Dataset of the 1: 50 000 Hydrogeological Map of the Plain Area of the Baiyangdian Lake Basin, Xiongan New Area
-
摘要:
本数据集依托2016年中国地质调查局"白洋淀流域平原区1:50 000水文地质调查"项目,在充分收集以往地质资料的基础上,开展了隶属雄安新区规划建设核心区域的安新县幅、雄县幅1:50 000水文地质及专项生态环境地质调查工作,编制了标准的1:50 000水文地质图及说明书,依照行业规范将此次调查获取的数据建立了1:50 000水文地质调查成果数据集。本数据集包含8种数据类型,包含895个基础调查数据,22个野外地质综合调查点数据,82个地层岩性界限调查点数据,540个水文地质调查点数据,22个环境地质调查点数据,12个钻孔基本情况数据,71个抽水试验综合成果数据,2 200个野外照片数据,共计3 844个数据。本数据集对认识白洋淀及周边区域水文地质条件,评价地下水资源,以及研究湿地生态功能退化等生态地质环境问题具有一定的参考意义。
-
关键词:
- 雄安新区 /
- 白洋淀流域 /
- 水文地质 /
- 湿地生态 /
- 1:50 000数据集
Abstract:This 1:50 000 hydrogeological survey dataset was created as a result of the CGS (China Geological Survey) project "Hydrogeological Survey (1:50 000) of the Plain Area of the Baiyangdian Lake Basin" in 2016, building on previously collected geological information. It was prepared in accordance with industrial specifications, using data acquired through this survey by conducting a 1:50 000 hydrogeological and specifically eco-environmental geological survey in the Anxin and Xiong Counties, both located within the core planning and building region of Xiongan New Area, and by preparing a standard 1:50 000 hydrogeological map with instructions for its use. This dataset has 8 types of data, including 895 basic survey data, 22 data from combined geological field survey points, 82 data from stratum lithological boundary survey points, 540 data from hydrogeological survey points, 22 data from environmental geological survey points, 12 data on basic information from drilled boreholes, 71 data from comprehensive results of pumping tests and 2 200 data from field pictures, in total 3 844 data. This dataset has implications as a reference work that are critical to understanding hydrogeological conditions in Baiyangdian Lake and its surroundings, evaluating groundwater resources and investigating problems relating to the eco-geological environment, such as degradation of wetland ecological functions.
-
Key words:
- Xiongan New Area /
- Baiyangdian Lake Basin /
- Hydrogeological /
- Wetland ecology /
- 1:50 000 dataset
-

-
表 1 数据库(集)元数据简表

表 2 调查数据类型统计表

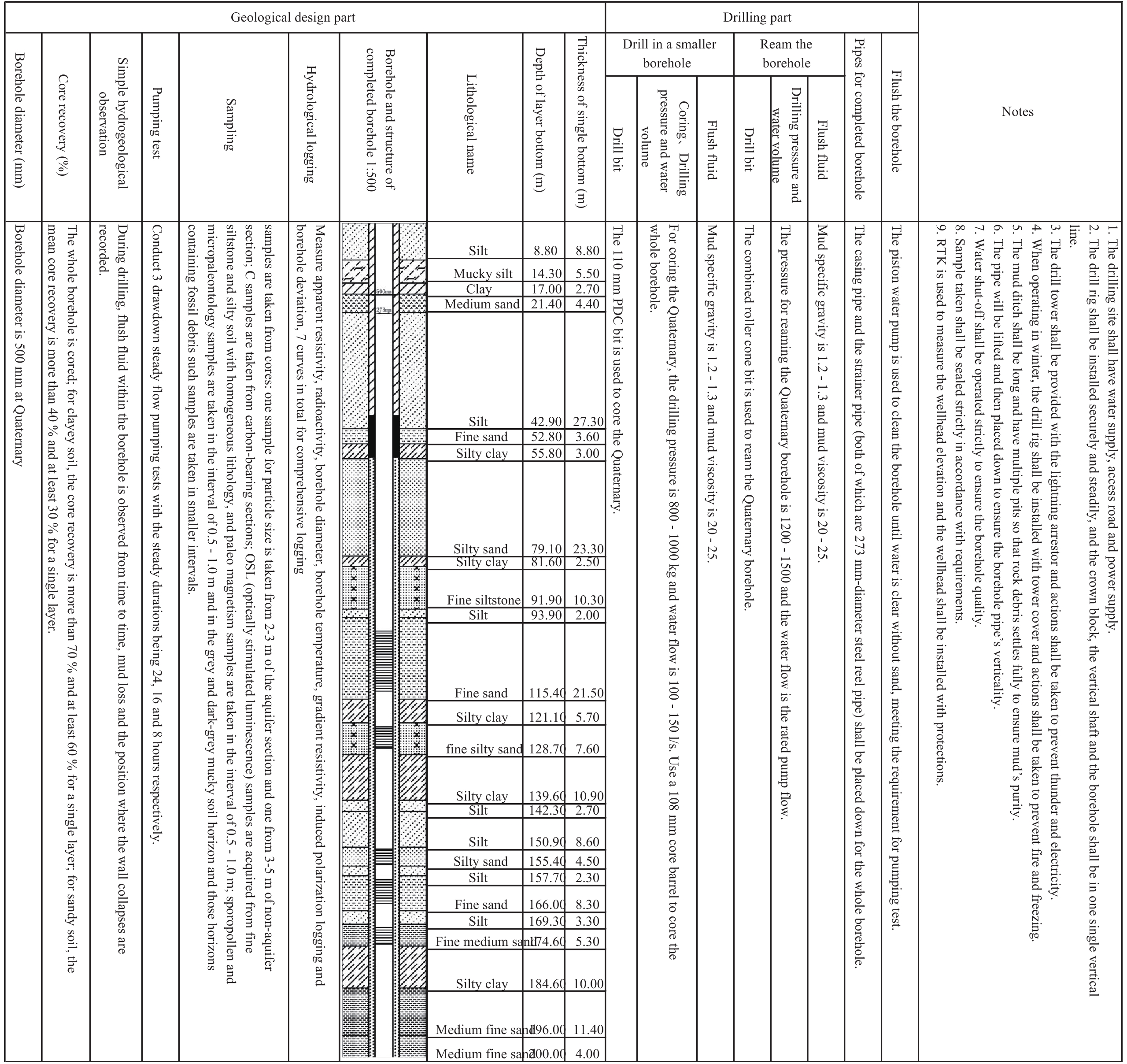
表 3 雄安新区白洋淀流域平原区1:50 000水文地质数据集基础调查数据属性表
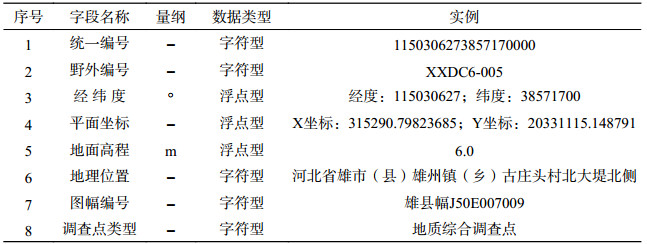
表 4 雄安新区白洋淀流域平原区1:50 000水文地质数据集野外地质综合调查点属性表
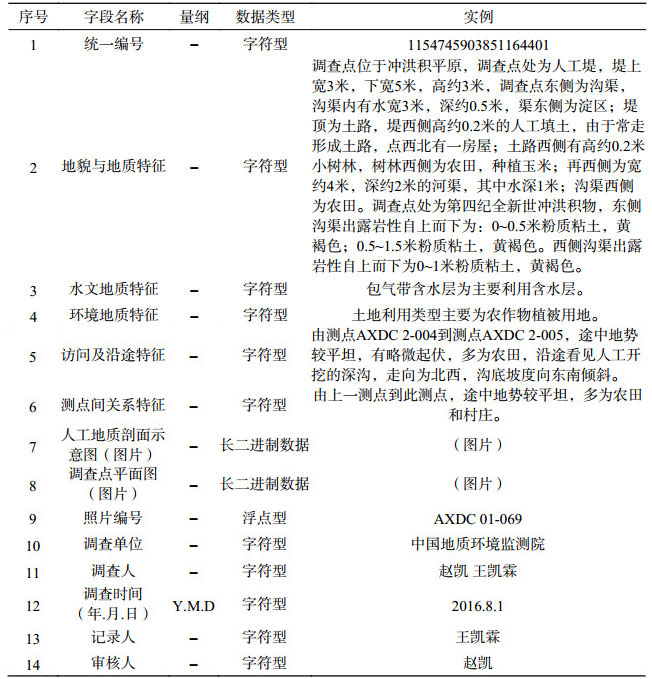
表 5 雄安新区白洋淀流域平原区1:50 000水文地质数据集地层岩性界限调查点属性表
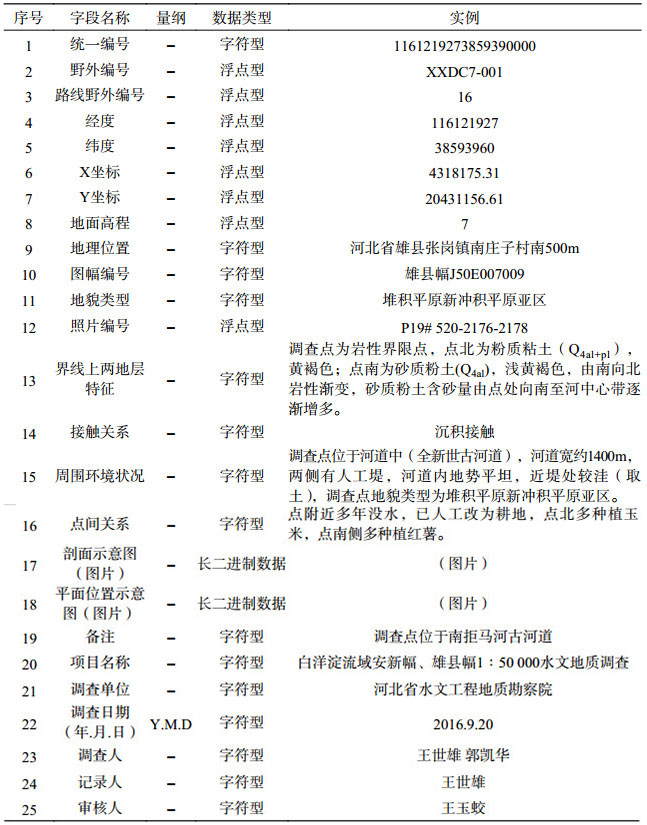
表 6 雄安新区白洋淀流域平原区1:50 000水文地质数据集水文地质调查点属性表
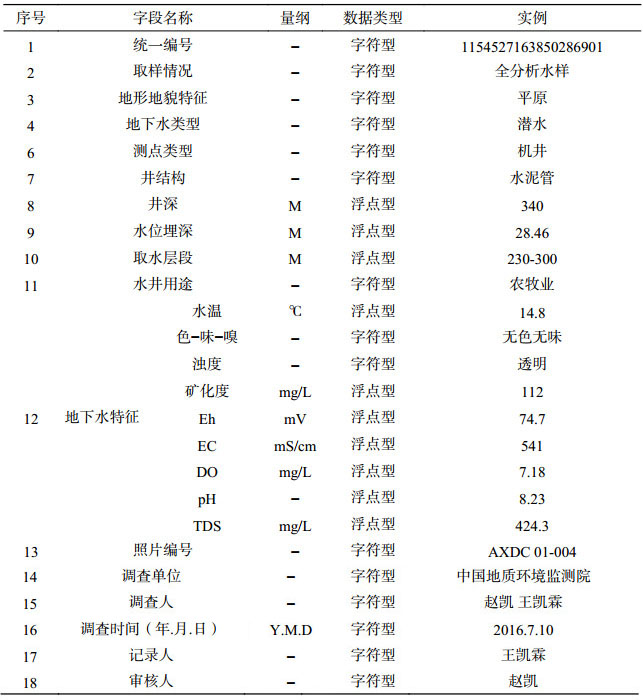
表 7 雄安新区白洋淀流域平原区1:50 000水文地质数据集环境地质调查点属性表

表 8 雄安新区白洋淀流域平原区1:50 000水文地质数据集钻孔基本情况属性表
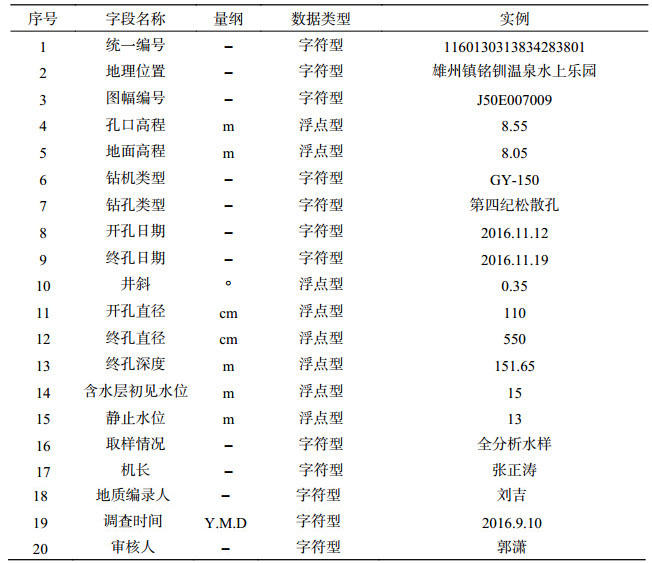
表 9 雄安新区白洋淀流域平原区1:50 000水文地质数据集抽水试验综合成果属性表
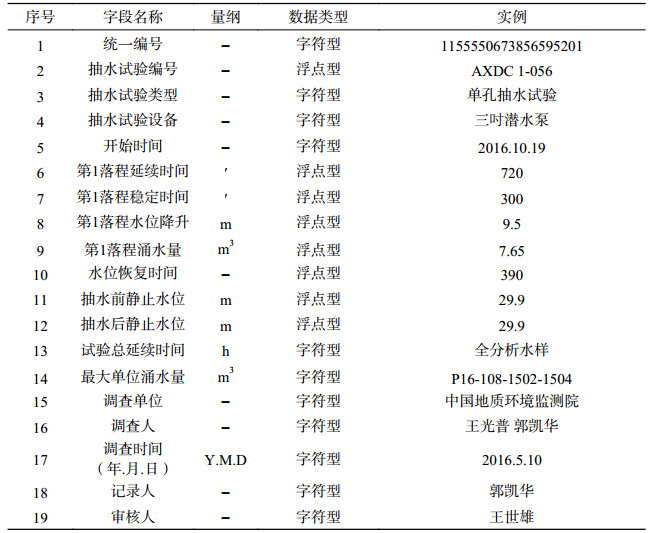
表 10 雄安新区白洋淀流域平原区1:50 000水文地质数据集野外照片属性表
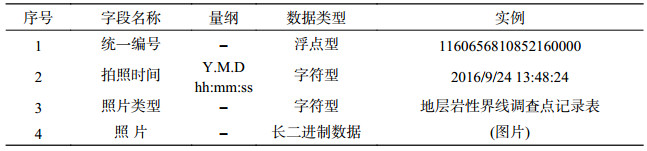
Table 1. Metadata table of database (dataset)
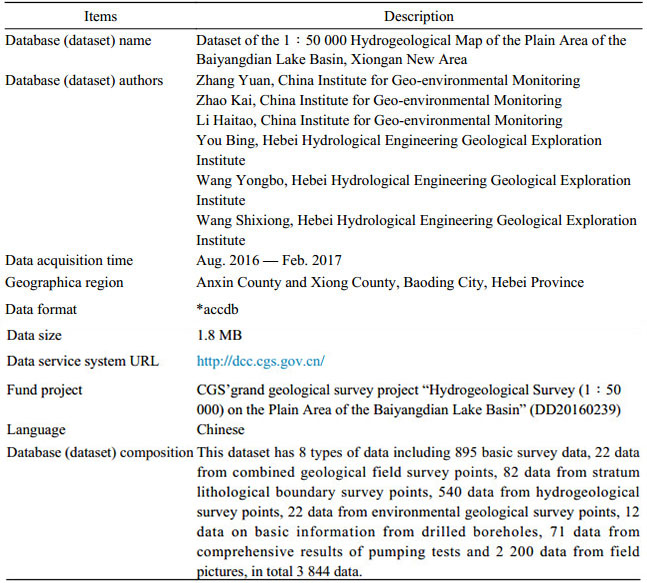
Table 2. Table of the category of surveyed data
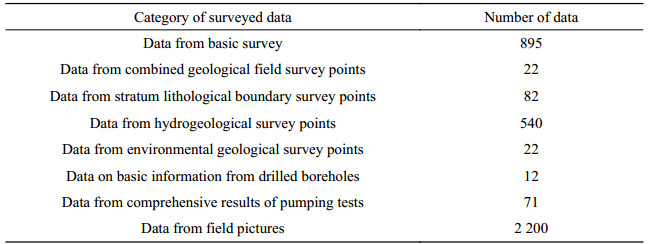
Table 3. Properties of data from basic survey for the dataset of the 1:50 000 hydrogeological map of the Plain Area of the Baiyangdian Lake Basin, Xiongan New Area
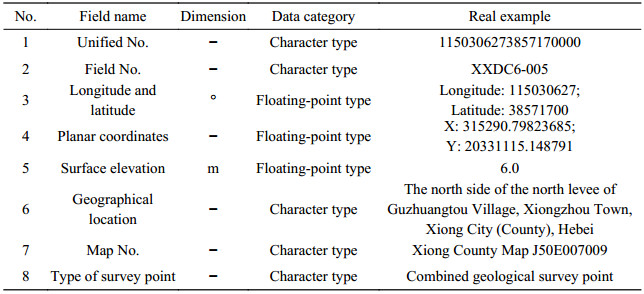
Table 4. Properties of data from combined geological field survey points for dataset of 1:50 000 hydrogeological map of the Plain Area of the Baiyangdian Lake Basin, Xiongan New Area

Table 5. Properties of data from stratum lithological boundary survey points for dataset of 1:50 000 hydrogeological map of the Plain Area of the Baiyangdian Lake Basin, Xiongan New Area

Table 6. Properties of data from hydrogeological survey points for the dataset of the 1:50 000 hydrogeological map of the Plain Area of the Baiyangdian Lake Basin, Xiongan New Area
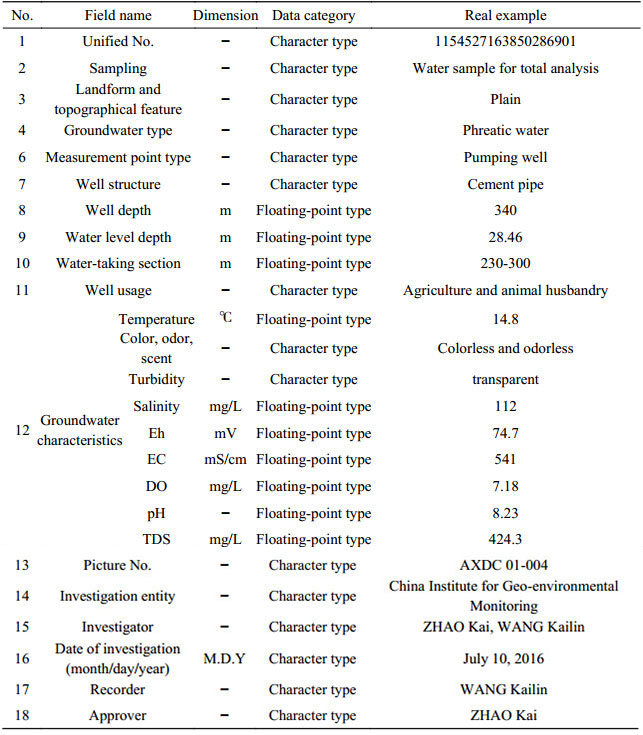
Table 7. Properties of data from environmental geological survey points for the dataset of the 1:50 000 hydrogeological map of the Plain Area of the Baiyangdian Lake Basin, Xiongan New Area
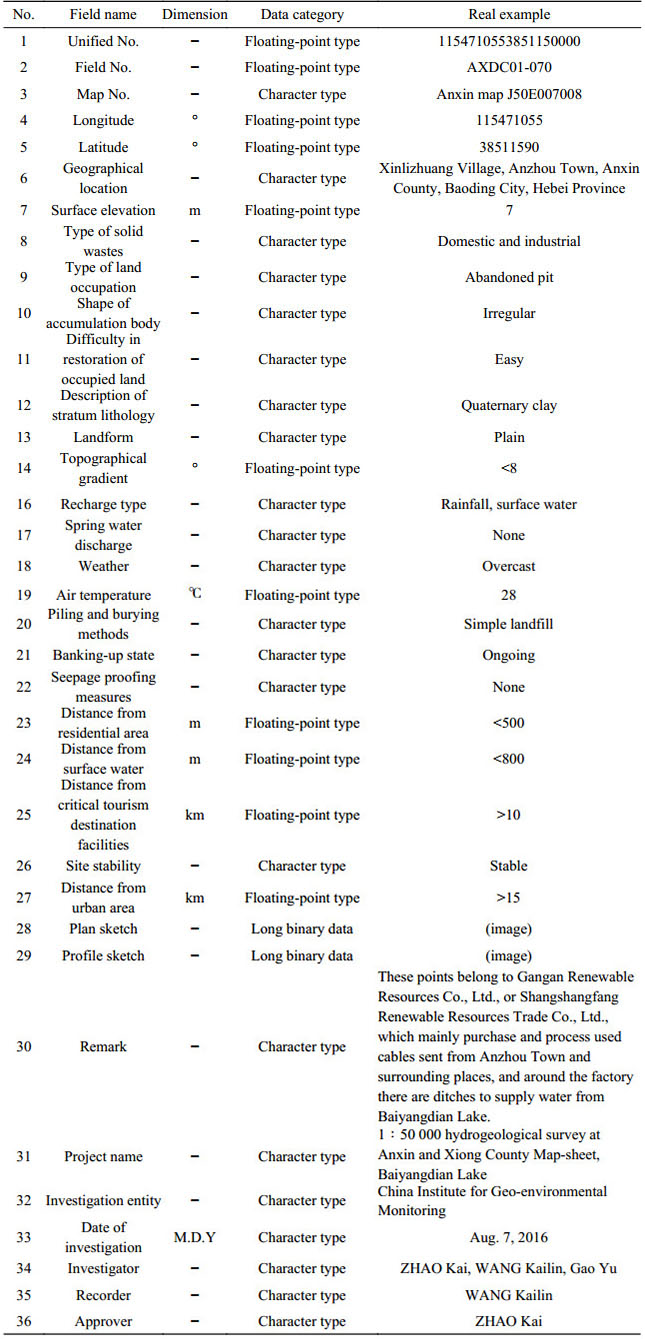
Table 8. Properties of data from basic information of drill boreholes for the dataset of the 1:50 000 hydrogeological map of the Plain Area of Baiyangdian Lake Basin, Xiongan New Area
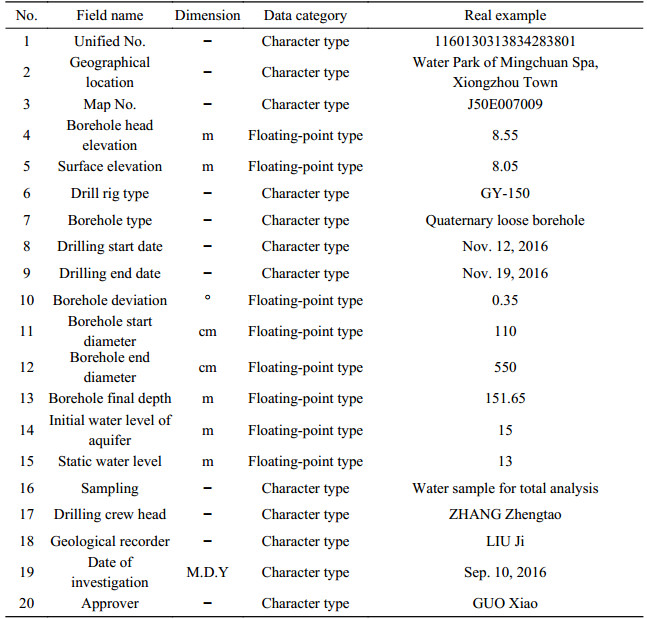
Table 9. Properties of data from comprehensive results of pumping tests for the dataset of the 1:50 000 hydrogeological map of the Plain Area of Baiyangdian Lake Basin, Xiongan New Area

Table 10. Properties of data from field pictures for the dataset of the 1:50 000 hydrogeological map of the Plain Area of the Baiyangdian Lake Basin, Xiongan New Area
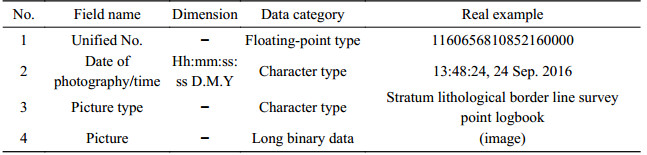
-
李英华, 崔保山, 杨志峰. 2004.白洋淀水文特征变化对湿地生态环境的影响[J].自然资源学报, 19(1):62-68 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.2004.01.008
庞健峰, 丁孝忠, 韩坤英, 曾勇, 陈安蜀, 张艳玲, 张庆合, 姚冬生. 2017.1:100万中华人民共和国地质图空间数据库[J].中国地质, 44(S1):8-18 http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2017S102&flag=1
文丽青. 2001.白洋淀水质污染分析及综合治理研究[J].河北环境科学(3):46-48 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200101710595
尹健梅, 程伍群, 严磊, 陈秀凤. 2009.白洋淀湿地水文水资源变化趋势分析[J].水资源保护, 25(1):52-54 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6933.2009.01.014
张素珍, 马静, 李贵宝. 2007.白洋淀湿地面临的生态问题及可持续发展对策[J].南水北调与水利科技, 5(4):53-56 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1683.2007.04.016
Li Yinghua, Cui Baoshan, Yang Zhifeng. 2004. Influence of hydrological characteristic change of Baiyangdian on the ecological environment in wetland[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 19(1):62-68 (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zrzyxb200401008
Pang Jianfeng, Ding Jianzhong, Han Kunying, Zeng Yong, Chen Anshu, Zhang Yanling, Zhang Qinghe, Yao Dongsheng. 2017. The National 1:1 000 000 Geological Map Spatial Database[J]. Geology in China, 44(S1):10-23 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/OA000006962
Wen Liqing. 2001. Analysis and comprehensive treatment of water pollution in Baiyang Lake[J]. Hebei environmental science, (3):46-48 (in Chinese)
Yin Jianmei, Cheng Wuqun, Yan Lei, et al. 2009. Change of water resources in the Baiyangdian Wetlang[J]. Water resources protection, 25(1):52-54 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Suzhen, Ma Jing, Li Guibao. 2007. The ecological problems and sustainable development countermeasures of the Bai Yang Dian Wet Land[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 5(4):53-56 (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nsbdyslkj200704016
-




 下载:
下载: