Late Holocene sedimentary records along the abandoned channel areas of the Yellow River and their response to flood hazards
-
摘要:
研究目的 黄河故道区蕴藏了丰富的古洪水灾害信息,深入挖掘地层中相应的沉积记录,有助于扩展黄河流域洪水记录的时空范围,增进对洪水灾害的科学认识。
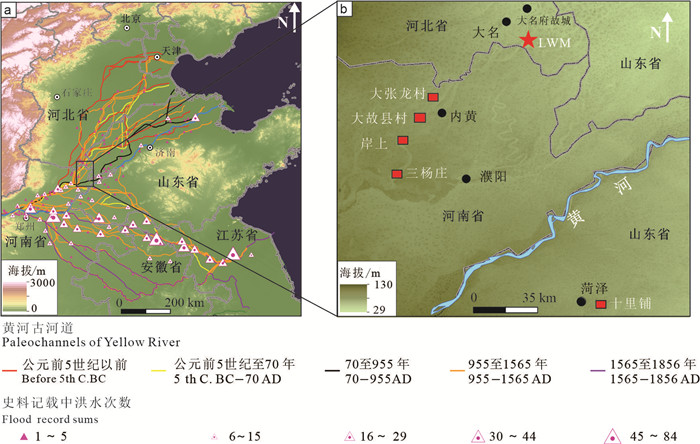
研究方法 本文选取河北大名龙王庙剖面作为黄河故道区的典型代表剖面,利用光释光、14C、粒度和地球化学元素等测试手段,综合对比洪水史料记载与区域研究成果。
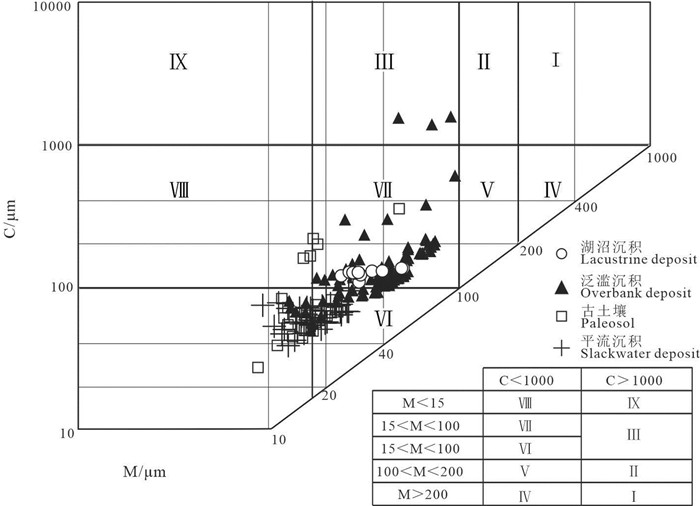
研究结果 研究认为:(1)古土壤、湖沼相沉积、泛滥沉积与平流沉积物之间存在一定的继承性与相关性;(2)晚全新世以来研究区内4次主要的洪水沉积单元,分别对应了周、西汉、北宋和明朝的异常洪水事件;(3)人类活动对流域洪水灾害产生了一定的影响,由高频低能的季节性洪水转变为低频高能的异常洪水事件。
结论 该项研究基本查明了黄河故道区不同沉积相的岩性特征及环境代用指标特征,探讨了人类活动对洪水特征的影响,为黄河故道区洪水灾害沉积记录的判别与重建提供了理论参考和示范,同时有助于进一步深入认识黄河流域洪水灾害的过程及演化机制。
Abstract:This paper is the result of hydrogeological survey engineering.
Objective Late Holocene sedimentary records along the abandoned channel areas contain lots of paleoflood information in the lower Yellow River, which can help to extend extreme flood records, and are of great value in understanding flood hazard patterns.
Methods This paper selects Longwangmiao (LWM) profile (located in Daming County), Hebei Province, as the typical paleoflood section in the lower Yellow River. Luminescence dating, radiocarbon dating, gransize, and geochemistry analyses are combined with a synthesis of historical flood records and regional previous works.
Results The study concluded that: (1) Different facies in LWM profile, including paleosols, lacustrine deposits, overbank deposits, and slackwater deposits, have some close relationships with the others. (2) Four major flood deposits during the late Holocene are corresponding to four abnormal flood events in Zhou Dynasty, Western Han Dynasty, Northern Song Dynasty, and Ming Dynasty in this area. (3) Human activities have a profound impact on flood scale and frequency in the lower Yellow River, from seasonal floods to extreme floods.
Conclusions The study identified the characteristics of different sedimentary facies on lithology and environmental proxies, and explored the influence of human activities on floods. It provides a reference for paleoflood research along the abandoned channels in the lower Yellow River, and helps to further understand the processes and evolutionary mechanisms of flood hazards in the Yellow River.
-
Key words:
- flood /
- abandoned channels /
- Late Holocene /
- grainsize /
- geochemical element /
- hydrogeological survey engineering /
- the Yellow River
-

-
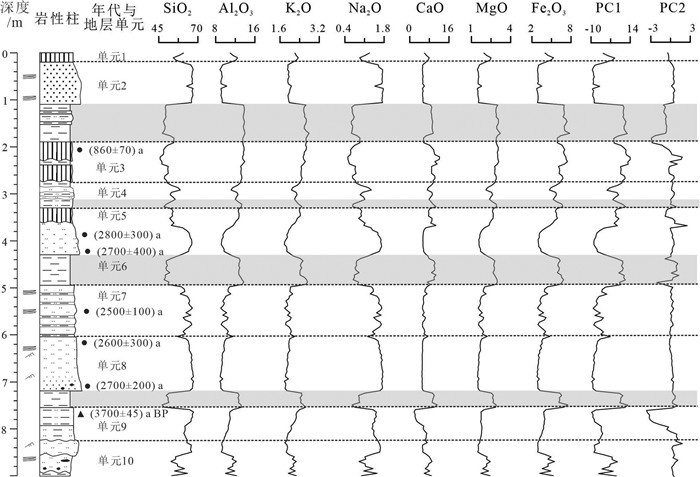
图 3 LWM剖面常量元素及主成分变化曲线(图例同图 2)
Figure 3.
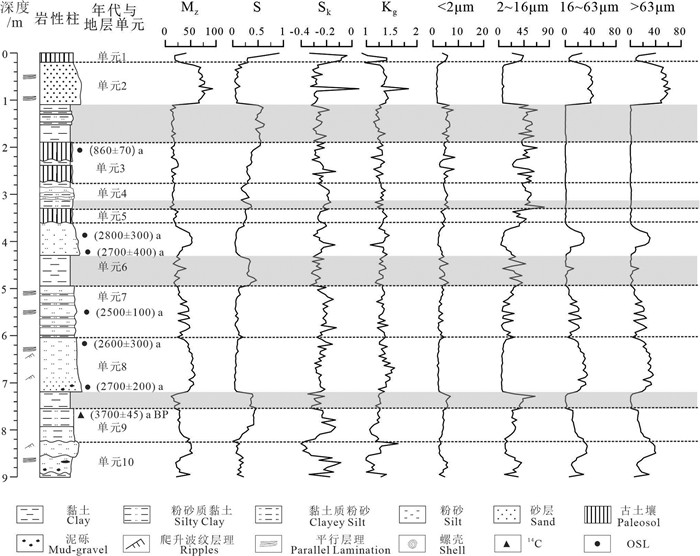
表 1 LWM地层划分及岩性描述
Table 1. Stratigraphic descriptions and subdivision units of the LWM profile

表 2 LWM剖面主量元素指标PC1和PC2与元素变量的相关系数
Table 2. Correlations between the first two principal components and major elements in LWM profile

表 3 LWM剖面AMS-14C和OSL测年结果
Table 3. AMS-14C and OSL dating results in LWM profile

-
Baker V R. 1987. Paleoflood hydrology and extraordinary flood events[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 96(1): 79-99.
Baker V R, Benito G, Brown A G, Carling P A, Enzel Y, Greenbaum N, Herget J, Kale V S, Latrubesse E M, Macklin M G, Nanson G C, Oguchi T, Thorndycraft V R, Ben Dor Y, Zituni R. 2022. Fluvial palaeohydrology in the 21st century and beyond[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 47(1): 58-81. doi: 10.1002/esp.5275
Benito G, Sánchez-Moya Y, Sopeña A. 2003. Sedimentology of high-stage flood deposits of the Tagus River, Central Spain[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 157(1/2): 107-132.
Chen Yunzhen. 2019. Flood dynamics of the lower Yellow River over the last 3000 years: Characteristics and implications for geoarchaeology[J]. Quaternary International, 521: 147-157. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2019.05.040
Chen Yunzhen, Syvitski J P M, Gao Shu, Overeem I, Kettner A J. 2012. Socio-economic impacts on flooding: A 4000-year history of the yellow river, China[J]. Ambio, 41(7): 682-698. doi: 10.1007/s13280-012-0290-5
Daming County Local Gazetteers Compilation Committee. 1994. Daming County Local Gazetteers[M]. Beijing: Xinhua Publishing House, 99-112 (in Chinese).
Dan M, Sawai Y, Yamada M, Namegaya Y, Shinozaki T, Takeda D, Fujino S, Tanigawa K, Nakamura A, Pilarczyk J E. 2016. Erosion and sedimentation during the September 2015 flooding of the Kinu River, central Japan[J]. Scientific Reports, 6(1): 34168. doi: 10.1038/srep34168
Disaster Investigation Team of the State Council. 2022. Investigation Report on "July 20th" Torrential Rain Disaster in Zhengzhou, Henan[R]. 1-8(in Chinese).
Gao Baishui, Jin Zhenkui, Li Yan, Shi Liang, Li Guizi. 2015. Sedimentary model and evolutionary process of crevasse splays: A case of crevasse splays around Fuqiancun village along Xinjiang River[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 36(5): 564-572 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Gelder A V, Berg J H V D, Cheng G, Xue C. 1994. Overbank and channelfill deposits of the modern Yellow River delta[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 90(3): 293-305.
George S S, Hefner A M, Avila J. 2020. Paleofloods stage a comeback[J]. Nature Geoscience, 13(12): 766-768. doi: 10.1038/s41561-020-00664-2
Grygar T M, Popelka J. 2016. Revisiting geochemical methods of distinguishing natural concentrations and pollution by risk elements in fluvial sediments[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 170: 39-57. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.08.003
Gu Jing, Zhou Jie, Zhao Jingbo. 2010. Flood events indicated by elements and compounds of sediment in the Jingyang reach of Jinghe River[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 30(2): 9-14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Guo Yongqiang, Ge Yonggang, Chen Xiaoqing, Liu Weiming, Mao Peini, Liu Tao. 2021. Progress in the reconstruction of palaeoflood events in the mountain canyon valleys around the Xizang Plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 28(2): 168-180 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang Chunchang, Pang Jiangli, Zha Xiaochun, Su Hongxia, Jia Yaofeng. 2011. Extraordinary floods related to the climatic event at 4200 a BP on the Qishuihe River, middle reaches of the Yellow River, China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 30: 460-468. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.12.007
Kidder T R, Zhuang Yujie. 2015. Anthropocene archaeology of the Yellow River, China, 5000-2000 BP[J]. The Holocene, 25(10): 1602-1623.
Kidder T, Liu Haiwang, Xu Qinghai, Li Minglin. 2012. The alluvial geoarchaeology of the Sanyangzhuang site on the Yellow River Floodplain, Henan Province, China[J]. Geoarchaeology, 27(4): 324-343. doi: 10.1002/gea.21411
Knight J, Evans M. 2017. The sediment stratigraphy of a flood event: An example from the Sabie River, South Africa[J]. Catena, 151: 87-97. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2016.12.015
Kochel R C, Baker V R. 1982. Paleoflood hydrology[J]. Science, 215(4531): 353-361. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4531.353
Li Huayong, Zhu Jiali, Zhang Hucai, Yuan Junying, Zhang Yanan, Zhang Wenqing, Wu Shuaihu. 2021. Grain-size characteristics of crevasse splays from the lower reaches of Dan River in northern Shandong province and reconstruction of sedimentary process[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 35(2): 176-182 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liang Hong, Yu Zhibing. 2011. The history of the Daming ancient city and its value[J]. China Ancient City, (6): 42-47 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lei Yanxiang, He Lei, Ye Siyuan, Zhao Lihong, Yuan Hongming, Yang Shixiong, Xue Chunting, Edward A. Laws. 2021. Paleochannel distribution, delta development and paleoenvironment evolution in Bohai Bay since the Late Pleistocene[J]. Geology in China, 48(6): 1947-1964 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Passega R. 1964. Grain size representation by CM patterns as a geologic tool[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 34(4): 830-847. doi: 10.1306/74D711A4-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Passega R. 1969. Grain size image of clastic deposits[J]. Sedimentology, (13): 233-252.
Reimer P J, Austin W E N, Bard E, Bayliss A, Blackwell P G, Bronk Ramsey C, Butzin M, Cheng H, Edwards R L, Friedrich M, Grootes P M, Guilderson T P, Hajdas I, Heaton T J, Hogg A G, Hughen K A, Kromer B, Manning S W, Muscheler R, Palmer J G, Pearson C, van der Plicht J, Reimer R W, Richards D A, Scott E M, Southon J R, Turney C S M, Wacker L, Adolphi F, Büntgen U, Capano M, Fahrni S M, Fogtmann-Schulz A, Friedrich R, Köhler P, Kudsk S, Miyake F, Olsen J, Reinig F, Sakamoto M, Sookdeo A, Talamo S. 2020. The IntCal20 Northern Hemisphere radiocarbon age calibration curve (-55 cal kBP)[J]. Radiocarbon, 62(4): 725-757. doi: 10.1017/RDC.2020.41
Storozum M, Lu Peng, Wang Sanying, Chen Panpan, Yang Ruixia, Ge Qifeng, Cao Jinping, Wan Junwei, Wang Hui, Qin Zhen, Liu Haiwang, Park E. 2020. Geoarchaeological evidence of the AD 1642 Yellow River flood that destroyed Kaifeng, a former capital of dynastic China[J]. Scientific Reports, 10(1): 1-12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56847-4
Storozum M, Qin Zhen, Ren Xiaolin, Li Haiming, Cui Yifu, Fu Kui, Liu Haiwang. 2018. The collapse of the North Song dynasty and the AD 1048-1128 Yellow River floods: Geoarchaeological evidence from northern Henan Province, China[J]. The Holocene, 28(11): 1759-1770. doi: 10.1177/0959683618788682
Tan Qixiang. 1962. Why the Yellow River experienced a long period of peaceful flow after the Eastern Han Dynasty[J]. Academic Monthly, (2): 23-35 (in Chinese).
Toonen W H J, Kleinhans M G, Cohen K M. 2012. Sedimentary architecture of abandoned channel fills[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 37(4): 459-472.
Toonen W H J, Winkels T G, Cohen K M, Prins M A, Middelkoop H. 2015. Lower Rhine historical flood magnitudes of the last 450 years reproduced from grain-size measurements of flood deposits using End Member Modelling[J]. Catena, 130: 69-81.
Wang Haoyu, Jia Yana, Zhang Yuzhu, Wang Ninglian, Luo Pingping, Qiu Haijun, AyidinaSailebieke, Xiao Qili, Chen Dou. 2021. Research progress of paleoflood events in the Yellow River Basin since the Last Deglaciation[J]. Progress in Geography, 40(7): 1220-1234 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Songna. 2017. Optically Stimulated Luminescence Dating of Flood Deposits at Sanyangzhuang Profile, Henan Province[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Science (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Yao, Chen Ruishan, Guo Chihui, Xia Zilong. 2021. Changes of resource and environmental pattern of the Yellow River Basin in the past 40 years and suggestions on geological work[J]. Geology in China, 48(1): 1-20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wilhelm B, Ballesteros Cánovas J A, Macdonald N, Toonen W H J, Baker V, Barriendos M, Benito G, Brauer A, Corella J P, Denniston R, Glaser R, Ionita M, Kahle M, Liu T, Luetscher M, Macklin M, Mudelsee M, Munoz S, Schulte L, George S S, Stoffel M, Wetter O. 2019. Interpreting historical, botanical, and geological evidence to aid preparations for future floods[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Water, 1(6): 1-22.
Wu Chen, Xu Qinghai, Ma Yonghong, Zhang Xiuqing. 1996. Palaeochannels on the North China Plain: Palaeoriver geomorphology[J]. Geomorphology, 18(1): 37-45.
Xia Zhengkai, Yang Xiaoyan. 2003. Preliminary study on the flood events about 4 ka B.P. in North China[J]. Quaternary Science, 23(6): 667-674 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Jinsong, Wang Yong, Yin Jinhui, Zhao Hua, Liu Zhe, Jiang Gaolei, Zhang Peng, Qi Jiahao. 2022. Progress and Prospects in Reconstruction of Flood Events in Chinese Alluvial Plains[J]. Earth Science, 47(11): 3944-3959 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Jinsong, Wang Yong, Yin Jinhui, Zhao Hua, Liu Zhe, Jiang Gaolei, Zhang Peng, Qi Jiahao. 2022. Progress and prospects in reconstruction of flood events in Chinese alluvial plains[J]. Earth Science, 47(11): 3944-3959 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Shiyong, Hou Zhanfang, Chen Xuexiang, Wang Yixuan, Song Yougui, Gao Mingkui, Pan Jianrong, Sun Ming, Fang Hui, Han Jianye, Kidder T R, Chen Fahu. 2020. Extreme flooding of the lower Yellow River near the Northgrippian-Meghalayan boundary: Evidence from the Shilipu archaeological site in southwestern Shandong Province, China[J]. Geomorphology, 350: 106878.
Zhang Peng, Yang Jinsong, Zhao Hua, Liu Zhe, Song Lei, Zhang Run, Cao Wengeng. 2020. Research progress of the Holocene paleoflood in the Yellow River basin and a future prospect[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 40(6): 178-188 (in Chinese with English abstract).
大名县县志编纂委员会. 1994. 大名县志[M]. 北京: 新华出版社, 99-112.
高白水, 金振奎, 李燕, 石良, 李桂仔. 2015. 河流决口扇沉积模式及演化规律——以信江府前村决口扇为例[J]. 石油学报, 36(5): 564-572. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201505005.htm
顾静, 周杰, 赵景波. 2010. 泾河泾阳段高河漫滩沉积元素与化合物指示的洪水事件[J]. 水土保持通报, 30(2): 9-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB201002006.htm
国务院灾害调查组. 2022. 河南郑州"7·20"特大暴雨灾害调查报告[R]. 1-2.
郭永强, 葛永刚, 陈晓清, 刘维明, 毛沛妮, 刘涛. 2021. 高山峡谷区古洪水事件重建研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 28(2): 168-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202102013.htm
李华勇, 朱佳丽, 张虎才, 袁俊英, 张雅楠, 张雯清, 吴帅虎. 2021. 鲁北丹河下游洪水决口扇沉积岩芯粒度特征与沉积过程重建[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 35(2): 176-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202102027.htm
梁洪, 蔚芝炳. 2011. 北京大名府的历史沿革及其价值所在[J]. 中国名城, (6): 42-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMI201106009.htm
雷雁翔, 何磊, 叶思源, 赵俐红, 袁红明, 杨士雄, 薜春汀, Edward A. Laws. 2021. 渤海湾晚更新世晚期以来古河道分布和三角洲发育及其古环境的演变[J]. 中国地质, 48(6): 1947-1964. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20210621?st=search
谭其骧. 1962. 何以黄河在东汉以后会出现一个长期安流的局面——从历史上论证黄河中游的土地合理利用是消弭下游水害的决定性因素[J]. 学术月刊, (2): 23-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XSYK196202004.htm
王浩宇, 贾雅娜, 张玉柱, 王宁练, 罗平平, 邱海军, 阿依迪那·赛勒别克, 肖奇立, 陈豆. 2021. 黄河流域末次冰消期以来古洪水事件研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展, 40(7): 1220-1234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKJ202107012.htm
王松娜. 2017. 河南三杨庄剖面洪水事件的光释光年代学研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学.
王尧, 陈睿山, 郭迟辉, 夏子龙. 2021. 近40年黄河流域资源环境格局变化分析与地质工作建议[J]. 中国地质, 48(1): 1-20. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20210101?st=search
夏正楷, 杨晓燕. 2003. 我国北方4 ka B.P. 前后异常洪水事件的初步研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 23(6): 667-674. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200306009.htm
杨劲松, 王永, 尹金辉, 赵华, 刘哲, 姜高磊, 张鹏, 戚甲豪. 2022. 我国冲积平原区洪水事件重建研究进展及展望[J]. 地球科学, 11(47): 3944-3959. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202211002.htm
张鹏, 杨劲松, 赵华, 刘哲, 宋磊, 张润, 曹文庚. 2020. 黄河流域全新世古洪水研究进展及展望[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 40(6): 178-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202006016.htm
-



 下载:
下载: