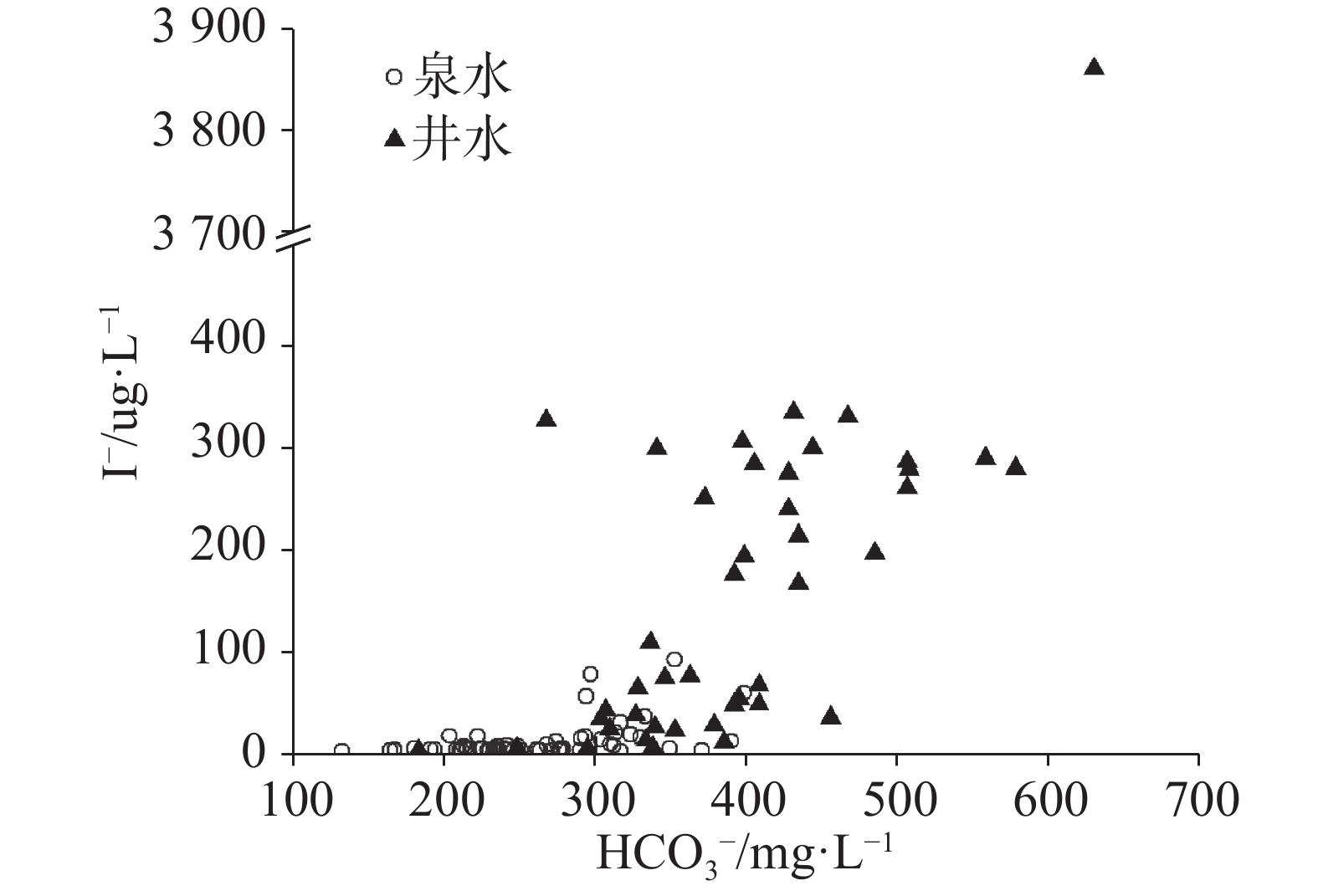
在湖南新田县部分岩溶区发现高碘地下水,威胁着周边居民的饮水安全,查明该区域地下水中碘的分布特征及其控制因素具有重要意义。采集新田县66组泉水样和45组井水样,采用水化学图解法、主成分分析法和GIS技术,分析了泉水和井水的水化学特征,查明了地下水中碘的空间分布特征,剖析了碘富集的主要控制因素。研究发现泉水与井水中碘含量分别为2.7~92.8 μg·L−1和4.15~3 861 μg·L−1,其中,53.3%井水样品碘含量超过《水源性高碘地区和高碘病区的划定》(GB 19380-2016)标准中的界定值100 μg·L−1。受沉积环境、pH、Eh和地下水径流条件影响,高碘地下水主要沿着一条NE−SW向的河谷分布,从峰林谷地地区到地势低洼的河谷平原地带,地下水碘含量整体随着径流条件变差呈现逐渐增加的趋势。海相沉积所形成的富碘富有机质地层是高碘地下水形成的地质基础,发生有机质降解和竞争吸附的弱碱性偏还原环境是导致碘被释放到地下水中的主要因素;此外,水流滞缓的封闭地下水环境也是控制高碘地下水形成的重要因素。
Abstract:Iodine is one of the essential trace elements for human body, which maintains the growth and normal metabolism of the organism. Iodine deficiency or excess will have different degrees of impact on human health. A large field of strontium-rich mineral water was discovered in Xintian county, Hunan Province. However, the iodine content in some strontium-rich groundwater is abnormal, threatening the drinking water safety of local residents. Therefore, it is important to find out the distribution characteristics of iodine in groundwater and the controlling factors of the formation of high iodine groundwater so as to implement the project for the safety of drinking water and to prevent endemic iodine diseases in the study area.
In a hydrogeological survey, 66 groups of spring water samples and 45 groups of well water samples were collected in Xintian county to analyze their hydrochemical characteristics, identify the spatial distribution characteristics of iodine in groundwater and analyze the main factors controlling iodine content in groundwater by means of hydrochemical graphical method, principal component analysis and GIS technology. The results showed that the iodine concentration in spring water and well water ranged from 2.7 to 92.8 μg·L−1 and 4.15 to 3,861 μg·L−1, respectively, with the respective median value of 5.4 μg·L−1 and 168 μg·L−1. It can be seen that all the groundwater with high iodine was well water, and 53.3% of well water samples had iodine concentration exceeding the permitted national standard of 100 μg·L−1 (GB 19380-2016). In contrast, the iodine content in spring water was relatively low, and the overall iodine-deficient groundwater was predominant. High iodine groundwater was mainly distributed along a river valley in the northeast-southwest direction. The iodine content in groundwater showed a gradual increase from the peak-forest valley to the plain area of low-lying river valley, and the hydrochemical type also changed from water with single HCO3-Ca type to water with complex HCO3-Na, HCO3-Na·Ca type, etc.
The marl stratum formed by marine sedimentation of Shetianqiao Formation is rich in iodine and organic matter, which provides good geological conditions for the enrichment of iodine in groundwater. The microbial degradation of organic matter occurs in the closed and partially reducible groundwater environment of the marl aquifer. CO2 generated by organic matter decomposition exists in groundwater mainly in the form of
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ -
Key words:
- karst groundwater /
- iodine /
- spatial distribution /
- principal component analysis /
- controlling factors
-

-
表 1 研究区地下水样品水化学分析统计表
Table 1. Hydrochemical analysis of groundwater samples in the study area
参数 单位 最小值 最大值 平均值 中间值 标准差 变异系数 TDS mg·L−1 136.91 732.81 334.20 322.52 118.05 0.35 总硬度 mg·L−1 65.56 612.20 271.70 254.13 88.49 0.33 Eh mV −96.2 123.9 47.8 64.5 50.13 1.05 pH 6.74 8.91 7.25 7.23 0.29 0.04 K+ mg·L−1 0.06 24.00 2.11 1.13 3.44 1.63 Na+ mg·L−1 0.28 219.72 15.61 2.29 34.76 2.23 Ca2+ mg·L−1 14.85 159.42 89.99 85.23 28.09 0.31 Mg2+ mg·L−1 0.94 59.05 11.40 4.94 13.39 1.17 Cl− mg·L−1 1.30 93.32 11.69 6.36 14.95 1.28 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ mg·L−1 4.89 236.34 25.48 16.17 27.02 1.06 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ mg·L−1 132.50 630.30 316.55 297.19 97.99 0.31 ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ mg·L−1 1.78 91.12 11.76 5.51 17.02 1.45 NO $_2^{−}$ mg·L−1 <0.002 8.650 0.290 <0.002 1.31 4.58 F− mg·L−1 0.04 3.50 0.35 0.16 0.55 1.58 TFe mg·L−1 <0.003 1.260 0.140 0.061 0.22 1.62 I− ug·L−1 2.7 3 861.0 116.7 12.5 401.83 3.44 CODMn mg·L−1 <0.50 2.29 0.53 0.54 0.53 1.00 游离CO2 mg·L−1 1.06 12.67 4.73 4.51 2.51 0.53 Sr2+ ug·L−1 2.9 8 465.0 1 002.2 195.0 1 811.83 1.81 表 2 新田岩溶地下水旋转因子载荷矩阵
Table 2. Rotation factor loading matrix of Xintian karst groundwater
因子 泉水 井水 F1 F2 F3 F1 F2 F3 F4 TDS 0.648 0.729 0.180 0.348 0.855 0.261 0.237 TH 0.444 0.857 0.085 −0.647 0.697 0.228 0.010 pH −0.062 -0.723 −0.119 0.764 −0.092 0.102 −0.047 K+ 0.821 0.011 0.179 −0.025 0.136 −0.001 0.887 Na+ 0.689 0.282 0.450 0.950 0.139 0.084 0.026 Ca2+ 0.291 0.901 0.130 -0.739 0.527 −0.364 0.075 Mg2+ 0.545 0.116 −0.100 −0.004 0.381 0.880 −0.091 Cl− 0.842 0.171 0.194 −0.071 0.747 0.022 0.117 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ 0.740 0.277 0.435 −0.039 0.545 0.335 0.373 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ 0.071 0.960 0.023 0.534 0.606 0.321 −0.260 ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ 0.904 −0.010 −0.031 −0.121 0.114 −0.170 0.882 F− 0.380 −0.017 0.809 0.844 −0.015 0.169 −0.034 I− −0.043 0.466 0.789 0.829 0.191 −0.116 −0.135 Sr2+ −0.263 0.695 0.409 0.217 0.064 0.908 −0.077 特征值 6.749 2.813 1.292 4.675 3.603 1.892 1.156 贡献率/% 48.2 20.1 9.2 33.4 25.7 13.5 8.3 累计方差贡献率/% 48.2 68.3 77.5 33.4 59.1 72.6 80.9 -
[1] Velasco I, Bath SC, Rayman MP. Iodine as essential nutrient during the first 1,000 days of life[J]. Nutrients, 2018, 10(3):290. doi: 10.3390/nu10030290
[2] 崔生. 碘过量来源及非甲状腺损伤作用研究进展[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2021, 36(1):23-25.
CUI Sheng. Research progress on sources of iodine excess and non-thyroid injury effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases, 2021, 36(1):23-25.
[3] 张万起, 陈艳婷. 碘过量对人体健康的影响[J]. 中华地方病学杂志, 2016, 35(6):449-455. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4255.2016.06.013
ZHANG Wanqi, CHEN Yanting. Iodine excess and its effects on human health[J]. Chinese Journal of Endemiology, 2016, 35(6):449-455. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4255.2016.06.013
[4] 申红梅. 中国水源性高碘危害防治与实践[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2019.
[5] 张二勇, 张福存, 钱永, 叶念军, 龚建师, 王雨山. 中国典型地区高碘地下水分布特征及启示[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(3):797-802. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.036
ZHANG Eryong, ZHANG Fucun, QIAN Yong, YE Nianjun, GONG Jianshi, WANG Yushan. The distribution of high iodine groundwater in typical areas of China and its inspiration[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(3):797-802. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.036
[6] 薛江凯, 邓娅敏, 杜尧, 罗义鹏, 程一涵. 长江中游沿岸地下水中有机质分子组成特征及其对碘富集的指示[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(11):4140-4149.
XUE Jiangkai, DENG Yamin, DU Yao, LUO Yipeng, CHENG Yihan. Molecular characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in shallow aquifer along middle reach of Yangtze River and its implications for iodine enrichment[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(11):4140-4149.
[7] Zhang Y, Chen L, Cao S, Tian X, Hu S, Mi X, Wu Y. Iodine enrichment and the underlying mechanism in deep groundwater in the Cangzhou region, North China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 28(9):10552-10563.
[8] 吴飞, 王曾祺, 童秀娟, 段磊. 我国典型地区浅层高碘地下水分布特征及其赋存环境[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2017, 28(2):99-104.
WU Fei, WANG Zengqi, TONG Xiujuan, DUAN Lei. The distribution characteristics and storage environments of rich iodine in shallow groundwater of typical areas in China[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2017, 28(2):99-104.
[9] Xue X, Li J, Xie X, Wang Y, Tian X, Chi X, Wang Y. Effects of depositional environment and organic matter degradation on the enrichment and mobilization of iodine in the groundwater of the North China Plain[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 686:50-62. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.391
[10] Duan L, Wang W, Sun Y, Zhang C, Sun Y. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and health effects of iodine in groundwater in Wei river basin[J]. Exposure and Health, 2020, 12(3):369-383. doi: 10.1007/s12403-020-00348-7
[11] 徐芬, 马腾, 石柳, 董一慧, 刘林, 钟秀, 王妍妍. 内蒙古河套平原高碘地下水的水文地球化学特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2012, 39(5):8-15. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2012.05.020
XU Fen, MA Teng, SHI Liu, DONG Yihui, LIU Lin, ZHONG Xiu, WANG Yanyan. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of high iodine groundwater in the Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2012, 39(5):8-15. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2012.05.020
[12] 王妍妍, 马腾, 董一慧, 徐芬, 闫雅妮, 刘林. 内陆盆地区高碘地下水的成因分析:以内蒙古河套平原杭锦后旗为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(4):66-73.
WANG Yanyan, MA Teng, DONG Yihui, XU Fen, YAN Yani, LIU Lin. The formation of inland-high-iodine groundwater: A case study in Hangjinhouqi, Hetao Plain[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(4):66-73.
[13] Li J X, Zhou H, Wang Y, Xie X, Qian K. Sorption and speciation of iodine in groundwater system: The roles of organic matter and organic-mineral complexes[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2017, 201:39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2017.04.008
[14] 张媛静, 张玉玺, 向小平, 孙继朝, 李亚松. 沧州地区地下水碘分布特征及其成因浅析[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(4):59-65. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2014.04.006
ZHANG Yuanjing, ZHANG Yuxi, XIANG Xiaoping, SUN Jichao, LI Yasong. Distribution characteristics and cause analysis of iodine in groundwater of Cangzhou region[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(4):59-65. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2014.04.006
[15] 苏春田, 黄晨晖, 邹胜章, 谢代兴, 赵光帅, 唐建生, 罗飞, 杨杨. 新田县地下水锶富集环境及来源分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(5):678-683.
SU Chuntian, HUANG Chenhui, ZOU Shengzhang, XIE Daixing, ZHAO Guangshuai, TANG Jiansheng, LUO Fei, YANG Yang. Enrichment environment and sources of strontium of groundwater in Xintian county, Hunan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(5):678-683.
[16] 赵光帅, 苏春田, 潘晓东, 谢代兴, 罗飞, 杨杨, 巴俊杰, 李小盼, 毕奔腾. 湖南新田锶矿泉水文地球化学分带特征分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(6):858-866.
ZHAO Guangshuai, SU Chuntian, PAN Xiaodong, XIE Daixing, LUO Fei, YANG Yang, BA Junjie, LI Xiaopan, BI Benteng. Hydrogeochemical zoning characteristics of the strontium mineral spring in Xintian county, Hunan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(6):858-866.
[17] 卢丽, 王喆, 裴建国, 杜毓超, 林永生, 樊连杰. 红水河中上游流域岩溶地下水水质影响因素的R型因子分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(4):415-419.
LU Li, WANG Zhe, PEI Jianguo, DU Yuchao, LIN Yongsheng, FAN Lianjie. R-mode analysis for influencing factors of karst groundwater quality in middle and upper reaches of the Hongshuihe river[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(4):415-419.
[18] Duan L, Wang W, Sun Y, Zhang C. Iodine in groundwater of the Guanzhong Basin, China: Sources and hydrogeochemical controls on its distribution[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(11):970. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-5781-4
[19] 周鑫, 王璨, 郑鹏飞, 姚腾飞, 巫政卿, 米茂生, 覃佐辉, 李杨. 湘南泥盆系碳酸盐岩区富锶饮用天然矿泉水成矿规律:以新田县新圩矿泉水为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(2):197-209.
ZHOU Xin, WANG Can, ZHENG Pengfei, YAO Tengfei, WU Zhengqing, MI Maosheng, QIN Zuohui, LI Yang. Metallogenic regularity of strontium-rich drinking natural mineral water in Devonian carbonate area in southern Hunan: Taking strontium-rich drinking mineral water in Xinxu town, Xintian county as an example[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(2):197-209.
[20] Hu Q H, Moran J E, Blackwood V. Geochemical cycling of iodine species in soils[M]//Preedy RV, Burrow NG, Watson R. Comprehensive Handbook of Iodine: Nutritional, biochemical, pathological and therapeutic aspects. Oxford: Academic Press, 2009: 93-95.
[21] 孙英, 周金龙, 梁杏, 周殷竹, 曾妍妍, 林丽. 塔里木盆地南缘浅层高碘地下水的分布及成因:以新疆民丰县平原区为例[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(8):2999-3011.
SUN Ying, ZHOU Jinlong, LIANG Xing, ZHOU Yinzhu, ZENG Yanyan, LIN Li. Distribution and genesis of shallow high-iodine groundwater in southern margin of Tarim Basin: A case study of plain area in Minfeng county, Xinjiang[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(8):2999-3011.
[22] 薛肖斌, 李俊霞, 钱坤, 谢先军. 华北平原原生富碘地下水系统中碘的迁移富集规律:以石家庄-衡水-沧州剖面为例[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(3):910-921.
XUE Xiaobin, LI Junxia, QIAN Kun, XIE Xianjun. Spatial distribution and mobilization of iodine in groundwater system of North China Plain: Taking hydrogeological section from Shijiazhuang, Hengshui to Cangzhou as an example[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(3):910-921.
[23] 钱永, 张兆吉, 费宇红, 陈京生, 李亚松. 华北平原饮用地下水碘分布及碘盐分区供应探讨[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2014, 30(1):9-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2014.01.002
QIAN Yong, ZHANG Zhaoji, FEI Yuhong, CHEN Jingsheng, LI Yasong. Spatial distribution of iodine in underground drinking water and discussion on region-specific supply of iodized salt in the North China Plain[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2014, 30(1):9-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2014.01.002
[24] 王雨婷, 李俊霞, 薛肖斌, 田小伟, 迟秀成. 华北平原与大同盆地原生高碘地下水赋存主控因素的异同[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(1):308-320.
WANG Yuting, LI Junxia, XUE Xiaobin, TIAN Xiaowei, CHI Xiucheng. Similarities and differences of main controlling factors of natural high iodine groundwater between North China Plain and Datong basin[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(1):308-320.
[25] 周海玲, 苏春利, 李俊霞, 谢先军. 大同盆地沉积物REE分布特征及其对碘富集的指示[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(2):298-306.
ZHOU Hailing, SU Chunli, LI Junxia, XIE Xianjun. Characteristics of rare earth elements in the sediments of the Datong basin and its indication to the iodine enrichment[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(2):298-306.
[26] 关林瑞, 钱坤, 李俊霞, 谢先军. 大同盆地地下水系统中碘迁移富集的生物标志物证据[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(1):235-242. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2019.0126
GUAN Linrui, QIAN Kun, LI Junxia, XIE Xianjun. Mobilization and enrichment of iodine in groundwater from the Datong basin: Evidences from biomarker study[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(1):235-242. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2019.0126
[27] 韩颖, 张宏民, 张永峰, 张欣. 大同盆地地下水高砷、氟、碘分布规律与成因分析及质量区划[J]. 中国地质调查, 2017, 4(1):57-68. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2017.01.09
HAN Ying, ZHANG Hongmin, ZHANG Yongfeng, ZHANG Xin. Distribution regularity, origin and quality division of high arsenic, fluorine and iodine contents in groundwater in Datong basin[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2017, 4(1):57-68. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2017.01.09
[28] Yuanjing Zhang, Yaoguo Wu, Jichao Sun, Sihai Hu, Yuxi Zhang, Xiaoping Xiang. Controls on the spatial distribution of iodine in groundwater in the Hebei Plain, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(17):16702-16709. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1843-3
[29] 朱沉静, 李俊霞, 谢先军. 大同盆地地下水中碳硫同位素组成特征及其对碘迁移富集的指示[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(12):4480-4491. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2021.12.dqkx202112016
ZHU Chenjing, LI Junxia, XIE Xianjun. Carbon and sulfur isotopic features and its implications for iodine mobilization in groundwater system at Datong basin, Northern China[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(12):4480-4491. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2021.12.dqkx202112016
-




 下载:
下载: