The environmental geological conditions of Land resources in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
-
摘要:
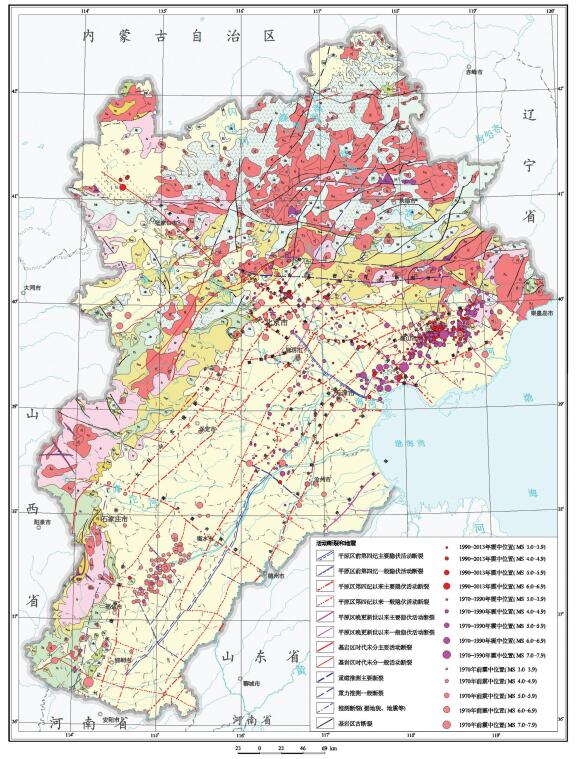
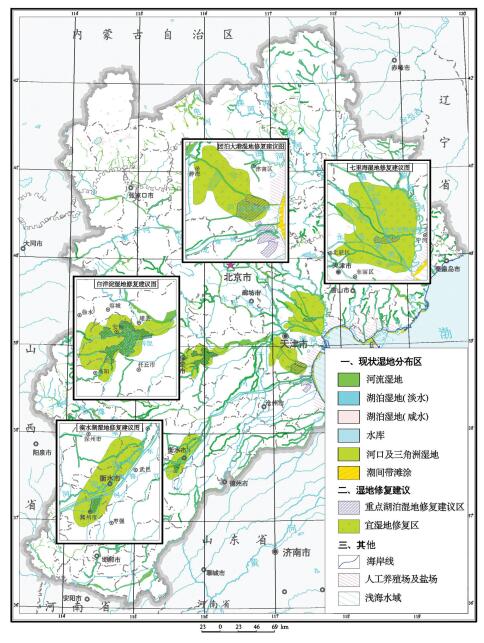
统计分析了京津冀地区土地资源、地下水、湿地、矿产、地热和地质景观等资源条件分布,结果显示,平原区土壤质量总体良好,良好及以上等级土壤分布面积约占平原区面积的80.89%,适宜种植绿色农产品的面积为96363 km2,富硒耕(园)地面积为1894 km2;地下水可开采资源总量为188亿m3/a,但呈现空间分布不均的特征;衡水湖等五大湿地分布面积约为614 km2,近30年来减少了35.57%;金属矿产和非金属矿产资源丰富,例如铁矿资源储量98.4亿t,铜矿资源量111.50万t,石油地质储量249635.02万t;地热资源丰富,开发利用地热资源可替代3.43亿t标准煤;地质遗迹资源丰富,约有300余处可纳入环首都国家公园规划建设。同时,分析了活动断裂与地震、地面沉降、地裂缝、崩滑流和地面塌陷、地下水污染和湿地退化等主要环境地质问题现状;在此基础上,针对城镇发展和重要基础设施建设、湿地保护与修复、地下水资源开发利用、优质耕地资源保护和地质遗迹资开发利用等方面提出了地学建议,为区域规划建设提供地质安全保障和资源保障。
Abstract:The statistics of such resources as land resources, groundwater, wetland, minerals, geothermal and geological relics show that the soil quality is very good and the area of good and above-good grade possesses about 81%, in which the area of green agricultural products is 96363 km2, the area of selenium-rich cultivated and garden lands is 1894 km2; and the total amount of groundwater exploitation is 188 billion m3/a, suggesting characteristics of uneven spatial distribution; the area of five biggest wetlands including Hengshui Lake is about 614 km2, which has been reduced by about 35.57% in the past 30 years; the metal mineral and non-metallic mineral resources are abundant:iron ore reserves have reached 9840 million tons, the amount of copper mineral resources is 111.50 million tons, and oil geological reserves are about 2496.35 million tons; geothermal resources are rich, and the development and utilization of geothermal resources can replace 343 million tons of standard coal; geological relics are abundant, and 300 sites can be included in the Central Capital National Park Planning. Meanwhile, based on an analysis of main environmental geological problems such as active faults and earthquakes, ground collapse and fissures, landslides, land subsidence, groundwater pollution and wetland degradation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, the authors put forward some geoscience suggestions for the urban and important infrastructure planning, wetland protection and restoration, groundwater exploitation, highquality arable land resources protection and geological relics development with the purpose of providing geological and resource safeguard for regional planning and construction.
-

-
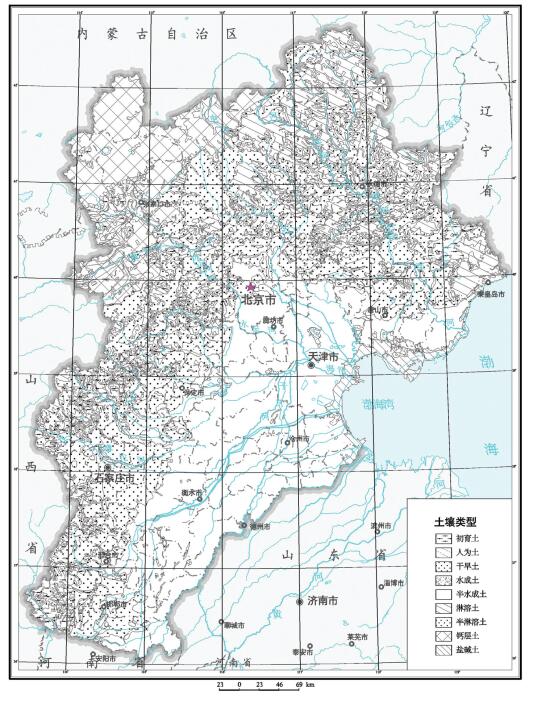
表 1 土壤类型分布
Table 1. Distribution of soil types
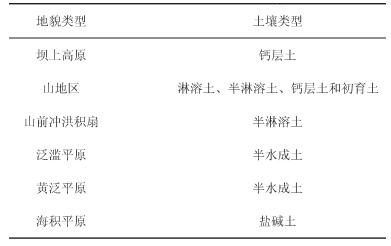
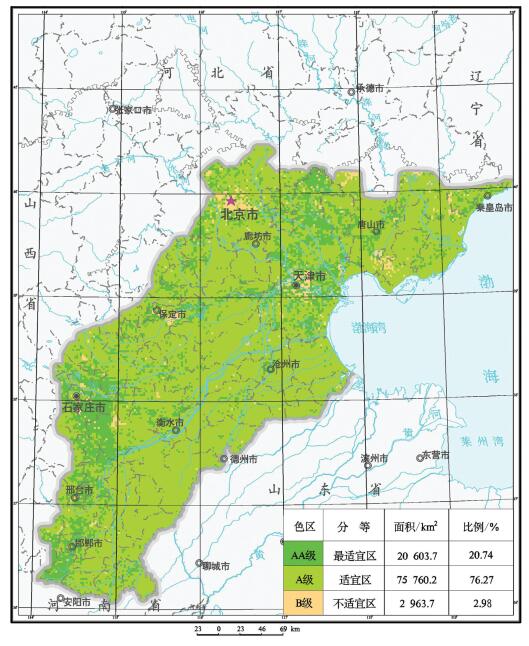
表 2 不同质量等级土壤分布
Table 2. Soil distribution of different quality grades

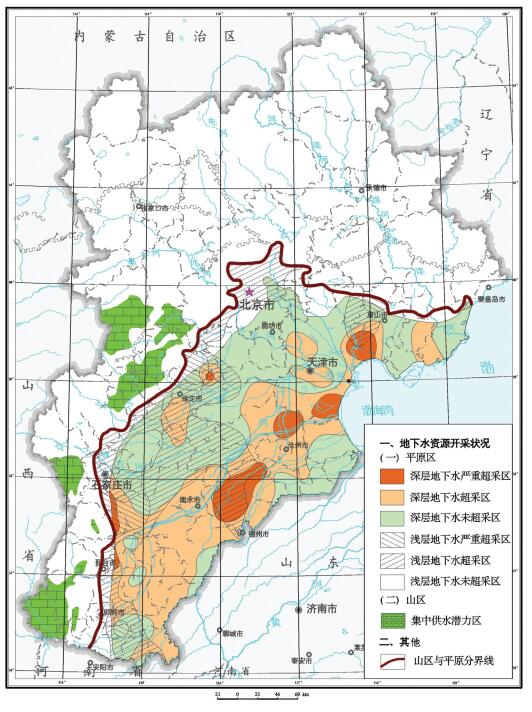
表 3 京津冀平原区地下水资源数据统计
Table 3. Statistics of groundwater resources in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei plain region
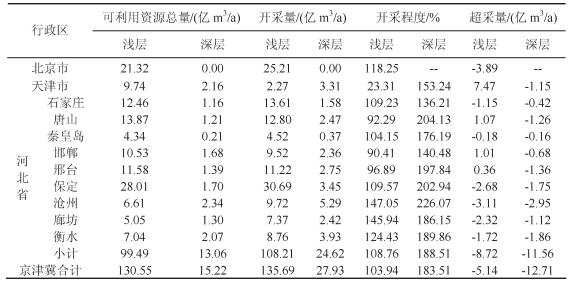
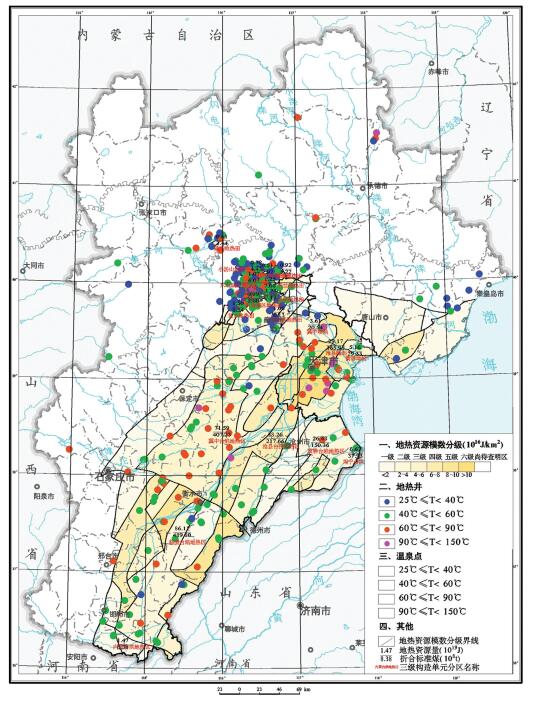
表 4 水热型地热资源数据统计
Table 4. Statistics of hydrothermal geotherm resources
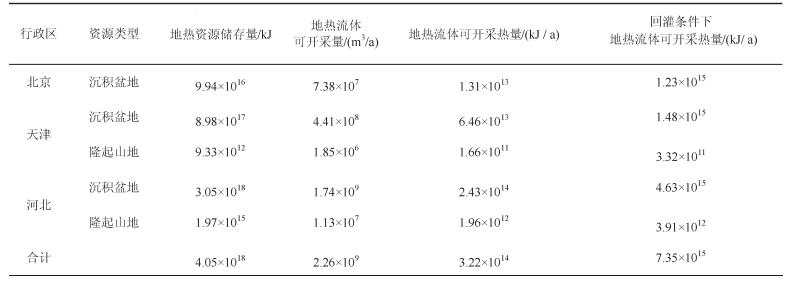
表 5 主要环境地质问题特征表
Table 5. Characteristics of main environmental geological problems

-
Bao Chao, He Dongmei.2017.Spatiotemporal characteristics of water resources exploitation and policy implications in the BeijingTianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration[J].Progress in Geography, 36(1):58-67(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.01.006
Dang Lijuan, Xu Yong.2015.Review of research progress in carrying capacity of water resources[J].Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 22(3):341-348(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_stbcyj201503062.aspx
Fan Jie.2015.Draft of major function oriented zoning of China[J].Acta Geographica Sinica, 70(2):186-201(in Chinese with English abstract).
Fan Jie, Zhou Kan, Chen Dong.2016.Reasonable organization of spatial framework for Bohai Rim-Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei-Capital (Circle)[J].Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 31(1):70-79(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265972734_Process_and...
Fang Chuanglin.2011.New structure and new trend of formation and development of urban agglomerations in China[J].Scientia Geographica Sinica, 31(9):1025-1034(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.doc88.com/p-0701910612235.html
Gao Jingchun, Zhao Yingping, Xu Zhiguo, Mao Guoliang, Zhang Congzhen, Li Dongsheng.2011.Study on moment magnitude of small and moderate earthquakes located by Hebei seismic network[J].North China Earthquake Sciences, 29(2):1-5(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hao Xiaoli.2015.Thoughts and counter-measures on excessively exploration of Groundwater Resources in Shijiazhuang City[J], Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology, 5(12):54-56(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_nyzhyj201512022.aspx
Hu Beibei, Jiang Yanxiang, Zhou Jun, Wang Jun, Xu Shiyuan. Assessment and Zonation of Land Subsidence Disaster Risk of Tianjin Binhai Area[J].Scientia Geographica Sinica, 28(5):693-697(in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang Chengfu, Liu Aanlin, Wang Ye.2010.A discussion on basic definition of disaster risk[J].Journal of Natural Disasters, 19(6):8-16(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/290266405_A_discussion_on...
Jia Huihui, Fu Daqing, Yang Lin, Chen Fenfen, Yin Lan.2016.Geological disaster characteristics and treatment measures of rock collapse in Chengde mountain area[J].Resources Economization & Environment Protection, 6:279-281(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang Manqi.2013.Reinterpret urban agglomeration and related concepts[J].Urban Development Studies, 20(5):30-35(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang Yuan, Yang Yan, Wang Haigang, Tian Fang.2014.Factors controlling land subsidence on the Beijing plain[J].Shanghai Land & Resources, 4(35):130-131(in Chinese with English abstract). http://or.nsfc.gov.cn/bitstream/00001903-5/261488/1/1000014198240.pdf
Jiao Qing, Qiu Zehua.2006.Research progress of major active faults in Beijing Plain area[J].Corpus of Crustal Structure and Crustal Stress, (18):72-84(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Jiuyi, Li Lijuan.2012.Water resources supporting capacity to regional socio-economic development of China[J].Acta Geographica Sinica, 67(3):410-419(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.geog.com.cn/EN/Y2012/V67/I3/410
Li Xindou, Xi Zhimin.2013.Evaluation of deep groundwater exploitation degree in Hebei Plain[J].South-to-north Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 11(6):129-132(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Fangcui, Qi Shengwen, Peng Jianbing, Luo Yong, Zhang Bin.2016.Characters of the ground fissures developing in Beijing[J].Journal of Engineering Geology, 24(6)1269-1277(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Hongwei, Ma Zhen, Chen Sheming, Guo Xu, Su Yongjun, Du Dong, Hu Yunzhuang.2015.Saltwater Intrusion Measurement in Laizhou Bay southern area based on hydro-chemical and geophysical methods[J].Geoscience, 29(2):337-343(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Liangang, Sun Xiaohua, Hao Chunyan, Jiao Runcheng.2015.The research of present situation of geoheritage and protection measures in Beijing area[J].Urban Geology, 10(4):1-5(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Yuan.2003.Risk analysis and zoning of geological hazards (chiefly landslide, rock fall and debris flow) in China[J].The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 14(1):95-99(in Chinese with English abstract).
Lu Dadao.2015.Function orientation and coordinating development of subregions within the Jing-Jin-Ji Urban Agglomeration[J].Progress in Geography, 34(3):265-270(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DLKJ201503001.htm
Meng Hui, Li Chunyan, Zhang Ruolin, Li Yamin.2017.Risk assessment of geological hazards for counties and districts of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J].Progress in geography, 36(3):327-334(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.03.008
Shi Jusong, Shi Ling, Wu Shuren.2007.Difficulties and problematical aspects of landslide risk assessment:An overview[J].Geological Review, 53(6):797-806(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Chenglong, Liu Hui, Zhang Mengtian.2016.The influence of administrative boundary on the spatial expansion of urban land:A case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration[J].Geographical Research, 35(1):173-183(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Lanhua, Ma Wuming, Li Mingming, Zhang Ying, Cui Kaipeng.2015.Suitability evaluation for underground space development in Binhai New Area, Tianjin[J], Geological Survey and Research, 38(4):299-304(in Chinese with English abstract). http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=...
Wang Min, Liu Dongyan.2001.Study on evaluation of damage susceptibility and failure loss in analyzing landslide disaster[J]. Geotechnical Investigation and Surveying, (3):7-11(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Bin, Song Xianfang, Han Dongmei, Guo Zhanrong, Xiao Guoqiang, Yang Jilong.2013.Seawater intrusion degree evaluation based on mathematical statistics and fuzzy mathematics in Qinhuangdao Yangdai River plain[J].Scientia Geographica Sinica, 33(3):342-348(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Jincai, Chu Lifeng, Xiao Zhen, Lu Zechang, Shen Ronghui, Chen Yingjie.2014.Main progress and achievements of land subsidence survey and monitoring in Hebei Plain[J].Geological Survey of China, 1(2):45-50(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Liang.2002.The theory and method of risk zonation of geohazard[J].Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2002, 11(4):323-328(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Maosheng, Tang Yaming.2008.Risk investigation method and practice of geohazards[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 27(8):1205-1216(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200808021.htm
Zhang Xue.2017.Study on the risk assessment of land subsidence in Beijing plain based on 3D modeling[J].South to North Water Transfers and Water Science & technology, 15(1):126-130(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Yingping, Yang Rui, Gao Jingchun, Wang Ning, Jia Jiong, Li Xueying, Cai Lingling, Wang Lichan.2016.Attenuation of ground motion and site response in Hebei region[J].North China Earthquake Sciences, 29(2):1-5.China earthquake engineering journal, 38(supp.2):330-338(in Chinese with English abstract).
鲍超, 贺东梅.2017.京津冀城市群水资源开发利用的时空特征与政策启示[J].地理科学进展, 36(1):58-67. http://www.progressingeography.com/CN/10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.01.006
党丽娟, 徐勇.2015.水资源承载力研究进展及启示[J].水土保持研究, 22(3):341-348. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-STBY201503062.htm
樊杰.2015.中国主体功能区划方案[J].地理学报, 70(2):186-201. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2015.02.016
樊杰, 周侃, 陈东.2016.环渤海-京津冀-首都(圈)空间格局的合理组织[J].中国科学院院刊, 31(1):70-79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KYYX201601009.htm
方创琳.2011.中国城市群形成发育的新格局及新趋向[J].地理科学, 31(9):1025-1034. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95809X/201109/39217732.html
高景春, 赵英萍, 徐志国, 毛国良, 张从珍, 李冬圣.2011.河北省测震台网中小地震矩震级的测定[J].华北地震科学, 29(2):1-5. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96861X/201102/38534858.html
郝晓莉.2015.石家庄市地下水资源的过量开采引发的思考及对策[J].农业灾害研究, 5(12):54-56. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyzhyj201512022
胡蓓蓓, 姜衍祥, 周俊, 王军, 许世远.2008.天津市滨海地区地面沉降灾害风险评估与区划[J].地理科学, 28(5):693-697. http://edu.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/Detail/dlkx200805018
黄崇福, 刘安林, 王野.2010.灾害风险基本定义的探讨[J].自然灾害学报, 19(6):8-16. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4488796
焦青, 邱泽华.2006.北京平原地区主要活动断裂带研究进展[J].地壳构造与地应力文集, (18):72-84. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/SEIS200600009.htm
贾会会, 傅大庆, 杨林, 陈芬芬, 尹岚.2016.承德山区岩质崩塌地质灾害特征及治理措施[J].资源节约与环保, 6:279-281.
江曼琦.2013.对城市群及其相关概念的重新认识[J].城市发展研究, 20(5):30-35. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90379X/201305/46894344.html
姜媛, 杨艳, 王海刚, 田芳.2014.北京平原区地面沉降的控制与影响因素[J].上海国土资源, 4(35):130-131. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SHAD201404033.htm
李九一, 李丽娟.2012.中国水资源对区域社会经济发展的支撑能力[J].地理学报, 67(3):410-419. doi: 10.11821/xb201203012
李新斗, 席志敏.2013.河北平原深层地下水开采程度评价[J].南水北调与水利科技, 11(6):129-132. http://www.oalib.com/paper/5051833
刘方翠, 祁生文, 彭建兵, 罗勇, 张彬.2016.北京市地裂缝分布与发育规律[J].工程地质学报, 24(6):1269-1277. http://html.rhhz.net/GCDZXB/html/20160629.htm
刘宏伟, 马震, 陈社明, 郭旭, 苏永军, 杜东, 胡云壮.2015.基于水化学与地球物理法的莱州湾南岸海(咸)水入侵勘查[J].现代地质, 29(2):337-343. https://www.cnki.com.cn/qikan-XDDZ201502018.html
刘连刚, 孙小华, 郝春燕, 焦润成.2015.北京地区地质遗迹现状与保护对策研究[J].城市地质, 10(4):1-5. http://doi.wanfangdata.com.cn/10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2015.04.001
柳源.2003.中国地质灾害(以崩滑、流为主)危险性分析与区划[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 14(1):95-99. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/71b350d77c1cfad6195fa778-3.html
陆大道.2015.京津冀城市群功能定位及协同发展[J].地理科学进展, 34(3):265-270. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2015.03.001
孟晖, 李春燕, 张若琳, 李亚民.2017.京津冀地区县域单元地质灾害风险评估[J].地理科学进展, 36(3):327-334. http://www.doc88.com/p-6854900068752.html
石菊松, 石玲, 吴树仁.2007.滑坡风险评估的难点和进展[J].地质论评, 53(6):797-806. http://www.docin.com/p-843401905.html
王成龙, 刘慧, 张梦天.2016.行政边界对城市群城市用地空间扩张的影响:基于京津冀城市群的实证研究[J].地理研究, 35(1):173-183. doi: 10.11821/dlyj201601015
王兰化, 马武明, 李明明, 张莺, 崔凯鹏.2015.天津滨海新区地下空间开发适宜性评价[J].地质调查与研究, 38(4):299-304. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-QHWJ201504009.htm
汪敏, 刘东燕.2001.滑坡灾害风险分析中的易损性及破坏损失评价研究[J].工程勘察, (3):7-11. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96187X/201006/33791520.html
章斌, 宋献方, 韩冬梅, 郭占荣, 肖国强, 杨吉龙.2013.运用数理统计和模糊数学评价秦皇岛洋戴河平原的海水入侵程度[J].地理科学, 33(3):342-348. http://dspace.xmu.edu.cn/handle/2288/104669?locale-attribute=en
张进才, 褚立峰, 肖震, 卢泽昌, 沈荣辉, 陈英杰.2014.河北平原地面沉降调查与监测主要进展及成果[J].中国地质调查, (2):45-50. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/72008X/201402/663857131.html
张茂省, 唐亚明.2008.地质灾害风险调查的方法与实践[J].地质通报, 27(8):1205-1216. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95894A/200808/28066054.html
张梁.2002.地质灾害风险区划理论与方法[J].地质灾害与环境保护, 11(4):323-328. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98499X/200004/4948818.html
张雪.2017.基于三维地质建模的北京市平原区地面沉降风险性评价[J].南水北调与水利科技, 15(1):126-130.
赵英萍, 杨锐, 高景春, 王宁, 贾炯, 李雪英, 蔡玲玲, 王莉婵.2016.河北地区地震动衰减和场地响应的研究[J].地震工程学报, 38(增2):330-338.
-



 下载:
下载: