Glomalin-related soil protein distribution and its relation to mineral weathering in the wetlands along the Bohai Sea, China
-
摘要:
研究目的 球囊霉素作为丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)分泌的一种难降解土壤蛋白, 广泛分布于陆地生态系统中, 是长期碳贮的重要组成。当前鲜有研究涉及其在滨海湿地中的分布。基于此, 本文对中国环渤海主要滨海湿地表层沉积物中球囊霉素相关土壤蛋白(GRSP)的空间分布进行表征, 探讨不同湿地生境下GRSP分布及其对沉积物风化的指示意义。
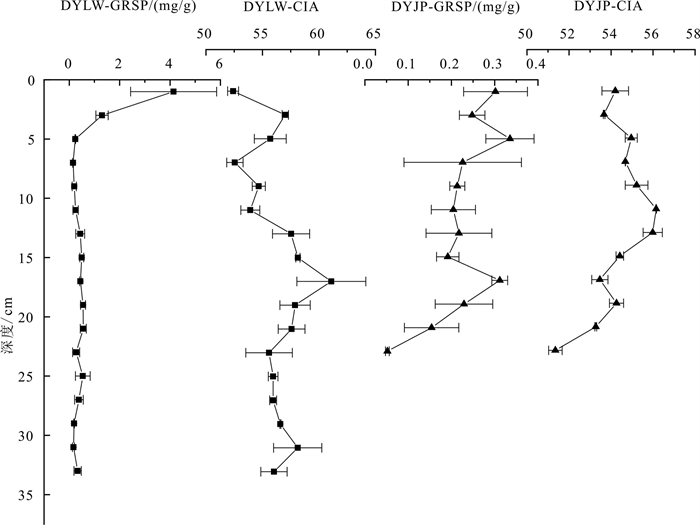
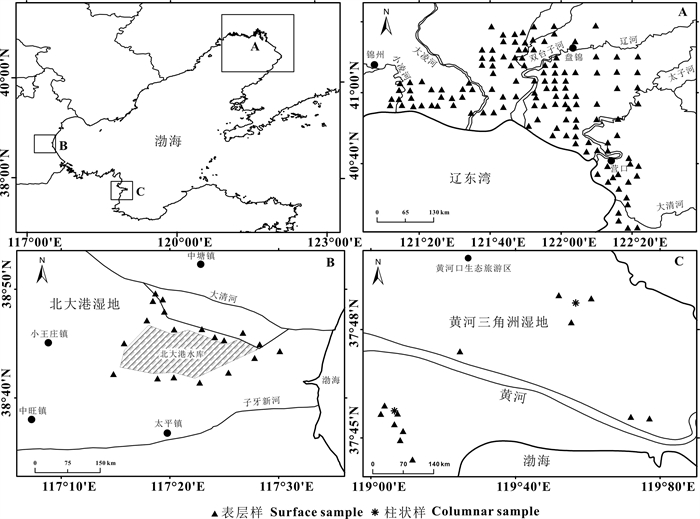
研究方法 本文选取辽河三角洲、北大港和黄河三角洲湿地作为研究区, 对166个表层样(0~5 cm)和4个柱状样(0~35 cm)的GRSP、粒度以及常量元素进行测定, 并计算化学蚀变系数(CIA)。
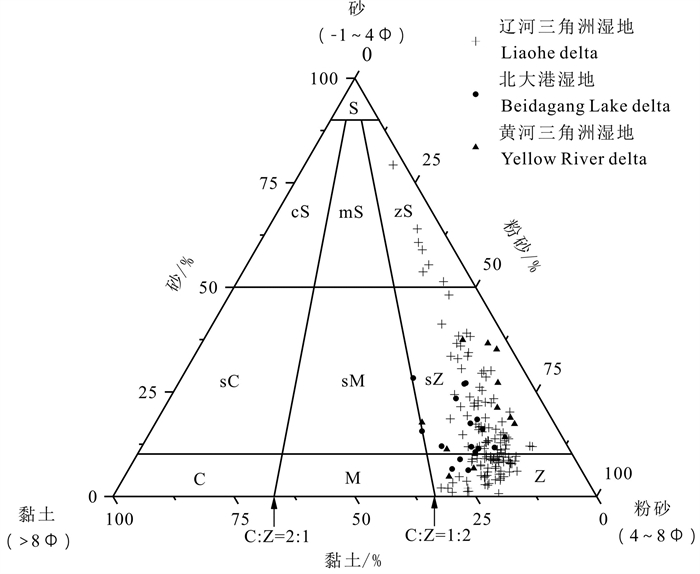
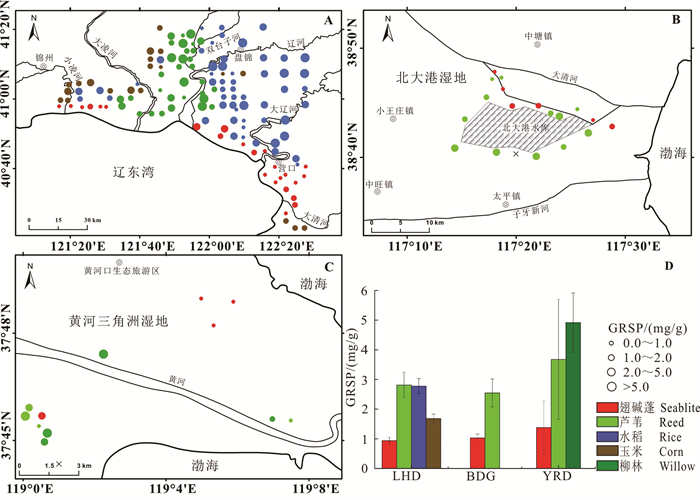
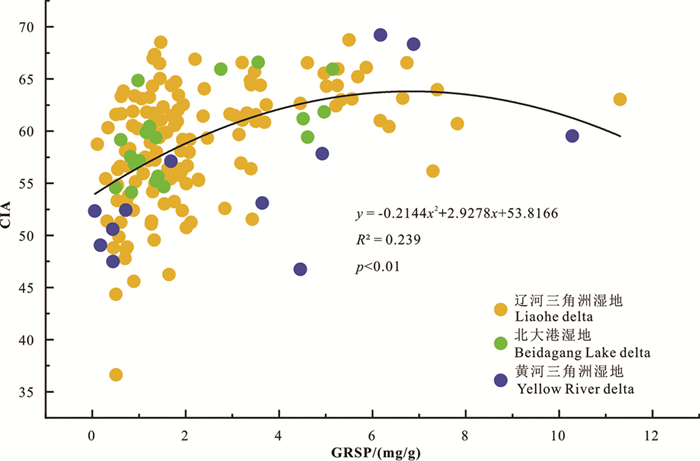
研究结果 研究区GRSP在空间上的动态变化受植被类型影响显著, 范围在0.06~11.31 mg/g, 均值为(2.35±0.16) mg/g; 沉积物以粉砂质砂和砂为主, CIA值分布范围为44.79~69.59, 部分区域达到中等化学风化; CIA与GRSP呈显著相关(R=~0.49, p < 0.01), 总体上CIA随GRSP的增加呈现先增加后减少的趋势。
结论 GRSP在滨海湿地沉积物中的分布受到生境差异性的影响, 其与CIA的相关性表征AMF及其代谢产物在地质体风化过程中发挥了潜在的生态功能。
-
关键词:
- 球囊霉素土壤相关蛋白 /
- 化学风化 /
- 环渤海湿地 /
- 环境地质调查工程
Abstract:This paper is the result of environmental geological survey engineering.
Objective As a refractory soil protein secreted by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF), glomalin-related soil protein (GRSP) is an important component of long-term carbon storage and widely distributed in sediment of terrestrial ecosystem.The distribution of GRSP in coastal wetlands is still not well documented.In this study, the spatial distribution of GRSP in the sediments of the typical wetlands along the Bohai Sea coasts in China were characterized, and the distribution of GRSP in different wetland habitats and its relation to sediment weathering in wetlands were discussed.
Methods Particle size, major elements and GRSPs of 166 surface samples (0-5 cm) and 4 sediment cores (~35 cm long) in the wetlands of the Liaohe delta (LHD), Beidagang Lake (BDG) and Yellow River delta (YRD) were tested, and the corresponding chemical index of alteration (CIA) was calculated.
Results The GRSP in surface sediments were significantly affected by the vegetation types, ranged from 0.06 to 11.31 mg/g, with an average of (2.35± 0.16) mg/g; The sediments in the three study areas were mainly silty sand and sand, the distribution range of CIA values were 44.79-69.59, some areas reached moderate chemical weathering; The concentrations of GRSP were significantly correlated with CIAs (R=~0.49, p < 0.01).In general, CIA increased first with increasing GRSP until the GRSP concentrations reached a certain critical level.
Conclusions The distribution of GRSP concentrations in coastal wetland sediments was affected by habitat differences, and its correlation with CIA indicated that AMF and its metabolites play potential ecological functions during the processes of geological weathering.
-

-
表 1 表层沉积物常量元素含量及相关变量统计
Table 1. Statistics on the content of macroelements and related variables in surface sediments

表 2 主要常量元素与平均粒径的相关性
Table 2. Correlation between major macroelements and average particle size
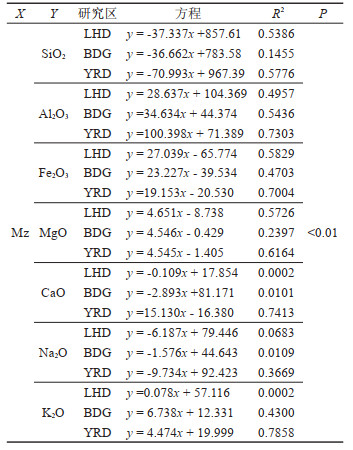
表 3 GRSP与常量元素关系及相关参数变量的相关性统计
Table 3. Correlation statistics between GRSP and macroelements and related variables

-
Adame M F, Neil D, Wright S F, Lovelock C E. 2010. Sedimentation within and among mangrove forests along a gradient of geomorphological settings[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 86(1): 21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2009.10.013
Arocena J M, Velde B, Robertson S J. 2012. Weathering of biotite in the presence of arbuscular mycorrhizae in selected agricultural crops[J]. Applied Clay Science, 64: 12-17. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2011.06.013
Bago B, Vierheilig H, Piché Y, AzcóN-Aguilar C. 1996. Nitrate depletion and pH changes induced by the extraradical mycelium of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices grown in monoxenic culture[J]. New Phytologist, 133(2): 273-280. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.1996.tb01894.x
Barker W W, Welch S A, Chu S, Banfield J F. 1998. Experimental observations of the effects of bacteria on aluminosilicate weathering[J]. American Mineralogist, 83(11/12 Part 2): 1551-1563. http://www.degruyter.com/dg/viewarticle.fullcontentlink:pdfeventlink/$002fj$002fammin.1998.83.issue-11$002fam-1998-1116$002fam-1998-1116.pdf/am-1998-1116.pdf?t:ac=j$002fammin.1998.83.issue-11$002fam-1998-1116$002fam-1998-1116.xml
Berner R A. 1997. The rise of plants and their effect on weathering and atmospheric CO2 [J]. Science, 276(8): 506-511.
Bradford M M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding [J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 72(s 1/2): 248-254.
Caravaca F, Alguacil M d M, Torres P, Roldán A. 2005. Microbial activities and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonization in the rhizosphere of the salt marsh plantInula crithmoides L. along a spatial salinity gradient[J]. Wetlands, 25(2): 350-355. doi: 10.1672/11
Cao Wanjie, Ji Hongbing, Zhu Xianfang, Zhao Xinyuan, Qiao Minmin. 2012. Contrast of geochemical features of the typical weathered profiles in Guizhou Plateau[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 31(2): 131-138(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201202005.htm
Chen Yang, Chen Jun, Liu Lianwen. 2001. Chemical composition and characterization of chemical weathering of late tertiary red clay in Xifeng, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 7(2): 167-175(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZLX200102011.htm
Driver J D, Holben W E, Rillig M C. 2005. Characterization of glomalin as a hyphal wall component of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 37(1): 101-106. http://www.osti.gov/cgi-bin/eprints/redirectEprintsUrl?http%3A%2F%2Fdbs.umt.edu%2Fresearch_labs%2Frilliglab%2FDriver%2520Holben%2520Rillig%25202005%2520SBB.pdf
Gao M, Hou G, Dang X, Huang X. 2020. Sediment distribution characteristics and environment evolution within 100 years in western Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China[J]. China Geology, 3(3): 445-454. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=7103027862
Guo X, Gong J. 2014. Differential effects of abiotic factors and host plant traits on diversity and community composition of root-colonizing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in a salt-stressed ecosystem[J]. Mycorrhiza, 24(2): 79. doi: 10.1007/s00572-013-0516-9
Harner M J, Ramsey P W, Rillig M C. 2004. Protein accumulation and distribution in floodplain soils and river foam[J]. Ecology Letters, 7(9): 829-836. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00638.x
He L, Xue C, Ye S, Laws E A, Yuan H, Yang S, Du X. 2018. Holocene evolution of the Liaohe Delta, a tide-dominated delta formed by multiple rivers in Northeast China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 152: 52-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.11.035
He L, Xue C, Ye S, Amorosi A, Yuan H, Yang S, Laws E A. 2019. New evidence on the spatial-temporal distribution of superlobes in the Yellow River Delta Complex[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 214: 117-138. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.05.003
He X, Li Y, Zhao L. 2010. Dynamics of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and glomalin in the rhizosphere of Artemisia ordosica Krasch. in Mu Us sandland, China[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 42(8): 1313-1319. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.03.022
Johansen A, Jakobsen I, Jensen E S. 1993. Hyphal transport by a vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus of N applied to the soil as ammonium or nitrate[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 16(1): 66-70. doi: 10.1007/BF00336518
Jongmans A G, van Breemen N, Lundström U, van Hees P A W, Finlay R D, Srinivasan M, Unestam T, Giesler R, Melkerud P A, Olsson M. 1997. Rock-eating fungi[J]. Nature, 389: 682. doi: 10.1038/39493
Kemper W D, Koch E J. 1966. Aggregate stability of soils from western United States and Canada. Measurement Procedure, correlation with soil constituents[M]. U.S. : Government Printing Office, .
Kleber M, Sollins P, Sutton R. 2007. A conceptual model of organo-mineral interactions in soils: Self-assembly of organic molecular fragments into zonal structures on mineral surfaces[J]. Biogeochemistry, 85(1): 9-24. doi: 10.1007/s10533-007-9103-5
Koele N, Dickie I A, Blum J D, Gleason J D, de Graaf L. 2014. Ecological significance of mineral weathering in ectomycorrhizal and arbuscular mycorrhizal ecosystems from a field-based comparison[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 69: 63-70. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.10.041
Li Gonggang, Hu Bangqi, Li Jun, Bu Ruyuan, Yang Ming, Dou Yanguang. 2012. Geochemistry of major elements in the surface sediments of the offshore area of Shandong peninsula and its geological implications [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, (3): 45-54(in Chinese with English abstract). http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2013MGQG...32...45L
Li Guanhua, Xia Dunsheng, Liu Jiabo, Wen Yanglei, Zhao Shuang, Jia Jia. 2013. Characteristics of major geochemical elements of tacheng loess deposits in xinjiang and its paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 33(4): 183-191(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Tongtong, Ye Siyuan, Han Zongzhu, Yuan Hongming, Pei Lixin. 2019. Weathering characteristics of the surface sediments and their indications for biological process in the Liaohe Delta wetlands [J]. Geological Review, 65(1): 40-51(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZLP201901008.htm
Liu Jin, Ye Siyuan, Wang Jiasheng. 2017. Organic carbon distribution, function and its burial processes in the coastal wetlands of the Liaohe Delta, Northeast of China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 38(b11): 83-86(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/322383988_Organic_Carbon_Distribution_Function_and_Its_Burial_Processes_in_the_Coastal_Wetlands_of_the_Liaohe_Delta_Northeast_of_China
López-Merino L, Serrano O, Adame M F, Mateo M á, Martínez Cortizas A. 2015. Glomalin accumulated in seagrass sediments reveals past alterations in soil quality due to land-use change[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 133: 87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2015.08.004
Lovelock C E, Wright S F, Clark D A, Ruess R W. 2004. Soil stocks of glomalin produced by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi across a tropical rain forest landscape[J]. Journal of Ecology, 92(2): 278-287. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-0477.2004.00855.x
McLennan S M. 1993. Weathering and Global Denudation[J]. Journal of Geology, 101(2): 295-303. doi: 10.1086/648222
Mo B, Lian B. 2010. Study on feldspar weathering and analysis of relevant impact factors[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(3): 281-289. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201003033.htm
Nesbitt H W, Markovics G, Price R C. 1980. Chemical processes affecting alkalis and alkaline earths during continental weathering[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 44(11): 1659-1666. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(80)90218-5
Nesbitt H W, Young G M, McLennan S M, Keays R R. 1996. Effects of chemical weathering and sorting on the petrogenesis of siliciclastic sediments, with implications for provenance studies[J]. Journal of Geology, 104(5): 525-542. doi: 10.1086/629850
Nichols, K A, Wright, S F. 2005. Comparison of glomalin and humic acid in eight native U.S. soils[J]. Soil Science, 170(170): 985-997. http://www.xueshufan.com/publication/2059334851
Rillig M C. 2004. Arbuscular mycorrhizae, glomalin, and soil aggregation[J]. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 84(4): 355-363. doi: 10.4141/S04-003
Rillig M C, Ramsey P W, Morris S, Paul E A. 2003. Glomalin, an arbuscular-mycorrhizal fungal soil protein, responds to land-use change[J]. Plant & Soil, 253(2): 293-299.
Singh A K, Rai A, Pandey V, Singh N. 2017. Contribution of glomalin to dissolve organic carbon under different land uses and seasonality in dry tropics[J]. J. Environ. Manage., 192: 142-149. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.01.041
Singh A K, Rai A, Singh N. 2016. Effect of long term land use systems on fractions of glomalin and soil organic carbon in the Indo-Gangetic plain[J]. Geoderma, 277: 41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.05.004
Spohn M, Giani L. 2010. Water-stable aggregates, glomalin-related soil protein, and carbohydrates in a chronosequence of sandy hydromorphic soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 42(9): 1505-1511. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.05.015
Treseder K K, Turner K M. 2007. Glomalin in Ecosystems[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 71(4): 1257-1266. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2006.0377
Tan Yuanlong, Qiao Yansong, Zhao Zhizhong, Wang Yan. 2013. Chemical weathering characteristics and paleoclimatic significance of the eolian deposits in Chengdu plain[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 19(1): 26-34(in Chinese with English abstract). http://engine.scichina.com/doi/pdf/2D4C282F458B46A4B3BC153DBD258042
Villa J A, Bernal B. 2018. Carbon sequestration in wetlands, from science to practice: An overview of the biogeochemical process, measurement methods, and policy framework[J]. Ecological Engineering, 114: 115-128. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.06.037
Wang Q, Li J, Chen J, Hong H, Lu H, Liu J, Dong Y, Yan C. 2018. Glomalin-related soil protein deposition and carbon sequestration in the Old Yellow River delta[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 625: 619-626. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.303
Wang Q, Lu H, Chen J, Hong H, Liu J, Li J, Yan C. 2018. Spatial distribution of glomalin-related soil protein and its relationship with sediment carbon sequestration across a mangrove forest[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 613-614: 548-556. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.140
Wang Q, Wang W, He X, Zhang W, Song K, Han S. 2015. Role and variation of the amount and composition of glomalin in soil properties in farmland and adjacent plantations with reference to a primary forest in North-Eastern China[J]. PLoS One, 10(10): e0139623. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139623
Weston N B, Neubauer S C, Velinsky D J. 2011. Accelerated microbial organic matter mineralization following salt-water intrusion into tidal freshwater marsh soils[J]. Biogeochemistry, 102(1/3): 135-151. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039498709010_d48b.html
Wilson G W T, Rice C W, Rillig M C, Springer A, Hartnett D C. 2009. Soil aggregation and carbon sequestration are tightly correlated with the abundance of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: Results from long-term field experiments[J]. Ecology Letters, 12(5): 452-461. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2009.01303.x
Wright S F, Franke-Snyder M, Morton J B, Upadhyaya A. 1996. Time-course study and partial characterization of a protein on hyphae of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi during active colonization of roots[J]. Plant and Soil, 181(2): 193-203. doi: 10.1007/BF00012053
Wright S F, Upadhyaya A. 1996. Extraction of an abundant and unusual protein from soil and comparison with hyphal protein of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Soil Science, 161(9): 575-586. doi: 10.1097/00010694-199609000-00003
Wright S F, Upadhyaya A. 1998. A survey of soils for aggregate stability and glomalin, a glycoprotein produced by hyphae of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Plant and Soil, 198(1): 97-107. doi: 10.1023/A:1004347701584
Xie H, Li J, Zhang B, Wang L, Wang J, He H, Zhang X. 2015. Long-term manure amendments reduced soil aggregate stability via redistribution of the glomalin-related soil protein in macroaggregates[J]. Scientific Reports, 5: 14687. doi: 10.1038/srep14687
Xu Z, Ban Y, Jiang Y, Zhang X, Liu X. 2016. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in wetland habitats and their application in constructed wetland: A review[J]. Pedosphere, 26(5): 592-617. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(15)60067-4
Ying Lichao, Liang Bin, Wang Quanwei, Zhu Bing, Hao Xuefeng, Liu Liang, Wen Long, Yan Zhonglin, Fu Xiaofang. 2013. Geochemical characteristics of Chengdu clay and their implications for provenance and weathering intensity [J]. Geology in China, 40(5): 1666-1674(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/287887673_Geochemical_characteristics_of_Chengdu_clay_and_their_implications_for_provenance_and_weathering_intensity
Ye S, Laws E A, Yuknis N, Ding X, Yuan H, Zhao G, Wang J, Yu X, Pei S, DeLaune R D. 2015. Carbon sequestration and soil accretion in coastal wetland communities of the Yellow River Delta and Liaohe Delta, China[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 38(6): 1885-1897. doi: 10.1007/s12237-014-9927-x
Zhang Z, Wang Q, Wang H, Nie S, Liang Z. 2017. Effects of soil salinity on the content, composition, and ion binding capacity of glomalin-related soil protein (GRSP)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 581: 657-665. http://www.researchgate.net/file.PostFileLoader.html?id=591e854aed99e124415383e9&assetKey=AS%3A495603227348992%401495172425950
Zhu Fei. 2010. Relationships among glomalin related soil protein, SOC and soil texture under different land use types [J]. Journal of Anhui Agri, 38(23): 12499-12502(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20103342806.html
Zhang Liankai, Ji Hongbing, Liu Xiuming, Wei Xiao, Luo Gang, Wang Shijie, Nguyen Dại Trung, Nguyen Quoc Dinh. 2021. Genetic mechanism and elemental evolution of weathering laterite crust overlying carbonate rocks in tropical areas[J]. Geology in China, 48(2): 651-660(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Wei, Dong Yingwei, Yu Yang, Liu Beibei, Li Yonghua, Li Yuanyuan, Wang Meixia. 2013. Chemical weathering of the loess in the south of Liaoning province and its implications for environmental change[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 33(5): 163-171(in Chinese with English abstract). http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2013MGQG...33..163Z
Zhu Yongguan, Duan Guilan, Chen Baodong, Peng Xinhua, Chen Zheng, Sun Guoxin. 2014. Mineral weathering and element cycling in soil-microbe-plant systems[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 1(6): 1107-1116(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4861-0
曹万杰, 季宏兵, 朱先芳, 赵兴媛, 乔敏敏. 2012. 贵州高原地区典型风化剖面地球化学特征及其对比研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 31(2): 131-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2012.02.004
陈旸, 陈骏, 刘连文. 2001. 甘肃西峰晚第三纪红粘土的化学组成及化学风化特征[J]. 地质力学学报, 7(2): 167-175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2001.02.012
李国刚, 胡邦琦, 李军, 布如源, 杨敏, 窦衍光. 2012. 山东半岛沿岸海域表层沉积物的常量元素及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, (3): 45-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201203010.htm
李冠华, 夏敦胜, 柳加波, 温仰磊, 赵爽, 贾佳. 2013. 新疆塔城黄土沉积常量地球化学元素特征及其环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 33(4): 183-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201304026.htm
李通通, 叶思源, 韩宗珠, 袁红明, 裴理鑫. 2019. 辽河三角洲湿地表层沉积物的风化特征及其对生物作用的指示意义[J]. 地质论评, 65(1): 40-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201901008.htm
刘瑾, 叶思源, 王家生. 2017. 辽河三角洲滨海湿地有机碳的时空演变、环境功能及其埋藏机制[J]. 地球学报, 38(b11): 83-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB2017S1022.htm
谭元隆, 乔彦松, 赵志中, 王燕. 2013. 成都平原风尘堆积的化学风化特征及其古气候意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 19(1): 26-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2013.01.003
应立朝, 梁斌, 王全伟, 朱兵, 郝雪峰, 刘亮, 文龙, 燕钟林, 付小方. 2013. 成都粘土地球化学特征及其对物源和风化强度的指示[J]. 中国地质, 40(5): 1666-1674. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.05.029 http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20130529?st=search
祝飞. 不同土地利用方式下球囊霉素相关土壤蛋白与有机碳及土壤质地的关系[J]. 安徽农业科学, (23): 12499-12502. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.23.072
张连凯, 季宏兵, 刘秀明, 魏晓, 罗刚, 王世杰, NGUYEN Dại Trung, NGUYEN Quoc Dinh. 2021. 热带地区碳酸盐岩上覆红色风化壳的成因机理及元素演化[J]. 中国地质, 48(2): 651-660. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20210221?st=search
张威, 董应巍, 于洋, 刘蓓蓓, 李永化, 李媛媛, 王美霞. 2013. 辽南黄土化学风化特点及其环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 33(5): 163-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201305022.htm
朱永官, 段桂兰, 陈保冬, 彭新华, 陈正, 孙国新. 2014. 土壤-微生物-植物系统中矿物风化与元素循环[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 1(6): 1107-1116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201406005.htm
-



 下载:
下载: