Water resources utilization and eco-environment problem of Fenhe River, branch of Yellow river
-
摘要:
研究目的 汾河是黄河第二大支流, 也是山西省的第一大河, 流域内水资源供需矛盾突出, 分析水资源开发利用现状及其生态环境问题是进行流域生态修复的前提。
研究方法 本文在分析汾河流域水资源特征及其开发利用现状的基础上, 系统总结了汾河径流量衰减、岩溶大泉断流和水质恶化等生态环境问题, 并对其成因进行了分析。
研究结果 研究表明: 汾河流域多年平均水资源量为33.59亿m3, 其中地下水资源是水资源的主要组成部分, 约占72%;2005年以后由于跨流域调水、地下水压采等汾河流域综合治理措施的实施, 水资源的供水结构发生了较大的变化, 地表水的供水比例由最初的30%提高到55%, 地下水供水比例由原来的62%降低到目前的37%。整体上, 汾河流域的水资源开发利用程度高达80%以上, 水资源的过度开发已导致汾河干流断流、入黄径流量大幅衰减、岩溶大泉断流等严重的生态环境问题。其中, 汾河流入黄河径流量从1955至2018年衰减程度达63.5%, 衰减的原因主要是降水量的减少和岩溶大泉的流量衰减; 汾河流域内8个岩溶大泉的总流量从1956至2018年的衰减程度达69%, 50%的岩溶大泉已在不同时期断流, 岩溶大泉的水质恶化问题也非常严重, 如晋祠泉和龙子祠泉的TDS和SO42-呈逐年升高的趋势, 煤矿开采是造成岩溶泉水SO42-含量快速升高的主要原因。
结论 汾河流域的水资源供需矛盾十分突出, 虽然通过跨流域调水等生态修复措施实现了汾河干流全年不断流、地下水位止降回升和地表水环境质量初步改善, 但生态环境恶化的趋势依然严峻。
Abstract:This paper is the result of the hydrogeological survey engineering.
Objective As the second largest tributary of the Yellow River, Fenhe River is the largest river in Shanxi Province.However, there is contradiction between the supply and demand of water resources in the basin.The analysis of water resources utilization and eco-environment problem is precondition of ecological remediation.
Methods Based on the analysis of water resources characteristics of the Fenhe River Basin and its utilization, this paper systematically summarizes the ecological and environmental problems of the Fenhe River watershed, such as attenuation of runoff, drying up of karst spring and deterioration in water quality.
Results Our result shows that the average amount of water resources in the Fenhe River Basin for multi-year average is 3.359 billion m3, groundwater resources are the main component of the total water resources, which is accounting for 72%.The structure of water supply of water resources has changed greatly due to the impact of comprehensive treatment measures in the Fen River Basin since 2005, such as cross-basin water transfer and groundwater pressure extraction.The water supply ratio of surface water has increased from 30% to 55%, and the water supply ratio of groundwater has been reduced from 62% to 37%.Overall, the utilization of water resources in the Fenhe River Basin is as high as 80%.Excessive exploitation of water resources has caused serious eco-environmental problems such as the cut-off of Fen River, the significant decline in the runoff of the Fen River into the Yellow River and the decline of karst spring flow.The percentage of runoff for Fenhe River enter the Yellow River has attenuated by 63.5% from 1955 to 2018.The main reasons for the attenuation are the decrease in precipitation and the flow attenuation of the karst spring.The total flow of the 8 large karst springs in the Fenhe River Basin has decreased by 69% from 1956 to 2018, and 50% of the large karst springs had dried up in different periods; The water quality of karst springs has been deteriorating seriously, for example, the TSD and SO42-of Jinci Spring and Longzici Spring have been increasing year by year.Coal mining is the main reason for the rapid increase of SO42- in karst springs.
Conclusions Although the inter-basin water transfer project construction has improve some of the eco-environment in the Fenhe River, such as the recovery of Fenhe River to perennial river, and the stopped falling of groundwater level in the basin, and the improvement of the quality of surface water environment, there is serious unbalance between supply and demand for water resources in Fenhe River Basin, finally the trend of deterioration of the ecological environment is still severe.
-

-
表 1 汾河流域水资源总量与供水量统计
Table 1. Water resources and supplying water in Fenhe River Basin

表 2 汾河流域不同行业用水量统计
Table 2. Water consumption statistics of different industries in Fenhe River Basin

表 3 汾河流域岩溶大泉泉水流量变化一览
Table 3. List of karst spring flow variation in Fenhe River Basin
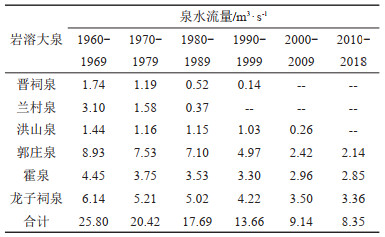
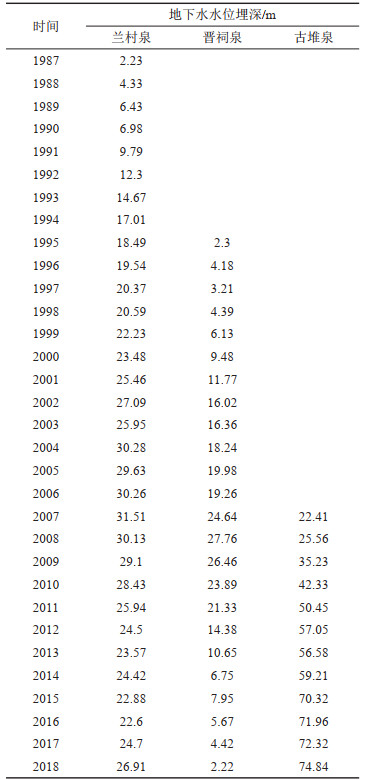
表 4 汾河流域断流岩溶大泉泉口岩溶地下水水位埋深(据杨士荣等,2020)
Table 4. Karst groundwater depth of dry karst spring in Fenhe River Basin(after Shirong et al., 2020)
-
Chang Jianzhong. 2020. Implement "five ideas enriching water" and build happy river in Shanxi Province[J]. China Water Resources, (19): 5-6(in Chinese).
Fan Duixiang. 2005. Evaluation of Water Resources in Shanxi Province[M]. Beijing: China water resources and Hydropower Press, 119-131(in Chinese).
Gao Bo. 2002. Cause analysis and countermeasures of flow attenuation in Guozhuang spring[J]. Water Resources Protection, (1): 64-65(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SZYB200201022.htm
Guo Dongyang, Wang Jing, Lin Dong. 2020. Investigation and consideration on water ecological protection and restoration of seven rivers basin in Shanxi Province[J]. Water Resources Planning and Design, (12): 17-18(in Chinese).
Guo Fangfang, Liang Yongping, Wang Zhiheng, Shen Haoyong, Zhao Chunhong. 2018. Attribution of spring fields and calculation of seepage of the second reservoir of Fenhe River in Xishan mountain, Taiyuan, Shanxi Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 37(3): 228-238(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGYR201804003.htm
Guo Zhenzhong, Zhang Hongda, Yu Kaining. 2002. Multiple causes of attenuation of karst spring discharge in Shanxi Province[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, (2): 22-25(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC200402006.htm
Hou Xinwei, Li Xiangquan, Chen Hao. 2008. Study on transforming relationship among surface water, precipitation and groundwater along Fenhe River in Taiyuan Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, (6): 38-39(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200806013.htm
Han Shuangbao, Li Fucheng, Wang Sai, Li Haixue, Yuan Lei, Liu Jingtao, Shen Haoyong, Zhang Xueqing, Li Changqing, Wu Xi, Ma Tao, Wei Shibo, Zhao Minmin. 2021. Groundwater resource and eco-environmental problem of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Geology in China, 48(4): 1014-1015(in Chinese with English abstract).
Han Xingrui, Lu Rongan, Li Qingsong. 1993. Karst Water System: Study on Karst Spring in Shanxi[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing Press, 125-266(in Chinese).
Jin Hua, Yangsuolin, Zheng Xiuqing, Li Cijun. 2005. Analysis of the reduction in flow from Jinci Springs[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 36(4): 488-490(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TYGY200504031.htm
Li Juan. 2020. Analysis on scheduling for beneficial use of Fenhe Reservoir[J]. Shanxi Water Resources, (11): 12-13(in Chinese).
Liang Yongping, Gao Xubo, Zhao Chunhong, Tang Chunlei, Shen Haoyong, Wang Zhiheng, Wang Yanxin. 2018. Review characterization, evolution, and environmental issues of karst water systems in Northern China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 26: 1371-1385. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1792-4
Liang Yongping, Wang Weitai, Zhao Chunhong, Wang Wei, Tang Chunlei. 2013. Variations of karst water and environmental problems in North China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 32(1): 34-41(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201301008.htm
Liang Yongping, Zhao Chunhong, Wang Zhiheng, Tang Chunlei, Zhao Yi, Xie Hao, Shi Weizhi. 2020. Thinking and practice on the reserch direction of karst water in north China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 40(3): 363-368(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liang Yongping, Zhang Fawang, Shen Haoyong, Tang Chunlei, Zhao Chunhong, Wang Zhiheng, Hou Hongbin, Ren Jianhui, Guo Fangfang. 2019. Recognition of the critical hydrogeological condition of Jinci Spring and Lancun Spring[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 46(1): 11-17(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SWDG201901002.htm
Lin Xinggui. 2020. Analysis of existing problems of ecological environment of Fenhe basin and general idea of its restoration[J]. Water Resources Planning and Design, (6): 32-34(in Chinese).
Liu Yufeng, Sun Hu, Yuan Zhihua. 2010. Characteristics and driving factors of runoff and sediment changes fluxes into the Yellow River from Fenhe River in recent 60 years[J]. Journal of Mountain Science 28(6): 668-671(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/ http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=SDYA201006006&dbcode=CJFD&year=2010&dflag=pdfdown
Ma Yonglai, Jiang Xiuhua, Liu Dongxu. 2017. Rivers and Lakes in the Yellow River Basin[M]. Zheng Zhou: Yellow River Water Conservancy Press, 40-42(in Chinese).
Meng Zhilong, Yang Yonggang, Qin Zuodong, Jiao Wentao. 2017. Isotopic tracing for nitrate pollution process of water body in the lower reaches of Fenhe River[J]. China Environmental Science, 37(3): 1066-1072(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGHJ201703033.htm
Shen Haoyong, Liang Yongping, Cheng Yang, Huang Chunling. 2017. Study on the regional evapotranspiration over different surface conditions of the Longzici spring drainage[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 36(2): 234-241(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201702011.htm
Shen Haoyong, Liang Yongping, Zhao Chunhong, Tang Chunlei, Wang Zhiheng. 2020. Hydro-Geological characteristics and demarcation of gudui spring karst groundwater system[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 50(1): 218-219(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shi Jiansheng, Zhang Fawang, Qin Yisu, Li Ruimin, Ye Hao, Liu Zuzhi, An Lizhong, Pei Hanhua, Guo Zhenzhong, Zhao Yunzhang, Wang Yanjun. 2000. Groundwater resources and main environment-geological problems in the Huanghe River Valley as well as some countermeasures[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, (2): 114-120(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1559210
Tang Chunlei, Liang Yongping, Wang Weitai, Zhao Chunhong, Shen Haoyong. 2017. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of the karst groundwater systems in Longzici spring basin[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 37(1): 52-58(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX201701007.htm
Wang Deng, Jian Shenqi, Hu Caihong. 2018. Impacts of climate change and human activities on runoff in Fenhe River Basin[J]. Arid Land Geography, 41(1): 25-29(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GHDL201801004.htm
Wang Zhiheng, Liang Yongping, Tang Chunlei, Shen Haoyong, Zhaochunhong, Guo Fangfang, Xie Hao, Zhao Yi. 2020. Ecological restoration pattern and quantitative evaluation of recirculation measures for northern discontinuous karst spring: A case study on Jinci Spring in Taiyuan City [J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1726-1738(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Zhiheng, Liang Yongping, Shen Haoyong, Zhaochunhong, Tang Chunlei, Xie Hao, Zhao Yi. 2021. Dynamic characteristics of karst groundwater in Jinci spring under superimposed influence of natural and human activities [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 51(6): 1823-1837(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xie Hao, Liang Yongping, Li Jun, Zou Shengzhang, Shen Haoyong, Zhao Chunhong, Wang Zhiheng. 2021. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of metal elements in groundwater in Longzici Spring area[J]. Environmental Science, 42(9): 4257-4258(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/354448392_Distribution_Characteristics_and_Health_Risk_Assessment_of_Metal_Elements_in_Groundwater_of_Longzici_Spring_Area
Wang Hong. 2011. Feasibility of spring reflow at Lancun village of Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 22(6): 177-179(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XBSZ201106044.htm
Yang Pingguo, Zheng Fengyan. 2008. Spatial and temporal variation of precipitation in Fenhe Valley for 50 years [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 22(12): 108-109(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH200812020.htm
Yang Shirong, Di Fan. 2020. Study on evaluation, protection and control countermeasures of karst springs in Fenhe River Basin[J]. Water Resources Development Research, (5): 20-25(in Chinese).
Yang Yonggang, Qin Zuodong, Xue Zhanjin. 2016. Study on Hydrology and Water Resources in Fenhe River Basin[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 28-30(in Chinese).
Zhang Jianguo, Zhao Huijun, Zhang Ruoqiong. 2003. Environment problems of water in the Yellow River Basin of Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Changjiang Institute of Technology, 20(4): 1-4(in Chinese with English abstract).
常建忠. 2020. 实施"五策丰水", 打造三晋幸福河[J]. 中国水利, (19): 5-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2020.19.009
范堆相. 2005. 山西省水资源评价[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 119-131.
高波. 2002. 郭庄泉流量衰减原因分析及对策[J]. 水资源保护, (1): 64-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6933.2002.01.020
郭东阳, 王晶, 蔺冬. 2020. 山西"七河"流域水生态保护及修复调研与思考[J]. 水利规划与设计, (12): 17-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2469.2020.12.004
郭芳芳, 梁永平, 王志恒, 申豪勇, 赵春红. 2018. 山西太原西山汾河二库的泉域归属及其渗漏量计算[J]. 中国岩溶, 37(4): 493-494. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201804003.htm
郭振中, 张宏达, 于开宁. 2002. 山西岩溶大泉衰减的多因复成性[J]. 工程勘察, (2): 22-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC200402006.htm
侯新伟, 李向全, 陈浩. 2008. 汾河中游干流河水与大气降水和浅层地下水的转化关系[J]. 水文地质工程地质, (6): 38-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2008.06.009
韩双宝, 李甫成, 王赛, 李海学, 袁磊, 刘景涛, 申豪勇, 张学庆, 李长青, 吴玺, 马涛, 魏世博, 赵敏敏. 2021. 黄河流域地下水资源状况及其生态环境问题[J]. 中国地质, 48(4): 1014-1015. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20210402?st=search
韩行瑞, 鲁荣安, 李庆松. 1993. 岩溶水系统: 山西岩溶大泉研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 125-266.
晋华, 杨锁林, 郑秀清, 李慈君. 2005. 晋祠岩溶泉流量衰竭分析[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 36(4): 488-490. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9432.2005.04.032
李娟. 2020. 汾河水库兴利调度研究[J]. 山西水利, (11): 12-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7042.2020.11.007
梁永平, 王维泰, 赵春红, 王玮, 唐春雷. 2013. 中国北方岩溶水变化特征及其环境问题[J]. 中国岩溶, 32(1): 34-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2013.01.006
梁永平, 申豪勇, 赵春红, 王志恒, 唐春雷, 赵一, 谢浩, 石维芝. 2021. 对中国北方岩溶水研究方向的思考与实践[J]. 中国岩溶, 40(3): 363-368. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202103001.htm
梁永平, 张发旺, 申豪勇, 唐春雷, 赵春红, 王志恒, 侯宏冰, 任建会, 郭芳芳. 2019. 山西太原晋祠—兰村泉水复流的岩溶水文地质条件新认识[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 46(1): 11-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201901002.htm
林兴贵. 2020. 汾河流域生态环境存在问题及生态修复总体思路探析[J]. 水利规划与设计, (6): 32-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2469.2020.06.008
刘宇峰, 孙虎, 原志华. 2010. 近60年来汾河入黄河水沙演变特征及驱动因素[J]. 山地学报, 28(6): 668-671. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2010.06.004
马永来, 蒋秀华, 刘东旭. 2017. 黄河流域河流与湖泊[M]. 郑州: 黄河水利出版社, 40-42.
孟志龙, 杨永刚, 秦作栋, 焦文涛. 2017. 汾河下游流域水体硝酸盐污染过程同位素示踪[J]. 中国环境科学, 37(3): 1066-1072. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201703033.htm
申豪勇, 梁永平, 程洋, 黄春玲. 2017. 龙子祠泉域不同下垫面陆面蒸散量的对比研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 36(2): 234-241. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201702011.htm
申豪勇, 梁永平, 赵春红, 唐春雷, 王志恒. 2020. 古堆泉岩溶地下水系统特征及系统圈划[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 50(1): 218-219. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202001018.htm
石建省, 张发旺, 秦毅苏, 李瑞敏, 叶浩, 刘祖植, 安立忠, 裴捍华, 郭振中, 赵云章, 王彦俊. 2000. 黄河流域地下水资源、主要环境地质问题及对策建议[J]. 地球学报, (2): 114-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200002000.htm
唐春雷, 梁永平, 王维泰, 赵春红, 申豪勇. 2017. 龙子祠泉域岩溶水水化学同位素特征[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 37(1): 52-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX201701007.htm
王登, 荐圣淇, 胡彩虹. 2018. 气候变化和人类活动对汾河流域径流情势影响分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 41(1): 25-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL201801004.htm
王宏. 2011. 山西兰村泉水复流的可行性分析[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 22(6): 177-179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201106044.htm
王志恒, 梁永平, 唐春雷, 申豪勇, 赵春红, 郭芳芳, 谢浩, 赵一. 2020. 北方断流岩溶大泉复流的生态修复模式与复流措施效果的定量评价——以太原晋祠泉为例[J]. 中国地质, 47(6): 1726-1738. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20200610?st=search
王志恒, 梁永平, 申豪勇, 赵春红, 唐春雷, 谢浩, 赵一. 2021. 自然与人类活动叠加影响下晋祠泉域岩溶地下水动态特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 51(6): 1823-1837. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202106017.htm
谢浩, 梁永平, 李军, 邹胜章, 申豪勇, 赵春红, 王志恒. 2021. 龙子祠泉域地下水金属元素分布特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 42(9): 4257-4258. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202109019.htm
杨萍果, 郑峰燕. 2008. 汾河流域50年降水量时空变化特征[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 22(12): 108-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH200812020.htm
杨士荣, 狄帆. 2020. 汾河流域岩溶大泉评价和保护治理对策研究[J]. 水利发展研究, (5): 20-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLFZ202005006.htm
杨永刚, 秦作栋, 薛占金. 2016. 汾河流域水文水资源研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 28-30.
张建国, 赵惠君, 张若琼. 2003. 山西省黄河流域的水环境问题[J]. 长江职工大学学报, 20(4): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0496.2003.04.001
-




 下载:
下载:





