The large deep-water turbidity fan system in southeastern South China Sea Basin: Formation and tectonic constraint
-
摘要:
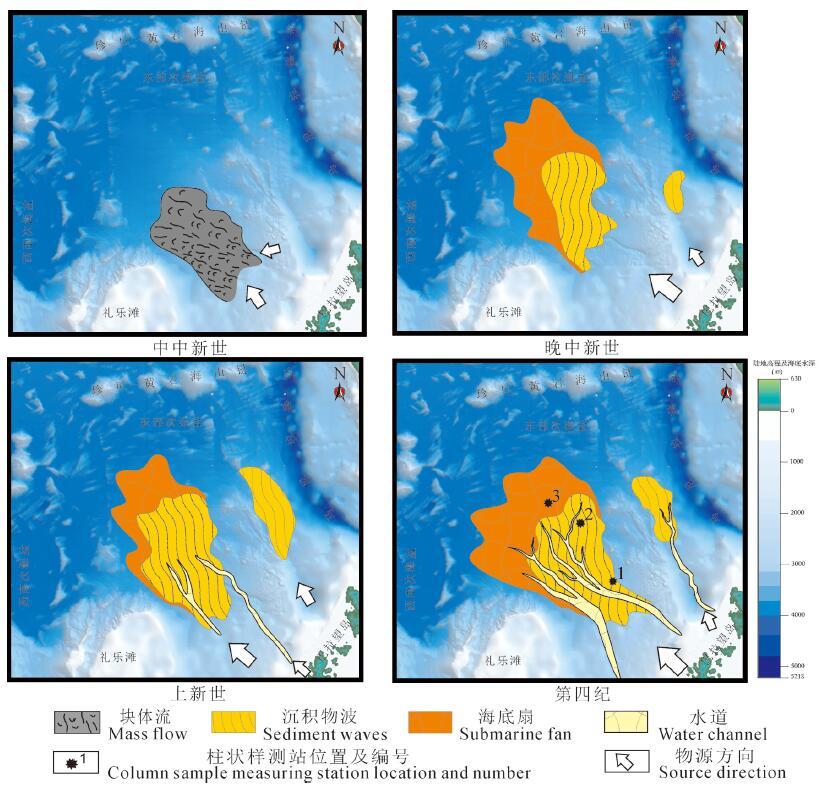
运用近年来海洋地质调查工程获取的最新地质地球物理数据,在南海海盆东南部水深2000~3800 m区域,发现中中新世到第四纪多期大型浊积扇沉积体系,揭示了南海南部深海沉积作用及沉积演化过程。该浊积扇体系以沉积物波、水道充填、海底扇、块体流等沉积体为主,总体上由海盆东南部向海盆中央呈扇形推进,推进距离为150~ 260 km,从老到新规模和结构不断变化,蕴含了丰富的海平面变化信息。垂向上浊流沉积层层叠置发育,形成厚层的浊积砂体。海底水道十分发育,水道砂体底部呈“V”型展布,由南向北延伸,揭示出物源主要来自礼乐滩及北巴拉望区域。该浊积扇的形成明显受到构造控制,与中中新世以来礼乐滩—巴拉望岛的隆升和晚中新世以来的岩浆活动密不可分。浊流发育位置处于南海东南部陆缘和深海平原之间,是陆源物质由浅海输送到深海平原的重要机制,构成南海南部“源-汇”沉积体系的重要环节。
Abstract:A large turbidite fan system was found from southeastern South China Sea basin through the latest multi-channel seismic profiles in the regional geological and geophysical measurement data set. This fan system occurred in the water depth from 2000 m to 3800 m of the present sea level, with forward northwest direction to the central basin edge 150-260 km in length. The fan system was interpreted to have been formed from middle Miocene to Quaternary with series of turbidite fan sequences, mainly composed of sediment waves, channel filling, submarine fans, and mass flows. In time scale, from the early to late stage, the size and architecture of fan system were constantly changing, underlying valuable information of sea level change, depositional process and tectonic evolution. In spatial scale, the turbidite sand bodies were formed by the superimposed layers of turbidite flow sediments. The channels were well developed on the seabed within this fan system. The bottom of the channel sand bodies are distributed on "V" shape in panel, extending from south to north, revealing mainly sources from Liyue Bank and north Palawan Island area. The turbidite fan's formation was obviously controlled by tectonic movement, on the one hand related to the uplift of Liyue Bank-Palawan Island since the middle Miocene and, and on the other hand related to magmatic activity since the late Miocene. The turbidite current mechanism occurred in the transition of continental margin to abyssal plain in the southeast of the South China Sea, driving particles transportation from shallow sea to deep basin. This new interpreted large turbidite fan system presents an important linkage of "source-to-sink" sedimentary system, and benefits to revealing deep-sea sedimentary evolution process in the South China Sea.
-

-
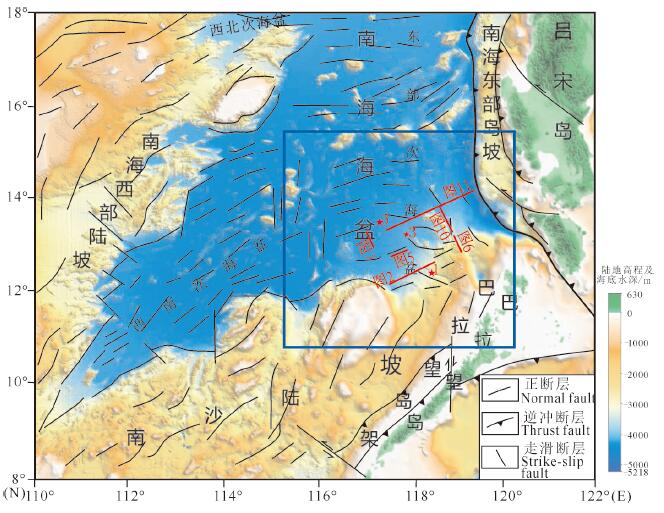
图 1 研究区位置(蓝框范围)及区域地质简图(底图为晕渲地形图,据杨胜雄等,2015)
Figure 1.
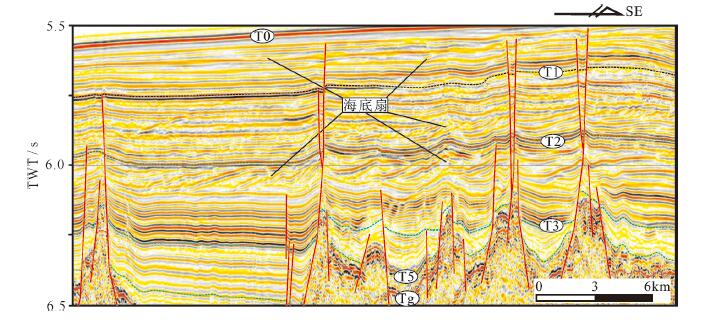
图 2 南海海盆东南部地震相及中中新统块体流沉积放大解译图(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 2.
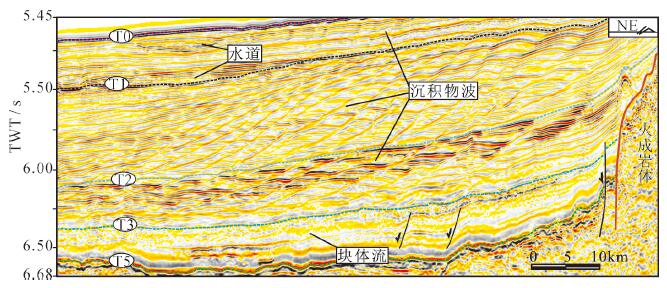
图 3 晚中新世以来海底扇沉积体发育特征(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 3.
图 5 晚中新世以来西侧沉积物波沉积体发育特征(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 5.
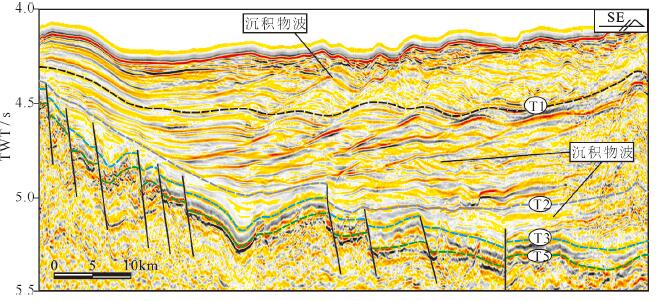
图 6 上新世以来东侧沉积物波地震相特征(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 6.
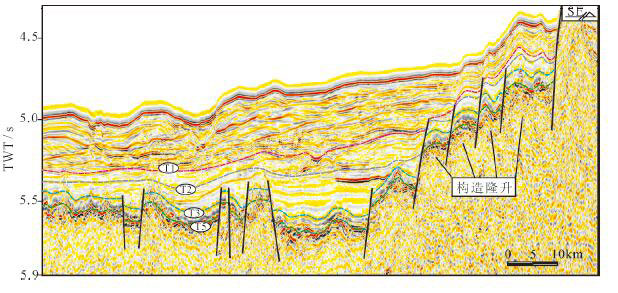
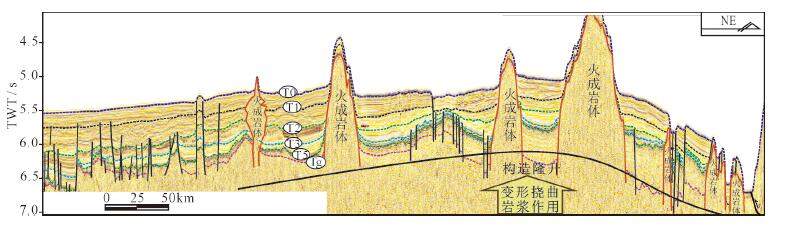
图 10 构造隆升对浊积体发育的控制(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 10.
图 11 构造挠曲和岩浆作用对浊积体发育的控制(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 11.
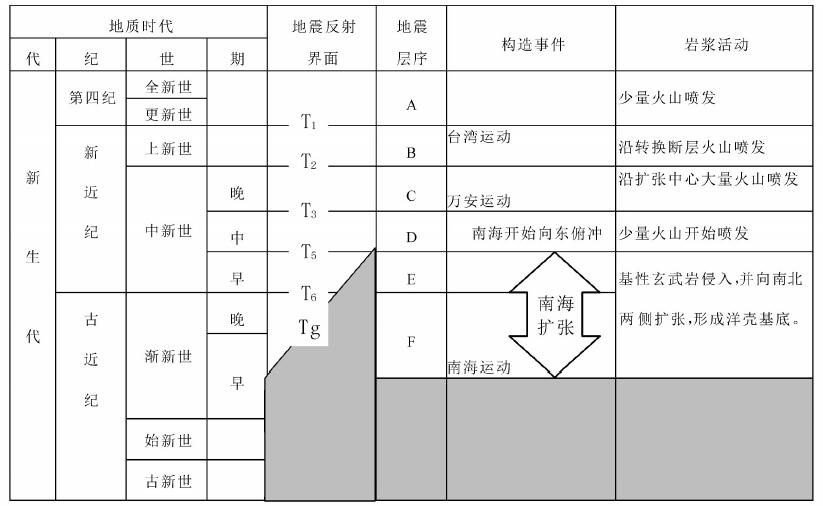
表 1 南海海盆区地震反射界面和地震层序划分
Table 1. Seismic reflection interface and seismic sequence of sea basin of South China Sea
-
Anthony E J, Julian M. 1999. Source- to- sink sediment transfers, environmental engineering and hazard mitigation in the steep Var River catchment, French Riviera, southeastern France[J]. Geomorphology, 31(1): 337-354. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912017303735
Briais A, Patriat P, Tapponnier P. 1993. Updated interpretation of magnetic anomalies and seafloor spreading stages in the South China Sea: Implications for the Tertiary tectonics of Southeast Asia[J]. J. Geophys. Res., 98(B4): 6299-6328. doi: 10.1029/92JB02280
Cai Guanqiang, Li Shun, Zhao Li, Gao Hongfang, Zhong Hexian. 2018. Geochemical characteristics of surface sediments from the middle deep-sea basin of South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 39(4): 23- 33(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201805009
Expedition 349 Scientists. 2014. South China Sea tectonics: Opening of the South China Sea and its implications for southeast Asian tectonis, climates, and deep mantle processes since the Late Mesozoic[R]. International Ocean Discovery Program Preliminary Report, 349. http://dx.doi.org/10.14379/iodp.pr.349.2014.
Lei Zhenyu, Zhang Li, Su Ming, Luo Shuaibing, Qian Xing, Zhang Boda. 2019. Types, characteristics and implication for hydrocarbon exploration of the Middle Miocene deep- water sediments in Beikang Basin, southern South China Sea[J]. China Geology, 2(1): 85-93. doi: 10.31035/cg2018094
Li C F, Xu X, Lin J, Sun Z, Zhu J, Yao Y, Zhao X, Liu Q S, Kulhanek D K, Wang J, Song T R, Zhao J F, Qiu N, Guan Y X, Zhou Z Y, Williams T, Bao R, Briais A, Brown E A, Chen Y F, Clift P D, Colwell F S, Dadd K A, Ding W W, Almeida I H, Huang X, Hyun S, Jiang T, Koppers A A P, Li Q Y, Liu C L, Liu Z F, Nagai R H, Peleoalampay A, Su X, Tejada M L G, Trinh H S, Yeh Y C, Zhang C L, Zhang F, Zhang G L. 2014. Ages and magnetic structures of the South China Sea constrained by deep tow magnetic surveys and IODP Expedition 349[J]. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 15(12):4958-4983. doi: 10.1002/2014GC005567
Li Mengjun, Bi Naishuang, Hu Lisha, Liu Xiaohang, Xu Jingping. 2018. Sedimentary characteristics and processes revealed by the push cores of the 140th dive of DSV"Jiaolong"in the Taiwan Submarine Canyon, Northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 39(4): 23 − 33(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201904003
Li Ruimin, Yin Zhiqiang, Wang Yi, Li Xiaolei, Liu Qiong, Gao Mengmeng. 2018. Geological resources and environmental carrying capacity evaluation review, theory and practice in China[J]. China Geology, 1(4): 556-565. doi: 10.31035/cg2018050
Li Yangchun, Zhang Kexin, He Weihong, Xu Yadong, Song Bowen, Yu Yang, Ke Xue, Kou Xiaohu, Luo Mansheng, Xin Houtian, Fu Junyu, Yang Zhuliang, Zhao Xiaoming, Yin Fuguang, Li Zhipei. 2018. Division of tectonic-strata superregions in China[J]. China Geology, l(2): 236-256. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2096519219300308
Lin Changsong, Xia Qinglong, Shi Hesheng, Zhou Xinhuai. 2015. Geomorphological evolution, source to sink system and basin analysis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(1): 9-20(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201501002
Lin Changsong, Liu Jingyan, Cai Shixiang, Zhang Yanmei, Lü Ming, Li Jie. 2001. Sedimentation and evolution background of large incised channel and submarine gravity flow system in Yingqiong basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 46(1): 69-72 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007/BF03183213
Liang Jinqiang, Deng Wei, Lu Jingan, Kuang Zenggui, He Yulin, Zhang Wei, Gong Yuehua, Liang Jin, Meng Miaomiao. 2020. A fast identification method based on the typical geophysical differences between submarine shallow carbonates and hydrate bearing sediments in the northern South China Sea[J]. China Geology, 3(1): 16-27. doi: 10.31035/cg2020021
Liu Rui, Zhou Jiangyu, Zhang Li, Liu Xiaofeng, Wei Zhenquan, Qian Xing, Shuai Qingwei, Liao Jinfang. 2013. Depositional architecture and evolution of deep water fan system in the northwestern Subbasin, South China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 31(4): 706-716(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0025322707002228
Moore G T. 1969. Interaction of rivers and oceans: Pleistocene petroleum potential[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 53(12): 2421-2430. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1068797109000455
Pang Xiong, Peng Dajun, Chen Changmin, Zhu Ming, He Min, Shen Jun, Liu Baojun. 2007. Three hierarchies"Source-Conduit-Sink" coupling analysis of the Pearl River deep- water fan system[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(6): 857- 864(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200706016
Peng Dajun, Pang Xiong, Chen Changmin, Zhu ming, Huang Xianlv, Shu Yu. 2006. The characteristics and controlling factors for the formation of deep-water fan system in South China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 24(1): 10- 19(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2468256X17300214
Peng Yongmin, Song Chuanchun, Wang Dengwen, Luo Qun, Huang Handong. 2011. Turbidity fans and hydrocarbon prospecting of lower 3rd Member of Shahejie Formation from well Che15, Jiyang depression[J]. Geology in China, 38(5): 1289- 1297(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201105016
Qin Xuwen, Zhao Bin, Li Fuyuan, Zhang Baojin, Wang Houjin, Zhang Ruwei, He Jiaxiong, Chen Xi. 2019. Deep structural research of the South China Sea: Progresses and directions[J]. China Geology, 2 (4): 530-540. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195116001190
Reading H G, Richards M. 1994. Turbidite systems in deep- water basin margins classified by grain-size and feeder system[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 78(5): 792-822. http://archives.datapages.com/data/bulletns/1994-96/data/pg/0078/0005/0750/0792.htm
Shanmugam G. 2000. 50 years of the turbidite paradigm (1950s1990s): deep- water processes and facies models: A critical perspective[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 17(2): 285-342. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00011-2
Shanmugam G. 2006. Deep- water Processes and Facies Models: Implications for Sandstone Petroleum Reservoirs[M]. Elsevier Science, 191-236.
Sømme T O, Jackson C A L, Vaksdal M. 2013. Source- to- sink analysis of ancient sedimentary systems using a subsurface case study from the Mør-Trøndelag area of southern Norway: Part 1depositional setting and fan evolution[J]. Basin Research, 25(5): 489-511. doi: 10.1111/bre.12013
Stow D A V, Johansson M. 2000. Deep-water massive sands: nature, origin and hydrocarbon implications[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 17(2): 145-174. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00051-3
Su Ming, Zhang Cheng, Xie Xinong, Wang Zhenfeng, Jiang Tao, He Yunlong, Zhang Cuimei. 2000. Controlling factors on the submarine canyon system: A case study of the Central Canyon System in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 44(8): 1807-1820(in Chinese with English abstract). https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11430-014-4878-4
Wang Hairong, Wang Yingmin, Qiu Yan, Peng Xuechao, Li Wencheng. 2008. Development and its tectonic activity´s origin of turbidity current sediment wave in Taiwan bank, northeastern South China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 26(1): 39−45(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Yahui, Zhang Daojun, Zhao Pengxiao, Chen Yang, Huang Can, Su Yufeng. 2016. A new consideration on the genetic mechanism of the central canyon in the Qiongdongnan Basin, the northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 38(11): 97- 124(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hyxb201611009
Xu Shumei, Peng W U, Zhang Wei, Zhang Haiyang, Liu Zhi, Dai Liming, Li Jianwei, Li Lingbo. 2013. Paleo-coastline changes in South China Sea in some critical times[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 33(1): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201301001
Yang Shengxiong, Qiu Yan, Zhu Benduo. 2015. Atlas of Geology and Geophysics of South China Sea(1:2000000)[M]. Tianjing: China Navigation Publications (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yao Bochu, Wang Ling, Wu Nengyou. 2004. Cenozoic plate tectonic activities in the Great South China Sea area[J]. Geology in China, 31(2):113-122(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200402001
Zhong Guangjian, Wu Nengyou, Lin Zhen, Yao Yongjian, Yi Hai.2008. Characteristics of faults on the northeastern continental slope of the South China Sea and their controls on basin evolution[J]. Geology in China, 35(3): 456- 462 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200803009
蔡观强, 李顺, 赵利, 高红芳, 钟和贤. 2018.南海海盆中部表层沉积物地球化学特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 38(5): 90−101. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201805009
李梦君, 毕乃双, 胡丽沙, 刘晓航, 徐景平. 2018.南海北部台湾峡谷"蛟龙号"第140潜次沉积物特征及其沉积过程指示意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 39(4): 23−33. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201904003
林畅松, 刘景彦, 蔡世祥, 张艳梅, 吕明, 李杰. 2001.莺琼盆地大型下切谷和海底重力流体系的沉积构成和发育背景[J].科学通报, 46(1): 69−72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb200101018
林畅松, 夏庆龙, 施和生, 周心怀. 2015.地貌演化、源-汇过程与盆地分析[J].地学前缘, 22(1): 9−20. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2015.01.002
刘睿, 周江羽, 张莉, 刘小峰, 韦振权, 钱星, 帅庆伟, 廖锦芳. 2013.南海西北次海盆深水扇系统沉积演化特征[J].沉积学报, 31(4): 706−716. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201304018
庞雄, 彭大钧, 陈长民, 朱明, 何敏, 申俊, 柳保军. 2007.三级"源-渠-汇"耦合研究珠江深水扇系统[J].地质学报, 81(6): 857−864. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200706016
彭大均, 庞雄, 陈长民, 朱明, 黄先律, 舒誉.2006.南海珠江深水扇系统的形成特征与控制因素[J].沉积学报, 24 (1): 10−19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200601002
彭勇民, 宋传春, 王登稳, 罗群, 黄捍东. 2011.济阳坳陷车15井区浊积扇沉积及油气勘探意义[J].中国地质, 38(5): 1289−1297. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201105016
苏明, 张成, 解习农, 王振峰, 姜涛, 何云龙, 张翠梅. 2014.深水峡谷体系控制因素分析——以南海北部琼东南盆地中央峡谷体系为例[J].中国科学:地球科学, 44(8): 1807−1820. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201408018
王海荣, 王英民, 邱燕, 彭学超, 李文成. 2008.南海东北部台湾浅滩陆坡的浊流沉积物波的发育及其成因的构造控制[J].沉积学报, 26(1): 39−45. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200801005
王亚辉, 张道军, 赵鹏肖, 陈扬, 黄灿, 苏榆丰. 2016.南海北部琼东南盆地中央峡谷成因新认识[J].海洋学报, 38(11): 97−124. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hyxb201611009
许淑梅, 吴鹏, 张威, 张海洋, 刘智, 戴黎明, 李健伟, 李灵波. 2013.南海关键地质历史时期的古海岸线变化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 33(1): 1−10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201301001
杨胜雄, 邱燕, 朱本铎. 2015.南海地质地球物理图系(1:2000000)[M].天津:中国航海图书出版社.
姚伯初, 万玲, 吴能有. 2004.大南海地区新生代板块构造活动[J].中国地质, 31(2): 113−122. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200402001
钟广见, 吴能有, 林珍, 姚永坚, 易海. 2008.南海东北部断裂特征及其对盆地演化的控制作用[J].中国地质, 35(3): 456−462.
-



 下载:
下载: