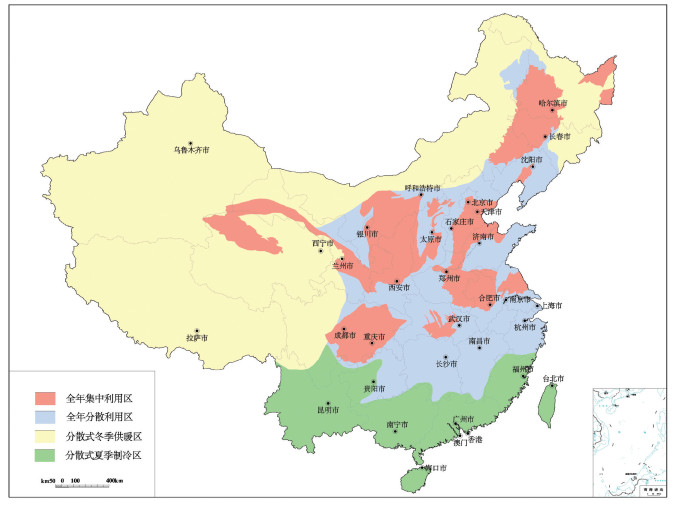
Characteristics and potential of shallow geothermal resources in provincial capital cities of China
-
摘要:
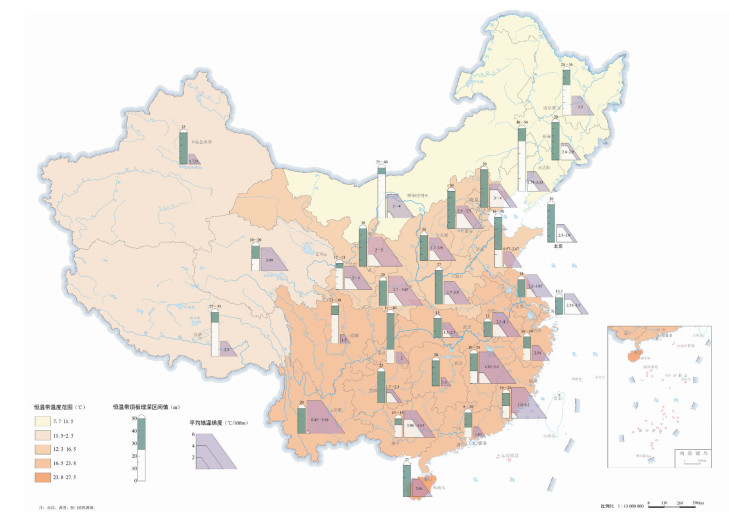
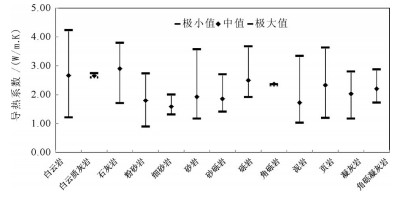
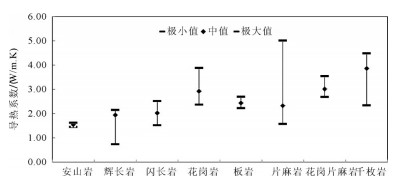
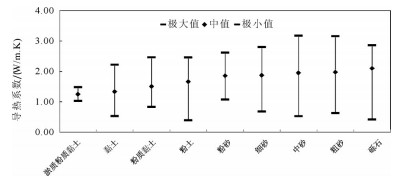
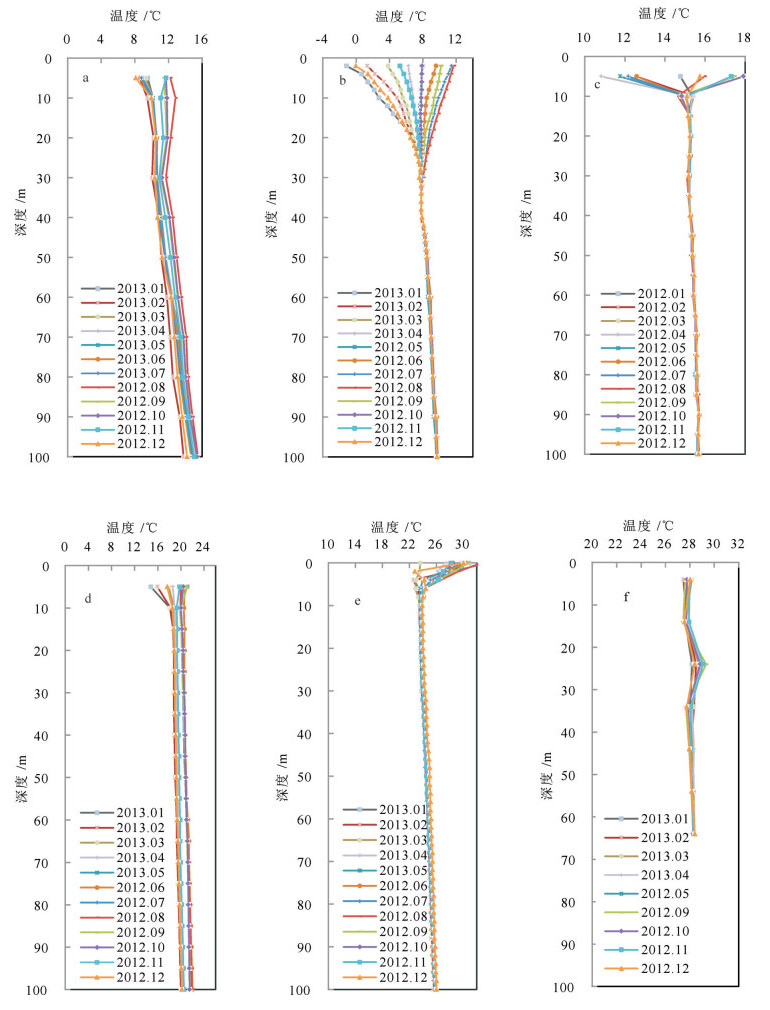
浅层地热能资源以其高效和环保的特点,近年来在中国得到了广泛的应用。地质条件、浅层地温场特征、岩土热物性特征等参数,是影响浅层地热能开发利用的重要参数。笔者在阐述浅层地热能开发利用条件的基础上,结合全国省会城市浅层地热能调查评价成果,对浅层地热能开发利用适宜性和资源潜力进行了评价。结果表明,在我国陆区范围内,恒温带温度受太阳辐射影响最大,恒温带顶板埋深与气温变化趋势相反,岩土体导热系数受岩性影响明显。中国浅层地热能资源主要用于建筑物供暖和制冷。我国31个省会城市80%的土地面积适宜利用浅层地热能,浅层地热能资源每年可开采量折合标准煤2.8亿t,可为供暖和制冷提供丰富的能源储备。按利用方式、需求程度将我国浅层地热能开发分为全年集中利用区、全年分散利用区、分散式冬季供暖区和分散式夏季制冷区4类。浅层地热能开发利用对推动中国绿色、低碳、节能型城市化发展,解决京津冀地区冬季雾霾和南方城市冬季供暖问题具有重要意义。
Abstract:Due to the superiority of high energy efficiency and environmental friendliness, shallow geothermal resources have been widely applied in recent years in China. Geological conditions, characteristics of shallow geotemperature field and thermophysical parameters of rocks and soils are important parameters for shallow geothermal resources. Based on relevant research on nationwide investigation and evaluation of shallow geothermal energy resources in 31 provincial capital cities in China, the authors evaluated the characteristics, resources and regional development planning of shallow geothermal resources in China. The results show that, in constant temperature zone, feature temperature is mostly affected by solar radiation, and the trend of buried depth is opposite to temperature change. What's more, thermal conductivity of soils and rocks is obviously influenced by lithology. The most important application of shallow geothermal resources is for heating and cooling in buildings. Over 80% of the provincial capital cities are suitable for shallow geothermal utilization and annual exploitable shallow geothermal resources of 31 provincial capital cities are equivalent to 280 million tons of standard coal, which is abundant for heating and cooling. Considering the way of utilization and the level of demand, the authors divided whole China into four types of areas, i.e., centralized utilization area (both heating and cooling), distributed utilization area (both heating and cooling), distributed utilization area only for heating and distributed utilization area only for cooling. The development and utilization of shallow geothermal resources are of great significance for promoting the development of China's green, low-carbon and energy-saving urbanization and can also solve the problem of winter smog in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and satisfy the demand of heating in winter in cities of southern China..
-

-
表 1 省会城市所在的温度带、地貌类型及地质条件
Table 1. Climatic regionalization, geomorphic types and geological conditions of provincial capital cities

表 2 地温监测孔位置及详细参数
Table 2. Locations and parameters for different ground temperature monitoring sites

表 3 全国31个省会城市地源热泵系统适宜性分区
Table 3. Result of suitability assessment of GSHP system in provincial capital cities of China

表 4 全国31个省会城市浅层地热能热容量、换热功率计算汇总
Table 4. Summary of the calculation of heat capacity and heat transfer rate of shallow geothermal resources of provincial capital cities in China

表 5 全国31个省会城市浅层地热能制冷/供暖面积计算结果汇总
Table 5. Summary of the calculation of potentials evaluation results of shallow geothermal resources of provincial capital cities in China

-
China Geological Survey. Handbook of Hydrogeology(Second Edition). Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2012(in Chinese).
Duo Ji, Wang Guiling, Zheng Keyan. Research on the Development and Utilization of Geothermal Resources in China[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2017(in Chinese).
Huang Jingrui. Analysis of Distribtion and Change Characteristics of Shallow Groundwater Temperature Field in Xi'an City[D]. Xi'an:Chang'an University, 2013 (in Chinese with English abstract).
http://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/html/10.11648.j.earth.20150406.13.html Lin Wenjing, Liu Zhiming, Wang Wanli, Wang Guiling. The assessment of geothermal resources potential of China[J]. Geology in China, 2013, 40(1):312-321(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/286072143_The_assessment_of_geothermal_resources_potential_of_China
Luo Jin, Rohn Joachim, Xiang Wei, Bertermann David, Blum Philipp.A review of ground investigations for ground source heat pump(GSHP) systems[J]. Energy and Buildings, 117, 2016:160-175. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2016.02.038
Liu Jianjun, Liu Hailei. Testing and analysis of thermal physical properties of rocks[J]. West China Exploration Engineering, 2009(4):144-148 (in Chinese). http://scienceviews.com/geology/rockproperties.html
Qin Xiangxi, Lin Qinglong, Lishaohua. Charateristics of geotemperature filed for shallow geothermal energy assessment and utilization in Hangzhou[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2017, 38 (3):833-837(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271308384_Preface_Hydrogeology_of_shallow_thermal_systems
Ran Weiyan, Li Ningbo, Yang Junwei, Yu Yuan. Some enlightenment gained from city shallow geothermal energy investigation and evaluation[J]. Urban Geology, 2014, 9(Z1):1-3(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.docin.com/p-1718708364.html
Standards of the Geological Mining Industry of the People's Republic of China. Specification for Shallow Geothermal Energy Investigation and Evaluation (DZ/T 0225-2009)[S]. Beijing:Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China, 2009(in Chinese).
Shen Xianjie, Yang Shuzhen, Zhang Wenren. Thermal Properties and Test of Rock[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1988 (in Chinese).
Wang Guiling, Zhang Wei, Liang Jiyun, Lin Wenjing, Liu Zhiming, Wang Wanli. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(4):449-459(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201704002.htm
Wang Wanli, Zhu Xi, Wang Guiling. Method of forecasting the temperature in constant temperature zone under warm temperate climates[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2016, 34(8):1112-1116(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0380133009001403
Wei Wanshun, Zheng Jiasen, Li Wenwei, et al. Shallow Geothermal Energy Resources Evaluation[M]. Beijing:China Earth Publishing House, 2010 (in Chinese).
Wei Wanshun, Zheng Jiasen, Luan Yingbo. Characteristics and influencing factors of the shallow geothermal field in beijing plain area[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(6):1733-1737 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SHAD201404023.htm
Xu Zhenzhang. A discussion of factors influencing thermophysical characteristics of rocks and their mechanisms[J].Pet Expolevelop, 1992, 19(6):84-89 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SKYK199206013.htm
Xu Mo, Wang Di, Jiang Liangwen, Qi Jihong. Review on thermal conductivity coefficient of rock and soil mass[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2011, 33(4):421-433 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201104016.htm
Zhang Wentong, Dong Wei. Advanced Tutorial on Statistical Analysis[M]. Beijing:Higher Education Press, 2004 (in Chinese).
Zhang Baokun, Zhu Gangkun. Climatic Regionalization of China(Draft)[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1959(in Chinese).
Zhang Huizhi, Shi Xuezheng, Yu Dongsheng, Wang Hongjie, Zhao Yongcun, Sun Weixia, Huang Baorong. Spatial prediction of soil temperature in China[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2009, 49(1):1-8(in Chinese with English abstract). http://pedologica.issas.ac.cn/trxben/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2009460101&flag=1
Zheng Jingyun, Yin Yunhe, Li Bingyuan. A New scheme for flimate regionalization in China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2010, 65(1):3-13(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.geog.com.cn/EN/Y2010/V65/I1/3
Zhao Yunzhang, Yan Zhenpeng, Liuxinhao, et al.Shallow Geothermal Energy in Henan Province[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2010(in Chinese).
Zhu Xi, Wang Wanli. Nationwide investigation and evaluation of shallow geothermal energy resources in cities above prefecture level fully completed[R]. News Letters of China Geological Survey, 2016, 2 (10):8-11(in Chinese).
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11053-015-9288-6 多吉, 王贵玲, 郑克棪.中国地热资源开发利用战略研究[M].北京:科学出版社, 2017.
黄景锐. 西安市浅层地温场分布特征及其变化分析[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2013.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10710-1014023094.htm 蔺文静, 刘志明, 王婉丽, 王贵玲.中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J].中国地质, 2013, 40(1):312-321. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130121&flag=1
刘建军, 刘海蕾.岩石热物理性质测试与分析[J].西部探矿工程, 2009(4):144-148. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=xbtk200904047&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
秦祥熙, 林清龙, 李少华.杭州市浅层地温资源温度场特征[J].太阳能学报, 2017, 38(3):833-837. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97895A/201303/47205070.html
冉伟彦, 李宁波, 杨俊伟, 于湲.城市浅层地温能勘查评价工作的几点启示[J].城市地质, 2014, 9(Z1):1-3. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/c69adac933687e21ae45a966.html
沈显杰, 杨淑贞, 张文仁.岩石热物理性质及其测试[M].北京:科学出版社, 1988.
王贵玲, 张薇, 梁继运, 蔺文静, 刘志明, 王婉丽.中国地热资源潜力评价[J].地球学报, 2017, 38(4):449-459. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.02
王婉丽, 朱喜, 王贵玲.暖温带地区恒温层温度的预测方法[J].可再生能源, 2016, 34(8):1112-1116. http://www.docin.com/p-1718708364.html
卫万顺, 郑佳森, 栾英波.北京市平原区浅层地温场特征及其影响因素研究[J].中国地质, 2010, 37(6):1733-1737. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100619&flag=1
卫万顺, 郑桂森, 李文伟, 等.浅层地温能资源评价[M].北京:中国大地出版社, 2010.
许模, 王迪, 蒋良文, 漆继红.岩土体导热系数研究进展[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2011, 33(4):421-433. http://www.doc88.com/p-910958122678.html
徐振章.试论影响岩石热物理性质的因素及机制[J].石油勘探与开发, 1992, 19(6):84-89. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90664X/199206/867157.html
张宝堃, 朱岗昆.中国气候区划(初稿).北京:科学出版社, 1959.
张慧智, 史学正, 于东升, 王洪杰, 赵永存, 孙维侠, 黄宝荣.中国土壤温度的空间预测研究.土壤学报.2009, 49(1):1-8. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/90156X/200901/29387642.html
张文彤, 董伟. Spss统计分析高级教程[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2004.
赵云章, 闫震鹏, 刘新号, 等.河南省城市浅层地热能[M].北京:地质出版社, 2010.
郑景云, 尹云鹤, 李炳元.中国气候区划新方案[J].地理学报, 2010, 65(1):3-13. doi: 10.11821/xb201001002
中国地质调查局.水文地质手册(第二版).北京:地质出版社, 2012.
中华人民共和国地质矿产行业标准. 浅层地热能勘查评价规范(DZ/T 0225-2009)[S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国国土资源部, 2009.
朱喜, 王婉丽. 全国地级以上城市浅层地温能调查评价全面完成[R]. 中国地质调查成果快讯, 2016, 2 (10): 8-11.
-



 下载:
下载: