Impact of future climate change on water resources in the arid regions of Northwest China based on surface water-groundwater coupling model: A case study of the middle reaches of the Heihe River
-
摘要:
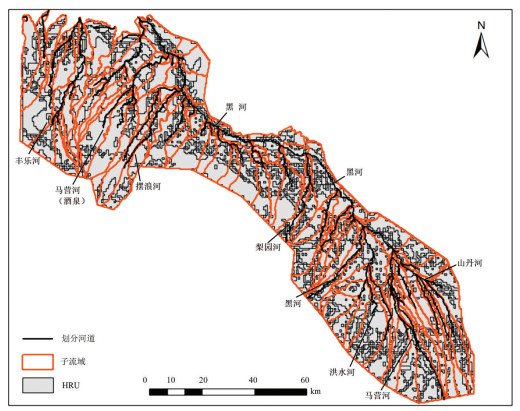
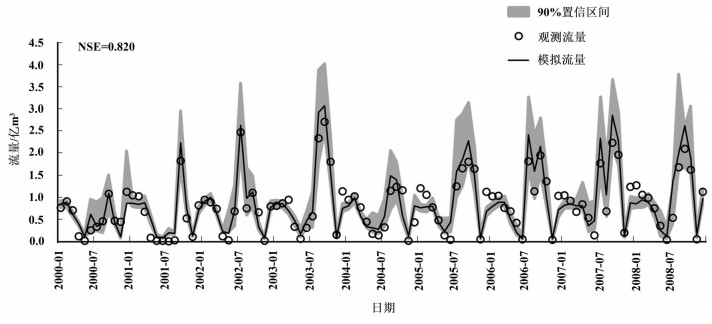
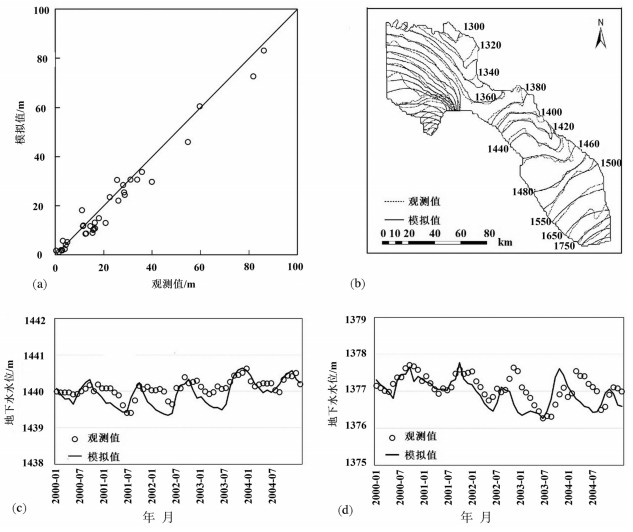
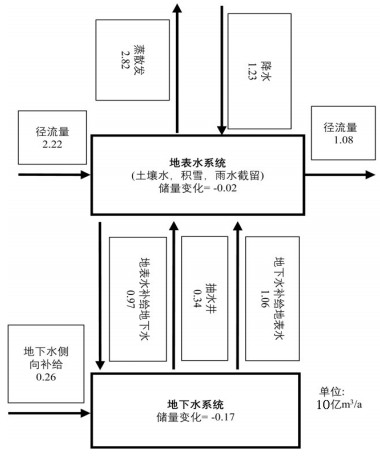
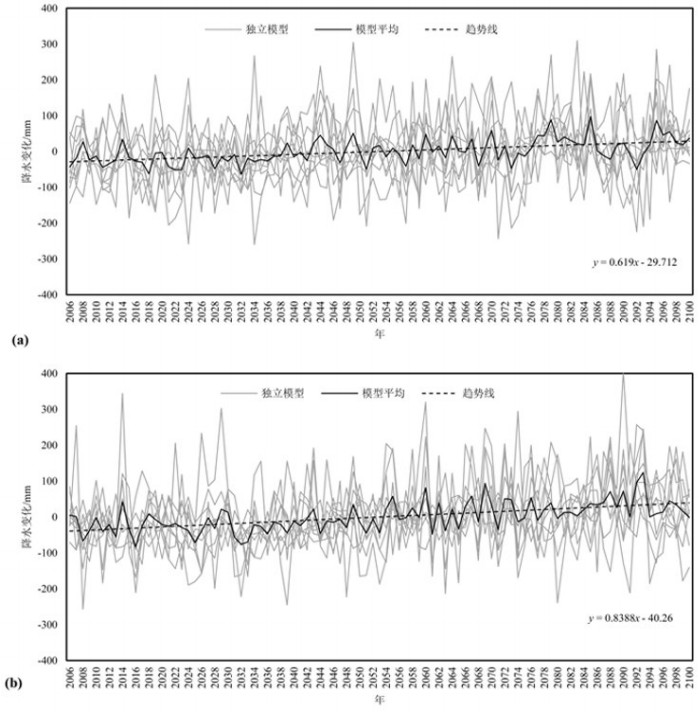
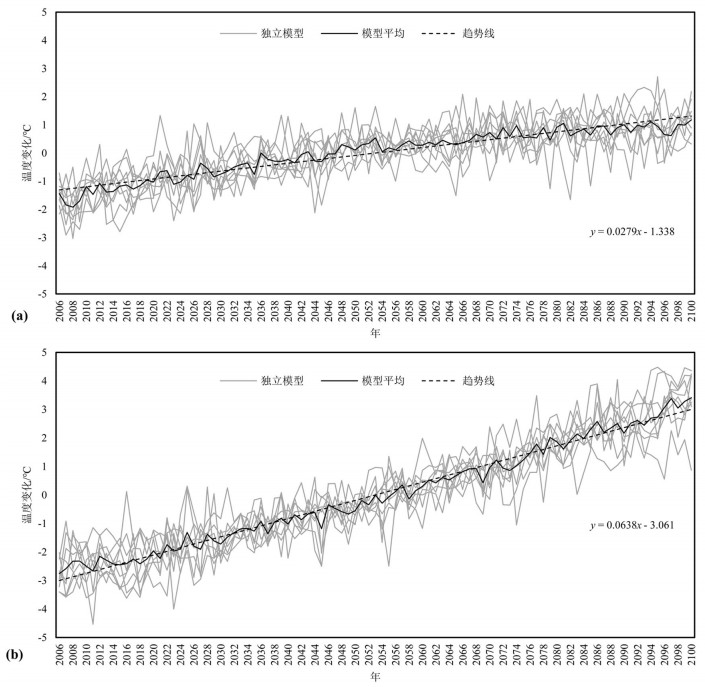
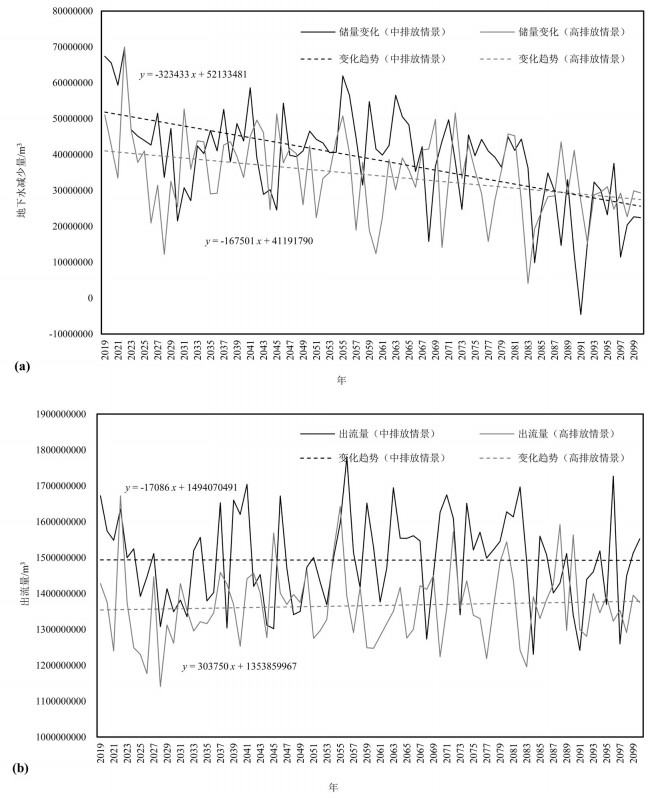
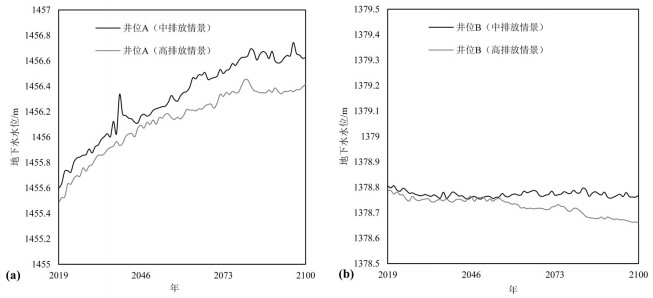
基于物理过程的地表-地下水耦合模型能全面、系统地刻画流域水循环过程,并为水资源管理提供详细信息。同时,未来水资源的变化趋势受到气候变化的影响显著,在未来气候情景下水资源如何变化将影响水资源管理措施。本文以黑河中游盆地为例,基于地表水-地下水耦合模型GSFLOW,评估区域水资源对气候变化的响应,预测未来气候情景(CMIP5)下区域水资源变化趋势,为西北干旱区水资源管理提供参考。研究表明:(1)GSFLOW模型能很好地模拟黑河中游盆地复杂的水循环过程。(2)在中等排放强度(RCP4.5)下,平均每年降水上升0.6 mm,温度上升0.03℃,地下水储量减少0.38亿m3;在高排放强度(RCP8.5)下,降水上升0.8 mm,温度上升0.06℃,地下水储量减少0.34亿m3。
Abstract:The integrated surface-groundwater model based on physical processes can comprehensively and systematically describe the water cycle process of the basin and provide detailed information for water resources management. At the same time, the future trends of water resources are significantly affected by climate change, and the problem as to how water resources change in future climate scenarios will affect water management measures. The authors evaluated the regional water resources response to climate change, based on the surface water-groundwater coupling model GSFLOW. By predicting the regional water resources change trend under the future climate scenario (CMIP5), the results can provide reference of water resources management for the arid regions. Some conclusions have been reached:(1) The GSFLOW model can simulate the complex water cycle of the middle reaches of the Heihe River. (2) Under the medium stabilization scenario (RCP4.5), precipitation in the region increases by an average of 0.6 mm per year, with an average temperature increase of 0.03 degrees Celsius per year, surface water flow of an average of 1.5 billion cubic meters per year, and groundwater reserves decreasing by an average of 38 million cubic meters per year. Under the high radioactive forcing scenario (RCP8.5), the average precipitation increases by 0.8 mm per year, the average temperature increases by 0.06 degrees Celsius per year, the surface water flow is 1.37 billion cubic meters per year, and the groundwater reserves decrease by an average of 34 million cubic meters per year.
-
Key words:
- climate change /
- integrated modeling /
- water resources /
- arid zone /
- groundwater
-

-
表 1 9种全球气候模式及机构
Table 1. Descriptions of the 9 models from CMIP5 applied in this study
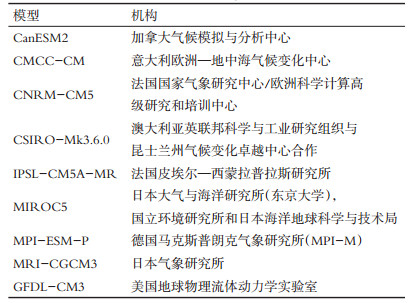
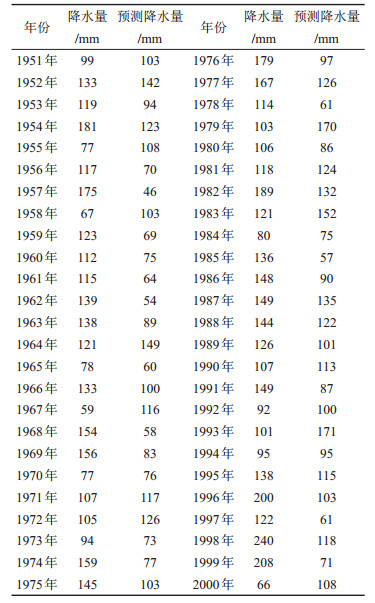
表 2 历年降水量与历年预测降水量
Table 2. Precipitation and predicted precipitation over years
-
Arnold J G, Srinivasan R, Muttiah R S, Williams J R. 1998. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment:Part Ⅰ. Model development[J]. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 34 (1):73-89.
Beven K J, Kirkby M J. 1979. A physically based, variable contributing area model of basin hydrology[J]. Hydrological Sciences Bulletin, 24 (1):43-69. doi: 10.1080/02626667909491834
Brunner P, Simmons C T. 2012. HydroGeoSphere:A fully integrated, physically based hydrological model[J]. Groundwater, 50 (2):170-176. doi: 10.1111/gwat.2012.50.issue-2
Chen Z, Nie Z, Zhang G, Wan L, Shen J. 2006. Environmental isotopic study on the recharge and residence time of groundwater in the Heihe River Basin, northwestern China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 14 (8):1635-1651. doi: 10.1007/s10040-006-0075-7
Graham N, Refsgaard A. 2001. MIKE SHE:A distributed, physically based modelling system for surface water/groundwater interactions[M]. Golden, Colorado.
Harbaugh A W. 2005. MODFLOW-2005, The U.S. Geological Survey modular ground-water model——the Ground-Water Flow Process[R]. U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods.
Hu L T, Chen C X, Jiao J J, Wang Z J. 2007. Simulated groundwater interaction with rivers and springs in the Heihe river basin[J]. Hydrological Processes, 21 (20):2794-2806. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1085
Kollet S J, Maxwell R M. 2006. Integrated surface-groundwater flow modeling:A free-surface overland flow boundary condition in a parallel groundwater flow model[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 26 (7):945-958. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=bb065107ee16cffb933c37f704d14571&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Leavesley G H, Lichty R W, Troutman B M, Saindon L G. 1983.Precipitation-runoff Modeling System——User's manual[R]. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report.
Markstrom S L, Niswonger R G, Regan R S, Prudic D E, Barlow P M. 2008. GSFLOW——Coupled Ground-Water and Surface-Water Flow Model Based on the Integration of the Precipitation-Runoff Modeling System (PRMS) and the Modular Ground-Water Flow Model (MODFLOW-2005)[R]. U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods.
Panday S, Huyakorn P S. 2004. A fully-coupled physically-based spatially distributed model for evaluating surface/subsurface flow[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 27 (4):361-382. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2004.02.016
Rigon R, Bertoldi G, Over T M. 2006. GEOtop:A distributed hydrological model with coupled water and energy budgets[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 7 (3):371-388. doi: 10.1175/JHM497.1
Schmidt S, Geyer T, Marei A, Guttman J, Sauter M. 2013.Quantification of long-term wastewater impacts on karst groundwater resources in a semi-arid environment by chloride mass balance methods[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 502:177-190. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.08.009
Sebben M L, Werner A D, Liggett J E, Partington D, Simmons C T. 2013. On the testing of fully integrated surface-subsurface hydrological models[J]. Hydrological Processes, 27 (8):1276-1285. doi: 10.1002/hyp.9630
Shen C, Niu J, Phanikumar M S. 2013. Evaluating controls on coupled hydrologic and vegetation dynamics in a humid continental climate watershed using a subsurface-land surface processes model[J]. Water Resources Research, 49 (5):2552-2572. doi: 10.1002/wrcr.20189
Simpson S C, Meixner T, Hogan J F. 2013. The role of flood size and duration on streamflow and riparian groundwater composition in a semi-arid basin[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 488:126-135. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.02.049
Sophocleous M. 2002. Interactions between groundwater and surface water:The state of the science[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 10 (1):52-67. doi: 10.1007/s10040-001-0170-8
Weill S, Mazzia A, Putti M, Paniconi C. 2011. Coupling water flow and solute transport into a physically-based surface-subsurface hydrological model[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 34 (1):128-136. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2010.10.001
Wen X, Wu Y, Su J, Zhang Y, Liu F. 2005. Hydrochemical characteristics and salinity of groundwater in the Ejina Basin, Northwestern China[J]. Environmental Geology, 48 (6):665-675. doi: 10.1007/s00254-005-0001-7
Wen X H, Wu Y Q, Lee L J E, Su J P, Wu J. 2007. Groundwater flow modeling in the Zhangye Basin, Northwestern China[J]. Environmental Geology, 53 (1):77-84. doi: 10.1007/s00254-006-0620-7
Wu B, Zheng Y, Tian Y, Wu X, Yao Y, Han F, Liu J, Zheng C. 2014.Systematic assessment of the uncertainty in integrated surface water-groundwater modeling based on the probabilistic collocation method[J]. Water Resources Research, 50 (7):5848-5865. doi: 10.1002/wrcr.v50.7
Wu Yanqng, Zhang Ynighua, Wen Xiaohu, Su Jianping. 2010.Hydrologic Cycle and Water Resource Modeling for the Heihe River Basin in Northwestern China[M]. Beijing:Science Press (in Chinese).
Yin L, Zhou Y, Ge S, Wen D, Zhang E, Dong J. 2013. Comparison and modification of methods for estimating evapotranspiration using diurnal groundwater level fluctuations in arid and semiarid regions[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 496:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.05.016
Zhang Hesheng, Ding Hongwei, Wei Yuguang, Jia Guiyi. 2003. Hexi Corridor Hroundwater Exploration Report[R]. Geol. Surv. of Gansu Province (in Chinese).
Zhang Yongshuang, Sun Lu, Yin Xiulan, Meng Hui. 2017. Progress and prospect of research on environmental geology of China:A review[J]. Geology in China, 44(5):901-912(in Chinese with English abstract).
仵彦卿, 张应华, 温小虎, 苏建平. 2010.中国西北黑河流域水文循环与水资源模拟[M].北京:科学出版社.
张荷生, 丁宏伟, 魏余广, 贾贵义. 2003.河西走廊地下水勘察报告[R].甘肃省地质调查局.
张永双, 孙璐, 殷秀兰, 孟晖. 2017.中国环境地质研究主要进展与展望[J].中国地质, 44(5):901-912. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170505&flag=1
-



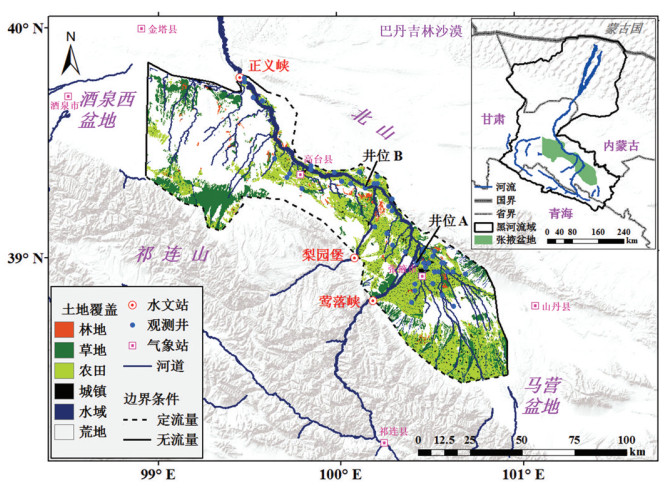
 下载:
下载: