The age and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in Taiyuan Formation limestone aquifer of the Huaibei coalfield
-
摘要:
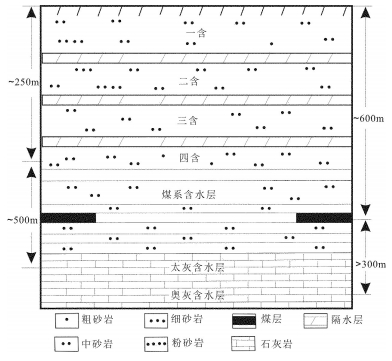
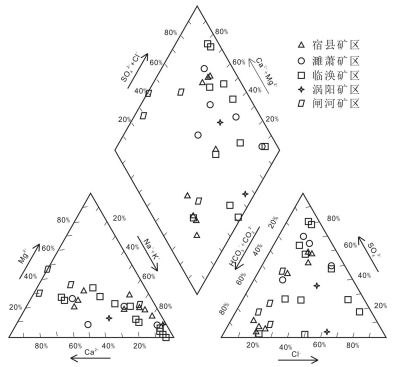
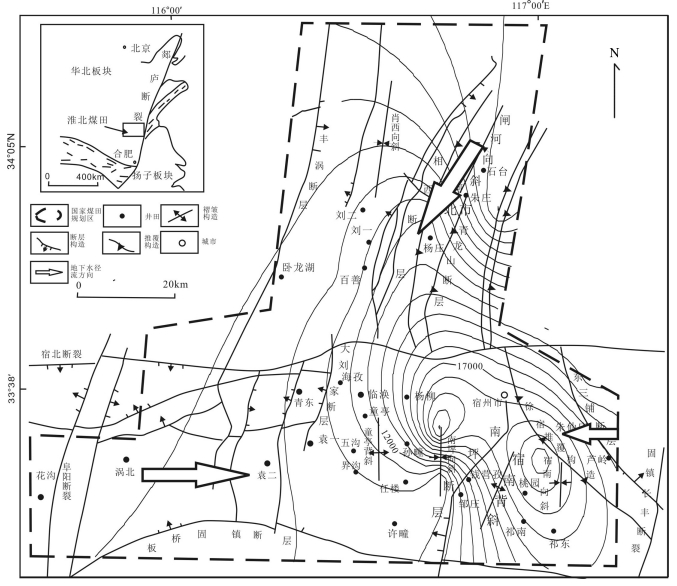
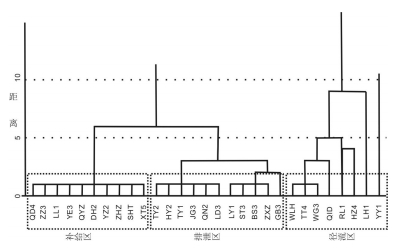
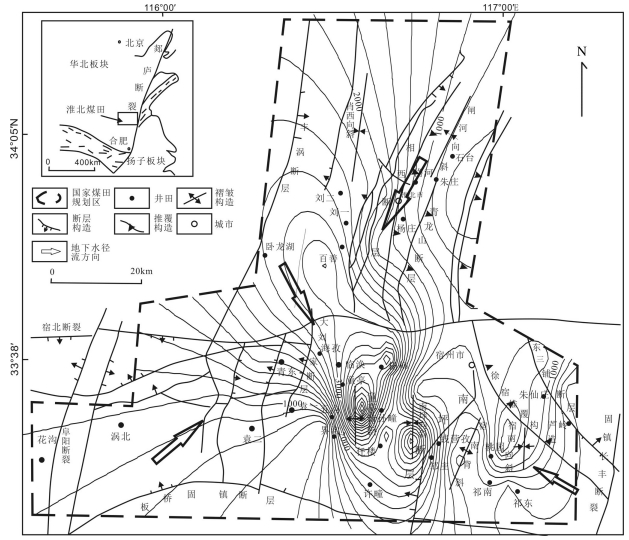
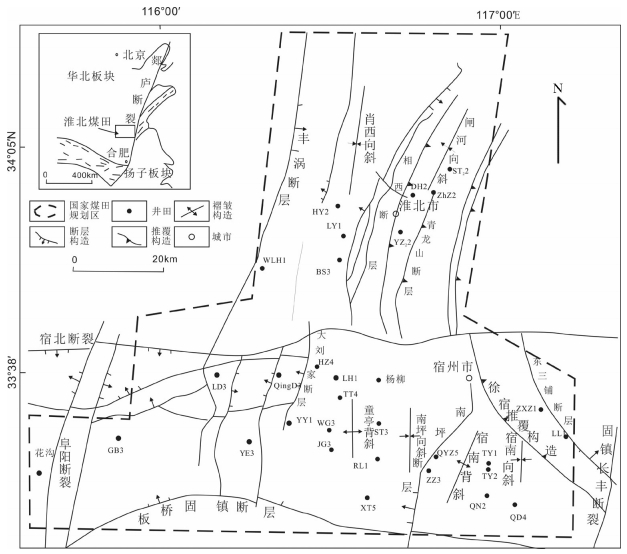
为了解淮北煤田太原组灰岩水年龄、水化学特征及演化,采集了淮北煤田29个矿井地下水样品进行水常规、氢氧同位素及14C测试。利用传统图示及统计方法探讨了地下水化学特征及演化,约束了地下水年龄及径流特征。结果表明:淮北煤田太原组灰岩水年龄在2900~21910 a之间变化,不同矿区之间灰岩水化学特征有明显差异。闸河矿区以较低的TDS浓度、最小的地下水年龄和最高的δD和δ18O值为特征,为淮北煤田太原组灰岩水主要的补给区;临涣矿区孙疃矿、宿县矿区桃园矿具有较大的地下水年龄、较高的TDS浓度和低的δD和δ18O值,为主要排泄区。TDS浓度等值线图和地下水年龄等值线图呈现一致的演化规律,淮北煤田东北部闸河矿区为主要补给区。太原组灰岩水径流特征主要受构造背景的控制,地下水补给条件及水岩相互作用程度决定了水体中TDS浓度和氢氧同位素富集特征。
Abstract:For the purpose of understanding the age, hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in Taiyuan Formation limestone aquifer in the Huaibei coalfield, twenty nine groundwater samples were collected from the Huaibei coalfield, and concentrations of major ions, hydrogen and oxygen isotopes and 14C radio isotopes were analyzed. The traditional graphic and statistical methods were used to discuss the evolution of groundwater and hydrochemical characteristics as well as the age and runoff characteristics of groundwater. Some conclusions have been reached:the ages of groundwater samples in Taiyuan Formation limestone aquifer vary from 2900a to 21920a, the hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater are different in different mining areas. The groundwater samples in the Zhahe mining area have lower TDS concentrations, the minimum age and the highest values of δD and δ18O, and hence this area could be regarded as the recharge area in the Huaibei coalfield. The groundwater samples in the Suntuan mine and Taoyuan mine have largest age, higher concentrations of TDS and lower δD and δ18O values, and such areas could be considered to be the drainage areas. The contour diagrams about TDS concentrations and groundwater age show consistent patterns, suggesting that the main recharge area of groundwater in Taiyuan Formation limestone aquifers lies in the northeast area of the Huaibei coalfield. The groundwater runoff characteristics in Taiyuan Formation are mainly controlled by the tectonic setting, and the recharge conditions and water-rock interaction degrees of groundwater are main factors for the concentrations of TDS and hydrogen and oxygen isotopes.
-
Key words:
- groundwater age /
- 14C /
- Taiyuan Formation /
- limestone groundwater /
- Huaibei coalfield
-

-
表 1 淮北煤田太原组灰岩水化学含量(mg/L)特征
Table 1. Compositions of hydrochemical components (mg/L) in groundwater from Limestone aquifer in Taiyuan Formation, the Huaibei coalfield
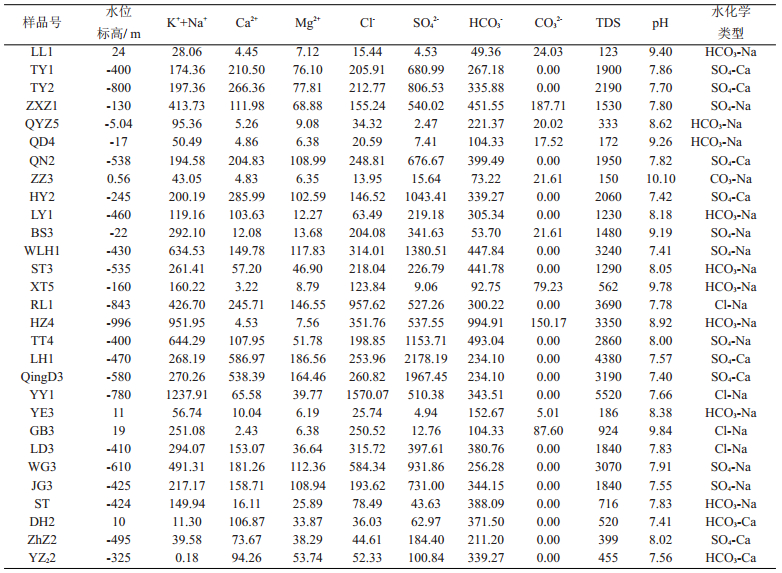
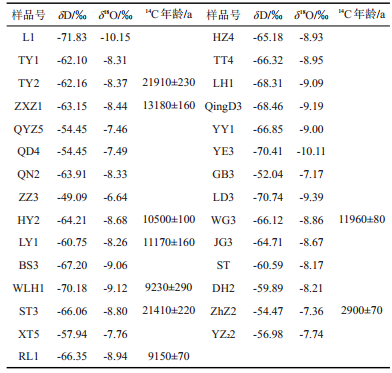
表 2 淮北煤田太原组灰岩水同位素特征
Table 2. Isotopic composition in groundwater from Taiyuan Formation aquifer in the Huaibei coalfield
-
Cao Xuechun, Qian Jiazhong, Sun Xingping. 2010. Hydrochemical classification and identification for groundwater system by using integral multivariate statistical models:A case study in Guqiao Mine[J].Journal of China Coal Society, S1:141-144 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-MTXB2010S1032.htm
Chen Luwang, Yin Xiaoxi, Xie Wenpin, Feng Xiaoqing. 2014.Calculating groundwater mixing ratios in groundwater inrushing aquifers based on environmental stable isotopes (D, 18O) and hydrogeochemistry[J]. Nat. Hazards, 71, 937-953. doi: 10.1007/s11069-013-0941-2
Chen Song. 2014. Evolution and Recognition of Groundwater Based on 3D Geological Structure Model in Sunan Mining Area[D]. China University of Mining and Technology (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen S, Gui H R, Sun L H. 2014. Quality evaluation and its controlling factors of groundwater from Wolonghu Mining area, northern Anhui Province, China[J]. Nature Environment and Pollution Technology, 13(3):577-582. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6afb1e2a02610345d345ebcfeb00d4c4&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Craig H. Isotopic variation in meteoric water[J]. Science, 1961, 133:1702-1703. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3465.1702
Gu Weizu, Pang Zhonghe, Wang Quanjiu. 2001. Isotope Hydrology[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 10-18(in Chinese).
Gui Herong, Chen Luwang, Song Xiaomei. 2005. Drift feature of oxygen and hydrogen stable isotopes in deep groundwater in mining area of Northern Anhui[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 37(1):111-114 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-HEBX200501029.htm
Gui Herong, Chen Luwang.2007. Hydrogeochemistric Evolution and Discrimination of Groundwater in Mining District[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 156-168 (in Chinese).
Gui Herong, Sun Linhua, Chen Luwang, Chen Song. 2011. Rare earth element geochemistry of groundwater from a deep seated sandstone aquifer, northern Anhui Province, China[J]. Mining Science and Technology, 21:477-482. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1674526411000779
Huang Pinghua, Chen Jiansheng, Ning Chao. 2012. The analysis of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in the groundwater of Jiaozuo mine area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 37(5):770-775 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201205010
Sun Houyun, Mao Qigui, Wei Xiaofeng, Zhang Huiqiong, Xi Yuze. 2018. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation evolutionary mechanism of the groundwater system in the Hami basin[J]. Geology in China, 45(6):1128-1141(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201806005
Tan Jingqiang, Ju Yiwen, Hou Quanlin, Zhang Wenyong, Tan Yongjie. 2009. Distribution characteristics and influences factors of present geotemperature field in Su-Lin mine area, Huaibei coalfield[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(3):732-739 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/CJFD_EN/Detail.ashx?url=/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200903018.htm
Wang Guiliang, Cao Daiyong, Jiang Bo.1992. Thrust Nappe, Extensional Gliding Nappe and Gravity Gliding Structures in the Southern Part of North China[M]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology Press, 18-25 (in Chinese).
Wei Wen, Chen Zongyu, Zhao Hongmei, Liu Jun, Wang Yin. 2011.Comparison of 4He and 14C dating of groundwater from Quaternary confined aquifers in Hebei Plain[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 41(4):1144-1150 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201104027.htm
Yuan Jianfei, Deng Guoshi, Xu Fen, Tang Yeqi, Li Pengyue. 2016. The multivariate statistical analysis of chemical characteristics and influencing factors of karst groundwater in the northern part of Bijie City, Guizhou Province[J]. Geology in China, 43(4):1446-1456(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201604029.htm
Zhang Hongping. 1989. Study on the background value of stable isotopes in precipitations of China[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology, 6:6-12 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=976c5ae39f771a607ba723db18b80c79&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
曹雪春, 钱家忠, 孙兴平. 2010.煤矿地下水系统水质分类判别的多元统计组合模型——以顾桥煤矿为例[J].煤炭学报, (S1):141-144. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96550X/2010S1/1003554554.html
陈松. 2014.基于三维地质结构模型的宿南矿区地下水演化与识别[D].中国矿业大学.
顾慰祖, 庞忠和, 王全九. 2001.同位素水文学[M].北京:科学出版社.
桂和荣, 陈陆望, 宋晓梅. 2005.皖北矿区地下水中氢氧同位素的漂移特征[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报, 37(1):111-114. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.2005.01.029
桂和荣, 陈陆望. 2007.矿区地下水水文地球化学演化与识别[M].北京:地质出版社.
黄平华, 陈建生, 宁超. 2012.焦作矿区地下水中氢氧同位素分析[J].煤炭学报, 37(5):770-775. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201205010
孙厚云, 毛启贵, 卫晓锋, 张会琼, 葸玉泽. 2018.哈密盆地地下水系统水化学特征及形成演化[J].中国地质, 45(6):1128-1141. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180604&flag=1
谭静强, 琚宜文, 侯泉林, 张文永, 谭永杰. 2009.淮北煤田宿临矿区现今地温场分布特征及其影响因素[J].地球物理学报, 52(3):732-739. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb200903016
王桂梁, 曹代勇, 姜波. 1992.华北南部的逆冲推覆、伸展滑覆与重力滑动构造[M].徐州:中国矿业大学出版社.
卫文, 陈宗宇, 赵红梅, 刘君, 王莹. 2011.河北平原第四系承压水4He与14C测年对比[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 41(4):1144-1150. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201104026
袁建飞, 邓国仕, 徐芬, 唐业旗, 李鹏岳. 2016.毕节市北部岩溶地下水水化学特征及影响因素的多元统计分析[J].中国地质, 43 (4):1446-1456. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160428&flag=1
张洪平. 1989.我国大气降水稳定同位素背景值的研究[J].勘察科学技术, 6:6-12. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/46571
-



 下载:
下载: