Geochemical characteristics and source mechanism of geothermal water in Tethys Himalaya belt
-
摘要:
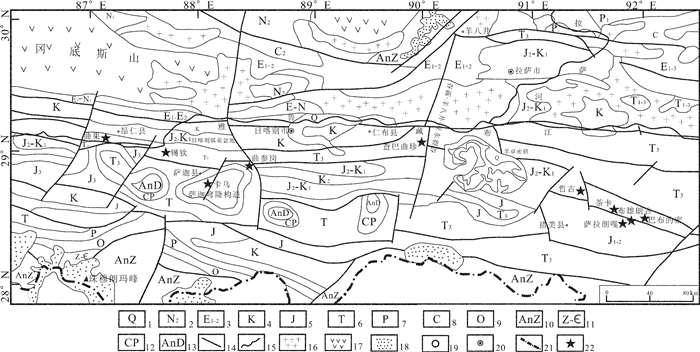
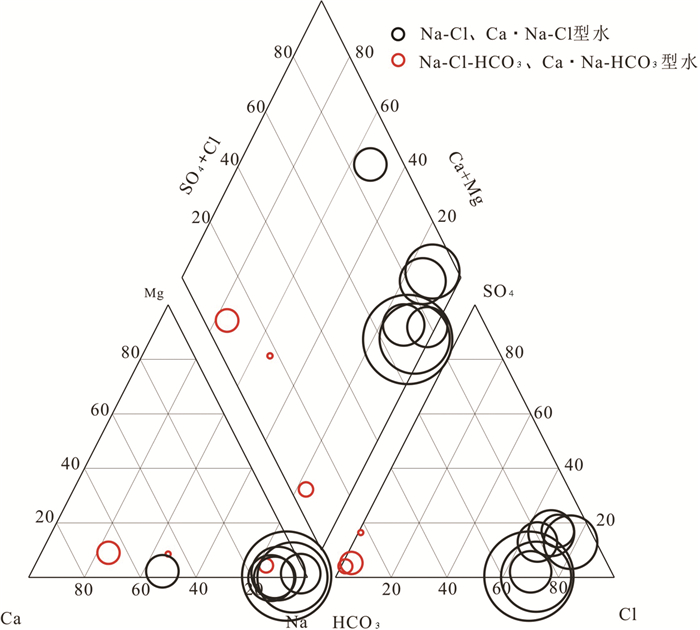
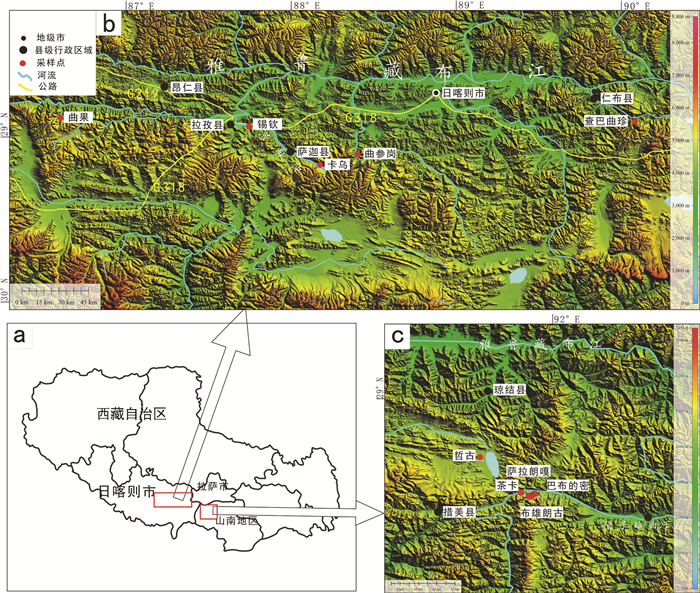
西藏地热资源丰富,特别是其南部特提斯喜马拉雅地热带是一条现今仍然十分活跃的地热带。通过对该地热带10处代表性温泉野外调查及采样分析,讨论了水化学特征及水体中异常富集元素的物源机制。根据热储温度、水化学类型及水体中溶解的典型稀有分散性元素浓度,这些温泉可划分为两大类:一类包括卡乌、曲参岗、查巴曲珍和古堆温泉群,这些温泉热储温度均高于120℃,水化学类型以Na-Cl-HCO3型为主,特征性稀有分散性元素如Li、B和As等显著富集;另一类包括锡钦、哲古和曲果温泉,热储层温度相对较低,变化于60~110℃,水化学类型以CaNa-HCO3和Na-HCO3型为主,Li、B和As等元素浓度较低。第一类温泉系统,水化学成分除与水循环深度大、热储温度高导致更强的水岩作用过程密切相关外,水体中异常富集的Li、B和As等特殊化学成分更可能与演化晚期的残余岩浆流体来源有关。相比之下,第二类温泉系统主要代表了水循环深度较浅、地下水更替频繁、冷水混入比例较大的温泉,水化学成分主要受控于水-岩作用的强弱。因此,特提斯喜马拉雅带地热水体异常富集的稀有分散性元素物源机制主要受控于深部富含这些元素的流体混入过程。
-
关键词:
- 特提斯喜马拉雅地热带 /
- 水化学特征 /
- 热储温度 /
- 物源机制
Abstract:Geothermal resources are very abundant in Tibet. A very active geothermal zone called the Tethys Himalaya geothermal belt has been developed in the southern part of the Tibetan Plateau. This belt is one of the most intense geothermal zones in modern as well as in ancient period in China's mainland, accounting for over 80 percent of the geothermal resources in Tibet. Through field investigations and sampling analyses for 10 typical hot springs from the geothermal area, the hydrochemical characteristics and source mechanisms are discussed. According to the thermal reservoir temperature, the hydrochemical type and the concentration of typical rare and dispersed elements dissolved in the water, the hot springs can be classified into two types:one type includes Kawu, Qucangang, Chabaquzhen and Gudui hot springs, their thermal reservoir temperatures are higher than 120℃ and they belong to NaCl-HCO3 type; some rare and dispersed elements such as Li, B and As are obviously enriched. The other type includes Xinqin, Zhegu and Quguo hot springs, their geothermal reservoir temperatures are relatively low (60-110℃); these springs show lower concentrations of elements of Li, B and As with water chemistry dominated by Ca-Na-HCO3 and Na-HCO3 type. The high concentration of water chemical composition in the first group is closely related to the deeper water circulation and the higher thermal reservoir temperature, and abnormal enrichment of Li, B and As in the hot springs are more likely to be related to the source of residual magmatic fluids. In contrast, the second group of hot springs mainly denotes a shallower water circulation depth and frequent cold groundwater replenishment and mixing. The formation and evolution of chemical compositions of water are mainly related to water/rock interactions.
-

-
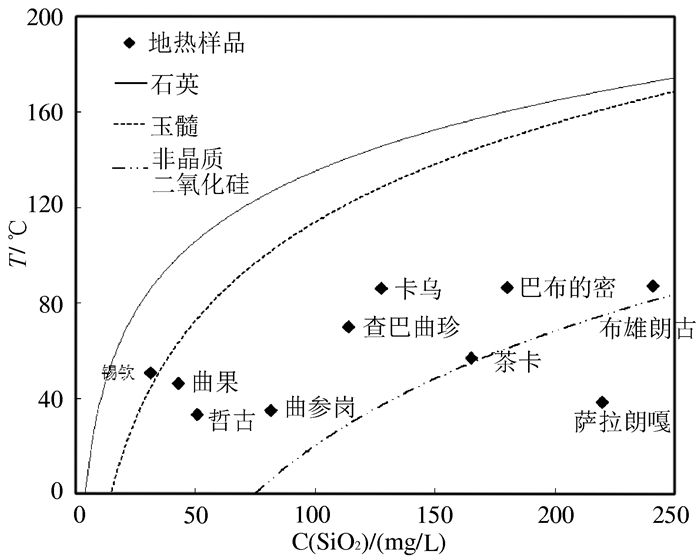
图 5 温泉水中C(SiO2)与温度的关系图(据孙红丽,2015)
Figure 5.
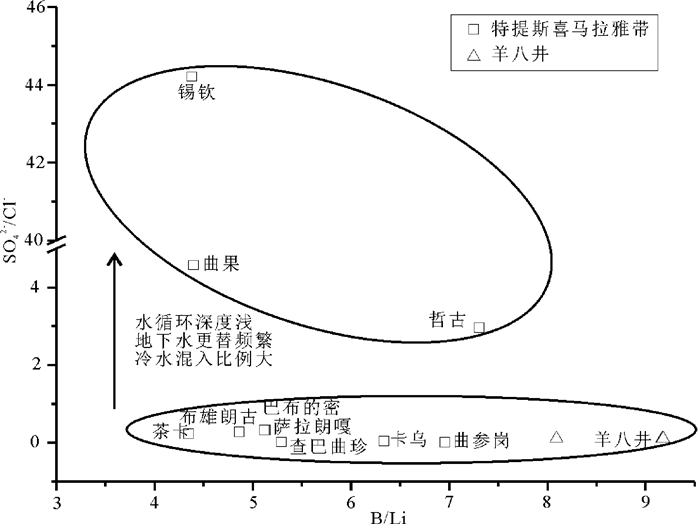
图 6 根据SO42-/Cl-和B/Li不同将温泉水分为水循环深度不同的两类(羊八井数据引自Guo et al., 2007)
Figure 6.
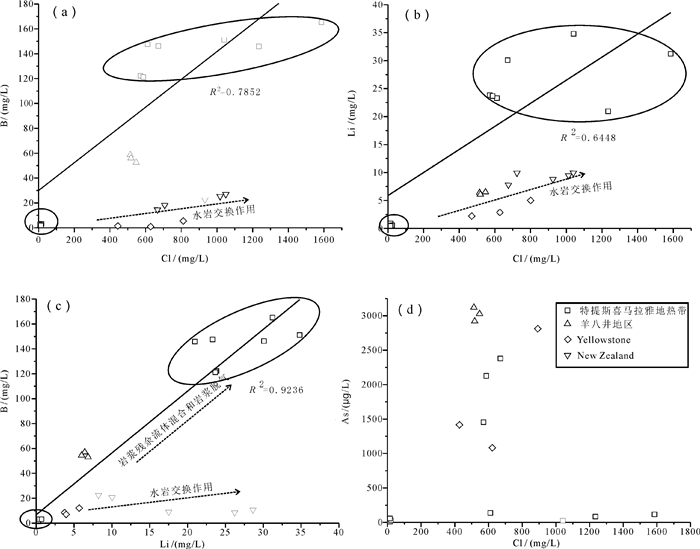
图 7 地热水中B、Li、As和Cl的相关关系图(a、b、d)及B和Li的相关关系图(c)(羊八井数据引自Guo et al., 2007, Yellowstone数据引自Sorey et al., 1997, New Zealand数据引自Millot et al., 2012)
Figure 7.
表 1 研究区温泉水化学特征一览
Table 1. Chemical characteristics of thermal water in the study area
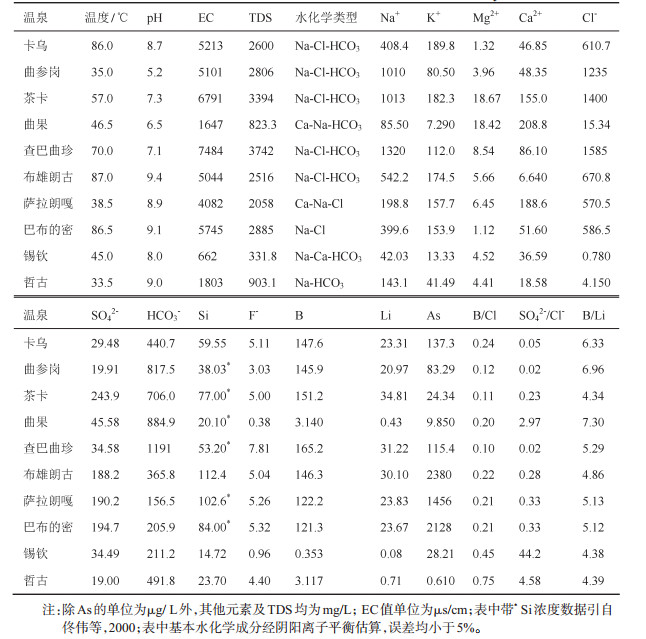
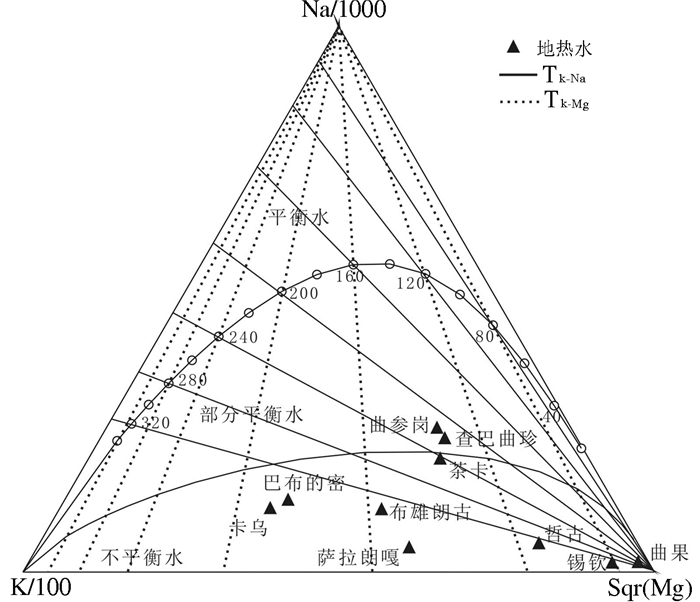
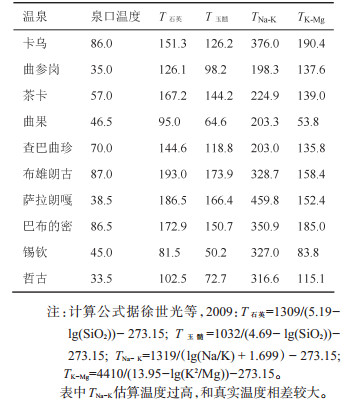
表 2 研究区地热流体地球化学温标计算结果
Table 2. Geochemical temperature calculations of geothermal fluids in the study area
-
Arnórsson S, Andrésdóttir A. 1995. Processes controlling the distribution of boron and chlorine in natural waters in Iceland[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(20):4125-4146. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00278-8
Arnórsson S. 2003. Arsenic in surface-and up to 90℃ ground waters in a basalt area, N-Iceland:processes controlling its mobility[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 18(9):1297-1312. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(03)00052-0
Barbier E. 2002. Geothermal energy technology and current status:an overview[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 6(1):3-65. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0230943360/
Chinese Academy of Sciences Comprehensive Survey Team of Qinghai Tibet Plateau. 1981. Tibet Hot Spring[M]. Beijing:Science Press (in Chinese).
Duo ji. 2003. The basic characteristics of the Yangbajing geothermal field-A typical high temperature geothermal system[J]. Engineering Sciences, 5(1):42-47(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GCKX200301007.htm
Delgado-Outeiriño I, Araujo-Nespereira P, Cid-Fernández J A, Mejuto J C, Martínez-Carballo E, Simal-Gándara J. 2009. Behaviour of thermal waters through granite rocks based on residence time and inorganic pattern[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 373(3):329-336. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ef43f8183683cd01f0a57a964bcd8151
Grimaud D, Huang S, Michard G, Zheng K. 1985. Chemical study of geothermal waters of central Tibet (China)[J]. Geothermics, 14(1):35-48. doi: 10.1016/0375-6505(85)90092-6
Giggenbach W F. 1988. Geothermal solute equilibria. Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 52(12):2749-2765. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90143-3
Gupta H K, Roy S. 2007. Geothermal Energy:An Alternative Resource for the 21 st Century[M]. Elsevier.
Guo Q, Wang Y, Liu W. 2007. Major hydrogeochemical processes in the two reservoirs of the Yangbajing geothermal field, Tibet, China[J]. Journal of Volcanology & Geothermal Research, 166(3):255-268. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-j.jvolgeores.2007.08.004/
Guo Q, Cao Y, Li J, Zhang X, Wang Y. 2015. Natural attenuation of geothermal arsenic from yangbajain power plant discharge in the Zangbo River, Tibet, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 62:164-170. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.01.017
Guo Q, Liu M, Li J, Zhou C. 2017. Geochemical Genesis of arsenic in the geothermal waters from the Rehai hydrothermal system, southwestern China[J]. Procedia Earth & Planetary Science, 17:49-52. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S187852201630056X
Huh Y, Chan, L H, Zhang, L, Edmond J M. 1998. Lithium and its isotopes in major world rivers:implications for weathering and the oceanic budget[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62(12):2039-2051. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00126-4
Li Zhenqing, Hou Zengqian, Nie Fengjun, Meng Xiangjin. 2005. Characteristic and distribution of the partial melting layers in the upper crust:Evidence from active hydrothermal fluid in the South Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(1):68-77(in Chinese with English abstract). http://link.springer.com/10.1007/3-540-27946-6_317
Li Zhenqing, Hou Zengqian, Nie Fengjun, Yang Zhusen. 2006. Enrichment of element cesium during modern geothermal action in Tibet, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(9):1457-1464(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200609019
Liao Zhongli, Mo Xuanxue, Pan Guitang, Zhu Dicheng, Wang Liquan, Zhao Zhidan, Geng Quanru, Dong Guochen. 2006. Tibet:Geochemical characteristics and geodynamic significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(4):845-854(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gyqx200602023
López D L, Bundschuh J, Birkle P, Armienta M A, Cumbal L, Sracek O, Cornejo L, Ormachea M. 2012. Arsenic in volcanic geothermal fluids of latin america[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 429(7):57-75. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4cf7859a384de5ccb9540f2cf7fd40c6
Lu Yuanyuan, Zhao Ping, Xu Ronghua, Xie Liewen. 2012. Geochemical study on boron isotopes in the Yangbajing geothermal field, Tibet[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 47(1):251-264(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Jiexiang, Guo Qinghai, Xu Zhengyan. 2017. Impact of clay mineral formation in high-temperature geothermal system on Accuracy of Na-K and K-Mg geothermometers[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 42(1):142-154. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201701011
Mou Baolei. 1999. Elemental Geochemistry[M]. Beijing:Peking University Press(in Chinese).
Millot R, Hegan A, Négrel P. 2012. Geothermal waters from the Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand:Li, B and Sr isotopes characterization[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 27(3):677-688. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.12.015
Peiffer L, Wanner C, Spycher N, Sonnenthal E L, Kennedy B M, Iovenitti J. 2014. Optimized multicomponent vs. classical geothermometry:Insights from modeling studies at the dixie valley geothermal area[J]. Geothermics, 51(July 2014):154-169. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S037565051300117X
Robinson B, Outred H, Brooks R, Kirkman J. 1995. The distribution and fate of arsenic in the waikato river system, north island, new zealand[J]. Chemical Speciation & Bioavailability, 7(3), 89-96. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/09542299.1995.11083250
Reye A G, Trompetter W J. 2012. Hydrothermal water-rock interaction and the redistribution of Li, Bi and Cl in the taupo volcanic zone, new zealand[J]. Chemical Geology, 314-317(4):96-112. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254112002100
Sorey M L, Colvard E M. 1997. Hydrologic investigations in the Mammoth Corridor, Yellowstone National Park and vicinity, U.S. A[J]. Geothermics, 26(2):221-249. doi: 10.1016/S0375-6505(96)00041-7
Smedley P L, Kinniburgh D G. 2002. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 17(5):517-568. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00018-5
Sun Hongli, Ma Feng, Ling Wenjing, Liu Zhao, Wang Guiling, Nan Dawa. 2015. Geochemical characteristics and geothermometer application in high temperature geothermal field in Tibet[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 34(3):171-177(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201503024.htm
Tan H, Zhang W, Chen J, Jiang S, Kong N. 2012. Isotope and geochemical study for geothermal assessment of the Xining basin of the northeastern Tibetan plateau[J]. Geothermics, 42(2):47-55. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e4b17a0c3adef38be24743952c5c810f
Tan H, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Kong N, Zhang Q, Huang J. 2014. Understanding the circulation of geothermal waters in the Tibetan plateau using oxygen and hydrogen stable isotopes[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 51(51):23-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ead00daae58fb412d742e5edc1193228
Tong Wei, Zhang Zhifei, Zhang Mingtao, Liao Zhijie, You Maozheng, Zhu Meixiang, Guo Guoying, Liu Shibin. 1978. The Himalayan Geothermal Belt[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, (1):76-88, 157(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0377-0273(98)00018-3/
Tong Wei, Zhu Meixiang, Chen Minyang. 1982. Sulfur-isotopic analysis and studies upon the Abyssal heat recharge of the Xizang's(Tibet's) hydrothermal activities[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, (2):81-87(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/19812608779.html
Tong Wei, Liao Zhijie, Liu Shibin. 2000. Tibet Hot Spring[M]. Beijing:Science Press(in Chinese).
Wang Shaoling. 1992. Palaeosinters and its significance in QingXizang Plateau[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, (4):29-31(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG199204011.htm
Xu Shiguang, Guo Yuansheng. 2009. Geothermal Foundation[M]. Science Press(in Chinese).
Yoshiike Y. 2003. Variation in the chemical composition of Obuki Spring, Tamagawa Hot Springs (1951-2000)[J]. Geochemical Journal, 37(6):649-662. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.37.649
Zhang Meng, Lin Wenjing, Liu Zhao, Liu Zhiming, Hu Xiancai, Wang Guiling. 2014. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genetic model of Gulu high-temperature geothermal system in Tibet, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), (3):382-392 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-CDLG201403015.htm
Zhang W, Tan H, Zhang Y, Wei H, Dong T. 2015. Boron geochemistry from some typical Tibetan hydrothermal systems:Origin and isotopic fractionation[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 63:436-445. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.10.006
Zhang Xigen. 1998. Sulfur mineralization of modern geothermal system in Yangbajing Basin of Xizang[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, (1):1-10(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Ping, Duo ji, Liang Tinli, Jin Jian, Zhang Haizheng. 1998. Tibet Yangbajing geothermal field gas geochemical characteristics[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 20(7):691-696(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Ping, Jin Jian, Zhang Haizheng, Duo Ji, Liang Tinli. 1998. Chemical composition of thermal water in the Yangbajing Gerthermal Field, Tibet[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, (1):62-73(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX801.007.htm
Zhao Yuanyi, Zhao Xitao, Ma Zhibang, Deng Jian. 2010. Chronology of the Gulu hot spring cesium deposit in Nagqu, Tibet and it geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(2):211-220(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Xiyu, Yang Shaoxiu. 1983. On the components of the saline lake water in Xizang[J]. Oceanologia Et Limnologia Sinica, 14(04):342-352(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Mianping, Xiang Jun, Wei Xinjun. 1989. Saline Lake in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[M]. Beijing:Beijing Science & Technology Press (in Chinese)
Zheng Mianping, Wang Qiuxia, Duo Ji. 1995. New Type of Hydrothermal Mineralization-Tibet Silicon Cesium Mine[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House(in Chinese).
Zheng Mianping. 2001. Study advances in saline lake resources on the Qinghai-Tibet Pleteau[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 22(2):97-102(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb200102001
佟伟, 张知非, 章铭陶, 廖志杰, 由懋正, 朱梅湘, 过帼颖, 刘时彬. 1978.喜马拉雅地热带[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), (1):76-88, 157. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y267873
佟伟, 朱梅湘, 陈民扬. 1982.西藏水热区硫同位素组成和深源热补给的研究[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), (2):81-87. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000001082910
佟伟, 廖志杰, 刘时彬. 2000.西藏温泉志[M].北京:科学出版社.
多吉. 2003.典型高温地热系统——羊八井热田基本特征[J].中国工程科学, 5(1):42-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2003.01.008
廖忠礼, 莫宣学, 潘桂棠, 朱弟成, 王立全, 赵志丹, 耿全如, 董国臣. 2006.西藏曲珍过铝花岗岩地球化学特征及地球动力学意义[J].岩石学报, 22(4):845-854. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200604008
李振清, 侯增谦, 聂凤军, 孟祥金. 2005.藏南上地壳低速高导层的性质与分布:来自热水流体活动的证据[J].地质学报, 79(1):68-77. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200501008
李振清, 侯增谦, 聂凤军, 杨竹森, 曲晓明, 孟祥金, 赵元艺. 2006.西藏地热活动中铯的富集过程探讨[J].地质学报, 80(9):1457-1464. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.09.019
吕苑苑, 赵平, 许荣华, 谢烈文. 2012.西藏羊八井地热田硼同位素地球化学特征初步研究[J].地质科学, 47(1):251-264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2012.01.021
李洁祥, 郭清海, 余正艳. 2017.高温地热系统中粘土矿物形成对NaK和K-Mg地球化学温标准确性的影响[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 42(1):142-154. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201701011
牟保磊. 1999.元素地球化学[M].北京:北京大学出版社.
孙红丽, 马峰, 蔺文静, 刘昭, 王贵玲, 男达瓦. 2015.西藏高温地热田地球化学特征及地热温标应用[J].地质科技情报, 34(3):171-177. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93477A/201503/665056110.html
王绍令. 1992.青藏高原古泉华及其意义[J].水文地质工程地质, (4):29-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000002885589
熊盛青, 杨海, 丁燕云, 李占奎. 2018.中国航磁大地构造单元划分[J].中国地质, 45 (4):658-680. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180402&journal_id=geochina
徐世光, 郭远生. 2009.地热学基础[M].科学出版社.
中国科学院青藏高原综合科学考察队编. 1981.西藏地热[M].北京:科学出版社.
赵平, 金建, 张海政, 多吉, 梁廷立. 1998.西藏羊八井地热田热水的化学组成[J].地质科学, (1):62-73. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800069865
赵平, 多吉, 梁廷立, 金建, 张海政. 1998.西藏羊八井地热田气体地球化学特征[J].科学通报, 20(7):691-696. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.07.004
赵元艺, 赵希涛, 马志邦, 邓坚. 2010.西藏谷露热泉型铯矿床年代学及意义[J].地质学报. 84(2):211-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.02.010
张锡根. 1998.西藏羊八井现代地下热水系统硫矿的成矿作用[J].化工矿产地质, (1):1-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800229529
张萌, 蔺文静, 刘昭, 刘志明, 胡先才, 王贵玲. 2014.西藏谷露高温地热系统水文地球化学特征及成因模式[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), (3):382-392. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2014.03.15
郑绵平, 向军, 魏新俊. 1989.青藏高原盐湖[M].北京:科学技术出版社.
郑绵平, 王秋霞, 多吉. 1995.水热成矿新类型——西藏铯硅华矿床[M].北京:地质出版社.
郑绵平. 2001.青藏高原盐湖资源研究的新进展[J].地球学报, 22(2):97-102. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2001.02.001
郑喜玉, 杨绍修. 1983.西藏盐湖成分及其成因探讨[J].海洋与湖沼, 14(4):342-352. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000005267084
-



 下载:
下载: