Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of Selenium in soil from Lianjiang Dam in Huishui County, Guizhou Province
-
摘要:
研究目的 涟江大坝位于贵州省惠水县,为查明该地区土壤硒分布特征,系统采集了表层土壤样品337件,成土母岩样品4件,土壤剖面样品16件,分析测定Se、养分元素和As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb、Zn重金属元素等含量。
研究方法 通过表层土壤、成土母岩、土壤剖面样品中Se、养分元素、重金属元素含量对比分析,结合相关性分析方法,对该区土壤Se分布特征进行评估。
研究结果 区内土壤偏酸性,土壤中Se元素含量范围为0.19~3.65 mg/kg;土壤中养分元素P、B和SOM含量高;区内不同成土母质表层土壤Se平均值具有上石炭统灰岩>中二叠统茅口组灰岩>中二叠统栖霞组灰岩>上白垩统茅台组砂岩>中三叠统罗楼组灰岩>中三叠统边阳组碎屑岩的变化规律;区内土壤剖面中Se含量随深度加深而降低。
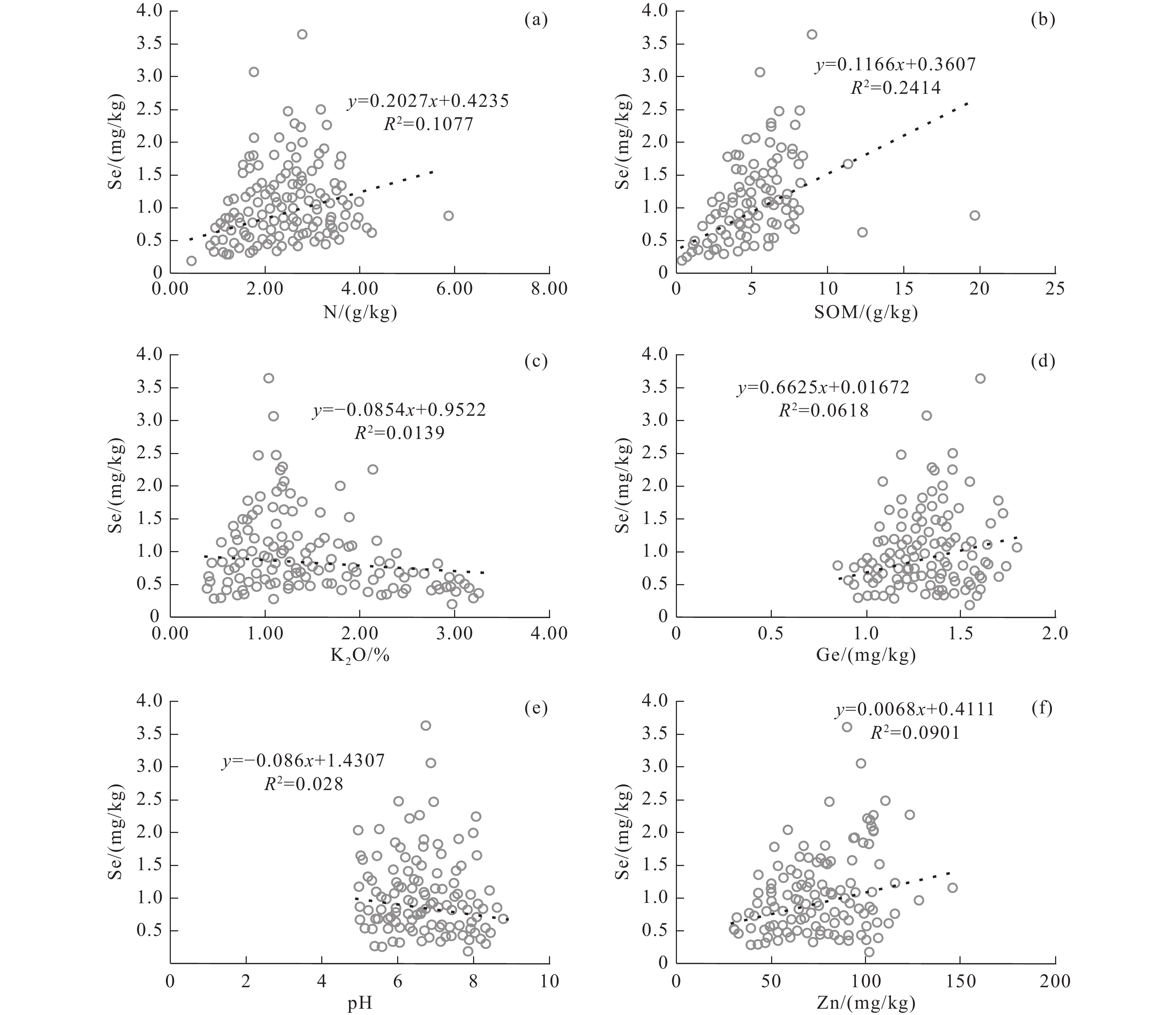
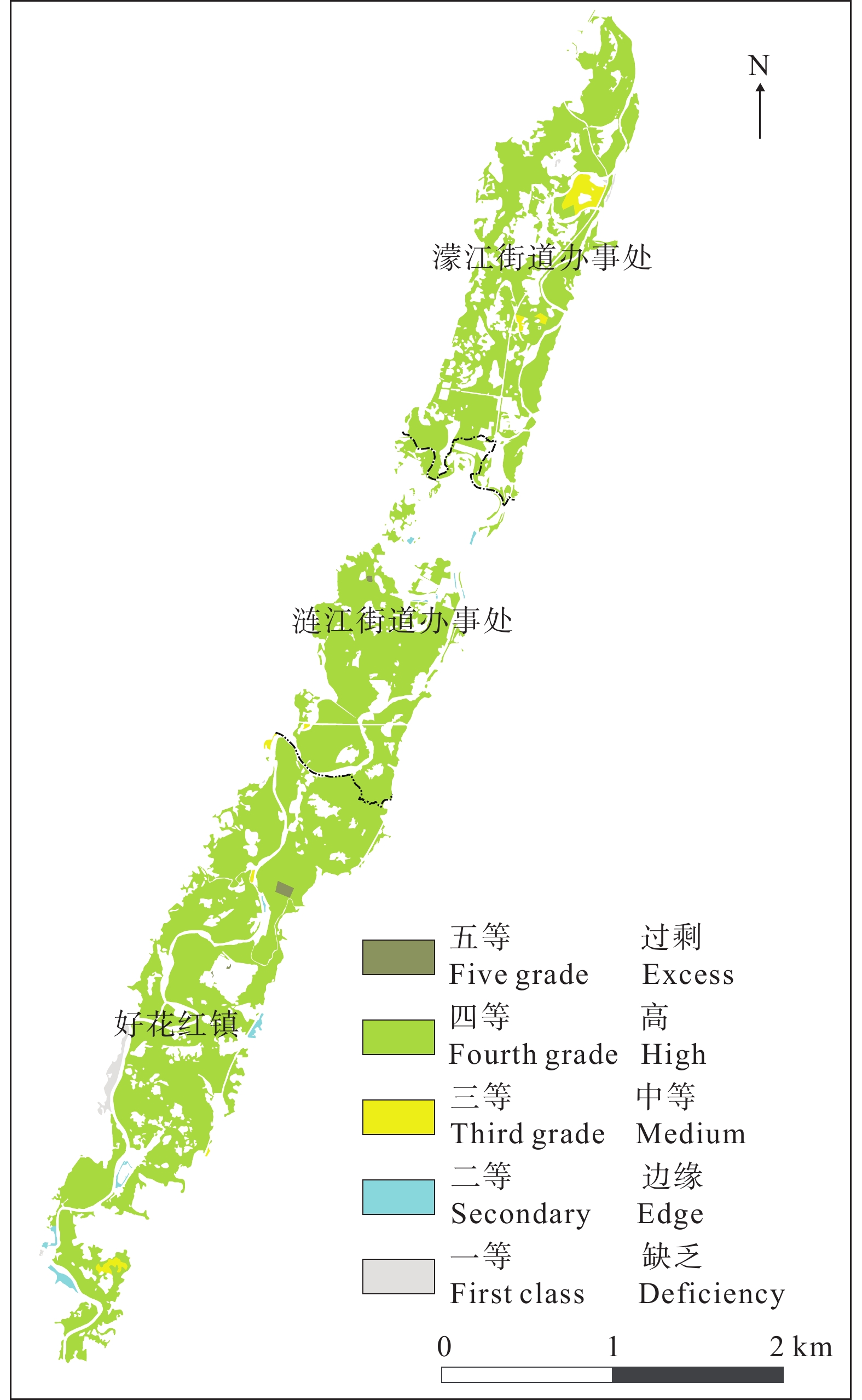
结论 区内富硒土壤丰富,主要为中等和高级,富硒土壤面积为42.94 km2;土壤中Se与SOM呈显著正相关关系,Se与K2O、pH呈显著负相关关系。
Abstract:This paper is the result of environmental geological survey engineering.
Objective Lianjiang Dam is located in Huishui County of Guizhou Province. To find out the Se distribution features of soil in Lianjiang Dam, 337 surface soil samples, 4 soil mother rock samples and 16 soil profile samples were collected, and the contents of Se, nutrient elements and heavy metal elements such as As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb、Zn were analyzed and determined.
Methods The contents of Se, nutrient elements and heavy metal elements in the samples from surface soil, soil mother rock and soil profile were compared and the Se distributions features of soil were evaluated based on correlative analysis method.
Results It showed that the soil in this area were acidic with the contents of Se in the soil from 0.19 to 3.65 mg/kg. The contents of nutrient elements such as P, B and SOM in the soil were high. The average Se values of surface soil of different mother rocks in this area appeared the transformation law: Upper Carboniferous limestone > Middle Permian Maokou Formation limestone > Middle Permian Qixia Formation limestone > Upper Cretaceous Maotai Formation sandstone > Middle Triassic Luolou Formation limestone > Middle Triassic Bianyang Formation clastic rocks. The Se contents of soil profile in this area decreased with the depth deepening.
Conclusion The Selenium−rich soil is abundant in this area, mainly of medium and high. The area of selenium−rich soil is about 42.94 km2. There is a significant positive correlation between Se and SOM, while a significant negative correlation between Se and K2O, and pH in soil.
-

-
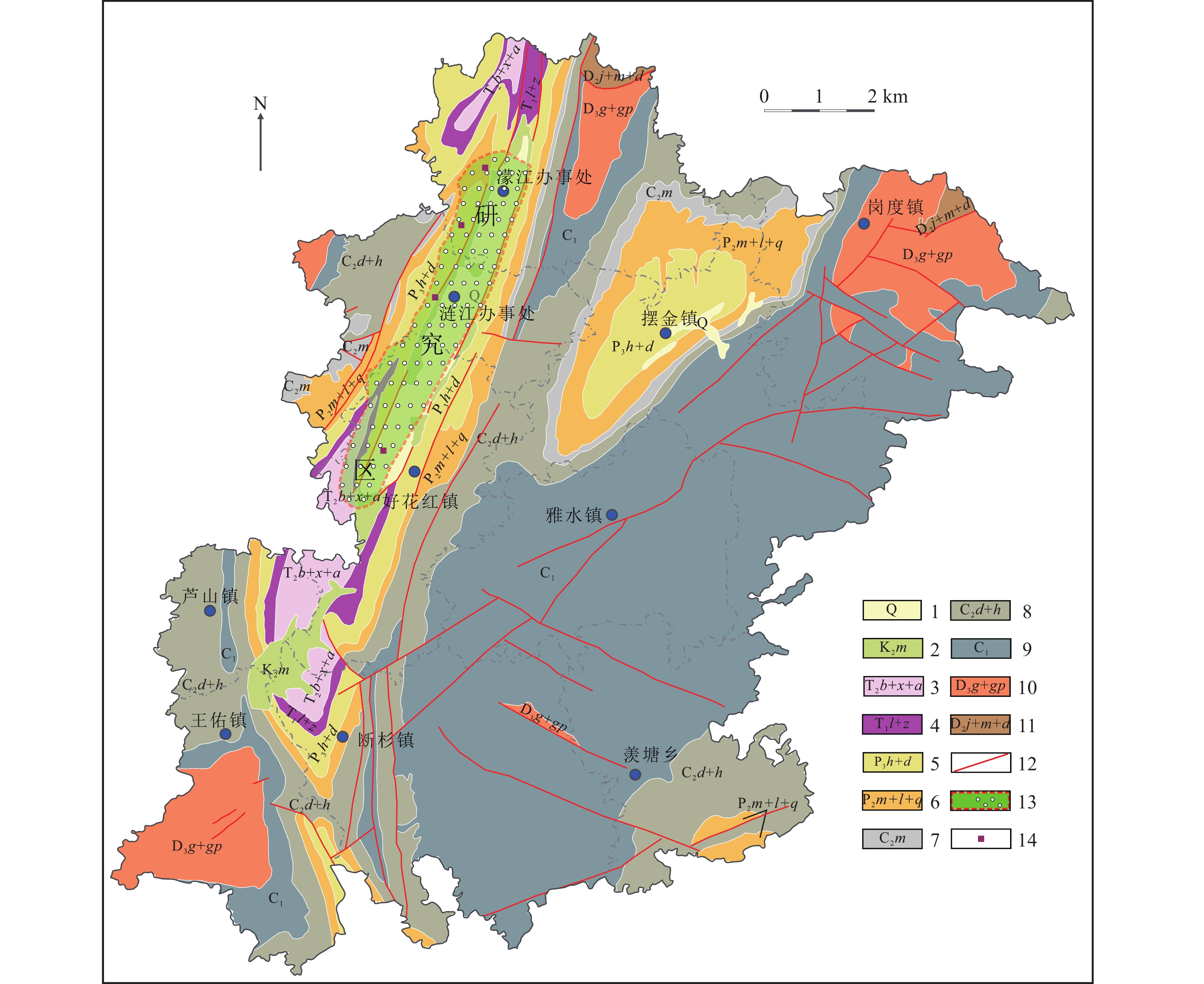
图 1 惠水县地质略图(据杨胜发等,2019)
Figure 1.
表 1 土壤样品分析方法及检出限
Table 1. Testing method and detection limits of soil sample
序号 项目 检测方法 方法检出限 规范限量 序号 项目 检测方法 方法检出限 规范限量 1 N VOL 18 20 13 Se AFS 0.003 0.01 2 P ICP−OES 2.38 10 14 V ICP−OES 1.18 5 3 K2O ICP−OES 0.2 0.5 15 Tl ICP−MS 0.02 0.1 4 B ES 0.48 1 16 As AFS 0.27 1 5 SOM VOL 0.2 1 17 Cd ICP−MS 0.02 0.03 6 pH ISE 0.01 0.1 18 Cr ICP−MS 0.82 5 7 Co ICP−MS 0.07 1 19 Cu ICP−MS 0.89 1 8 F ISE 85 100 20 Hg AFS 0.0004 0.0005 9 Ge AFS 0.07 0.1 21 Ni ICP−MS 0.439 2 10 I COL 0.2 0.5 22 Pb ICP−MS 0.96 2 11 Mn ICP−MS 2.91 10 23 Zn ICP−MS 2.15 4 12 Mo ICP−MS 0.04 0.3 注:K2O、SOM单位为g/kg;pH无量纲;其他元素 mg/kg;元素报出率100%;SOM为有机质。 表 2 涟江大坝表层土壤元素特征参数统计表(n=337)
Table 2. Characteristic parameters statistical of elements in topsoil of Lianjiang Dam (n=337)
项目 涟江大坝表层土壤 贵州省
土壤贵州省
耕地土壤中国土壤 R1 R2 R3 最大值 最小值 平均值 标准差 中位数 变异系数 A层背景值 N 5.86 0.44 2.11 0.73 2.02 0.34 6.2 0.34 P 1720.00 302.00 512.83 145.51 489.00 0.28 0.4 1282.07 K2O 3.25 0.39 1.17 0.62 0.98 0.53 1.6 1.8 1.9 0.73 0.65 0.62 B 119.00 31.60 68.53 14.40 67.40 0.21 72.8 2 47.8 0.94 34.27 1.43 SOM 19.64 0.34 4.21 1.89 3.96 0.45 4.3 0.7 3.1 0.98 6.02 1.36 pH 8.78 4.96 - 0.87 6.64 0.13 6.2 15.1 6.7 1.09 0.45 1.00 Co 35.20 2.29 9.62 4.65 8.70 0.48 19.2 12.7 0.50 0.76 F 1474.00 254.00 608.44 180.67 586.00 0.30 1066 478 0.57 1.27 Ge 1.79 0.85 1.26 0.17 1.25 0.13 1.8 1.7 0.70 0.74 I 18.20 0.38 1.13 1.17 0.86 1.03 8.6 3.8 0.13 0.30 Mn 1297.00 54.90 286.20 209.65 215.00 0.73 794 583 0.36 0.49 Mo 27.60 1.16 6.27 4.33 5.03 0.69 2.4 2 2.61 3.14 Se 3.65 0.19 0.85 0.45 0.73 0.53 0.4 0.3 2.13 2.84 V 252.00 60.30 122.21 33.61 117.00 0.28 138.8 82.4 0.88 1.48 Tl 1.14 0.27 0.62 0.17 0.61 0.27 0.7 0.6 0.88 1.03 As 18.10 2.23 8.49 3.51 8.61 0.41 20 11.7 0.42 0.73 Cd 1.29 0.01 0.47 0.21 0.42 0.46 0.7 0.1 0.67 4.66 Cr 141.00 26.50 80.87 18.97 80.90 0.23 95.9 61 0.84 1.33 Cu 83.00 14.70 31.54 10.05 30.10 0.32 32 22.6 0.99 1.40 Hg 0.56 0.01 0.12 0.07 0.12 0.54 0.1 0.1 1.23 1.23 Ni 63.80 8.15 26.30 9.81 24.90 0.37 39.1 26.9 0.67 0.98 Pb 91.60 13.40 25.44 6.95 25.10 0.27 35.2 26 0.72 0.98 Zn 145.00 30.00 65.17 19.90 61.80 0.31 99.5 74.2 0.65 0.88 注:N、SOM单位g/kg;K2O、变异系数%,其他元素单位 mg/kg;R1为元素含量平均值/贵州省土壤A层背景值;R2为养分含量平均值/贵州省耕地土壤;R3为元素含量平均值/中国土壤A层背景值。 表 3 不同乡镇表层土壤特征参数(mg/kg)
Table 3. Characteristic parameters in topsoil of the towns in the Lianjiang Dam (mg/kg)
乡镇 n 最大值 最小值 平均值 标准差 变异系数/% R2 濛江街道 17 0.87 0.30 0.54 0.16 0.30 1.80 涟江街道 73 1.67 0.29 0.69 0.30 0.43 2.30 好花红镇 247 3.65 0.19 0.92 0.48 0.52 3.07 注:n为取样数量;R2为养分含量平均值/贵州省耕地土壤。 表 4 不同成土母岩表层土壤Se元素特征参数(mg/kg)
Table 4. Characteristic parameters of Se in topsoil in the different parent rocks (mg/kg)
地层 岩性 n 最大值 最小值 平均值 标准差 变异系数/% K2m 上白垩统茅台组砂岩 190 2.50 0.29 0.82 0.39 0.47 T2b 中三叠统边阳组碎屑岩 6 0.83 0.30 0.57 0.18 0.32 T1l 下三叠统罗楼组灰岩 27 1.81 0.40 0.73 0.29 0.40 P2m 中二叠统茅口组灰岩 58 3.65 0.29 0.88 0.52 0.59 P2q 中二叠统栖霞组灰岩 37 3.08 0.19 0.84 0.49 0.58 C2d 上石炭统大埔组灰岩 19 2.48 0.43 1.11 0.58 0.53 表 5 不同土地利用类型表层土壤Se元素特征参数(mg/kg)
Table 5. Characteristic parameters of Se in topsoil of different land use types (mg/kg)
项目 n 最大值 最小值 平均值 标准差 变异系数/% 水田 270 3.65 0.19 0.83 0.46 0.55 旱地 54 2.28 0.41 0.95 0.40 0.42 果园 13 1.81 0.33 0.82 0.41 0.49 表 6 土壤类型Se元素含量特征参数
Table 6. Content characteristic parameter of Se in the different soil type
项目 n 最大值 最小值 平均值 标准差 变异系数/% 水稻土 169 3.65 0.19 0.87 0.52 0.60 黄壤 101 2.30 0.34 0.77 0.33 0.42 紫色土 67 2.28 0.33 0.93 0.40 0.43 表 7 土壤剖面Se元素特征参数
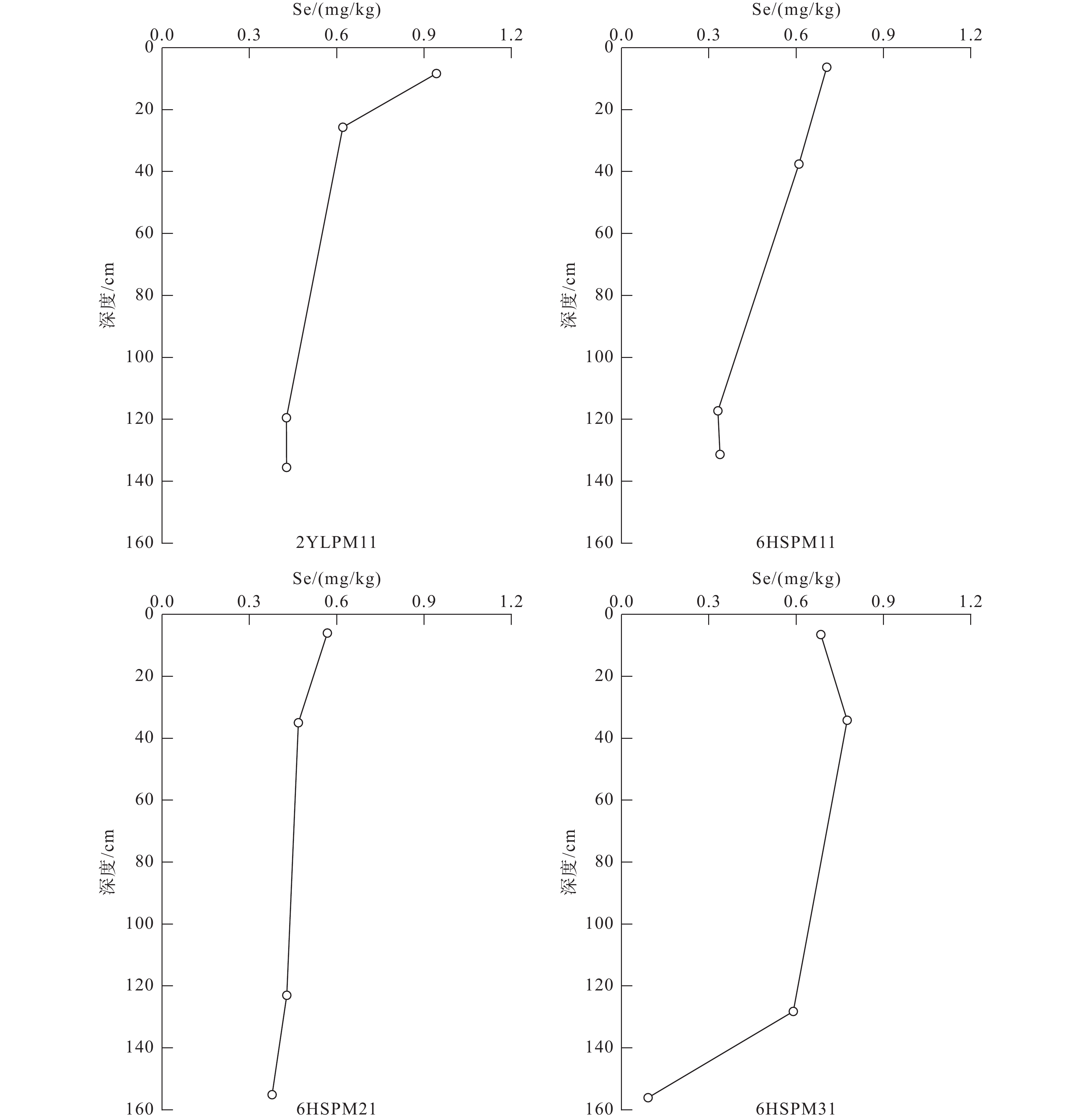
Table 7. Se element characteristic parameter of soil profile
采样地点 项目 地层 岩性 剖面标高/cm 样品编号 Se/(mg/kg) 濛江街道赤土村 成土母岩 P2m 灰岩 2YLYS11 0.02 好花红镇兴涟村 P2m 灰岩 6HSYS11 0.28 涟江街道大坡村 K2m 砂岩 6HSYS21 0.05 濛江街道首创村 K2m 砂岩 6HSYS31 0.13 濛江街道赤土村 土壤剖面 腐殖层 0~15 2YLPM11 0.95 濛江街道赤土村 淋溶层 15~40 2YLPM12 0.61 濛江街道赤土村 淀积层 40~120 2YLPM13 0.44 濛江街道赤土村 母质层 120~150 2YLPM14 0.44 好花红镇兴涟村 腐殖层 0~15 6HSPM11 0.77 好花红镇兴涟村 淋溶层 15~35 6HSPM12 0.62 好花红镇兴涟村 淀积层 35~117 6HSPM13 0.30 好花红镇兴涟村 母质层 117~131 6HSPM14 0.30 涟江街道大坡村 腐殖层 0~10 6HSPM21 0.55 涟江街道大坡村 淋溶层 10~35 6HSPM22 0.49 涟江街道大坡村 淀积层 35~125 6HSPM23 0.44 涟江街道大坡村 母质层 125~150 6HSPM24 0.39 濛江街道首创村 腐殖层 0~10 6HSPM31 1.92 濛江街道首创村 淋溶层 10~35 6HSPM32 2.11 濛江街道首创村 淀积层 35~125 6HSPM33 1.83 濛江街道首创村 母质层 125~150 6HSPM34 0.85 -
[1] Abdulah R, Miyazaki K, Nakazawa M, Koyama H. 2005. Low contribution of rice and vegetables to the daily intake of selenium in Japan[J]. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 56(7): 463−471. doi: 10.1080/09637480500490640
[2] An Yonghui, Li Xufeng, He Jin, Jia Xiaofeng, Li Liang. 2010. Distribution characteristics of Kaschin−Beck disease in relation to geological environment of Zoige County[J]. Geology in China, 37(3): 587−593 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Bridges C C, Zalups R K. 2005. Molecular and ionic mimicry and the transport of toxic metals[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 204(3): 274−308. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2004.09.007
[4] Chen X S, Yang G Q, Chen J S, Chen X C, Wen Z M, Ge K Y. 1980. Studies on the relations of selenium and Keshan disease[J]. Biological Trace Element Research, 2(2): 91−107. doi: 10.1007/BF02798589
[5] Chen Xuhui. 2001. Variations of soil nutrient content and fertilization in Guizhou[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 7(2): 121−128 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] Combs G F. 2001. Selenium in global food systems[J]. British Journal of Nutrition, 85(5): 517−547. doi: 10.1079/BJN2000280
[7] Gailer J. 2007. Arsenic−selenium and mercury−selenium bonds in biology[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 251(1/2): 234−254.
[8] Gao Xue, Chen Haiyan, Tong Qianqian. 2013. Nutrient status of surface soil of cultivated land in Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 41(12): 87−91 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Girling C A. 1984. Selenium in agriculture and the environment[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment, 11(1): 37−65. doi: 10.1016/0167-8809(84)90047-1
[10] Haug A, Graham R D, Christophersen O A, Lyons G H. 2007. How to use the world’s scarce selenium resources efficiently to increase the selenium concentration in food[J]. Microbial Ecology in Health and Disease, 19(4): 209−228. doi: 10.1080/08910600701698986
[11] Huang Chunlei, Wei Yingchun, Jian Zhonghua, Song Mingyi. 2013. Study on selenium contents and combined forms of typical selenium−rich soil in the central part of Zhejiang Province[J]. Earth and Environment, 41(2): 155−159 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Najmeddin A, Rahmani F. 2012. The role of Selenium and selected trace elements in the etiology of esophageal cancer in high risk Golestan Province of Iran[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 433: 89−97. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.04.033
[13] Li Tong. 1976. Chemical element abundances in the Earth and it's major shells[J]. Geochimica, (3): 167−174 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Li Yigen, Dong Yanxiang, Zheng Jie, Li Yan, Wu Xiaoyong, Zhu Chaohui. 2005. Selenium: abundant soil survey and assessment in Zhejiang[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 25(3): 323−330 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Li Yuchao, Wang Chengyu, Yu Chengguang. 2020. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soil from Dandong area[J]. Liaoning Province Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 50(6): 1766−1775 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Liao Qilin, Cui Xiaodan, Huang Shunsheng, Huang Biao, Ren Jinghua, Gu Xueyuan, Fan Jian, Xu Hongting. 2020. Element geochemistry of selenium−enriched soil and its main sources in Jiangsu Province[J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1813−1825 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Liao Qilin, Hua Ming, Feng Jinshun, Jin Yang, Wu Xinmin, Yan Chaoyang, Zhu Baiwan. 2007. Natural Se−rich tea in local Se−rich soils in southern Jiangsu[J]. Geology in China, 34(2): 347−353 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Liao Qilin, Ren Jinghua, Xu Weiwei, Cui Xiaodan, Jin Yang, Li Wenbo, Fan Jian, Zhu Bowan. 2016. Geological and geochemical background of Se−rich production in Yili area, Jiangsu Province[J]. Geology in China, 43(5): 1791−1802 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Litov R E, Combs G F. 1991. Selenium in pediatric nutrition[J]. Pediatrics, 87(3): 339−351. doi: 10.1542/peds.87.3.339
[20] Liu Xiujin, Yang Ke, GuoFei, Tang Shiqi, Liu Yinghan, Zhang Li, Cheng Hangxin, Liu Fei. 2022. Effects and mechanism of igneous rock on selenium in the tropical soil−rice system in Hainan Province, South China[J]. China Geology, 5(1): 1‒11.
[21] Liu Yanjuan. 2009. Investigation of Selenium, Zinc and Germanium in Soil and Special Agricultural Products in Yanhe County, Guizhou Province[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Lü Yaoyao, Yu Tao, Yang Zhongfang, Zhao Wanfu, Guo Wei, Huang Boming, Li Peng. 2012. The regulation mechanism of selenium distribution in Kaschin−Beck disease area: A case study in Aba area, Sichuan Province[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 31(7): 935−944 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Lü Y Y, Yu T, Yang Z F, Zhao W F, Zhang M, Wang Q. 2014. Constraint on Selenium bioavailability caused by its geochemical behavior in typical Kaschin−Beck disease areas in Aba, Sichuan Province of China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 493: 737−749. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.050
[24] Luo Weiqun, Jiang Zhongcheng, Hu Zhaoxin, Xie Yunqiu, Huang Jing, Liang Jianhong. 2018. Large area of selenium−rich soil and selenium−rich Hylocereus undulates discovered in Pingguo County, Guangxi[J]. Geology in China, 45(3): 630−631 ( in Chinese).
[25] Qin Jianxun, Fu Wei, Zheng Guodong, Deng Bin, Wu Tiansheng, Zhao Xinjin, Lu Bingke, Qin Yongxin. 2020. Selenium distribution in surface soil layer of Karst area of Guangxi and its affecting factors: acase study of Wuming County[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 57(5): 1299−1310 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Rayman M P. 2000. The importance of selenium to human health[J]. The Lancet, 356(9225): 233−241. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02490-9
[27] Shi Zhangliang, Jin Lixin, Liao Chao, Bao Yuhan, Liu Xiaobo, Deng Huan, Xu Kequan. 2020. Content characteristics and genesis of soil selenium in important cultivated areas of Leibo County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 44(5): 1253−1260 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] State Department of Environmental Conservation. 1990. Background Value of Soil Environment in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press (in Chinese).
[29] Stone R. 2009. A medical mystery in middle China[J]. Science, 324(5933): 1378−1381. doi: 10.1126/science.324_1378
[30] Sun Zhao, Hou Qingye, Yang Zhongfang, Yang Xiaoyan, Huang Yong, Chen Enke. 2010. Factors controlling the transport and transformation of selenium in typical soil environments: A case study of the Chengdu economic zone in Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 37(6): 1760−1768 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Supriatin S, Weng L P, Comans R N J. 2016. Selenium−rich dissolved organic matter determines selenium uptake in wheat grown o low−selenium Arable land soils[J]. Plant and Soil, 408(1/2): 73−94.
[32] Tan Jianan. 1996. Environmental Life Elements and Keshan Disease: A Study on Ecological Chemiscogeography[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press(in Chinese).
[33] Vinogradov A P, Ryabchikov D I. 1962. Detection and Analysis of Rare Elements[M]. London: Oldbourne Press.
[34] Wang Jinda, Yu Junbao, Zhang Xuelin. 2000. Geochemical features of elements of selenium etc. in soil of Leoss Plateau[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 20(5): 469−473 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Wang Renqi, Zhang Zhimin, Chao Xu, Feng Haiyan, Yang Zhongfang. 2022. A study of the selenium speciation in paddy soil and status of selenium−enriched rice in western part of Ankang City, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(2): 398−408 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Wang Renqi, Tan Keyan, Sun Qian, Li Hang, Zhang Longlong, Wang Yu, Yuan Xin, Zhu Xiaohua, Cai Jingyi. 2024. Health risk assessment of heavymetals in typical oats production region of Bashang area in Zhangjiakou, Hebei Province[J]. Geology in China, 51(1): 264−275 (in Chinese withEnglish abstract).
[37] Wang Rui, Yu Tao, Yang Zhongfang, Hou Qingye, Zeng Qingliang, Ma Honghong. 2018. Bioavailability of soil selenium and its influencing factors in selenium−enriched soil[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 27(7): 1647−1654 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Wang Shiji, Wu Xiaoyong, Liu Junbao. 2004. Characteristics of elemental selenium in soils and evaluation of eco−environmental effects in northern Zhejiang[J]. Geology in China, 31(S): 118−125 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Wang Z J, Gao Y X. 2001. Biogeochemical cycling of selenium in Chinese environments[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 16(1112): 1345−1351.
[40] Wei Zhenshan, Tu Qijun, Tang Shuhong, Wang Huabing, Zhao Xuejiao, Bai Jinqi. 2016. A discussion on the geochemical features and origin of selenium−rich soil on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains from Urumqi to Shawan County[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 40(5): 893−898 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Wen Bangyong, Zhang Taoliang, Li Xizhou, Xie Zhengdong. 2014. A feasibility study of selenium−rich soil development in Longnan County of Jiangxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 41(1): 256−263 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Wu Jun. 2018. The distribution of soil selenium in Shouning County of Fujian Province and its influencing[J]. Geology in China, 45(6): 1167−1176 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Xi Chaozhuang, Wu Linfeng, Zhang Pengfei, Yang Mingtai, Fan Yunfei, Huang Danyan. 2022. Investigation and evaluation of soil heavy metal pollution: A case study of Lianjiang high−efficiency agricultural park in Huishui, Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Hunan City University (Natural Science), 31(4): 51−56 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] Xi Chaozhuang, Zhang Pengfei, Wu Linfeng, Yang Mingtai, Fan Yunfei, Deng Huijuan. 2023. Investigation and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in cultivated land in Huishui County, Guizhou Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 42(7): 1228−1239 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Xia Weiping, Tan Jianan. 1990. A comparative study of selenium content in Chinese rocks[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 10(2): 125−131 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] Yan Mingcai, Chi Qinghua. 1997. Chemical Composition of the Crust and Rocks of Eastern China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese).
[47] Yang Shengfa, Yang Mingtai, Fan Yunfei, Wang Furui, Li Yantao, Liao Junkai, Xu Pengfei. 2019. A Geochemical Survey and Evaluation Report on Cultivated Land Quality in Huishui County, Guizhou Province[R]. Guiyang: Nuclear Resources Geological Survey, Non−ferrous Metals and Nuclear Industry Geological Exploration Bureau of Guizhou (in Chinese).
[48] Yang Xiaoxiao, Zeng Daoming, Luo Xianrong, Sun Binbin, Wu Chao, Huang Wenbin, Yang Chunli. 2020. Geochemical characteristics of Selenium, Fluorine and Iodine in surface soils of the Xinhui area, the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Earth and Environment, 48(2): 181−189 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[49] Yu Tao, Yang Zhongfang, Wang Rui, Zeng Qingliang, Hou Wanling. 2018. Characteristics and sources of soil selenium and other elements in typical high selenium soil area of Enshi[J]. Soils, 50(6): 1119−1125 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[50] Zeng Qingliang, Yu Tao, Wang Rui. 2018. The influencing factors of selenium in soils and classifying the selenium−rich soil resources in the typical area of Enshi, Hubei[J]. Geoscience, 32(1): 105−112 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[51] Zhang Dong, Li Yongchun, Su Rilige, Yuan Guoli, Tai Surigala, Wang Yongliang, Chen Guodong, Zhou Wenhui, Du Yuchunzi, Yang Jianyu. 2024. Ecological health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in Wuyuan County, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 51(1): 248−263 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[52] Zhu Jianming, Liang Xiaobing, Ling Hongwen, Wang Mingshi, Wang Fushun, Liu Shirong. 2003. Advances in studying occurrence modes of selenium in environment[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 22(1): 75−81 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[53] 安永会, 李旭峰, 何锦, 贾小丰, 李亮. 2010. 若尔盖县大骨节病分布特征及其与地质环境的关系[J]. 中国地质, 37(3): 587−593. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.007
[54] 陈旭晖. 2001. 贵州土壤养分含量的变化与施肥管理[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 7(2): 121−128. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2001.02.001
[55] 高雪, 陈海燕, 童倩倩. 2013. 贵州耕地耕层土壤养分状况评价[J]. 贵州农业科学, 41(12): 87−91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2013.12.022
[56] 国家环境保护局. 1990. 中国土壤环境背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社.
[57] 黄春雷, 魏迎春, 简中华, 宋明义. 2013. 浙中典型富硒区土壤硒含量及形态特征[J]. 地球与环境, 41(2): 155−159.
[58] 黎彤. 1976. 化学元素的地球丰度[J]. 地球化学, (3): 167−174. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1976.03.004
[59] 郦逸根, 董岩翔, 郑洁, 李琰, 吴小勇, 朱朝晖. 2005. 浙江富硒土壤资源调查与评价[J]. 第四纪研究, 25(3): 323−330. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2005.03.008
[60] 李玉超, 王诚煜, 于成广. 2020. 辽宁丹东地区土壤Se元素地球化学特征及其影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 50(6): 1766−1775.
[61] 廖启林, 崔晓丹, 黄顺生, 黄标, 任静华, 顾雪元, 范健, 徐宏婷. 2020. 江苏富硒土壤元素地球化学特征及主要来源[J]. 中国地质, 47(6): 1813−1825. doi: 10.12029/gc20200617
[62] 廖启林, 华明, 冯金顺, 金洋, 吴新民, 颜朝阳, 朱伯万. 2007. 苏南局部富硒土壤及其天然富硒茶叶初步研究[J]. 中国地质, 34(2): 347−353.
[63] 廖启林, 任静华, 徐伟伟, 崔晓丹, 金洋, 李文博, 范健, 朱伯万. 2016. 江苏宜溧富硒稻米产区地质地球化学背景[J]. 中国地质, 43(5): 1791−1802.
[64] 刘艳娟. 2009. 贵州省沿河县土壤及特色农产品硒锌锗调查研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学.
[65] 吕瑶瑶, 余涛, 杨忠芳, 赵万伏, 郭伟, 黄波铭, 李鹏. 2012. 大骨节病区硒元素分布的调控机理研究—以四川省阿坝地区为例[J]. 环境化学, 31(7): 935−944.
[66] 罗为群, 蒋忠诚, 胡兆鑫, 谢运球, 黄静, 梁建宏. 2018. 广西平果县发现大面积富硒土壤与富硒火龙果[J]. 中国地质, 45(3): 630−631. doi: 10.12029/gc20180316
[67] 覃建勋, 付伟, 郑国东, 邓宾, 吴天生, 赵辛金, 卢炳科, 覃勇新. 2020. 广西岩溶区表层土壤硒元素分布特征与影响因素探究—以武鸣县为例[J]. 土壤学报, 57(5): 1299−1310.
[68] 时章亮, 金立新, 廖超, 包雨函, 刘晓波, 邓欢, 徐克全. 2020. 四川雷波县重点耕地区土壤硒含量特征及其成因分析[J]. 物探与化探, 44(5): 1253−1260.
[69] 孙朝, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 杨晓燕, 黄勇, 陈恩科. 2010. 典型土壤环境中硒的迁移转化影响因素研究—以四川省成都经济区为例[J]. 中国地质, 37(6): 1760−1768. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.06.023
[70] 谭见安. 1996. 环境生命元素与克山病—生态化学地理研究[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社.
[71] 王金达, 于君宝, 张学林. 2000. 黄土高原土壤中硒等元素的地球化学特征[J]. 地理科学, 20(5): 469−473. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2000.05.014
[72] 王仁琪, 张志敏, 晁旭, 冯海艳, 杨忠芳. 2022. 陕西省安康市西部稻田土壤硒形态特征与水稻富硒状况研究[J]. 中国地质, 49(2): 398−408.
[73] 王仁琪, 谭科艳, 孙倩, 李航, 张隆隆, 王玉, 袁欣, 朱晓华, 蔡敬怡. 2024. 河北省张家口坝上典型莜麦产区重金属元素健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 51(1): 264−275.
[74] 王锐, 余涛, 杨忠芳, 侯青叶, 曾庆良, 马宏宏. 2018. 富硒土壤硒生物有效性及影响因素研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 27(7): 1647−1654.
[75] 王世纪, 吴小勇, 刘军保. 2004. 浙北地区土壤硒元素特征及其生态环境效益评价[J]. 中国地质, 31(增刊): 118−125.
[76] 魏振山, 涂其军, 唐蜀虹, 王化兵, 赵雪娇, 白金启. 2016. 天山北坡乌鲁木齐至沙湾地区富硒土壤地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 40(5): 893−898.
[77] 文帮勇, 张涛亮, 李西周, 谢振东. 2014. 江西龙南地区富硒土壤资源开发可行性研究[J]. 中国地质, 41(1): 256−263. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.021
[78] 吴俊. 2018. 福建省寿宁县土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 中国地质, 45(6): 1167−1176. doi: 10.12029/gc20180607
[79] 息朝庄, 吴林锋, 张鹏飞, 杨茗钛, 范云飞, 黄丹艳. 2022. 土壤重金属污染现状调查与评价: 以贵州惠水涟江高效农业园区为例[J]. 湖南城市学院学报(自然科学版), 31(4): 51−56.
[80] 息朝庄, 张鹏飞, 吴林锋, 杨茗钛, 范云飞, 邓会娟. 2023. 贵州惠水耕地土壤重金属污染调查与评价[J]. 地质通报, 42(7): 1228−1239.
[81] 夏卫平, 谭见安. 1990. 中国一些岩类中硒的比较研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 10(2): 125−131.
[82] 鄢明才, 迟清华. 1997. 中国东部地壳与岩石的化学组成[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
[83] 杨胜发, 杨茗钛, 范云飞, 王福瑞, 李艳桃, 廖俊凯, 徐鹏飞. 2019. 贵州省惠水县耕地质量地球化学调查评价报告[R]. 贵阳: 贵州省有色金属和核工业地质勘查局核资源地质调查院.
[84] 杨笑笑, 曾道明, 罗先熔, 孙彬彬, 吴超, 黄文斌, 杨春丽. 2020. 珠三角新会地区表层土壤硒、氟、碘地球化学特征研究[J]. 地球与环境, 48(2): 181−189.
[85] 余涛, 杨忠芳, 王锐, 曾庆良, 侯宛苓. 2018. 恩施典型富硒区土壤硒与其他元素组合特征及来源分析[J]. 土壤, 50(6): 1119−1125.
[86] 曾庆良, 余涛, 王锐. 2018. 土壤硒含量影响因素及富硒土地资源区划研究—以湖北恩施沙地为例[J]. 现代地质, 32(1): 105−112.
[87] 张栋, 李永春, 苏日力格, 袁国礼, 邰苏日嘎拉, 王永亮, 陈国栋, 周文辉, 杜雨春子, 杨建雨. 2024. 内蒙古五原县某地土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 51(1): 248−263.
[88] 朱建明, 梁小兵, 凌宏文, 王明仕, 汪福顺, 刘世荣. 2003. 环境中硒存在形式的研究现状[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 22(1): 75−81.
-



 下载:
下载: