Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soil in Silong and Beiwan towns, Baiyin city, Gansu Province
-
摘要:
研究目的 甘肃省白银地区矿业发达,矿山开采导致土壤重金属污染严重,掌握当地土壤重金属污染及对生态健康风险的影响对生态环境保护具有重要意义。
研究方法 以甘肃省白银地区四龙镇—北湾镇耕地区表层土壤为研究对象,采用单因子指数法、内梅罗综合指数法、地积累指数法和潜在生态危害指数法四种方法对区内表层土壤重金属(As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb、Zn)污染进行了分析和评价。
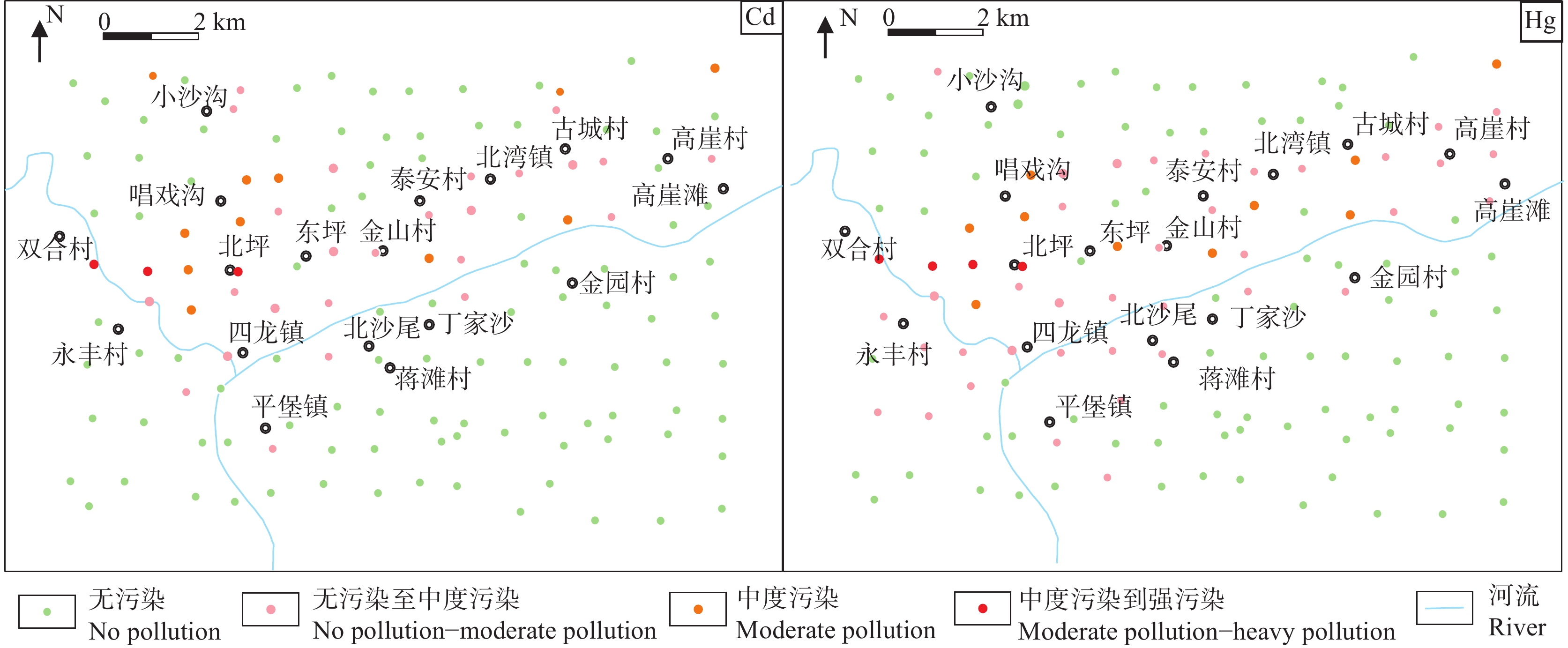
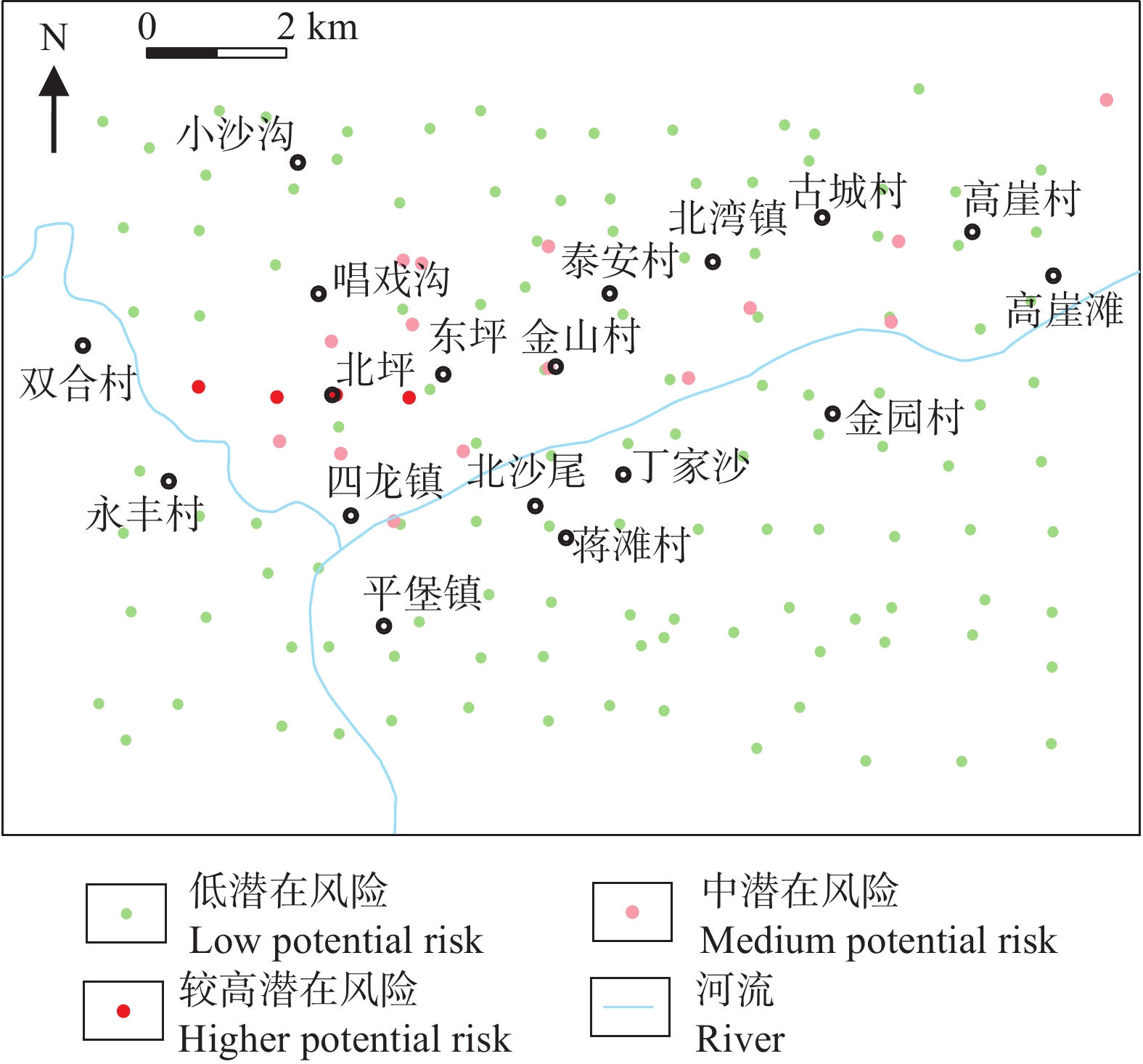
研究结果 单因子指数法统计结果显示研究区土壤污染主要为Cd、As的污染,单因子指数PCd显示89.21%的土壤为一等清洁,8.63%为二等轻微污染,0.72%为三等轻度污染,1.44%为四等中度污染。单因子指数PAs显示94.24%为土壤为一等清洁,5.04%为二等轻微污染,0.72%四等中度污染。内梅罗综合指数Pz介于0.339~2.869,均值为0.603;Pz显示85.61%的土壤为清洁,7.91%为轻微污染,5.04%为轻度污染,1.44%为中度污染。地积累指数法结果显示研究区土壤重金属污染总体处于0~2级,以Cd、Hg、As、Pb污染为主。潜在生态危害指数法结果显示,研究区污染以Cd、Hg污染为主;Cd潜在生态风险最大,10.07%属于中潜在风险,5.04%属于较高潜在风险,1.44%属于很高潜在风险;潜在生态危害综合指数平均值为211.80,表明该地区土壤总体处于中等危害程度。四种方法评价结果总体一致,即研究区以Cd、As、Hg污染为主,应加强监测。
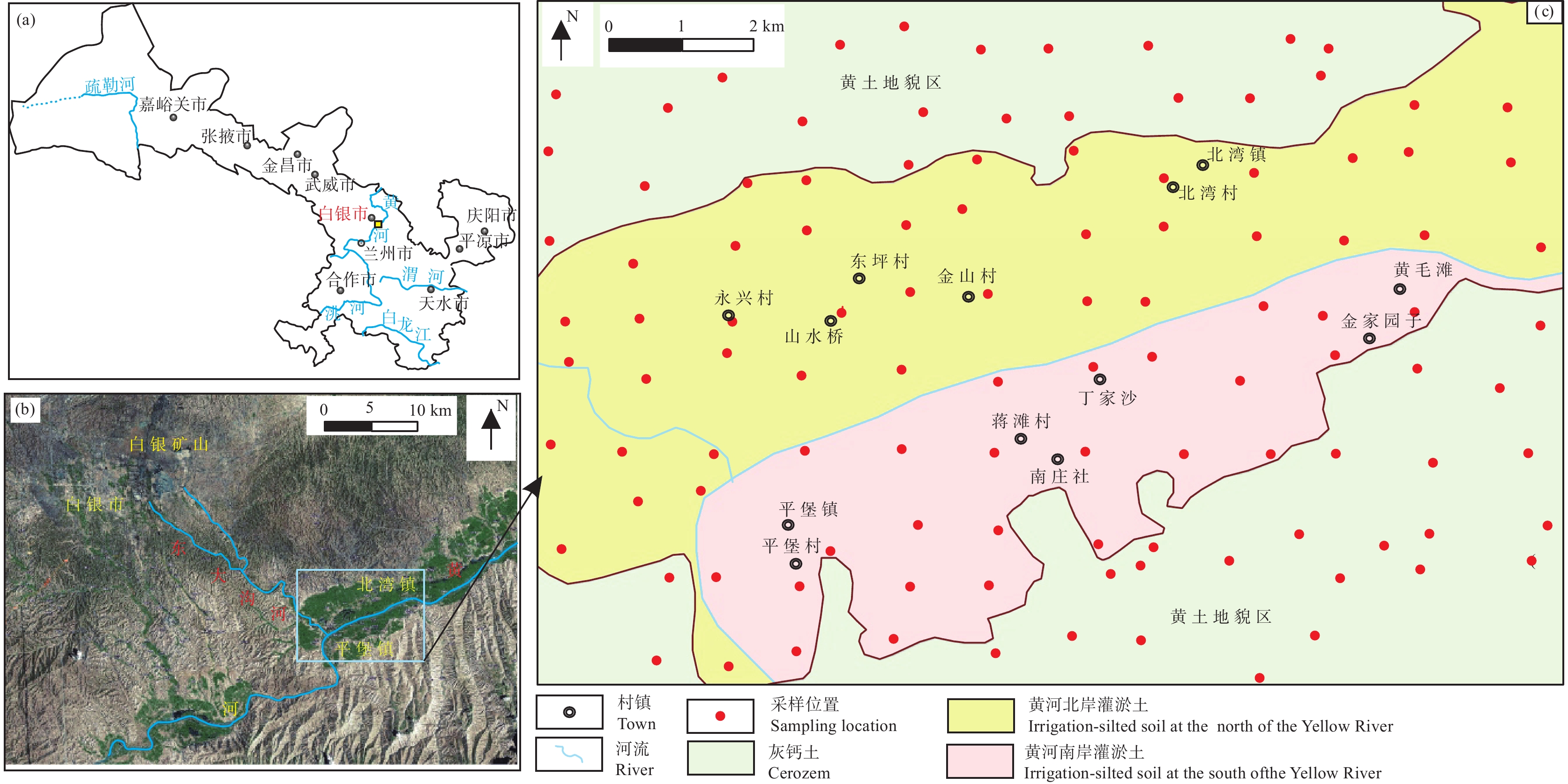
结论 以黄河为界对调查区进行分区研究,结果显示北岸灌淤土区(B区)污染最为严重,与东大沟河交界位置污染程度最高,水体及底泥样品重金属分析结果也证实东大沟河污染也较为明显,进一步证实了研究区北部主要受白银矿山东大沟河流域污染为主,而黄河南岸土壤相对清洁,但也受到不同程度的影响。近些年,随着引黄灌溉及矿山环境治理等措施,土壤污染有所缓解,但土壤中累积的重金属需要长时间的自然降解或迁移,对高风险区仍应加强监测及治理。
Abstract:This paper is the result of environmental geological survey engineering.
Objective The mining industry in the Baiyin region of Gansu Province is well−developed, leading to severe heavy metal soil contamination. Grasping the influence of heavy metal contamination of the soil and its potential risks to ecological health is significant in protecting the environment.
Methods Taking the surface soils in the four−dragon town−north bay town farmland area of Baiyin region of Gansu Province as the research object, four methods, namely the single−factor index, Nemerow comprehensive index (PZ), geochemical accumulation index, and potential ecological risk index (RI), were used to analyze and evaluate the heavy metal (As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, Zn) contamination in the region.
Results The single−factor index results showed that the soil pollution in the study area was mainly Cd and As, in which the levels of PCd were at firstclass cleanliness (89.21%), slight second−class pollution (8.63%), third−class light pollution (0.72%), fourth−class medium pollution (1.44%), and the levels of PAs was at first−class cleanliness (94.24%), slight second−class pollution (5.04%), fourth−class medium pollution (0.72%). PZ ranged from 0.339 to 2.869, with an average of 0.603, indicating that 85.61% of the soil was clean, 7.91% was slightly polluted, 5.04% was lightly polluted, and 1.44% was moderately polluted. The geochemical accumulation index results showed that the heavy metal contamination of the soil in the study area was generally at the level of 0−2, mainly Cd, Hg, As, and Pb. In the potential ecological risk area, Cd and Hg were the main pollution factors. Cd had the highest potential ecological risk, with 10.07% belonging to medium potential risk, 5.04% to relatively high potential risk, and 1.44% to very high potential risk. The average value of the RI was 211.80, indicating that the soil in the area was generally at a medium danger level. The four evaluation methods were consistent overall, indicating that the study area was mainly contaminated by Cd, As, and Hg and should be strengthened for monitoring.
Conclusion Through the divisional study of the survey area with the Yellow River as the boundary, the results showed that the soil of the north bank of the irrigation and silt area (Area B) was the most polluted, and the pollution level was the highest at the junction of East Dagou River. The heavy metal analysis results of the water and sediment samples also confirmed that the pollution of East Dagou River was more obvious, further confirming that the north of the study area was mainly polluted by the East Dagou River basin of Baiyin mine, while the soil on the south bank of the Yellow River was relatively clean, but was still affected to a certain extent. In recent years, soil pollution has been alleviated to some extent with the measures of Yellow River irrigation and mining environmental governance. However, the heavy metals accumulated in the soil need long−term natural degradation or migration, and monitoring and governance should be strengthened for the high−risk areas.
-

-
表 1 土壤样品分析方法
Table 1. Soil samples analysis method
序号 分析方法 项数 测定元素 1 等离子体质谱法(ICP−MS/AES) 3 Cu、Cd、Ni 2 X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) 3 Cr、Pb、Zn 3 原子荧光光谱法(AFS) 2 As、Hg 表 2 表层土壤重金属描述性统计
Table 2. Descriptive statistics of heavy metals in surface soil
重金属元素 平均值/
(mg/kg)中位数/
(mg/kg)标准差 变异系数
(Cv)最大值/
(mg/kg)最小值/
(mg/kg)甘肃省土壤环境背景值
(mg/kg)调查区平均值/甘肃省
土壤环境背景值全国丰度/
(mg/kg)As 14.61 13.5 5.68 0.39 73.6 9 12.7 1.15 10 Hg 0.0543 0.0350 53.20 0.98 0.3560 0.0130 0.02 2.72 0.04 Cd 0.0418 0.0275 0.44 1.05 3.1130 0.0960 0.116 0.36 0.09 Cr 73.65 73.80 4.87 0.07 85.1 58.40 70.2 1.05 65 Cu 26.98 24.50 6.11 0.23 56 18.00 24.1 1.12 24 Ni 30.35 30.10 3.04 0.10 39.4 20.80 35.2 0.86 26 Pb 27.44 24.20 9.90 0.36 101.2 19.70 18.8 1.46 23 Zn 75.96 67.20 22.37 0.29 186.2 45.50 68.5 1.11 68 注:甘肃省土壤环境背景值参考中国环境监测总站(1990)编《中国土壤元素背景值》 ;全国丰度参考鄢明才等(1997)。 表 3 利用GeoIPAS计算的土壤重金属元素背景值及异常下限
Table 3. Background levels of heavy metals insoil by GeoIPAS software
重金属元素 As Hg Cd Cr Cu Ni Pb Zn 背景值/(mg/kg) 13.49 0.0326 0.2674 73.73 24.79 30.08 24.49 66.76 甘肃省土壤环境背景值/(mg/kg) 12.7 0.02 0.116 70.2 24.1 35.2 18.8 68.5 异常下限 15.54 0.0627 0.4681 78.12 30.06 33.56 29.97 82.19 表 4 研究区黄河两岸分区土壤元素地球化学参数统计
Table 4. Geochemistry parameter statistics of heavy metals on both sides of the Yellow River in the study area
研究区分区 重金属
元素平均值/
(mg/kg)标准差 最大值/
(mg/kg)最小值/
(mg/kg)A区
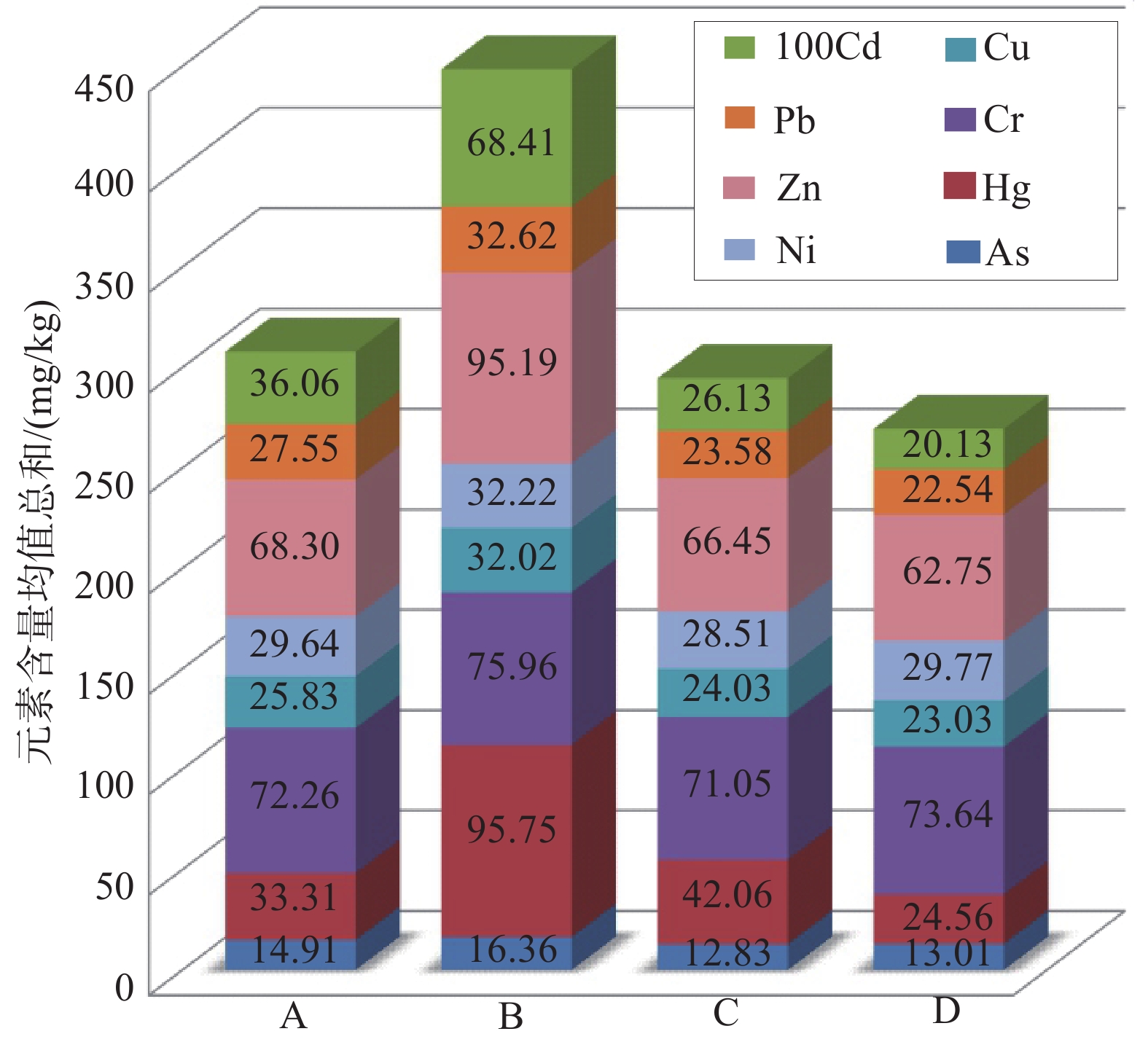
(35个样品)As 14.91 10.17 73.60 9.33 Hg 33.31 30.48 200.73 15.33 Cd 0.3606 508.62 3.1127 0.0960 Cr 72.26 5.78 80.10 58.40 Cu 25.83 4.86 41.61 19.15 Ni 29.64 2.96 35.79 23.00 Pb 27.55 13.77 101.20 19.70 Zn 68.3 14.41 127.5 47.8 B区
(47个样品)As 16.36 3.12 25.41 12.35 Hg 95.75 68.31 356.38 20.41 Cd 0.6841 502.2300 2.7944 0.2333 Cr 75.96 5.05 85.10 59.00 Cu 32.02 6.64 55.96 21.33 Ni 32.22 2.99 39.43 26.72 Pb 32.62 9.54 69.00 21.60 Zn 95.19 25.97 186.20 63.80 C区(24个样品) As 12.83 1.24 14.66 9.01 Hg 42.06 18.40 87.66 14.06 Cd 0.2613 6271.17 0.4554 0.1262 Cr 71.05 3.42 75.30 62.00 Cu 24.03 2.77 29.44 17.98 Ni 28.51 2.44 31.79 20.77 Pb 23.58 1.96 26.90 20.30 Zn 66.45 8.82 87.60 45.50 D区(30个样品) As 13.01 0.90 15.71 11.34 Hg 24.56 6.25 43.00 13.02 Cd 0.2013 40.4600 298.9100 133.3900 Cr 73.64 1.80 79.10 70.60 Cu 23.03 1.32 26.44 19.35 Ni 29.77 1.73 33.44 26.13 Pb 22.54 1.35 25.10 20.00 Zn 62.75 3.14 71.60 58.30 表 5 土壤重金属环境质量等级划分及其表达
Table 5. Classification and expression of heavy metal environment quality in soil
指标 一等 二等 三等 四等 五等 单因子污染
指数描述Pi≤1
清洁1<Pi≤2
轻微污染2<Pi≤3
轻度污染3<Pi≤5
中度污染Pi>5
重度污染内梅罗综合
指数描述PZ≤0.7
清洁0.7<PZ≤1
轻微污染1<PZ≤2
轻度污染2<PZ≤3
中度污染PZ>3
重度污染表 6 地积累指数和潜在生态风险评价等级划分及其表达
Table 6. Classification standards of geo-accumulation index
指标 一等 二等 三等 四等 五等 六等 七等 地积累指数
描述Igeo<0
无污染0≤Igeo<1
无污染到中度污染1≤Igeo<2
中度污染2≤Igeo<3
中度污染到强污染3≤Igeo<4
强污染4≤Igeo<5
强污染到极强污染Igeo≥5
极强污染单项潜在生态风险系数
描述Eri<40
低潜在风险40≤Eri<80
中潜在风险80≤Eri<160
较高潜在风险160≤Eri<320
很高潜在风险Eri≥320
极高潜在风险潜在生态风险指数
描述RI<150
低潜在风险150≤RI<300
中潜在风险300≤RI<600
较高潜在风险RI≥600
很高潜在风险表 7 研究区土壤重金属元素单因子污染指数和内梅罗指数法评价等级样品数占比统计
Table 7. Proportion of samples evaluated by single factor pollution index and Nemerow index method in the soil of the investigated area
评价指标 一等 二等 三等 四等 五等 单因子污染
指数描述Pi≤1
清洁1<Pi≤2
轻微污染2<Pi≤3
轻度污染3<Pi≤5
中度污染Pi>5
重度污染Cd 89.21% 8.63% 0.72% 1.44% 0 As 94.24% 5.04% 0 0.72% 0 内梅罗综合
指数描述PZ≤0.7
清洁0.7<PZ≤1
轻微污染1<PZ≤2
轻度污染2<PZ≤3
中度污染PZ>3
重度污染Pz 85.61% 7.91% 5.04% 1.44% 表 8 调查区土壤重金属元素地累积指数法评价等级样品数占比统计(%)
Table 8. Statistics on the number of samples of geochemical grade evaluation of heavy metal elements in the study area (%)
评价 指标 一等 二等 三等 四等 五等 六等 七等 地
累
积
指
数
法Igeo
描述Igeo<0
无污染0≤Igeo<1
无污染到中度污染1≤Igeo<2
中度污染2≤Igeo<3
中度污染到强污染3≤Igeo<4
强污染4≤Igeo<5
强污染到极强污染Igeo≥5
极强污染As 94.96 4.32 0.72 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Hg 62.59 26.62 7.91 2.88 0.00 0.00 0.00 Cd 69.78 19.42 8.63 2.16 0.00 0.00 0.00 Cr 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Cu 92.09 7.91 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Ni 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Pb 89.93 9.35 0.72 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Zn 89.93 10.07 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 表 9 调查区土壤重金属元素潜在生态风险法评价等级样品数占比统计(%)
Table 9. Statistics on the number of samples of geochemical grade evaluation of heavy metal elements in the study area(%)
评价 指标 一等 二等 三等 四等 五等 单项潜在生态风险系数 Eri
描述Eri<40
低潜在风险40≤Eri<80
中潜在风险80≤Eri<160
较高潜在风险160≤Eri<320
很高潜在风险Eri≥320
极高潜在风险As 99.28 0.72 0.00 0.00 0.00 Cd 70.50 20.14 7.19 2.16 0.00 Cr 83.45 10.07 5.04 1.44 0.00 Cu 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Hg 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Ni 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Pb 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Zn 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 潜在生态风险指数 RI
描述RI<150
低潜在风险150≤RI<300
中潜在风险300≤RI<600
较高潜在风险RI≥600
很高潜在风险RI 86.33 10.79 2.88 表 10 水体中重金属含量统计特征
Table 10. Statistical characteristics of the heavy mental contents in the water samples
元素 最大值/
(mg/L)平均值/
(mg/L)标准差 变异系数 地表水环境
Ⅳ级标准/(mg/L)Cu 30.63 4.796 10.55 2.20 1 Pb 1.019 0.1759 0.28 1.61 0.05 Zn 77.35 13.34 25.25 1.89 2 Cd 0.8633 0.2164 0.27 1.23 0.005 As 0.152 0.048 0.05 1.12 0.1 Hg 0.00279 0.00057 0.0009 1.49 0.001 表 11 底泥中重金属含量统计特征
Table 11. Statistical characteristics of the heavy mental contents in the sediments
元素 最大值/10−6 平均值/10−6 标准差 变异系数 甘肃省土壤
背景值/10−6Cr 80.1 61.6 10.6 0.2 70.2 Zn 13800 5999.3 4417.7 0.7 68.5 Pb 15900 4819.5 5387.4 1.1 18.8 Cu 8449.8 1795.6 2282.6 1.3 24.1 Cd 2908 502.816 832.31 1.7 0.116 Hg 476.6 65.07 129.15 2 0.02 -
[1] Bao Liran, Deng Hai, Jia Zhongmin, Li Yu, Dong Jinxiu, Yan Mingshu, Zhang Fenglei. 2020. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil of northwest Xiushan, Chongqing[J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1625−1636 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] Cai Kui, Duan Yamin, Luan Wenlou, Li Qian, Ma Yunchao. 2016. Geochemical behavior of heavy metals Pb and Hg in the farmland soil of Hebei plain[J]. Geology in China, 43(4): 1420−1428 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Cai Xiaodong, Sun Chengsheng, Cai Liqun. 2014. Study on evaluation and spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metal pollution in arable layer soil of Baiyin district[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 30(32): 194–200 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Chen Wei, Wang Ting. 2020. Speciation features and health risk assessment of Cd in soil–wheat system in Baiyin sewage irrigation area in China[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 34(4): 878−886 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Chen Zhenyu, Zhao Yuanyi, Chen Danli, Huang Haitao, Zhao Yu, Wu Yujing. 2023. Ecological risk assessment and early warning of heavy metal cumulation in the soils near the Luanchuan molybdenum polymetallic mine concentration area, Henan Province, central China[J]. China Geology, 6(1): 15−26.
[6] China Environmental Monitoring Station. 1990. Background Values of Soil Elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1−501(in Chinese)
[7] Cui Xingtao, Luan Wenlou, NiuYanbin, Li Suimin, Song Zefeng. 2011. An assessment of the heavy metal pollution and potential ecological hazards in urban soil of Tangshan City[J]. Geology in China, 38(5): 1379−1386 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Cui Xingtao, Luan Wenlou, Song Zefeng, Ma Yunchao. 2016. A study of the spatial distribution and source of heavy metals in urban soil in Shijiazhuang City[J]. Geology in China, 43(2): 683−690 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Dai Jierui, Pang Xugui, Song Jianhua, Dong Jian, Hu Xueping, Li Xiaopeng. 2018. A study of geochemical characteristics and ecological risk of elements in soil of urban and suburban areas of Zibo City, Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 45(3): 617−627 (in Chinese with English abstract
[10] Dong Qiuyao, Wen Haotian, Wang Pan, Song Chao, Lai Shuya, Yang Zhenjing, Zhao Yuanyi, Yan Mingjiang. 2023. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and crops in a mining area (Au–Ag–Cu–trona–oil et al.) of the Nanyang Basin, Henan Province, China[J]. China Geology, 6(4): 567−579.
[11] Gong Xiaofeng, Chen Chunli, Zhou Wenbin, Jian Minfei, Zhang Zhenhui. 2006. Assessment on heavy metal pollution in the sediment of Poyang lake[J]. Environmental Science, 27(4): 732−736 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Guan Honchun, Li Yunhuai, Peng Miaozhi, Liu Daobin. 2013. The evaluation of heavy metal pollution and its potential ecological risk of urban topsoil in Huangshan city[J]. Geology in China, 40(6): 1949−1958 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Guo Yuanxin, Wang Fang, Zhang Zhaorong, Hei Huan, Duan Xingxing. 2019. Investigation on soil corn pollution in Silongtown, Baiyincity, Gansu Province[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 31(5): 162–164 (in Chinese).
[14] Hakanson L. 1980. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach[ J]. Water Research, 14: 975–1001.
[15] He Zhipeng, Song Jinming, Zhang Naixing, Xu Yayan, Zheng Guoxia, Zhang Peng. 2008. Variation characteristics and controlling factors of heavy metals in the south Yellow sea surface seawater[J]. Environmental Science, 29(5): 1153−1162 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Lei Siwei, Wu Guozhen, Wang Xingfeng. 2017. Investigation and analysis of heavy metal distribution patterns in soil and spring wheat in Baiyindistrict[J]. Gansu Metallurgy, 29(4): 86–88 (in Chinese).
[17] Li Xiangmin, Ma Zhongping, Sun Jiming, Yu Jiyuan. 2009. A LA–ICP–MS chronological study of basic volcanics in Baiyin ore–field, Gansu, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(7): 901−906 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Li Xiaohu, Tang Zhongli, Chu Fengyou. 2008. Analysis on speciation and transportation of heavy metals in water and sediment in Baiyin mine[J]. Earth and Environment, 36(3): 218−224 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Li Youwen, Cao Chun, Ju Tianzhen, Zhao Xutao, Mou Ruiqiang, Liu Siqi, Du Mingzhuo. 2015. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of different vegetable soils of Baiyin, Gansu, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34(11): 3205−3213 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Li Youwen, Wang Jing, Ju Tianzhen, Wang Li, Lin Ning, Zhang Shengnan, Zha Xianghao. 2017. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and human health risk assessment in soils from different functional areas of Baiyin, Gansu, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36(5): 1408−1418 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Lin Jin, Liang Wenjing, Jiao Yang, Yang Li, Fan Yaning, Tian Tao, Liu Xiaomeng. 2021. Ecolcgical and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil around the gold mining area in Tongguan of Shaanxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 48(3): 749−763 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Liu Bailin, Ma Xinwang, Zhu Saiyang, Ai Shiwei, Zhang Wenya, Zhang Yingmei. 2014. Speciations and risk assessment of heavy metals in different layers of lands irrigated by the Yellow river in Baiyin[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University(natural sciences), 50(3): 431−436 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Liu Bailin. 2017. Heavy Metal Contamination in Farmland Soils and Its Transfer in the Soil–Crop–Human System within the Dongdagou Watershed, Baiyin, Gansu[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University(in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Liu Ruiping, Xu Youning, Zhang Jianghua, Wang Wenke, Rafaey M Elwardany. 2020. Effects of heavy metal pollution on farmland soils and crops: A case study of the Xiaoqinling Gold Belt, China[J]. China Geology, 3: 402−410.
[25] Liu Tong, Liu Chuanpeng, Deng Jun, Kang Pengyu, Wang Kaikai, Zhao Yuyan. 2022. Ecological health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in eastern Yinan County, Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(5): 1497−1508 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Ma Tingmin, Gao Jianfeng, Wang Chengkui, Shui Qingchuan, Zhang Chunxia, Chen Jing. 2015. Heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk assessment of surface soil in Dongdagou sewage irrigation area of Baiyincity[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, (15): 215–217 (in Chinese).
[27] Ni Dingwen, Nan Hai, Wang Ting. 2015. Current situation and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution in Baiyin city[J]. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, (8): 67–70 (in Chinese).
[28] Sun Chao, Chen Zhenlou, Bi Chunjuan, Liu Yaolong, Zhang Cui, Wang Dongqi, Shi Guitao, Ye Mingwu. 2009. Evaluation on environmental quality of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Chongming island, Shanghai[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 64(5): 619−628 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Sun Chengsheng, Cai Xiaodong, Zhang Renzhi, Cai Liqun. 2014. GIS–based spatial variability and pollution evalution studies of heavy metal in arable layer of Baiyin district[J]. Arid land geography, 37(4): 750−758 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Tian Qingchun, Yang Taibao, Shi Peihong, Zeng Chaosheng, Wang Taixiang. 2012. Analysis of heavy metal sources and measures for preventing and controlling them in Baiyin city[J]. Environment Monitoring in China, 28(6): 40−45 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Wan Jinbao, Wang Jianyong, Wu Dan. 2008. Current assessment on heavy metal pollution in the sediment of Le'an river[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 31(11): 130−133 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Wang Fangting, Bao Ke, Huang Changsheng, Liu Ruiping, Han Wenjing, Yi Chengyun, Li Long, Zhou Yun. 2022. Distribution, characteristics, and research status of microplastics in the trunk stream and main lakes of the Yangtze River: A review[J]. China Geology, 5: 171−184.
[33] Wang Ting, Ni Dingwen. 2015. Research advances on Cd pollution in farmland soil in Baiyin district[J]. Gansu Agrculture Science and Technology, (9): 80−84 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Wei Jikang, Yu Xiaoxia, Wang Baoxin, Wang Gang. 2021. The speciation, bioavailability and influence factors of soil heavy metals in typical areas along the eastern coast of Zhejiang[J]. Environmental Pollution and Control, 43(10): 1231−1237 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Xu Wanling, Wang Yuting, Li Huijie, Zhu Weihong. 2014. Researth on environmental quality and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals for soil in ginseng plantation of Changbai Mountain area—A case study of Dunhua city[J]. Journal of Yanbian University (Natural Science), 40(1): 89−94 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Xu Zhengqi, Ni Shijun, TuoXianguo, Zhang Chengjiang. 2008. Calculation of heavy metals' Toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 31(2): 112−115 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Yan Mingcai, Gu Tiexin, Chi Qinghua, Wang Chunshu. 1997. abundance of chemical elements of soils in China and super genesis geochemistry characteristics[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 21(3): 161−167 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Yin Dechao, Qi Xiaofan, Wang Yushan, Xu Rongzhen, An Yonghui, Wang Xuqing, Geng Hongjie. 2022. Geochemical characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Baiyangdian Lake, Xiong'an New Area[J]. Geology in China, 49(3): 979−992 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Zhang Hui, Ma Xinpeng, Su Hang, Sui Hongjun Shi Xiaolei, Li Xinyang, Yang Huan, Zheng Zhizhi. 2018. Soil heavy metal background values and pollution degree in southern Songnen Plain of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 36(6): 230−236 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Zhang Jiamian. 2020. Characteristics of selenium enrichment and heavy metal pollution in Baiyin city[J]. Gansu Science and Technology, 36(18): 35−37 (in Chinese).
[41] Zhang Jianghua, Zhao Aning, Wang Zhongfu, Ke Hailing, Chen Huaqing. 2010. Discussion on the differences of heavy metals contamination in soil assessment with Nemerou index and Geo–accumulation index with Xiaoqinling gold belt as example[J]. Gold, 31(8): 43−46 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Zhang Xiangnian, Xin Cunlin, Li Chunliang. 2010. Geochemical characteristics of heavy metal's contamination and its surface geochemical mechanism in Baiyin City, Gansu Province[J]. Geoligical Science and Technology Information, 29(4): 124−131 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Zhang Zhaorong, Duan Xingxing, Xia Minzhe. 2019. Contamination situation and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in water and sediments of Dongdagou area, Baiyin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 43(3): 649−657 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] Zhao Baowei, Wang Gang. 2010. Preliminary investigation and assessment of farmland soils contaminated by heavy metal around Baiyin City[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 33(11): 79−81 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Zhou Yalong, Guo Zhijuan, Wang Chengwen, Chen Jie, Peng Min, Cheng Hangxin. 2019. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of soils in Zhenxiong County, Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 43(6): 1358−1366 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] Zong Zijiu.1987. Research on the atmospheric diffusion law and pollution control strategies in Baiyinregion[J]. Environmental Engineering, (5): 56–62 (in Chinese).
[47] 鲍丽然, 邓海, 贾中民, 李瑜, 董金秀, 严明书, 张风雷. 2020. 重庆秀山西北部农田土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 47(6): 1625−1636.
[48] 蔡奎, 段亚敏, 栾文楼, 李倩, 马云超. 2016. 河北平原农田土壤重金属元素Pb、Hg地球化学行为的影响因素[J]. 中国地质, 43(4): 1420−1428.
[49] 蔡小冬, 孙成胜, 蔡立群. 2014. 基于改进AHP与GIS的白银区耕层土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 中国农学通报, 30(32): 194−200.
[50] 陈伟, 王婷. 2020. 白银市污灌区土壤–小麦系统镉赋存特征及其健康风险评价[J]. 核农学报, 34(4): 878−886.
[51] 崔邢涛, 栾文楼, 牛彦斌, 李随民, 宋泽峰. 2011. 唐山城市土壤重金属污染及潜在生态危害评价[J]. 中国地质, 38(5): 1379−1386.
[52] 崔邢涛, 栾文楼, 宋泽峰, 马云超. 2016. 石家庄城市土壤重金属空间分布特征及源解析[J]. 中国地质, 43(2): 683−690.
[53] 代杰瑞, 庞绪贵, 宋建华, 董建, 胡雪平, 李肖鹏. 2018. 山东淄博城市和近郊土壤元素地球化学特征及生态风险研究[J]. 中国地质, 45(3): 617−627. doi: 10.12029/gc20180314
[54] 弓晓峰, 陈春丽, 周文斌, 简敏菲, 张振辉. 2006. 鄱阳湖底泥中重金属污染现状评价[J]. 环境科学, 27(4): 732−736.
[55] 管后春, 李运怀, 彭苗枝, 刘道彬. 2013. 黄山城市土壤重金属污染及其潜在生态风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 40(6): 1949−1958.
[56] 郭远新, 王芳, 张钊熔, 黑欢, 段星星. 2019. 甘肃省白银市四龙镇土壤——玉米污染情况调查[J]. 西部探矿工程, 31(5): 162−164.
[57] 贺志鹏, 宋金明, 张乃星, 徐亚岩, 郑国侠, 张蓬. 2008. 南黄海表层海水重金属的变化特征及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 29(5): 1153−1162. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.05.001
[58] 雷思维, 吴国振, 王兴峰. 2007. 白银区土壤和春小麦中重金属分布规律调查分析[J]. 甘肃冶金, (4): 86−88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4461.2007.04.031
[59] 李向民, 马中平, 孙吉明, 余吉远. 2009. 甘肃白银矿田基性火山岩的LA–ICP–MS同位素年代学[J]. 地质通报, 28(7): 901−906.
[60] 李小虎, 汤中立, 初凤友. 2008. 白银矿山水体和沉积物中重金属及其化学形态分布特征[J]. 地球与环境, 36(3): 218−224.
[61] 李有文, 曹春, 巨天珍, 赵旭涛, 牟瑞强, 刘思琪, 杜名倬. 2015. 白银市不同区域蔬菜地土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 34(11): 3205−3213.
[62] 李有文, 王晶, 巨天珍, 王莉, 林宁, 张胜楠, 查向浩. 2017. 白银市不同功能区土壤重金属污染特征及其健康风险评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 36(5): 1408−1418.
[63] 林荩, 梁文静, 焦旸, 杨莉, 范亚宁, 田涛, 刘晓萌. 2021. 陕西潼关县金矿矿区周边农田土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 48(3): 749−763. doi: 10.12029/gc20210306
[64] 刘白林, 马新旺, 朱赛勇, 艾世伟, 张文雅, 张迎梅. 2014. 白银黄灌农业区不同土层重金属赋存形态及其风险评价[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 50(3): 431−436.
[65] 刘白林. 2017. 甘肃白银东大沟流域农田土壤重金属污染现状及其在土壤–作物–人体系统中的迁移转化规律[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学.
[66] 刘同, 刘传朋, 邓俊, 康鹏宇, 王凯凯, 赵玉岩. 2022. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 49(5): 1497−1508. doi: 10.12029/gc20220509
[67] 马廷民, 高建峰, 王承魁, 水清川, 张春霞, 陈静. 2015. 白银市东大沟污灌区表层土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 现代农业科技, (15): 215−217.
[68] 倪鼎文, 南海, 王婷. 2015. 白银市土壤重金属污染现状及来源分析[J]. 甘肃农业科技, (8): 67−70.
[69] 孙超, 陈振楼, 毕春娟, 刘耀龙, 张翠, 王东启, 史贵涛, 叶明武. 2009. 上海市崇明岛农田土壤重金属的环境质量评价[J]. 地理学报, 64(5): 619−628. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2009.05.011
[70] 孙成胜, 蔡小冬, 张仁陟, 蔡立群. 2014. 基于GIS的白银区耕地耕层土壤重金属空间分异及污染评价[J]. 干旱区地理, 37(4): 750−758.
[71] 田庆春, 杨太保, 石培宏, 曾潮生, 王泰祥. 2012. 白银市土壤重金属污染源分析及防治措施[J]. 中国环境监测, 28(6): 40−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2012.06.009
[72] 万金保, 王建永, 吴丹. 2008. 乐安河沉积物重金属污染现状评价[J]. 环境科学与技术, 31(11): 130−133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.11.037
[73] 王婷, 倪鼎文. 2015. 白银区农田土壤Cd污染研究概述[J]. 甘肃农业科技, (9): 80−84.
[74] 韦继康, 余晓霞, 王保欣, 王刚. 2021. 浙江东部沿海典型地区土壤重金属赋存形态、生物有效性及其影响因素研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 43(10): 1231−1237.
[75] 徐万玲, 王钰婷, 李会杰, 朱卫红. 2014. 长白山地区园参地土壤环境质量及重金属潜在生态风险评价——以敦化市为例[J]. 延边大学学报(自然科学版), 40(1): 89−94.
[76] 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 张成江. 2008. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, 31(2): 112−115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.02.030
[77] 鄢明才, 顾铁新, 迟清华, 王春书. 1997. 中国土壤化学元素丰度与表生地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 21(3): 161−167.
[78] 尹德超, 祁晓凡, 王雨山, 徐蓉桢, 安永会, 王旭清, 耿红杰. 2022. 雄安新区白洋淀表层沉积物重金属地球化学特征及生态风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 49(3): 979−992.
[79] 张慧, 马鑫鹏, 苏航, 隋虹均, 史晓磊, 李昕阳, 杨欢, 郑志志. 2018. 松嫩平原黑龙江省南部土壤重金属背景值及污染程度分析[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 36(6): 230−236. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2018.06.34
[80] 张嘉冕. 2020. 白银土壤富硒与重金属污染特征[J]. 甘肃科技, 36(18): 35−37.
[81] 张江华, 赵阿宁, 王仲复, 柯海玲, 陈华清. 2010. 内梅罗指数和地质累积指数在土壤重金属评价中的差异探讨——以小秦岭金矿带为例[J]. 黄金, 31(8): 43−46.
[82] 张祥年, 辛存林, 李春亮. 2010. 甘肃省白银市土壤重金属污染地球化学特征及其表生地球化学成因[J]. 地质科技情报, 29(4): 124−131.
[83] 张钊熔, 段星星, 夏明哲. 2019. 白银东大沟水体和底泥中重金属污染评价[J]. 物探与化探, 43(3): 649−657.
[84] 赵保卫, 王刚. 2010. 白银市郊区农田土壤重金属污染初步调查与评价[J]. 环境科学与技术, 33(11): 79−81.
[85] 中国环境监测总站主编. 1990. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 中国环境科学出版社.
[86] 周亚龙, 郭志娟, 王成文, 陈杰, 彭敏, 成杭新. 2019. 云南省镇雄县土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评估[J]. 物探与化探, 43(6): 1358−1366.
[87] 宗子就. 1987. 白银地区大气扩散规律及污染控制对策研究[J]. 环境工程, (5): 56−62.
-



 下载:
下载: