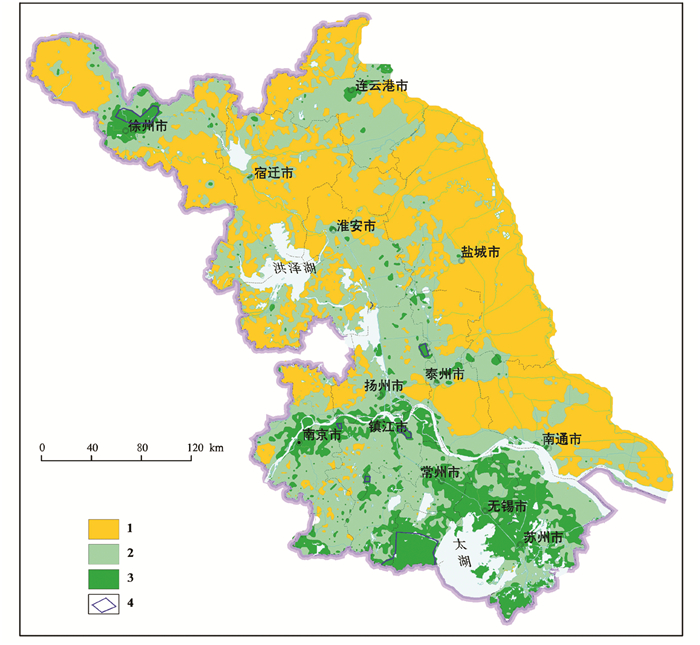
Element geochemistry of selenium-enriched soil and its main sources in Jiangsu Province
-
摘要:
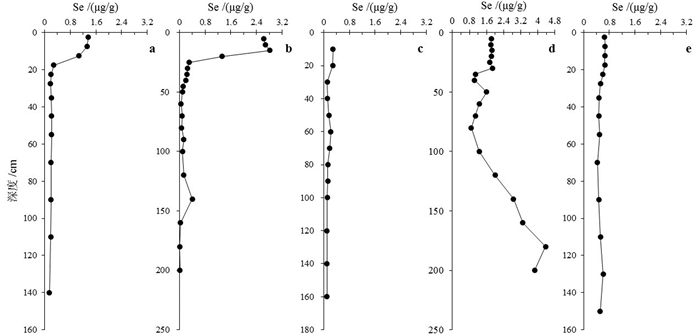
有关生态地球化学调查工程的成果应用已经受到高度关注。本文以江苏区域生态地球化学调查工程所获取的土壤、岩石等元素含量数据为基础,探讨了富硒土壤的分布特点、元素地球化学特征、物质来源与成因类型。研究结果显示:(1)全省富硒土壤的Se含量一般介于0.3~15 mg/kg,同时伴有S、TOC、Zn、Sb、Cd、Pb、As、Cr、Ni、Fe等相对富集;(2)富硒土壤可分为原岩风化残积型、煤矸石风化迁移型、湖相沉积型、粉煤灰型、污染叠加型、多金属矿化伴生型等6个成因类型,以产于苏南酸性土壤环境的原岩风化残积型富硒土壤利用价值最高,该类富硒土壤也是天然富硒农产品的主要产地;(3)富硒土壤物质来源具有多源复合性,表现为先天性物质来源(自然)、后天性物质来源(人为)及复合性物质来源(自然与人为叠加)等3种形式;(4)在先天性物质来源所形成的富硒土壤中,Se与S、TOC等呈显著正相关性,且Cd、Zn、Pb、As等未超标,富硒土壤厚度不受耕作层限制、深度可超过2 m。
Abstract:The problem of how to use geological results or data, especially from the eco-geochemical survey engineering, has been an issue attracting extensive attention since the 21th Century. By studying the regional eco-geochemical survey and some petrogeochemical survey data of Se distribution in soil, the authors investigated and summarized relevant selenium-rich soil space distribution characteristics in Jiangsu Province, element geochemistry, material sources and genetic types, and some other problems. The main research results are as follows:1) The proportion of selenium-enriched soil is less than 3% in Jiangsu Province, and Se concentration in the selenium-enriched soil is generally 0.3-15.0 mg/kg. In addition, ,there are restively higher element values of S, TOC (total organic carbon), Zn, Sb, Cd, Pb, As, Cr, Ni, Fe, etc., in the soil; 2) the above selenium-enriched soil can be divided into 6 genetic types, i.e., the original rock weathering residual type, coal gangue weathering migration type, local lacustrine sediments Se-rich type, coal flyash type, superposition type of some heavy metals pollution, and polymetallic mineralization associated type. Meanwhile, the utilization values of the original rock weathering residual type selenium-rich soil are the highest and it is mainly from acid soil environment in southern Jiangsu Province, and this type Se-rich soil is the main production area of Jiangsu's natural selenium-rich agricultural products; 3) the material sources present multi-origin compound attributes in the Se-rich soil, and they are manifested as three main material forms in the Se-rich soil, namely the congenital materials sources of natural origin, acquired materials sources of man-made origin, and compound materials sources of natural and man-made common origin; 4) there exist significant positive correlation between Se and S, TOC, etc., in the Se-rich soil formed by congenital materials sources of natural origin, and the values of some heavy metals such as Cd, Zn, Pb and As rarely exceed the standards of national farmland security utilization in this kind of Se-rich soil. Moreover, the category or thickness of this kind of Se-rich soil are not restricted by the cultivated layer, and the most thick soil of Se-rich areas can exceed 2 meters in depth.
-

-
表 1 江苏部分土类双层土壤硒含量(mg/kg)分布特征参数统计结果
Table 1. Eigenvalue statistics of Se concentrations(mg/kg) in some genetic types of double-layer soil in Jiangsu Province
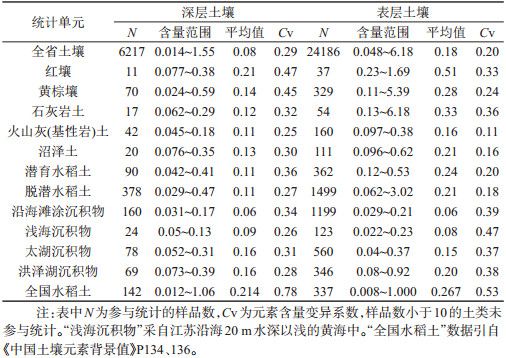
表 2 江苏典型富硒土壤区元素分布等采样分析结果(mg/kg)
Table 2. Analytical results of some elements concentrations(mg/kg) from the typical Se-enriched soils in Jiangsu Province
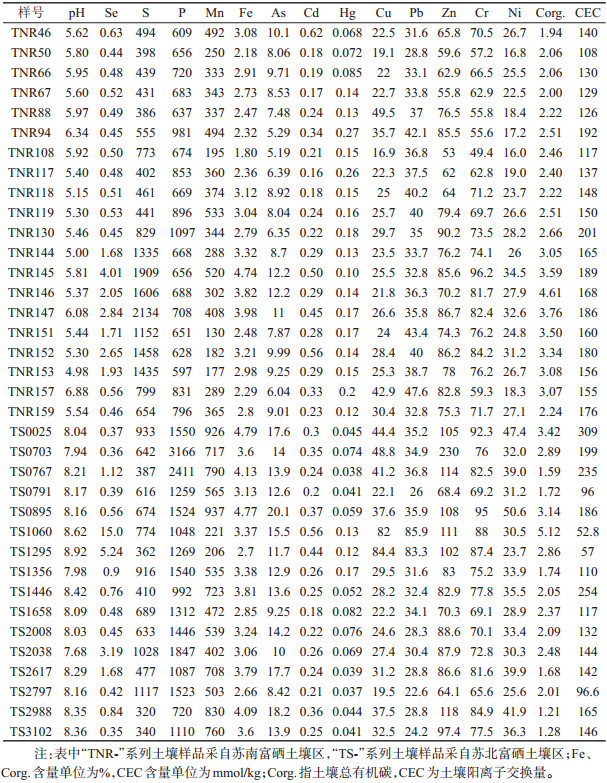
表 3 江苏省部分富硒岩石Se等元素含量(mg/kg)统计对比
Table 3. The statistics of relevant element content (mg/kg) in some Se-enriched rock in Jiangsu Province
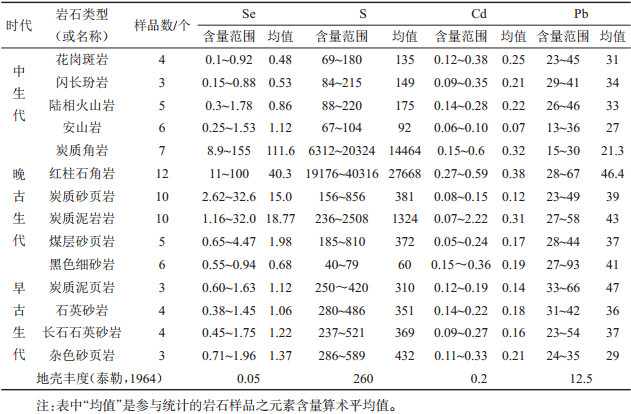
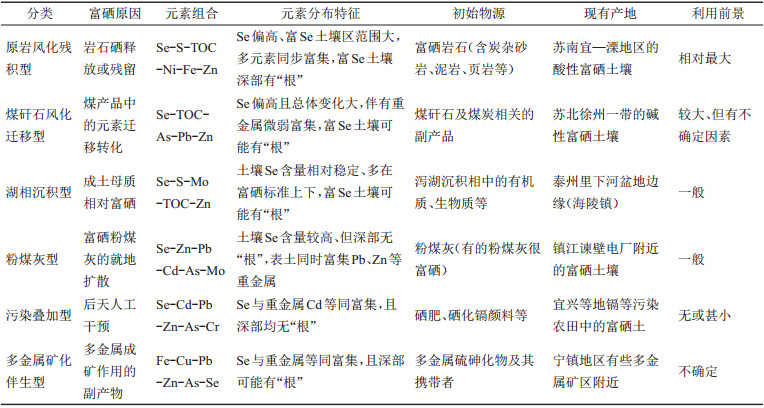
表 4 江苏主要富硒土壤成因类型及其基本特征
Table 4. Basic features of Se-rich soil from different genetic types in Jiangsu Province
-
Cao Z H, Wang X C, Yao D H, Zhang X L, Wong M H. 2011.Selenium geochemistry of paddy soils in Yangtze River Delta[J]. Environment International, 26:335-339. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11392748
Chen Jinping, Liu Yongxian, Zeng Chengcheng, Pan Liping, Xing Ying, Liao Qing, Liang Panxia, Jiang Zepu. 2019.Research advances in the effects of rainfall on soil selenium migration and transformation[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(6):1909-1915(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-STXZ201906035.htm
Chen Song, Gui Herong. 2019. The age and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in Taiyuan Formation limestone aquifer of the Huaibei coalfield[J]. Geology in China, 46(2):337-345(in Chinese with English abstract).
Cui Xingtao, Luan Wenlou, Song Zefeng, Ma Yunchao. 2016. A study of the spatial distribution and source of heavy metals in urban soil in Shijiazhuang City[J]. Geology in China, 43(2):683-690(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201602027.htm
Dai Huimin, Gong Chuandong, Dong Bei, Liu Chi, Sun Shumei, Zheng Chunying. 2015. Distribution of soil selenium in the northeast china plain and its influencing factors[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 52(6):1356-1364 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201506015.htm
Dai Jierui, Pang Xugui, Song Jianhua, Dong Jian, Hu Xueping, Li Xiaopeng. 2018. A study of geochemical characteristics and ecological risk of elements in soil of urban and suburban areas of Zibo City, Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 45(3):617-627(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201803015.htm
Deng Xiaofang, Liu Kezhi, Li Mingfeng, Zhang Wei, Zhao Xiaohu, Zhao Zhuqing, Liu Xinwei. 2017. Difference of selenium uptake and distribution in the plant and selenium form in the grains of rice with foliar spray of selenite or selenate at different stages[J]. Field Crop Research, 211:165-171. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2017.06.008
Han Xiao, Zhou Yue, Wu Wenliang, Meng Fanqiao. 2018. Selenium contents of farmland soils and their relationship with main soil properties in Fengcheng, Jiangxi[J].Journal of Agro-environmant Science, 37(6):1177-1183 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/326317271_Selenium_contents_of_farmland_soils_and_their_relationship_with_main_soil_properties_in_Fengcheng_Jiangxi
Hu Juwu, Xiong Hua. 2019. Study on properties of natural Seenrichment soil and the antagonistic effect of Se to heavy metals[J]. Biological Chemical Engineering, 5(2):11-16 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hu T, Li W F, Nie Y W, Xiang C G. 2014. Spatial distribution of selenium and selenium-rich crop in Zhangjiajie[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 35(6):821-824 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-NXDH201406026.htm
Johnsson L. 1991. Selenium uptake by plants as a function of soil type, organic matter content and pH[J]. Plant Soil, 133:57-64. doi: 10.1007/BF00011899
Letavayova L, Vlckova V, Brozmanova J. 2006. Selenium:from cancer prevention to DNA damage[J]. Toxicology, 227:1-14 doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.07.017
Liao Qilin, Hua Ming, FengJinshun, Jin Yang, Wu Xinmin, Yan Zhaoyang, Zhu Bowan. 2007. Natural Se-rich tea in local Se-rich soils in southern Jiangsu[J]. Geology in China, 34(2):347-353(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/289633399_Natural_Se-rich_tea_in_local_Se-rich_soils_in_southern_Jiangsu
Liao Qilin, Liu Cong, Wang Yi, Jin Yang, Zhu Bowan, Ren Jinghua, Cao Lei. 2015. Geochemical characteristics of rice uptake of cadmium and its main controlling factors:A case study of the Suxichang (Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou) typical area[J]. Geology in China, 42 (5):1212-1223 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201505029
Liao Qilin, Liu Cong, Xu Yan, Jin Yang, Wu Yunzhao, Hua Ming, Zhu Bowan, Weng Zhihua. 2011. Geochemical baseline values of elements in soil of Jiangsu Province[J]. Geology in China, 38(5):1363-1378 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201105024.htm
Liao Qilin, Ren Jinghua, Xu Weiwei, Cui Xiaodan, Jin Yang, Li Wenbo, Zhu Bowan. 2016. Geological and geochemical background of Se-rich rice production in Yili area, Jiangsu Province[J]. Geology in China, 43 (5):1791-1802 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201605027.htm
Liu Yongxian, Chen Jinping, Pan Liping, Wu Tiansheng, Yang Bin, Xing Ying, Liao Qing1, Liang Panxia, Jiang Zepu. 2018. Studies on causes and influential factors of selenium-rich soil in Xunyu Plain[J]. Soils, 50(6):1139-1144(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-TURA201806013.htm
Qin Haibo, Zhu Jianming, Liang Liang, Wang Mingshi, Su Hui. 2013.The bioavailability of selenium and risk assessment for human selenium poisoning in high-Se areas, China[J]. Environment International, 52:66-74 doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2012.12.003
Rayman M. 2000. The importance of Selenium to human health[J]. Lancet, 356:233-241. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02490-9
Shi Yajing, Shi Yajuan, Wang Yurong, Wang Huimin, Qin Likai. 2019.Effects of inorganic selenium fertilizer on available nitrogen content in soil and spinach quality[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 25(2):274-283(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_journal-plant-nutrition-fertilizers_thesis/0201270635474.html
Shi Yanfu, Zong Lianggang, Zhang Yan-ping, Shen Bi-yunzhu, Yang Yu-han. 2018. Characteristic differences of selenium in the rhizospheric and non-rhizospheric soils of tea planta-tions, and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of Agro-environmant Science, 37(9):1903-1909 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/328627891_Characteristic_differences_of_selenium_in_the_rhizospheric_and_non-rhizospheric_soils_of_tea_plantations_and_its_influencing_factors
Sun Weixia, Huang Biao, Zhao Yongcun, Shi Xuezheng, Darilek Jeremy Landon, Deng Xihai, Wang Hongjie, Zou Zhong. 2009.Spatial variability of soil selenium as affected by geologic and pedogenic processes and its effect on ecosystem and human health[J]. Geochemical Journal, 43:217-225. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0019
Sun Zhao, Hou Qingye, Yang Zhongfang, Yang Xiaoyan, Huang Yong, Chen Enke. 2010. Factors controlling the transport and transformation of selenium in typical soil environments:A case study of the Chengdu economic zone in Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 37(6):1760-1768(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201006024.htm
Tan J A, Huang Y J. 1991. Selenium in geo-ecosystem and its relations to endemic diseases in China[J]. Water, Air, Soil Pollut., 57:59-68. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00282869
Tian Yichao, Huang Yuanlin, Zhang Qiang, Tao Jin, Zhang Yali, Xie Xiaokui, Wang Riming. 2019. Soil erosion and Selenium loss in Qinjiang River Basin in Beibu Gulf coastal zone[J]. China Environmental Science, 39(1):257-273 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/333209018_Soil_erosion_and_Selenium_loss_in_Qinjiang_River_Basin_in_Beibu_Gulf_coastal_zone
Wang Changyu, Zhang Surong, Liu Jihong, Xing Yi, Yang Junquan. 2019. Evaluation of the characteristic land resources with Zn, Se and their ecological effects in Raoyang county of Hebei province[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 42(1):49-56. http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_geological-survey-research_thesis/0201270248696.html
Wen Bangyong, Zhang Taoliang, Li Xizhou, Xie Zhendong. 2014. A feasibility study of selenium-rich soil development in Longnan County of Jiangxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 41(1):256-263(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DIZI201401022.htm
Wu Jun. 2018. The distribution of soil selenium in Shouning County of Fujian Province and its influencing factors[J]. Geology in China, 45(6):1167-1176(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201806008.htm
Xu Youning, Zhang Jianghua, Ke Hailing, Liu Runping, Chen Huaqing. 2013. Cd contamination of farmland soil in a gold mining area and its environmental effects[J]. Geology in China, 40(2):636-643 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_geology-in-china_thesis/0201252103847.html
Yan Hongze, Zhou Guohua, Sun Binbin, He Ling, Liu Yinfei, Hou Shujun. 2018. Geochemical characteristics of the bayberry producing area in Longhai, Fujian[J]. Geology in China, 45(6):1155-1166(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201806007.htm
Yang Shengji. 2019. Distribution of soil selenium in Zhouning County of Fujian and its influencing factors[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 33 (1):42-45 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-HBDK201901008.htm
Yu Tao, Yang Zhongfang, Wang Rui, Zeng Qingliang, Hou Wanling. 2018. Characteristics and sources of soil selenium and other elements in typical high selenium soil area of Enshi. Soils, 50(6):1119-1125(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_soils_thesis/0201270613974.html
Zhou Guohua, Zeng Daoming, He Ling, Zhu Xiaoting, Sun Binbin, Bai Jinfeng, Zhou Ziqi. 2015. Eco-geochemical characteristics of the Tieguanyin tea gardens in Fujian Province[J]. Geology in China, 42(6):2008-2018(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201506027.htm
Zhu Jianmin, Thomas M, Robert B, Zheng Baoshan, Ivana Sýkorová, Jiri Pešek. 2012. The occurrence and origin of selenium minerals in Se-rich stone coals, spoils and their adjacent soils in Yutangba, China[J]. Chemical Geology, 330-331:27-38. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.08.023
陈锦平, 刘永贤, 曾成城, 潘丽萍, 邢颖, 廖青, 梁潘霞, 江泽普. 2019.降雨对土壤硒迁移转化的影响研究进展[J].生态学杂志, 38(6):1909-1915. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/stxzz201906035
陈松, 桂和荣. 2019.淮北煤田太原组灰岩水年龄及同位素地球化学特征[J].中国地质, 46(2):337-345. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190210&flag=1
崔邢涛, 栾文楼, 宋泽峰, 马云超. 2016.石家庄城市土壤重金属空间分布特征及源解析[J].中国地质, 43 (2):683-690. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160227&flag=1
代杰瑞, 庞绪贵, 宋建华, 董建, 胡雪平, 李肖鹏. 2018.山东淄博城市和近郊土壤元素地球化学特征及生态风险研究[J].中国地质, 45(3):617-627. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180314&flag=1
戴慧敏, 宫传东, 董北, 刘驰, 孙淑梅, 郑春颖.2015.东北平原土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J].土壤学报, 52(6):1356-1364. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90156X/20156/666680219.html
韩笑, 周越, 吴文良, 孟凡乔. 2018.富硒土壤硒含量及其与土壤理化性状的关系:以江西丰城为例[J].农业环境科学学报, 37(6):1177-1183. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NHBH201806017.htm
胡居吾, 熊华. 2019.天然富硒土壤的性质及硒对重金属的拮抗研究[J].生物化工, 5(2):11-16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SWHG201902003.htm
胡婷, 李文芳, 聂亚文, 向昌国. 2014.张家界市土壤硒分布规律和富硒作物研究[J].农业现代化研究, 35(6):821-824. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NXDH201406026.htm
廖启林, 华明, 冯金顺, 金洋, 吴新民, 颜朝阳, 朱伯万. 2007.苏南局部富硒土壤及其天然富硒茶叶初步研究[J].中国地质, 34(2):347-353. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070218&flag=1
廖启林, 刘聪, 王轶, 金洋, 朱伯万, 任静华, 曹磊. 2015.水稻吸收Cd的地球化学控制因素研究——以苏锡常典型区为例[J].中国地质, 42 (5):1212-1223. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150529&flag=1
廖启林, 刘聪, 许艳, 金洋, 吴昀昭, 华明, 朱伯万, 翁志华. 2011.江苏省土壤元素地球化学基准值[J].中国地质, 38(5):1363-1378. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110523&flag=1
廖启林, 任静华, 许伟伟, 崔晓丹, 金洋, 李文博, 范健, 朱伯万. 2016.江苏宜溧富硒稻米产区地质地球化学背景[J].中国地质, 43 (5):1791-1802. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160527&flag=1
刘永贤, 陈锦平, 潘丽萍, 吴天生, 杨彬, 邢颖, 廖青, 梁潘霞, 江泽普. 2018.浔郁平原富硒土壤成因及其影响因素研究[J].土壤, 50(6):1139-1144. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tr201806012
史雅静, 史雅娟, 王玉荣, 王慧敏, 秦礼凯. 2019.无机硒肥对土壤有效氮含量及菠菜品质的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 25(2):274-283. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zwyyyflxb201902011
史艳芙, 宗良纲, 张艳萍, 沈碧云珠, 杨雨菡. 2018.茶树根际与非根际土壤硒特性及其影响因素分析[J].农业环境科学学报, 37 (9):1903-1909. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_nyhjbh201809013.aspx
孙朝, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 杨晓燕, 黄勇, 陈恩科. 2010.典型土壤环境中硒的迁移转化影响因素研究——以四川省成都经济区为例[J].中国地质, 37(6):1760-1768. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100623&flag=1
田义超, 黄远林, 张强, 陶进, 张亚丽, 谢小魁, 王日明. 2019.北部湾钦江流域土壤侵蚀及其硒元素流失评估[J].中国环境科学, 39(1):257-273. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGHJ201901034.htm
王昌宇, 张素荣, 刘继红, 邢怡, 杨俊泉. 2019.河北省饶阳县富锌、硒特色土地及其生态效应评价[J].地质调查与研究, 42(01):49-56. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92480B/20191/7001771547.html
文帮勇, 张涛亮, 李西周, 谢振东. 2014.江西龙南地区富硒土壤资源开发可行性研究[J].中国地质, 41(1):256-263. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140121&flag=1
吴俊. 2018.福建省寿宁县土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J], 现代地质, 45(6):1167-1176. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=DIZI201806008
徐友宁, 张江华, 柯海玲, 刘瑞萍, 陈华清. 2013.某金矿区农田土壤镉污染及其环境效应[J].中国地质, 40(2):636-643. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130227&flag=1
严洪泽, 周国华, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 刘银飞, 候树军. 2018.福建龙海杨梅产地元素地球化学特征[J].中国地质, 45(6):1155-1166. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180606&flag=1
杨生吉. 2019.福建周宁县表层土壤硒含量分布及影响因素[J].资源环境与工程, 33 (1):42-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HBDK201901008.htm
余涛, 杨忠芳, 王锐, 曾庆良, 侯宛苓. 2018.恩施典型富硒区土壤硒与其他元素组合特征及来源分析[J].土壤, 50(6):1119-1125. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94853X/20186/6100012558.html
周国华, 曾道明, 贺灵, 朱晓婷, 孙彬彬, 白金峰, 周子琦. 2015.福建铁观音茶园生态地球化学特征[J].中国地质, 42(6):2008-2018. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150627&flag=1
-



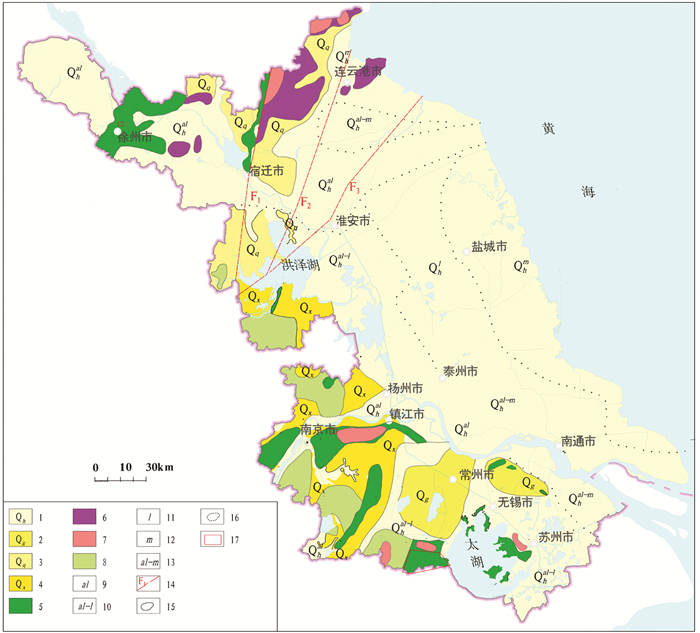
 下载:
下载: