Sedimentary characteristics of the bioherm in Cambrian Changshan Formation in Jinzhou area, Liaoning Province
-
摘要:
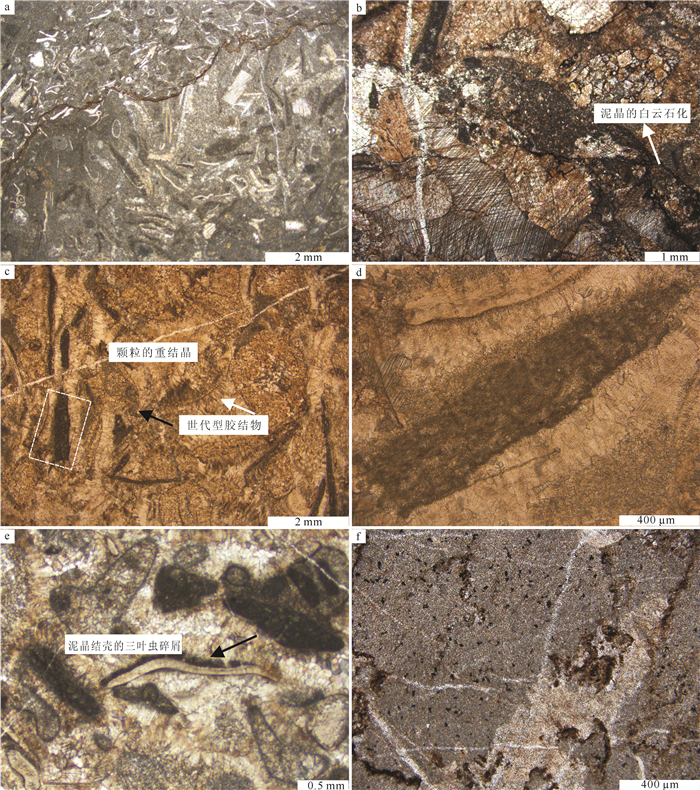
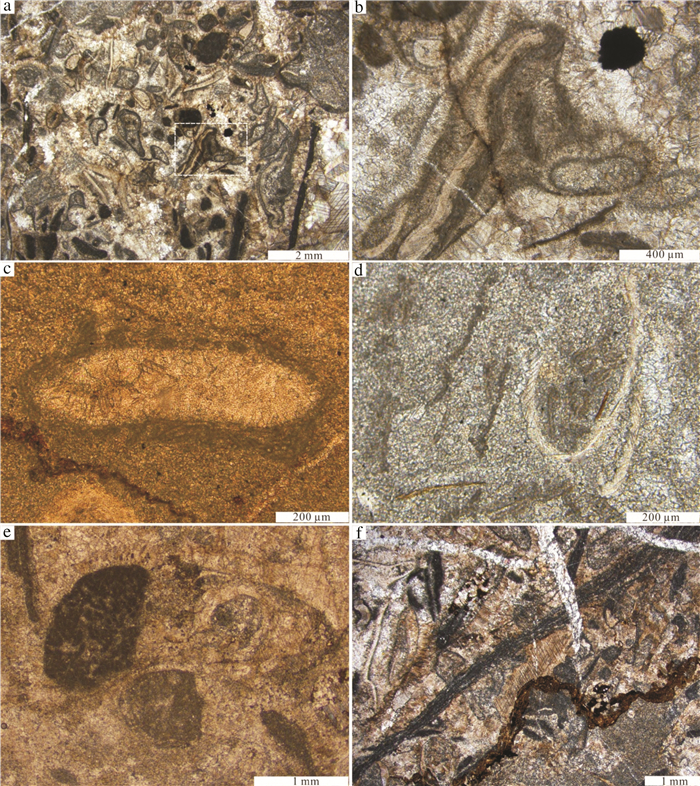
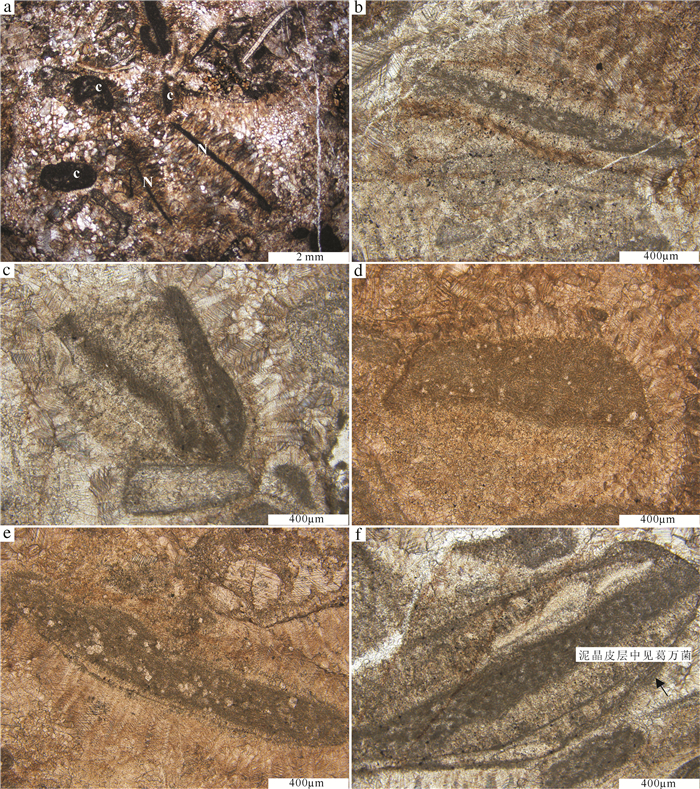
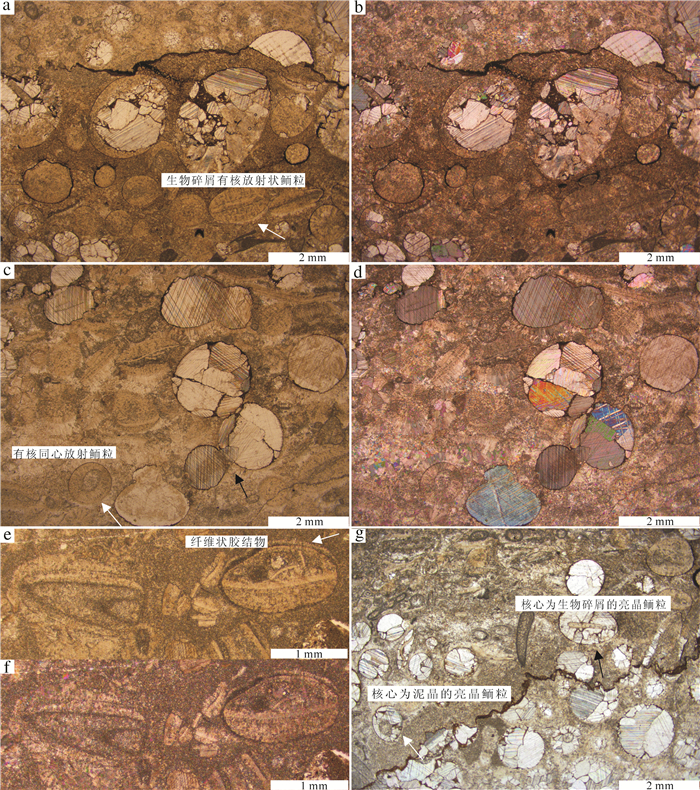
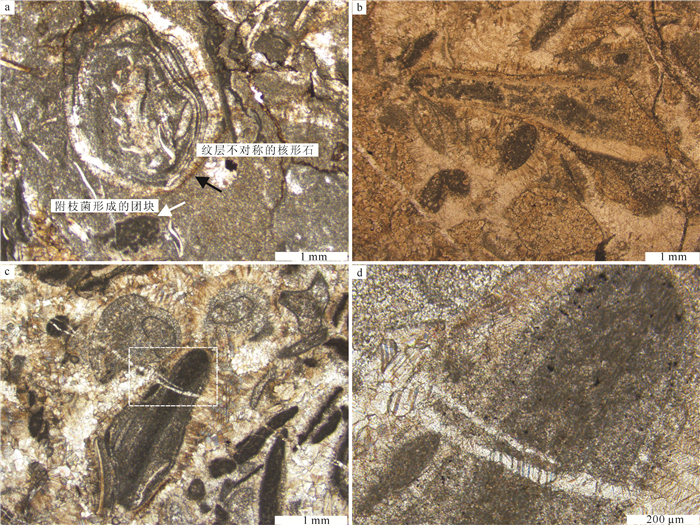
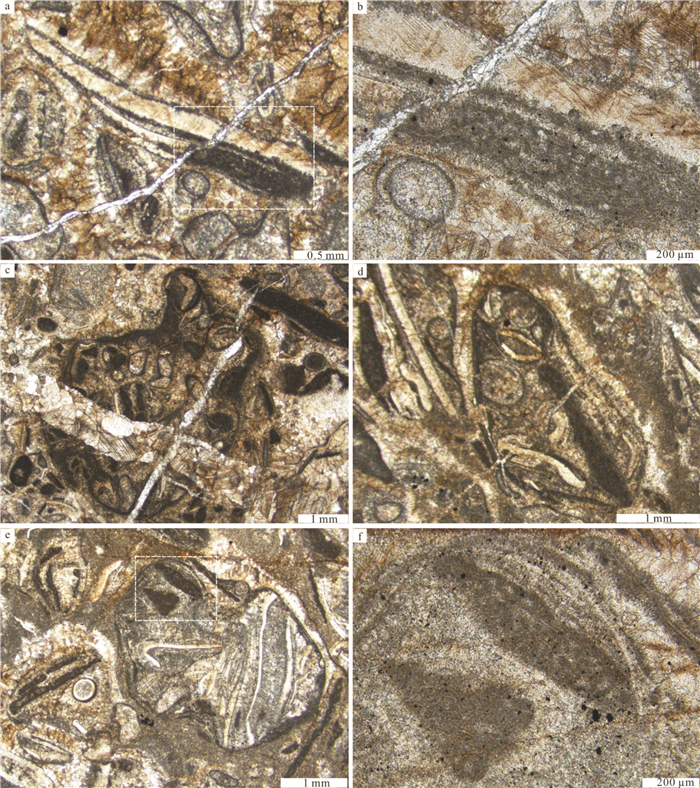
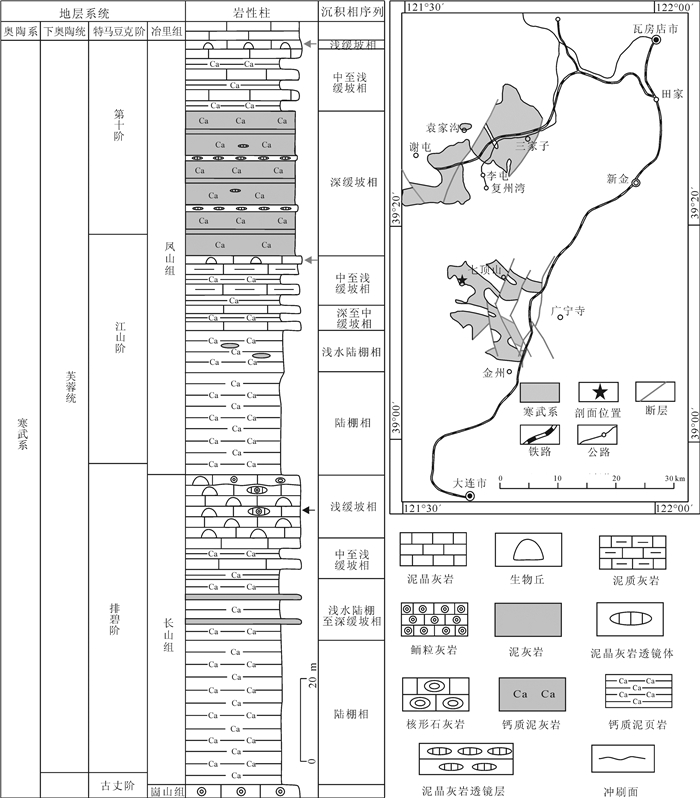
在辽宁金州寒武系长山组顶部,发育一层厚约15 m的生物丘。宏观上,生物丘主要由凝块石和均一石组成;微观上,由致密泥晶组构和各种类型的颗粒组成。在生物丘内部,各种类型的颗粒如钙化微生物、底栖鲕粒、核形石、生物碎屑和凝块等的发育,显示了生物丘复杂的显微组构。其中,三叶虫碎屑表面的泥晶结壳,表现出建设性和破坏性泥晶化作用。泥晶中分散分布的生物碎屑,反映了生物丘形成过程中泥晶较强的黏聚作用。致密泥晶中大量黄铁矿颗粒的发育,反映了异养细菌活动对泥晶形成的贡献。生物丘内部各种类型的颗粒与黄铁矿颗粒的共生,反映了生物丘形成过程中存在复杂的微生物作用,这为微生物沉积作用的研究提供了基础素材,也为生物丘内部各种类型颗粒的研究提供了重要实例和线索。
Abstract:A bioherm 15m in thickness is exposed at the top of Cambrian Changshan Formation in Jinzhou area, Liaoning Province. Macroscopically, the bioherm is made up of thrombolite and leiolite, and microscopically, it is mainly composed of dense micrites and different kinds of grains. There are different types of grains, such as calcified microbes, benthic oolites, oncolites, bioclasts and clots, in the inner part of the bioherm, which indicates complex microfabric of the bioherm. The surface of trilobite skeletal clastics encrusted by micrites shows constructive and destructive micritization. Bioclasts dispersedly distributed within the dense micrite reflect relatively strong binding during the development of the bioherm. Large quantities of pyrite crystals existent in the dense micrites demonstrate that the formation of dense micrite was genetically related to heterotrophy-bacteria activities. Together with pyrite crystals, all kinds of grains within the bioherm reflect complex microbial activities during the formation of the bioherm, which provides not only prerequisite for the study of microbial sedimentation but also an important example and clue for the research on different types of grains within the bioherm.
-
Key words:
- sedimentary features /
- bioherm /
- Changshan Formation /
- Cambrian /
- Jinzhou in Liaoning Province
-

-
Adachi N, Nakai T, Ezaki Y, Liu J. 2014. Late Early Cambrian archaeocyath reefs in Hubei Province, South China:Modes of construction during their period of demise[J]. Facies, 60:703-717. doi: 10.1007/s10347-013-0376-y
Arp G, Reimer A, Reitner J. 2002. Calcification of cyanobacterial filaments:Girvanella and the origin of lower Paleozoic lime mud:Comment and Reply[J]. Geology, 30(6):579-580. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0579:COCFGA>2.0.CO;2
Bahniuk A M, Anjos S, França A B, Matsuda N, Eiler J, Mckenzie J A, Vasconcelos C. 2015. Development of microbial carbonates in the Lower Cretaceous Codó Formation (north-east Brazil):Implications for interpretation of microbialite facies associations and palaeoenvironmental conditions[J]. Sedimentology, 62:155-181. doi: 10.1111/sed.12144
Bosence D, Gibbons K, Le Heron D P, Morgan W A, Pritchard T, Vining B A. 2015. Microbial carbonates in space and time: introduction[C]//Bosence D W J, Gibbons K A, Le Heron D P, Morgan W A, Pritchard T, Vining B A (eds.). Microbial Carbonates in Space and Time: Implications for Global Exploration and Production. London: Geological Society Special Publications, 418: 1-15.
Brasier M D. 1995. The basal Cambrian transition and Cambrian bioevents (from terminal Proterozoic extinctions to Cambrian biomeres)[C]//Walliser O H (ed.). Global Events and Event Stratigraphy in the Phanerozoic. Berlin & Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 113-138.
Brock T D, Madigan M T, Martinko J M, Parker J. 1994. Biology of Microorganisms[M]. New Jersey:Prentice Hall, 271-282.
Castanier S, Le Métayer-Levrel G, Perthuisot J P. 1999. Cacarbonates precipitation and limestone genesis——the microbiogeologist point of view[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 126(1):9-23. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0037073899000287
Chafetz H S, Buczynski C. 1992. Bacterially induced lithification of microbial mats[J]. Palaios, 7:277-293. doi: 10.2307/3514973
Chafetz H S, Guidry S A. 1999. Bacterial shrubs, crystal shrubs, and ray-crystal shrubs:Bacterial vs. abiotic precipitation[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 126(1):57-74 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0037-0738(99)00032-9/
Chen J, Lee J H, Woo J. 2014. Formative mechanisms, depositional processes, and geological implications of Furongian (late Cambrian) reefs in the North China Platform[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 414:246-259. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.09.004
Cumings E R, Shrock R R. 1928. Niagaran coral reefs of Indiana and adjacent states and their stratigraphic relations[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 39(2):579-620. doi: 10.1130/GSAB-39-579
Défarge C, Trichet J, Coute A. 1994. On the appearance of cyanobacterial calcification in modern stromatolites[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 94(1/2):11-19. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0037073894901449
Dong Xiping, Hao Weicheng, Wang Renhou, Wei Xi, Zhang Fang, Li Yan. 2001. Conodont biostratigraphy of Late Cambrian and Early Ordovician in the East Part of Liaohe Fault Basin[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 18(3):219-228 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=wtgswxb200103001
Dupraz C, Visscher P T, Baumgartner L K, Reid R P. 2004. Microbemineral interactions:early carbonate precipitation in a hypersaline lake (Eleuthera Island, Bahamas)[J]. Sedimentology, 51(4):745-765. doi: 10.1111/sed.2004.51.issue-4
Dupraz C, Reid R P, Braissant O, Decho A W, Norman R S, Visscher P T. 2009. Processes of carbonate precipitation in modern microbial mats[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 96(3):141-162. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2008.10.005
Fan Junxuan, Peng Shanchi, Hou Xudong, Chen Dongyang. 2015.Official website of the International Commission on Stratigraphy and the release of the International Chronostratigraphic Chart(v2015/01)[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 39(2):125-134 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201502001.htm
Flügel E. 2004. Microfacies of carbonate rocks:analysis, interpretation and application[M]. Berlin & Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag, 73-571.
Gerdes G, Dunajtschik-Piewak K, Riege H, Taher A G, Krumbein W E, Reineck H E. 1994. Structural diversity of biogenic carbonate particles in microbial mats[J]. Sedimentology, 41(6):1273-1294. doi: 10.1111/sed.1994.41.issue-6
Gong Yunyun. 2016. Sedimentary Fabrics for Cambrian thrombolytic bioherm:An example from the Zhangxia Formation in Werstern Shandong Province[J]. Geoscience, 30(2):436-444 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hong J, Cho S H, Choh S J, Woo J, Lee D J. 2012. Middle Cambrian siliceous sponge-calcimicrobe buildups (Daegi Formation, Korea):Metazoan buildup constituents in the aftermath of the Early Cambrian extinction event[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 253:47-57. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0226518840/
Kah L C, Riding R. 2007. Mesoproterozoic carbon dioxide levels inferred from calcified cyanobacteria[J]. Geology, 35(9):799-802. doi: 10.1130/G23680A.1
Kobluk D R, Risk M J. 1977. Micritization and carbonate-grain binding by endolithic algae[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 61(70):1069-1082.
Krumbein W E. 1979. Calcification by bacteria and algae[C]//Trudinger P A, Swaine D J (eds.). Biogeochemical Cycling of Mineral-forming Elements. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 47-68.
Lee J H, Lee H S, Chen J, Woo J, Chough S K. 2014. Calcified microbial reefs in Cambrian Series 2, North China Platform:Implications for the evolution of Cambrian calcified microbes[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 403:30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.03.020
Lee J H, Chen J, Chough S K. 2015. The middle-late Cambrian reef transition and related geological events:A review and new view[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 145:66-84. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.03.002
Liu L, Wu Y, Yang H, Riding R. 2016. Ordovician calcified cyanobacteria and associated microfossils from the Tarim Basin, Northwest China:systematics and significance[J]. Journal of Systematic Palaeontology, 14(3):183-210. doi: 10.1080/14772019.2015.1030128
Lu Yanhao, Zhang Wentang, Zhu Zhaoling, Xiang Liwen, Lin Huanling, Zhou Zhiyi, Yuan Jingliang, Peng Shanchi, Qian Yi, Zhang Sengui, Li Shanji, Guo Hongjun, Luo Huilin. 1994. The suggestion of building stage about Cambrian in China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 18(4):318 (in Chinese).
Luchinina V A. 2009. Renalcis and Epiphyton as different stages in the life cycle of calcareous algae[J]. Paleontological Journal, 43(4):463-468. doi: 10.1134/S0031030109040169
Maslov V P. 1954. On the Lower Silurian of eastern Siberia[C]//Shatskiy N S (ed.). Matters of Geology of Asia. Moscow: Academy of Sciences of SSSR, 495-529.
Mei Mingxiang. 2001. A review on genetic-textural classification of limestones and the discussion of relative problems[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 20(4):12-18 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-dzkq200104003.htm
Mei Mingxiang. 2007a. Revised classification of microbial carbonates:complementing the classification of limestones[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(5):222-234 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1872-5791(07)60044-X
Mei Mingxiang. 2007b. Discussion on advances of microbial carbonates from the terminological change of thrombolites[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 26(6):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb200706001
Nealson K H. 1997. Sediment bacteria:who's there, what are they doing, and what's new?[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 25(1):403-434. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.25.1.403
Peng Shanchi, Babcock L E, Lin Huanling, Chen Yongan, Qi Yuiping, Zhu Xuejian. 2004. Global Standard Stratotype-section and Point for the Paibian Stage and Furongian Series of Cambrian System[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 28(2):104-113 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dcxzz200402002
Peng Shanchi. 2006. A new global framework with four series for Cambrian System[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 30(2):147-148 (in Chinese). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dcxzz200602010
Peng S, Babcock L E, Cooper R A. 2012. The Cambrian Period[C]//Gradstein F M, Ogg J G, Schmitz M D, Ogg G (eds.). The Geologic Time Scale 2012. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2: 437-488.
Perry C T. 1999. Biofilm-related calcification, sediment trapping and constructive micrite envelopes:a criterion for the recognition of ancient grass-bed environments?[J]. Sedimentology, 46(1):33-45. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.1999.00201.x
Pratt B R. 1982. Stromatolitic framework of carbonate mudmounds[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 52(4):1203-1227.
Pratt B R. 2000. Microbial contribution to reefal mud-mounds in ancient deep-water settings: evidence from the Cambrian[C]//Riding R E, Awramik S M (eds.). Microbial sediments. Berlin & Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 282-288.
Pratt B R. 2001. Calcification of cyanobacterial filaments:Girvanella and the origin of Lower Paleozoic lime mud[J]. Geology, 29(9):763. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0763:COCFGA>2.0.CO;2
Reid R P, Macintyre I G, Browne K M, Steneck R S, Miller T. 1995.Modern marine stromatolites in the Exuma Cays, Bahamas:Uncommonly common[J]. Facies, 33(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/BF02537442
Reitner J. 1996. Globale und regionale Steuerungsfaktoren biogener Sedimentation: DFG-Schwerpunktprogramm[M]. Göttingen: Geologische Institute der Georg-August-Universität Göttingen, 1-428.
Riding R. 1991. Calcified cyanobacteria[C]//Riding R (ed.).Calcareous Algae and Stromatolites. Berlin: Springer, 55-87.
Riding R. 2000. Microbial carbonates:the geological record of calcified bacterial-algal mats and biofilms[J]. Sedimentology, 47(1):179-214. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1046-j.1365-3091.2000.00003.x/
Riding R E, Awramik S M. 2000. Microbial Sediments[M]. Berlin:Springer Science & Business Media, 1-331.
Riding R, Fan J. 2001. Ordovician calcified algae and cyanobacteria, northern Tarim Basin subsurface, China[J]. Palaeontology, 44(4):783-810. doi: 10.1111/pala.2001.44.issue-4
Riding R. 2002a. Structure and composition of organic reefs and carbonate mud mounds:concepts and categories[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 58(1):163-231. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0012-8252(01)00089-7/
Riding R. 2002b. Biofilm architecture of Phanerozoic cryptic carbonate marine veneers[J]. Geology, 30(1):31-34. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0031:BAOPCC>2.0.CO;2
Riding R. 2006a. Microbial carbonate abundance compared with fluctuations in metazoan diversity over geological time[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 185(3):229-238. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c56d19de9a1d789e146a154c19b80e25
Riding R. 2006b. Cyanobacterial calcification, carbon dioxide concentrating mechanisms, and Proterozoic-Cambrian changes in atmospheric composition[J]. Geobiology, 4(4):299-316. doi: 10.1111/gbi.2006.4.issue-4
Riding R. 2011a. Microbialites, stromatolites, and thrombolites[C]//Reitner J, Thiel V (eds.). Encyclopedia of Geobiology. Dordrecht: Springer, 635-654.
Riding R. 2011b. Calcified cyanobacteria[C]//Reitner J, Thiel V (eds.). Encyclopedia of Geobiology. Dordrecht: Springer, 211-223.
Rowland S M, Shapiro R S. 2002. Reef patterns and environmental influences in the Cambrian and earliest Ordovician[J]. Phanerozoic Reef Patterns, 12:95-128.
Sepkoski Jr J J. 1992. Proterozoic-Early Cambrian diversification of metazoans and metaphytes[C]//Schopf J K, Klein C (eds.). The Proterozoic Biosphere. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 553-564.Shapiro R S. 2000. A comment on the systematic confusion of thrombolites[J]. Palaios, 15(2): 166-169.
Spincer B R. 1998. Oolitized fragments of filamentous calcimicrobes and the pseudofossil affinity of Nuia maslov from the Upper Cambrian rocks of central Texas[J]. Journal of Paleontology, 72(3):577-584. doi: 10.1017/S0022336000024355
Sun Yunzhu. 1924. Cambrian Animals' Fossils in the Northern China[M]. Palaeontologia Sinica, B species, 1, 4. Beijing: Science Press, 1-109 (in Chinese).
Thompson J B, Ferris F G. 1990. Cyanobacterial precipitation of gypsum, calcite, and magnesite from natural alkaline lake water[J]. Geology, 18(10):995-998. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<0995:CPOGCA>2.3.CO;2
Thompson J B. 2000. Microbial whitings[C]//Riding R, Awramik S M (eds.). Microbial Sediments. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 250-260.
Toomey D F, Klement K W. 1966. A problematical micro-organism from the El Paso Group (Lower Ordovician) of west Texas[J]. Journal of Paleontology, 40(6):1304-1311. http://www.jstor.org/stable/1301946
Turner E C, Narbonne G M, James N P. 1993. Neoproterozoic reef microstructures from the Little Dal Group, northwestern Canada[J]. Geology, 21:259-262. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0259:NRMFTL>2.3.CO;2
Turner E C, James N P, Narbonne G M. 2000. Taphonomic control on microstructure in Early Neoproterozoic reefal stromatolites and thrombolites[J]. Palaios, 15(2):87-111. doi: 10.1669/0883-1351(2000)015<0087:TCOMIE>2.0.CO;2
Wang Wenzhi, Yang Yueming, Wen Long, Luo Bing, Luo Wenjun, Xia Maolong, Sun Sainan. 2016. A study of sedimentary characteristics of microbial carbonate:A case study of the Sinian Dengying Formation in Gaomo area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Geology in China, 43(1):306-318 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201601023.htm
Wood R. 1999. Reef Evolution[M]. Oxford:Oxford University Press, 413-414.
Woods A D. 2013. Microbial ooids and cortoids from the Lower Triassic (Spathian) Virgin Limestone, Nevada, USA:Evidence for an Early Triassic microbial bloom in shallow depositional environments[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 105:91-101. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.07.011
Wu Shuang, Ma Qingli, Hu Zhenghui. 2008. Study on paleontology and sedimentary environment of Cambrian sequences in East Liaodong Peninsula[J]. Resources and Industries, 10(1):119-123 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xiang Liwen, Zhu Zhaoling, Li Shanji, Zhou Zhiqiang. 2000.Stratigraphical Lexicon of China·Cambrian[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-95 (in Chinese).
Yang Renchao, Fan Aiping, Han Zuozhen, Chi Naijie. 2011. Status and prospect of studies on oncoid[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 26(5):465-474 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkxjz201105001
Yang Xinde, Li Xingyun. 1997. A Correlation Study of Multiple Stratigraphic Division in China:the Rock Strata in Liaoning Province[M]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences Press, 58-85 (in Chinese).
Zhu Zhaoling, Xiang Liwen, Liu Shucai, Luo Kunli, Du Shengxian, Liang Zongwei. 2005. New advance in the Study of the Upper Cambrian Kushanian Stage of North China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 29(S1):462-466 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200501746392
Zhuravlev A Y, Wood R A. 1996. Anoxia as the cause of the midEarly Cambrian (Botomian) extinction event[J]. Geology, 24:311-314. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1996Geo....24..311Z
董熙平, 郝维城, 王仁厚, 魏喜, 张放, 李岩. 2001.辽河断陷东部晚寒武世至早奥陶世牙形石生物地层[J].微体古生物学报, 18(3):219-228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0674.2001.03.001
樊隽轩, 彭善池, 侯旭东, 陈冬阳. 2015.国际地层委员会官网与《国际年代地层表》 (2015/01版)[J].地层学杂志, 39(2):125-134. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=DCXZ201502001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
贡云云. 2016.寒武系凝块石生物丘的沉积组构:以鲁西地区张夏组为例[J].现代地质, 30(2):436-444. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.02.020
卢衍豪, 张文堂, 朱兆玲, 项礼文, 林焕令, 周志毅, 袁金良, 彭善池, 钱逸, 章森贵, 李善姬, 郭鸿俊, 罗惠麟. 1994.关于我国寒武系建阶的建议[J].地层学杂志, 18(4):318. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ404.018.htm
梅冥相. 2001a.灰岩成因——结构分类的进展及其相关问题讨论[J].地质科技情报, 20(4):12-18. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb200104003
梅冥相, 马永生. 2001b.华北北部晚寒武世层序地层及海平面变化研究——兼论与北美晚寒武世海平面变化的对比[J].地层学杂志, 25(3):201-206. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dcxzz200103007
梅冥相. 2007a.微生物碳酸盐岩分类体系的修订:对灰岩成因结构分类体系的补充[J].地学前缘, 14(05):222-234. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200705022
梅冥相. 2007b.从凝块石概念的演变论微生物碳酸盐岩的研究进展[J].地质科技情报, 26(6):1-9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb200706001
彭善池, Babcock L E, 林焕令, 陈永安, 祁玉平, 朱学剑. 2004.寒武系全球排碧阶及芙蓉统底界的标准层型剖面和点位[J].地层学杂志, 28(02):104-113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2004.02.002
彭善池. 2006.全球寒武系四统划分框架正式确立[J].地层学杂志, 30(02):147-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2006.02.010
孙云铸. 1924.中国北部寒武纪动物化石, 第四册[M].北京: 农商部地质调查所, 1-109.
王文之, 杨跃明, 文龙, 罗冰, 罗文军, 夏茂龙, 孙赛男. 2016.微生物碳酸盐岩沉积特征研究——以四川盆地高磨地区灯影组为例[J].中国地质, 43(1):306-318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.023 http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160123&flag=1
武爽, 麻清莉, 胡争辉. 2008.辽东半岛寒武纪地层古生物及沉积环境[J].资源与产业, 10(1):119-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2464.2008.01.031
项礼文, 朱兆玲, 李善姬, 周志强. 2000.中国地层典·寒武系[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-95.
杨仁超, 樊爱萍, 韩作振, 迟乃杰. 2011.核形石研究现状与展望[J].地球科学进展, 26(05):465-474. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201105001
杨欣德, 李星云. 1997.全国地层多重划分对比研究:辽宁省岩石地层[M].北京:中国地质大学出版社, 58-85.
朱兆玲, 项礼文, 章森桂, 刘书才, 雒昆利, 杜圣贤, 梁宗伟. 2005.华北上寒武统崮山阶研究新进展[J].地层学杂志, 29(S1):462-466. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7065166
-



 下载:
下载: