Heavy minerals, Sr-Nd isotopic composition of sandy land in Hulun Buir, Inner Mongolia and their implications for Asian aeolian dust system
-
摘要:
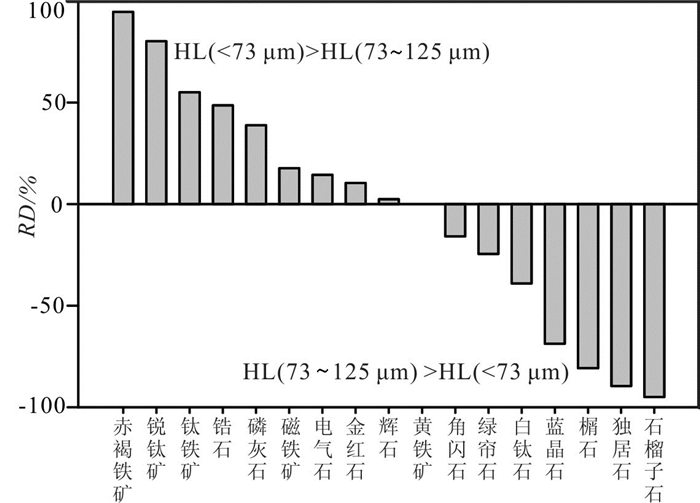
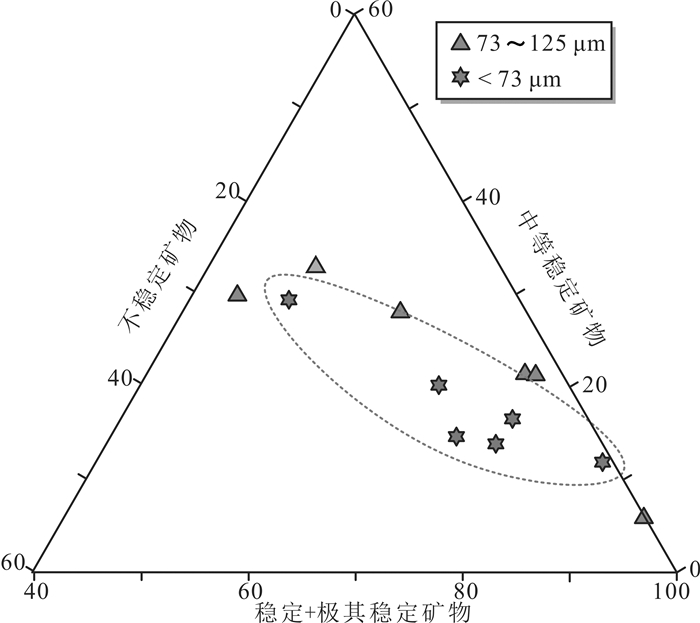
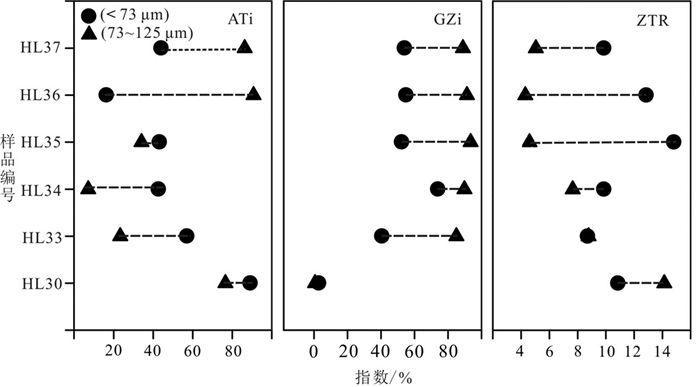
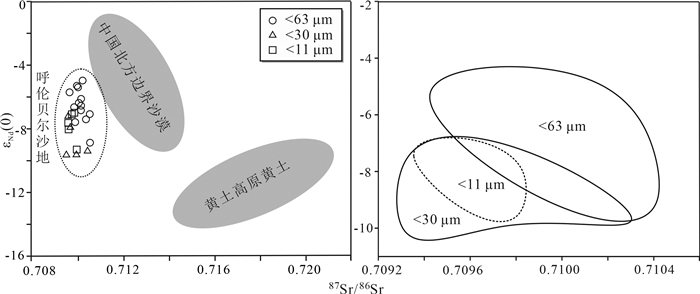
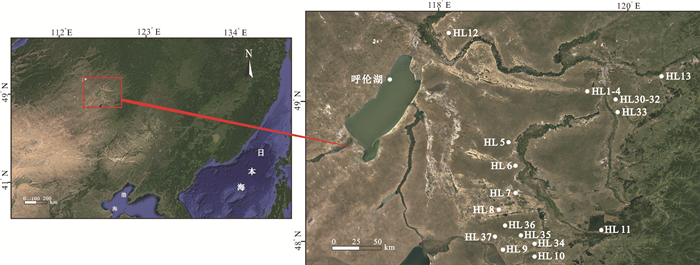
呼伦贝尔沙地作为中国北方沙漠的重要组成部分,对其物质组成的深入探讨对于亚洲风尘系统的研究具有重要意义。重矿物特征和Sr-Nd同位素组成是解开沉积物演化过程和物源示踪的重要工具,但分选作用所造成的"粒度效应"一直是沙地重矿物和Sr-Nd同位素组成的制约因素。为分析呼伦贝尔沙地的物质组成及探讨分选作用对重矿物和Sr-Nd同位素组成的影响,采集了呼伦贝尔沙地19个风成沙和河流沙样品,并进行了分粒级处理。其中,对12个子样(< 73 μm和73~125 μm两个粒级)进行了重矿物的鉴定分析,对23个子样(< 63 μm、 < 30 μm和 < 11 μm三个粒级)进行了Sr-Nd同位素的测定。结果表明:不同粒度组分的重矿物含量、重矿物指数(ATi、GZi和ZTR)和重矿物组合存在明显差异;稳定和极其稳定矿物优先富集于细颗粒,使细颗粒沉积物的总体稳定程度加强。与以往Sr-Nd同位素粒度控制的研究结果不同,本文研究结果显示,87Sr/86Sr比值受粒度的影响很小,但Nd同位素组成明显受粒度效应的影响,并表现出粗颗粒组分有更高Nd同位素比值的趋势。Sr-Nd同位素组成存在时间效应,随时间发生变化,表明了风尘源区地球化学组成的不稳定性,这对于利用重矿物和Sr-Nd同位素进行亚洲风尘系统研究具有重要指示,在物源示踪时必须考虑宽/多粒度窗口以及充足的样品量以弥补粒度和时间效应带来的偏差。
Abstract:As an important part of Northern China Desert, Hulun Buir sandy land is of great significance to the study of dust system in Asia. The characteristics of heavy minerals and the composition of Sr-Nd isotopes are the important tools to reveal the sediment evolution process and trace the provenance. But the "grain size effect" caused by sedimentary sorting has always been the limiting factor for the composition of heavy minerals and Sr-Nd isotopes in sandy land. Totally 19 aeolian sand and fluvial sand samples were collected from Hulun Buir sandy land and screened to analyze the material composition and discuss the effect of separation on the composition of heavy minerals and Sr-Nd isotopes. Among them, 12 sub-samples (< 73 μm and 73-125 μm) were identified and analyzed for heavy minerals, and 23 sub-samples (< 63 μm, < 30 μm and < 11 μm) were determined for Sr-Nd isotopes. The results show that there are significant differences in heavy mineral content, heavy mineral index (ATi, GZi and ZTR) and heavy mineral assemblage with different particle sizes. The stable and extremely stable minerals are concentrate preferentially onto the finer particles, which enhances the overall stability of the fine-grained sediments. Different from previous studies on Sr-Nd isotopic grain size control, our results show that the 87Sr/86Sr ratio is slightly affected by the grain size effect, but the Nd isotopic composition is significantly affected by it, and the coarse-grained components tend to have a higher Nd isotopic ratio. The Sr-Nd isotopic composition of Hulun Buir sandy land has "time effect". It shows that the geochemical composition of the dust source area is unstable. This study is of great significance for the understanding of Asian aeolian dust system study using heavy mineral and Sr-Nd isotopic composition. The wide or multiple grain size window as well as substantial amount of samples must be considered for source tracing.
-

-
表 1 呼伦贝尔沙地重矿物种类及含量(%)
Table 1. Heavy mineral types and contents in Hulun Buir sandy land(%)
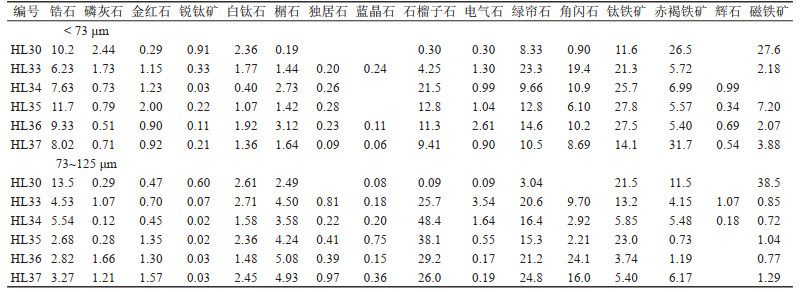
表 2 呼伦贝尔沙地矿物稳定性分类
Table 2. Classification of mineral stability in Hulun Buir sandy land
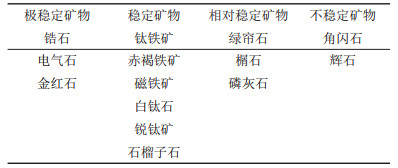
表 3 呼伦贝尔沙地重矿物特征指数
Table 3. Characteristic index of heavy minerals in Hulun Buir Sandy Land
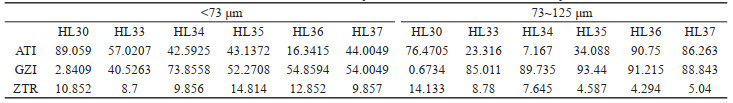
表 4 呼伦贝尔沙地的Sr-Nd同位素组成
Table 4. Sr and Nd isotopic compositions of the Hulun Buir sandy land
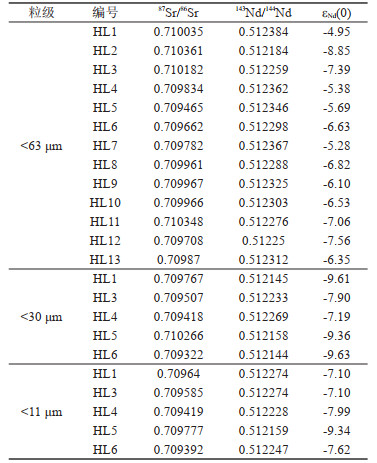
-
Bayon G, Toucanne S, Skonieczny C, André L, Bermell S, Cheron S, Dennielou B, Etoubleau J, Freslon N, Gauchery T, Germain Y, Jorry S J, Ménot G, Monin L, Ponzevera E, Rouget M L, Tachikawa K, Barrat J A. 2015. Rare earth elements and neodymium isotopes in world river sediments revisited[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 170: 17-38. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.08.001
Bi L, Yang S, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Dou Y, Li C, Zheng H. 2017. Provenance study of the Holocene sediments in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) estuary and inner shelf of the East China sea[J]. Quaternary International, 441: 147-161. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.12.004
Chen J, Li G, Yang J, Rao W, Lu H, Balsam W, Ji J. 2007. Nd and Sr isotopic characteristics of Chinese deserts: Implications for the provenances of Asian dust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(15): 3904-3914. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.04.033
Chen J, Li G. 2011. Geochemical studies on the source region of Asian dust[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(9): 1279. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4269-z
Chen Z, Li G. 2013. Evolving sources of eolian detritus on the Chinese Loess Plateau since early Miocene: Tectonic and climatic controls[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 371: 220-225. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035850043710_5d75.html
Dasch E J. 1969. Strontium isotopes in weathering profiles, deep-sea sediments, and sedimentary rocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 33(12): 1521-1552. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(69)90153-7
Derry L A, France Lanord C. 1996. Neogene Himalayan weathering history and river 87Sr86Sr: Impact on the marine Sr record[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 142(1-2): 59-74. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(96)00091-X
DouY, Yang S, Shi X, Clift P. D, Liu S, Liu J, Li C, Bi L, Zhao Y. 2016. Provenance weathering and erosion records in southern Okinawa Trough sediments since 28 ka: Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic evidences[J]. Chemical Geology, 425: 93-109. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.01.029
Feng J L, Zhu L P, Zhen X L, Hu Z G. 2009. Grain size effect on Sr and Nd isotopic compositions in eolian dust: implications for tracing dust provenance and Nd model age[J]. Geochemical Journal, 43(2): 123-131. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0007
Goldstein S L, O'nions R K, Hamilton P J. 1984. A Sm-Nd isotopic study of atmospheric dusts and particulates from major river systems[J]. Earth and planetary Science letters, 70(2): 221-236. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(84)90007-4
Grousset F E, Biscaye P E. 2005. Tracing dust sources and transport patterns using Sr, Nd and Pb isotopes[J]. Chemical Geology, 222(3/4): 149-167. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035367242910_60a4.html
Li G, Pettke T, Chen J. 2011. Increasing Nd isotopic ratio of Asian dust indicates progressive uplift of the north Tibetan Plateau since the middle Miocene[J]. Geology, 39(3): 199-202. doi: 10.1130/G31734.1
Li G, Chen J, Ji J, Yang J, Conway T. M. 2009. Natural and anthropogenic sources of East Asian dust[J]. Geology, 37(8): 727-730. doi: 10.1130/G30031A.1
Li T, Xu Z, Lim D, Chang F, Wan S, Jung H, Choi J. 2015. Sr-Nd isotopic constraints on detrital sediment provenance and paleoenvironmental change in the northern Okinawa Trough during the Late Quaternary[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 430: 74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.04.017
Liu Haijiang, Chai Huixia, Cheng Weiming, Zhong Decai, Zhou chenghu. 2008. A research of aeolian landform in northern China based on remote sensing imagery[J]. Geographical Research, 27(1): 109-118 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Jin, Wang Yong, Yao Peiyi. 2015. A study of paleoclimate changes in east Inner Mongolia since the Last deglaciation on the basis of aeolian sand-paleosoil series geochemical records[J]. Geology in China, (4): 1103-1114(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90050X/201504/665692386.html
Meyer I, Davies G R, Stuut J B W. 2011. Grain size control on Sr-Nd isotope provenance studies and impact on paleoclimate reconstructions: An example from deep-sea sediments offshore NW Africa[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 12(3): 1-4. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Gareth_Davies11/publication/252464960_Grain_size_control_on_Sr-Nd_isotope_provenance_studies_and_impact_on_paleoclimate_reconstructions_An_example_from_deep-sea_sediments_offshore_NW_Africa/links/547332910cf24bc8ea19ca1c.pdf
Morton A C, Hallsworth C R. 1999. Processes controlling the composition of heavy mineral assemblages in sandstones[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 124(1/4): 3-29. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000034154346310_40ae.html
Morton A C, Hallsworth C. 1994. Identifying provenance-specific features of detrital heavy mineral assemblages in sandstones[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 90(3/4): 241-256. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000033951464210_0af4.html
Morton A C, Johnsson M J. 1993. Factors influencing the composition of detrital heavy mineral suites in Holocene sand of the Apure River drainage basin, Venezuela[C]//Processes Controlling the Composition of Siliciclastic Sediments. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap, 284: 171-185.
Morton A C. 1985. Heavy Minerals in provenance studies[C]//Provenance of Arenites. Springer, Dordrecht: 249-277.
Morton A, Hurst A. 1995. Correlation of sandstones using heavy minerals: An example from the Statfjord Formation of the Snorre Field, northern North Sea[J]. Geological Society, 89(1): 3-22. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1995.089.01.02
Nakai S, Halliday A N, Rea D K. 1993. Provenance of dust in the Pacific Ocean[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letteers, (1/2): 143-157.
Nie J S, Peng W B, Pfaff K, Möller A, Garzanti E, Andò S, Stevens T, Birde A, Chang H, Song YG, Liu SP, Ji SC, 2013. Controlling factors on heavy mineral assemblages in Chinese loess and Red Clay[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 381/382: 110-118. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.04.020
Nie J, Peng W, Möller A, Song Y, Stockli D F, Stevens T, Gong H. 2014. Provenance of the upper Miocene-Pliocene Red Clay deposits of the Chinese loess plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 407: 35-47. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2014.09.026
Nie J, Peng W. 2014. Automated SEM-EDS heavy mineral analysis reveals no provenance shift between glacial loess and interglacial paleosol on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Aeolian Research, 13: 71-75. doi: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2014.03.005
Peng W B, Wang Z, Song Y G, Pfaff K, Luo Z, Nie J S, Chen W H, 2016. A comparison of heavy mineral assemblage between the loess and the Red Clay sequences on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Aeolian Research, 21: 87-91. doi: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2016.02.004
Pettijohn F J, Potter Paul E, Siever Raymond. 1977. Sand and Sandstone[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 35-40(in Chinese with English abstract).
Rao W, Chen J, Yang J, Ji J, Li G, Tan H. 2008. Sr-Nd isotopic characteristics of eolian deposits in the Erdos Desert and Chinese Loess Plateau: Implications for their provenances[J]. Geochemical Journal, 42(3): 273-282. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.42.273
Rao W, Mao C, Wang Y, Huang H, Ji J. 2017. Using Nd-Sr isotopes and rare earth elements to study sediment provenance of the modern radial sand ridges in the southwestern Yellow Sea[J]. Applied geochemistry, 81: 23-35. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.03.011
Rao W, Yang J, Chen J, Li G. 2006. Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of eolian dust of the arid-semiarid areas in China: Implications for loess provenance and monsoon evolution[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51(12): 1401-1412. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Gaojun_Li/publication/225765192_Sr-Nd_isotope_geochemistry_of_eolian_dust_of_the_arid-semiarid_areas_in_China_Implications_for_loess_provenance_and_monsoon_evolution/links/56aefc2908ae43a3980eab15.pdf
Rao Wenbo, Yang Jiedong, Chen Jun, Ji Junfeng, Li Gaojun. 2005. Discussion on the influencing factors of Sr-Nd isotopic composition change in northern dust[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 25(4): 531-532(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shi Z, Liu X. 2011. Distinguishing the provenance of fine-grained eolian dust over the Chinese Loess Plateau from a modelling perspective[J]. Tellus B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 63(5): 959-970. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0889.2011.00561.x
Smith J, Vance D, Kemp R A, Archer C, Toms P, King M, Zárate M. 2003. Isotopic constraints on the source of Argentinian loess-with implications for atmospheric circulation and the provenance of Antarctic dust during recent glacial maxima[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 212(1/2): 181-196. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035464487210_3211.html
Sun J. 2002. Provenance of loess material and formation of loess deposits on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 203(3/4): 845-859. http://www.kenrahn.com/DustClub/Articles/Sun%202002%20Material%20and%20formation%20of%20loess.pdf
Sun J. 2002. Source regions and formation of the loess sediments on the high mountain regions of northwestern China[J]. Quaternary Research, 58(3): 341-351. doi: 10.1006/qres.2002.2381
Wang Zhongbo, Yang Shouye, Li ping, LI Congxian, Cai Jingong. 2006. Detrial mineral compositions of the Changjiang River sediments and their tracing implications[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 24(4): 570-578(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu P, Xie Y Y, Chi Y P, Kang C G, Sun L, Wei Z Y, Zhang M, Zhang Y X. 2021. Loess accumulation in Harbin with implications for Late Quaternary aridification in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 570(1): 110365. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031018221001504
Yang Shouye, Li Congxian. 1999. Element composition and tracer action of modern surface sediments in Yangtze River and Yellow River[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 9(10): 930-937(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yuan Fang, Xie Yuanyun, Chi Yunping. 2018. Material characteristics of dust fallouts during the dust-storm weather in Harbin: Constraint on the provenance[J]. Geology in China, 45(6): 1177-1187(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/332712105_Material_characteristics_of_dust_fallouts_during_the_dust-storm_weather_in_Harbin_Constraint_on_the_provenance
Zhang X Y, Arimoto R, An Z S. 1997. Dust emission from Chinese desert sources linked to variations in atmospheric circulation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 102(D23): 28041-28047. doi: 10.1029/97JD02300
Zhao Hongge, Liu Chiyang. 2003. Approaches and prospects of provenance analysis[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 21(3): 409-415(in Chinese with English abstract).
刘瑾, 王永, 姚培毅, 迟振卿, 李廷栋, 耿树方. 2015. 末次冰消期以来内蒙古东部气候变化——基于风成砂-古土壤序列的地球化学记录[J]. 中国地质, 42(4): 1103-1114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.04.024 http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150424&flag=1
刘海江, 柴慧霞, 程维明, 钟德才, 周成虎. 2008. 基于遥感的中国北方风沙地貌类型分析[J]. 地理研究, 27(1): 109-118. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2008.01.012
饶文波, 杨杰东, 陈骏, 季峻峰, 李高军. 2005. 北方风尘中Sr-Nd同位素组成变化的影响因素探讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 25(4): 531-532. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2005.04.018
王中波, 杨守业, 李萍, 李从先, 蔡进功. 2006. 长江水系沉积物碎屑矿物组成及其示踪意义[J]. 沉积学报, 24(4): 570-578. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.04.015
杨守业, 李从先. 1999. 长江与黄河现代表层沉积物元素组成及其示踪作用[J]. 自然科学进展, 9(10): 930-937. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.1999.10.010
袁方, 谢远云, 迟云平. 2018. 哈尔滨尘暴天气沉降物的物质组成及其对物源的限制[J]. 中国地质, 45(6): 1177-1187. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180608&flag=1
赵红格, 刘池洋. 2003. 物源分析方法及研究进展[J]. 沉积学报, 21(3): 409-415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2003.03.007
-



 下载:
下载: