Re–Os and Ar–Ar dating of the Dahu Au (Mo) deposit in the Xiaoqinling area, West Henan: Constraint on its metallogenetic stages
-
摘要:
研究目的 位于华北克拉通南缘的东秦岭钼矿带是全球第二大钼矿带,其北缘蕴含有著名的小秦岭造山型金矿田。近年来通过地质调查工程的实施,在小秦岭大湖金(钼)矿区深部发现具有工业意义的钼矿化,并已开始开采钼矿,限定其成矿期次,有助于研究金钼成矿规律。
研究方法 本文基于小秦岭地区危机矿山深部找矿工作,研究了金钼深部成矿模式,分析了辉钼矿Re–Os和钾长石40Ar/39Ar同位素定年在划分成矿期次中的作用。
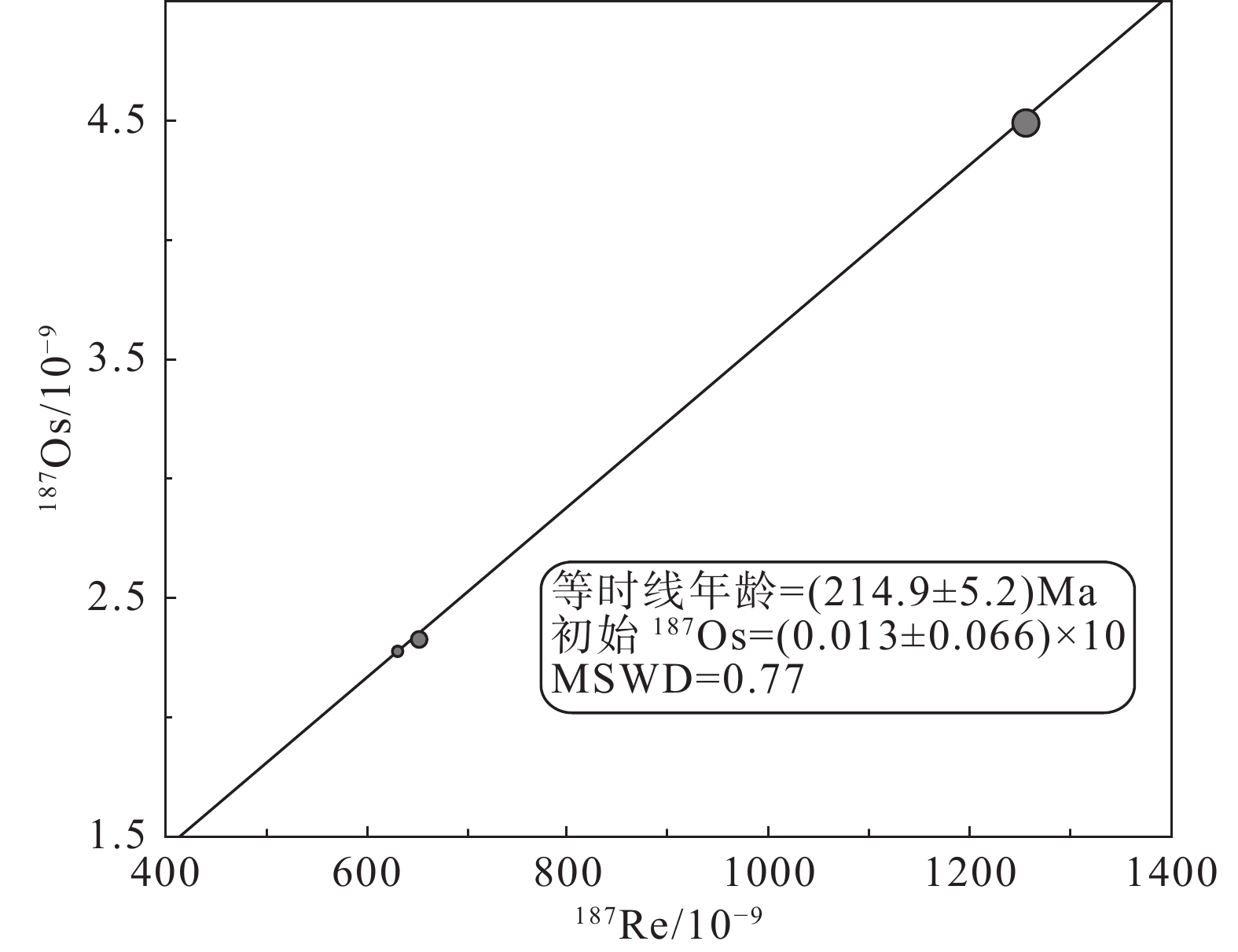
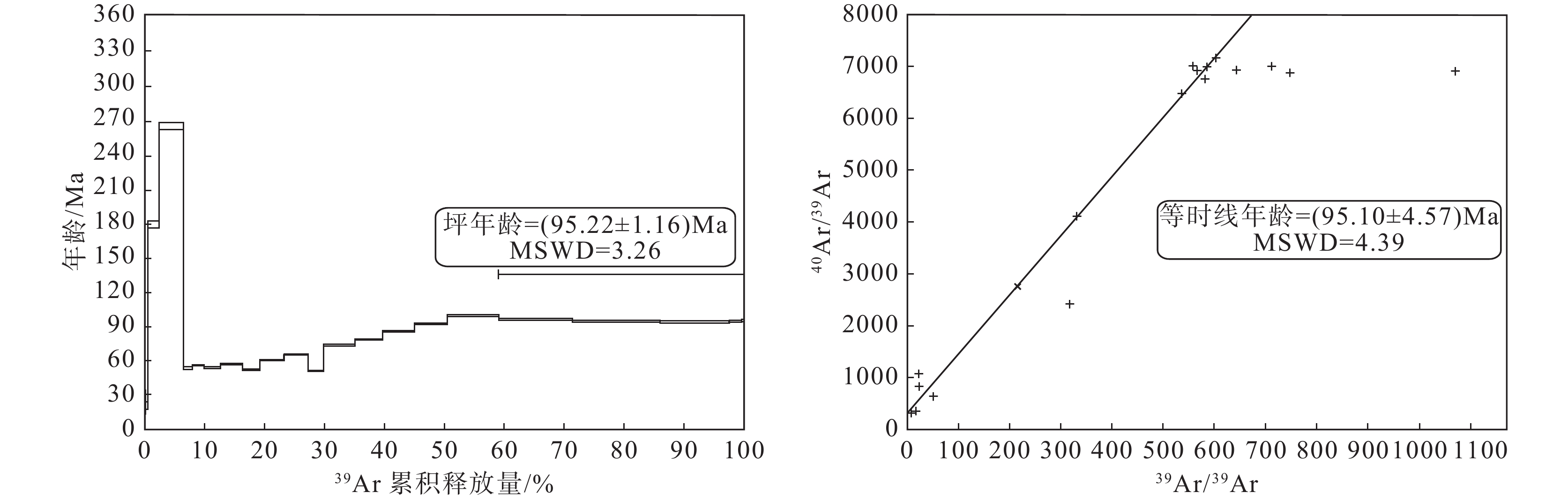
研究结果 来自S35矿脉的6件辉钼矿样品Re–Os模式年龄介于(192.3±2.9)~(223.4±3.2)Ma,等时线年龄为(214.9±5.2)Ma(MSWD=0.77),来自F5矿脉中钾长石晶体40Ar/39Ar坪年龄为(95.22±1.16)Ma,其等时线年龄为(95.10±4.57)Ma。
结论 辉钼矿年龄代表了印支期钼矿化事件,钾长石年龄反映存在燕山中期新的构造−岩浆−热事件,这期热事件对于金钼矿床的成矿活动可能有积极意义,叠加改造了印支期的钼矿化事件。结合手标本和BSE图像分析结果,认为大湖金(钼)矿区与金钼矿化相关的热事件应不低于两期。
-
关键词:
- 钼矿化 /
- Re–Os同位素年龄 /
- 40Ar/39Ar同位素年龄 /
- 印支期 /
- 燕山期 /
- 矿产勘查工程 /
- 大湖金(钼)矿床 /
- 小秦岭 /
- 豫西
Abstract:This paper is the result of mineral exploration engineering.
Objective The East Qinling molybdenum belt which located in the North China craton is the second largest Mo belt in the world, among which occur the most famous orogenic gold deposits of the Xiaoqinling. In recent years, through the implementation of geological survey engineering, molybdenum mineralization with industrial significance has been found in the deep of Dahu Au (Mo) deposit from Xiaoqinling area, and molybdenum ore mining has begun. Through the constraint on its metallogenetic stages, it is helpful to study the Au−Mo metallogenic regularity.
Methods In this paper, based on the Crisis Mine deep−seated deposits prospecting in Xiaoqinling area, we studied the metallogenic model of deep Au (Mo) deposit, and analyzed the role of molybdenite Re–Os and K–feldspar 40Ar/39Ar isotope dating in the classification of metallogenic stages.
Results Six molybdenite samples from the S35 ore vein yield Re–Os isotopic isochron age of (214.9±5.2) Ma (MSWD=0.77), with model ages ranging from (192.3±2.9) Ma to (223.4±3.2) Ma. K–feldspar samples from F5 ore vein yield Ar–Ar weighted plateau age of (95.22±1.16) Ma and the isochron age of (95.10±4.57) Ma.
Conclusions Molybdenite age suggests that the Mo mineralization in S35 vein occurred in Indosinian period, and K–feldspar age indicates a new tectono–magmatic–thermal event during the Middle Yanshanian, and this hydrothermal event may contribute to metallogenic activity of Au (Mo) deposit, which superimposed the molybdenum mineralization events of Indosinian. Combined with the results of hand samples and BSE images analysis, it is concluded that there are at least two episodes of hydrothermal event related to Au (Mo) mineralization in Dahu Au (Mo) ore district.
-

-
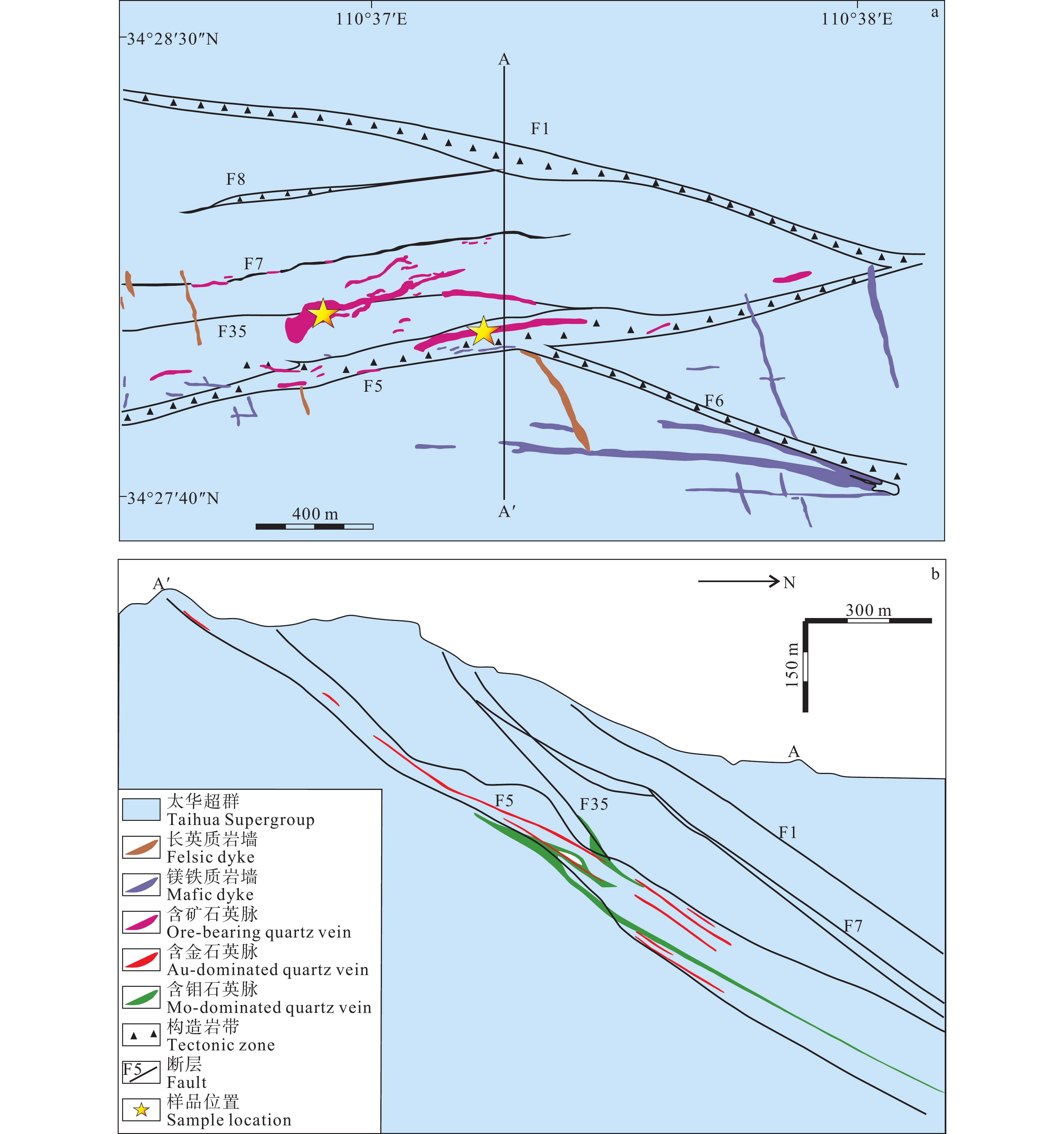
图 1 大湖金(钼)矿床区域地质图(据陈衍景, 2006; Li et al., 2011修改)
Figure 1.
图 2 大湖金(钼)矿床地质图(据Li et al., 2011修改)
Figure 2.
表 1 大湖金(钼)矿床辉钼矿Re–Os同位素测年数据
Table 1. Re–Os isotope data of molybdenites in the Dahu Au (Mo) deposit
原样名 样重/g Re/10−9 C普Os/10−9 187Re/10−9 187Os/10−9 模式年龄/Ma 测值 误差 测值 误差 测值 误差 测值 误差 测值 误差 S35-008 0.07022 1002 8 0.0323 0.0023 629.7 5.3 2.279 0.019 216.9 3.1 S35-007 0.02775 485 5 0.1098 0.0074 305.0 3.4 0.988 0.018 194.2 4.5 S35-008 0.04595 1035 9 0.0426 0.0025 650.3 5.6 2.335 0.022 215.2 3.3 S35-009 0.20069 1111 9 0.1384 0.0020 698.1 5.6 2.604 0.023 223.4 3.2 S35-012 0.03127 905 8 0.0570 0.0079 569.1 5.3 1.827 0.016 192.3 2.9 S35-013 0.08465 1990 16 0.0814 0.0022 1251.1 10.1 4.501 0.036 215.5 3.0 表 2 大湖金(钼)矿床钾长石40Ar–39Ar阶段升温年龄分析结果
Table 2. Results of 40Ar–39Ar step-heating dating of K-feldspar in the Dahu Au (Mo) deposit
温度/℃ 40Ar/39Ar 37Ar/39Ar 36Ar/39Ar 40Ar*/39Ark 40Ar*/% 39Ark/% 年龄/Ma(±2σ) 750 45.88686 0.09939 0.14585 2.796694 6.09 0.13 23.7±11.0 840 18.50686 0.03110 0.05433 2.454568 13.26 0.41 20.8±3.7 890 34.22425 0.01072 0.04086 22.150356 64.72 1.91 179.7±2.9 920 46.30595 0.00520 0.04285 33.643726 72.65 3.94 266.4±3.4 950 11.94427 0.03280 0.01887 6.370618 53.33 1.51 53.6±1.3 1040 7.58016 0.01399 0.00315 6.649467 87.72 2.01 55.9±0.5 1080 6.61393 0.00265 0.00062 6.431189 97.24 2.75 54.1±0.5 1110 6.99281 0.00482 0.00066 6.798917 97.23 3.61 57.1±0.5 1130 6.45763 0.00552 0.00094 6.181301 95.72 2.82 52.0±0.5 1140 7.46603 0.00300 0.00074 7.247358 97.07 4.09 60.8±0.5 1160 8.05913 0.00325 0.00096 7.774168 96.46 4.08 65.1±0.5 1170 6.25936 0.00796 0.00066 6.063206 96.87 2.54 51.0±0.4 1190 9.20474 0.00147 0.00134 8.809144 95.70 5.20 73.6±0.6 1210 9.85899 0.00210 0.00141 9.443653 95.79 4.70 78.8±0.6 1230 10.76914 0.00238 0.00155 10.309731 95.73 5.31 85.9±0.6 1250 11.62351 0.00304 0.00172 11.115128 95.63 5.47 92.4±0.8 1280 12.52454 0.00180 0.00179 11.996324 95.78 8.56 99.6±0.9 1310 12.15080 0.00107 0.00176 11.630633 95.72 12.37 96.6±0.9 1340 11.94156 0.00113 0.00171 11.436564 95.77 14.67 95.0±0.8 1370 11.83086 0.00143 0.00166 11.341123 95.86 11.42 94.3±0.9 1400 12.00702 0.00565 0.00186 11.457699 95.42 2.06 95.2±0.7 1450 12.33680 0.03253 0.00302 11.448060 92.79 0.44 95.1±1.4 -
[1] Chen Li. 2006. Characteristic of Ore–forming Fluid and Ore Genesis of Dahu Gold Deposit, in Xiaoqinling Gold Area[D]. Beijing: China University of Geoscience (Beijing), 1–97 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] Chen Li, Mao Jingwen, Ye Huishou. 2010. Ore–forming fluids and ore genesis of the Dahu gold deposit in the Xiaoqinling gold field[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 30(2): 103−107 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Chen Yanjing. 2006. Orogenic–type deposits and their metallogenic model and exploration potential[J]. Geology in China, 33(6): 1181−1196 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Chen Yanjing. 2010. Indosinian tectonic setting, magmatism and metallogenesis in Qinling Orogen, central China[J]. Geology in China, 37(4): 854−865 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Chen Y J, Guo G J, Li X. 1998. Metallogenic geodynamic background of gold deposits in granite–greenstone terrains of North China Craton[J]. Science in China (Series D), 41(2): 113−120. doi: 10.1007/BF02932429
[6] Chen Y J, Pirajno F, Qi J P. 2008. The Shanggong gold deposit, Eastern Qinling Orogen, China: Isotope geochemistry and implications for ore genesis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 33: 252−266. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.12.002
[7] Du Andao, He Hongliao, Yin Ningwan, Zou Xiaoqiu, Sun Yali, Sun Dezhong, Chen Shaozhen, Qu Wenjun. 1994. A study on the Rhenium–Osmium geochronometry of molybdenites[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 68(4): 339−347 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Du Andao, Qu Wenjun, Wang Denghong, Li Houming, Feng Chengyou, Liu Hua, Ren Jing, Zeng Fagang. 2007. Subgrain–size decoupling of Re and 187Os within molybdenite[J]. Mineral Deposits, 26(5): 572−580 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Faure G. 1998. Isotope geochronology and its applications to geology[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 5(1/2): 17−39.
[10] He H Y, Wang X L, Zhou Z H, Jin F, Wang F, Yang L K, Ding X, Boven A, Zhu R X. 2006. 40Ar/39Ar dating of Lujiatun Bed (Jehol Group) in Liaoning, northeastern China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33: L04303.
[11] Huang Dianhao, Wu Chengyu, Du Andao, He Hongliao. 1994. Re–Os isotope ages of molybdenum deposits in East Qinling and their significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 13(3): 221−230 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Huang Y G, Xiong C L, Jia X C, Yang X J, Luo G. 2019. Zircon U–Pb ages of the two–periods magmatism from the Xiuwacu Mo–W–Cu deposit, northwest Yunnan, China[J]. China Geology, 3: 391−392.
[13] Huang Y, Ren M H, Liang W, Li G M, Heilbronn K, Dai Z W, Wang Y Y, Zhang L. 2020. Origin of the Oligocene Tuolangla porphyry–skarn Cu–W–Mo deposit in Lhasa terrane, southern Xizang[J]. China Geology, 3: 369−384.
[14] Jiang Shaoyong, Dai Baozhang, Jiang Yaohui, Zhao Haixiang, Hou Minglan. 2009. Jiaodong and Xiaoqinling: Two orogenic gold provinces formed in different tectonic settings[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(11): 2727−2738 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Jiao Jiangang, Tang Zhongli, Qian Zhuangzhi, Yuan Haichao, Yan Haiqing, Sun Tao, Xu Gang, Li Xiaodong. 2010. Metallogenic mechanism, magma source and zircon U–Pb age of Jinduicheng granitic porphyry, East Qinling[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 35(6): 1011−1022 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.114
[16] Kerrich R, Goldfarb R, Groves D, Garwin S. 2000. The characteristics, origins, and geodynamic settings of supergiant gold metallogenic provinces[J]. Science in China (Series D), 43(Supp): 1−68.
[17] Li Houmin, Ye Huishou, Mao Jingwen, Wang Denghong, Chen Yuchuan, Qu Wenjun, Du Andao. 2007. Re–Os dating of molybdenites from Au (–Mo) deposits in Xiaoqinling gold ore district and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 26(4): 417−424 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Li Huaqin, Liu Jiaqi, Wei Lin. 1993. The Chronological Study of Fluid Inclusion and Its Geological Application in Hydrothermal Deposit[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese).
[19] Li N, Chen Y J, Fletcher I R, Zeng Q T. 2011. Triassic mineralization with Cretaceous overprint in the Dahu Au–Mo deposit, Xiaoqinling gold province: Constraints from SHRIMP monazite U–Th–Pb geochronology[J]. Gondwana Research, 20: 543−552. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2010.12.013
[20] Li Nuo, Chen Yanjing, Zhang Hui, Zhao Taiping, Deng Xiaohua, Wang Yun, Ni Zhiyong. 2007. Molybdenum deposits in East Qinling[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(5): 186−198 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Li Nuo, Sun Yali, Li Jing, Xue Liangwei, Li Wenbo. 2008. Molybdenite Re–Os isotope age of the Dahu Au–Mo deposit, Xiaoqinling and the Indosinian mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(4): 810−816 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Lu Xinxiang, Li Mingli, Wang Wei, Yu Zaiping, Shi Yongzhi. 2008. Indosinian movement and metallogenesis in Qinling orogenic belt[J]. Mineral Deposits, 27(6): 762−773 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Mao Jingwen, Hua Renmin, Li Xiaobo. 1999. A preliminary study of large–scale metallogenesis and large clusters of mineral deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 18(4): 291−299 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Mao Jingwen, Xie Guiqing, Zhang Zuoheng, Li Xiaofeng, Wang Yitian, Zhang Changqing, Li Yongfeng. 2005. Mesozoic large–scale metallogenic pulses in North China and corresponding geodynamic settings[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(1): 169−188 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Mao J W, Goldfarb R J, Zhang Z W, Xu W Y, Qiu Y M, Deng Jun. 2002. Gold deposits in the Xiaoqinling–Xiong’ershan region, Central China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 37(3): 306−325.
[26] Mao J W, Xie G Q, Bierlein F, Qü W J, Du A D, Ye H S, Pirajno F, Li H M, Guo B J, Li Y F, Yang Z Q. 2008. Tectonic implications from Re–Os dating of Mesozoic molybdenum deposits in the East Qinling–Dabie orogenic belt[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72: 4607−4626. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.06.027
[27] Ni Zhiyong, Li Nuo, Guan Shenjin, Zhang hui, Xue Liangwei. 2008. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and ore genesis of the Dahu Au–Mo deposit in the Xiaoqinling gold field, Henan Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(9): 2058−2068 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Ni Zhiyong, Li Nuo, Zhang Hui, Xue Liangwei. 2009. Sr–Nd–Pb isotope constraints on the source of ore–forming elements of the Dahu Au–Mo deposit, Henan province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(11): 2823−2832 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Ni Z Y, Chen Y J, Li N, Zhang H. 2012. Pb–Sr–Nd isotope constraints on the fluid source of the Dahu Au–Mo deposit in Qinling Orogen, central China, and implication for Triassic tectonic setting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 46: 60−67. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.01.004
[30] Qiang Shanfeng, Bi Shijian, Deng Xiaodong, Guo Lianqiao, Li Jianwei. 2013. Monazite U–Th–Pb ages of the Qinnan gold deposits, Xiaoqinling district: Implications for regional metallogenesis and tectonic setting[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 38(1): 43−56 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2013.005
[31] Qiao G B, Wu Y Z, Liu T. 2021. Zircon U–Pb age of pegmatite veins in Dahongliutan lithium deposit, western Kunlun[J]. China Geology, 4: 185−187.
[32] Qiu Qinglun, Yan Changhai, Chen Ruibao, Lu Shuwei. 2008. The geodynamic settings of Yanshanian large–scale metallogenic pulses in Xiaoqinling–Xiong’ershan area[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 23(4): 281−286 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Shi G H, Lei W Y, He H Y, Ng Y N, Liu Y, Liu Y X, Yuan Y, Kang Z J, Xie G. 2014. Superimposed tectono–metamorphic episodes of Jurassic and Eocene age in the jadeite uplift, Myanmar, as revealed by 40Ar/39Ar dating[J]. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 464−474. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.08.007
[34] Shi Yonghong, Wang Yong, Chen Bailin, Tan Renwen, Gao Yun, Shen Jinghui. 2022. Characteristics of silicon-calcium surface ore-controlling in Fengtai ore−concentration areas, West Qinling Mountains: Examples from Qiandongshan Pb−Zn deposit[J]. Geology in China, 49(1): 226–240 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Steiger R H, Jäger E. 1977. Subcommision on geochronology: Conventionon the use of decay constants in geo– and cosmochronology[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 36: 359−362. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(77)90060-7
[36] Tang Y, Liu Y P, Wang P, Tang W Q, Qin Y D, Gong X D, Wang D B, Wang B D. 2021. A new understanding of Demala Group complex in Chayu Area, southeastern Qinghai–Xizang Plateau: Evidence from zircon U–Pb and mica 40Ar/39Ar dating[J]. China Geology, 4: 77−94.
[37] Wang Xiuzhang, Cheng Jingping, Zhang Baogui, Fan Wenling, Bai Zhenghua, Liang Huaying. 1992. Transformation Type Gold Deposits of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
[38] Wang Yitian, Mao Jingwen, Lu Xinxiang, Ye Anwang. 2002. 40Ar–39Ar dating and geological implication of auriferous altered rocks from the middle–deep section of Q875 gold quartz vein in Xiaoqinling area, Henan, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(18): 1427−1431 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2002-47-18-1427
[39] Xue Liangwei, Pang Jiqun, Wang Xiangguo, Zhou Changming. 1999. Rb–Sr and 40Ar–39Ar dating of fluid inclusion of the No. 303 quartz vein in Xiaoqinling region[J]. Geochimica, 28(5): 473−478 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Yang Jihong, Zhang Jinchun, Miao Cuimei. 2007. Rules and application of F5 structure mineralization control in Dahu gold fields of Xiaoqinling[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science), 26(6): 659−663 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Yao Shuzhen, Ding Zhenju, Zhou Zonggui, Chen Shouyu. 2002. Metallogenic syestems of Qinling Orogen[J]. Earth Science, 27(5): 599−604 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Zhang Jinjiang, Zheng Yadong, Liu Shuwen. 2003. Mesozoic tectonic evolution and ore–deposits formation in the gold mine field of Xiaoqinling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 38(1): 74−84 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Zhang Qi, Jin Weijun, Li Chengdong, Wang Yualong. 2009. Yanshanian large–scale magmatism and lithosphere thinning in Eastern China: Relation to large igneous province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(2): 21−51 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] Zhang Siming, Chen Zhenghui, Shi Guanghai, Li Lixia, Qu Wenjun, Li Chao. 2011. Re–Os isotopic dating of molybdenite from Dajishan tungsten deposit in Jiangxi Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 30(6): 1113−1121 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Zhang Y, Song Q H, Han S J, Ding J H. 2021. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Hekoulinchang Sn polymetallic deposit in Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. China Geology, 4: 1−14.
[46] Zhao Haijie, Mao Jingwen, Ye Huishou, Hou Kejun, Liang Huishan. 2010a. Chronology and petrogenesis of Shijiawan granite porphyry in Shannxi Province: Constrains from zircon U–Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic compositions[J]. Mineral Deposits, 29(1): 143−157 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[47] Zhao Haijie, Mao Jingwen, Ye Huishou, Xie Guiqing, Yang Zongxi. 2010b. Geochronology and geochemistry of the alkaline granite porphyry and diabase dikes in Huanglongpu area of Shaanxi Province: Petrogenesis and implications for tectonic environment[J]. Geology in China, 37(1): 12−27 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[48] Zhao Haijie, Ye Huishou, Li Chao. 2013. Re–Os dating of molybdenite from the Shijiawan molybdenum deposit in Shaanxi Province and its geological implications[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 32: 90−98 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[49] Zhao H B, Zhang Y, Liu L. 2021. Hydrothermal alteration processes in the giant Dahutang tungsten deposit, South China: Implications from litho–geochemistry and mass balance calculation[J]. China Geology, 4: 230−244.
[50] Zhao H X, Frimmel H E, Jiang S Y, Dai B Z. 2011. LA–ICP–MS trace element analysis of pyrite from the Xiaoqinling gold district, China: Implications for ore genesis[J]. Ore Geology Review, 43: 142−153. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.07.006
[51] Zhu L M, Zhang G W, Chen Y J, Ding Z J, Guo B, Wang F, Lee B. 2011. Zircon U–Pb ages and geochemistry of the Wenquan Mo–bearing granitioids in West Qinling, China: Constraints on the geodynamic setting for the newly discovered Wenquan Mo deposit[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 39: 46−62. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2010.10.001
[52] 陈莉. 2006. 小秦岭大湖金矿床成矿流体特征及矿床成因探讨[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1–97.
[53] 陈莉, 毛景文, 叶会寿. 2010. 小秦岭大湖金矿成矿流体特征及矿床成因[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 30(2): 103−107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2010.02.017
[54] 陈衍景. 2006. 造山型矿床、成矿模式及找矿潜力[J]. 中国地质, 33(6): 1181−1196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.06.001
[55] 陈衍景. 2010. 秦岭印支期构造背景、岩浆活动及成矿作用[J]. 中国地质, 37(4): 854–865.
[56] 杜安道, 何红蓼, 殷宁万, 邹晓秋, 孙亚利, 孙德忠, 陈少珍, 屈文俊. 1994. 辉钼矿的铼锇同位素地质年龄测定方法研究[J]. 地质学报, 68(4): 339−347. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1994.04.005
[57] 杜安道, 屈文俊, 王登红, 李厚明, 丰成友, 刘华, 任静, 曾法刚. 2007. 辉钼矿亚晶粒范围内Re和187Os的失耦现象[J]. 矿床地质, 26(5): 572−580. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.05.010
[58] 黄典豪, 吴澄宇, 杜安道, 何红蓼. 1994. 东秦岭地区钼矿床的铼锇同位素年龄及其意义[J]. 矿床地质, 13(3): 221−230.
[59] 蒋少涌, 戴宝章, 姜耀辉, 赵海香, 侯明兰. 2009. 胶东和小秦岭: 两类不同构造环境中的造山型金矿省[J]. 岩石学报, 25(11): 2727−2738.
[60] 焦建刚, 汤中立, 钱壮志, 袁海潮, 闫海卿, 孙涛, 徐刚, 李小东. 2010. 东秦岭金堆城花岗斑岩体的锆石U–Pb年龄、物质来源及成矿机制[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 35(6): 1011−1022.
[61] 李厚民, 叶会寿, 毛景文, 王登红, 陈毓川, 屈文俊, 杜安道. 2007. 小秦岭金(钼)矿床辉钼矿铼–锇定年及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 26(4): 417−424. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.04.005
[62] 李华芹, 刘家齐, 魏林. 1993. 热液矿床流体包裹体年代学研究及其地质应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
[63] 李诺, 陈衍景, 张辉, 赵太平, 邓小华, 王运, 倪智勇. 2007. 东秦岭斑岩钼矿带的地质特征和成矿构造背景[J]. 地学前缘, 14(5): 186−198. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.05.019
[64] 李诺, 孙亚莉, 李晶, 薛良伟, 李文博. 2008. 小秦岭大湖金钼矿床辉钼矿铼锇同位素年龄及印支期成矿事件[J]. 岩石学报, 24(4): 810−816.
[65] 卢欣祥, 李明立, 王卫, 于在平, 时永志. 2008. 秦岭造山带的印支运动及印支期成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 27(6): 762−773. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2008.06.009
[66] 毛景文, 华仁民, 李晓波. 1999. 浅议大规模成矿作用与大型矿集区[J]. 矿床地质, 18(4): 291−299. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.1999.04.001
[67] 毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 李晓峰, 王义天, 张长青, 李永峰. 2005. 中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 21(1): 169−188. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2005.01.017
[68] 倪智勇, 李诺, 管申进, 张辉, 薛良伟. 2008. 河南小秦岭金矿田大湖金–钼矿床流体包裹体特征及矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 24(9): 2058−2068.
[69] 倪智勇, 李诺, 张辉, 薛良伟. 2009. 河南大湖金钼矿床成矿物质来源的锶钕铅同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 25(11): 2823−2832.
[70] 强山峰, 毕诗健, 邓晓东, 郭连巧, 李建威. 2013. 豫西小秦岭地区秦南金矿床热液独居石U–Th–Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 38(1): 43−56.
[71] 邱庆伦, 燕长海, 陈瑞保, 卢书炜. 2008. 小秦岭—熊耳山地区燕山期大规模成矿的地球动力学背景[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 23(4): 281−286.
[72] 石永红, 王永, 陈柏林, 谭人文, 高允, 申景辉. 2022. 西秦岭凤太矿集区铅锌矿床硅钙面控矿作用—以铅硐山铅锌矿床为例[J]. 中国地质, 49(1): 226–240.
[73] 王秀璋, 程景平, 张宝贵, 樊文苓, 白正华, 梁华英. 1992. 中国改造型金矿床地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
[74] 王义天, 毛景文, 卢欣祥, 叶安旺. 2002. 河南小秦岭金矿区Q875脉中深部矿化蚀变岩的40Ar–39Ar年龄及其意义[J]. 科学通报, 47(18): 1427−1431. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2002.18.015
[75] 薛良伟, 庞继群, 王祥国, 周长命. 1999. 小秦岭303号石英脉流体包裹体Rb–Sr, 40Ar–39Ar成矿年龄测定[J]. 地球化学, 28(5): 473−478. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1999.05.007
[76] 杨继红, 张进春, 苗翠梅. 2007. 小秦岭大湖金矿区F5控矿规律及其应用研究[J]. 河南理工大学学报, 26(6): 659−663.
[77] 姚书振, 丁振举, 周宗桂, 陈守余. 2002. 秦岭造山带金属成矿系统[J]. 地球科学, 27(5): 599−604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2002.05.020
[78] 张进江, 郑亚东, 刘树文. 2003. 小秦岭金矿田中生代构造演化与矿床形成[J]. 地质科学, 38(1): 74−84. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2003.01.008
[79] 张旗, 金惟俊, 李承东, 王元龙. 2009. 中国东部燕山期大规模岩浆活动与岩石圈减薄: 与大火成岩省的关系[J]. 地学前缘, 16(2): 21−51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.02.002
[80] 张思明, 陈郑辉, 施光海, 李丽侠, 屈文俊, 李超. 2011. 江西省大吉山钨矿床辉钼矿铼–锇同位素定年[J]. 矿床地质, 30(6): 1113−1121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.06.011
[81] 赵海杰, 毛景文, 叶会寿, 侯可军, 梁慧山. 2010a. 陕西洛南县石家湾钼矿相关花岗斑岩的年代学及岩石成因: 锆石U–Pb年龄及Hf同位素制约[J]. 矿床地质, 29(1): 143−157.
[82] 赵海杰, 毛景文, 叶会寿, 谢桂青, 杨宗喜. 2010b. 陕西黄龙铺地区碱性花岗斑岩及辉绿岩的年代学与地球化学: 岩石成因及其构造环境示踪[J]. 中国地质, 37(1): 12−27.
[83] 赵海杰, 叶会寿, 李超. 2013. 陕西洛南县石家湾钼矿Re–Os同位素年龄及地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 32: 90−98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.01.007
-




 下载:
下载: