Analysis of nitrate sources in surface water in northern Yantai based on nitrogen and oxygen isotopes and MixSIAR model
-
摘要:
研究目的 地表水硝酸盐污染是全世界关注的一个环境问题,因此识别硝酸盐的来源和转化是改善水质的基础。
研究方法 为准确识别烟台北部地表水硝酸盐来源及转化过程,利用水化学方法及硝酸盐氮氧双同位素技术,对烟台北部大沽夹河、辛安河、沁水河、汉河等不同流域地表水进行采样分析,并结合贝叶斯同位素混合模型MixSIAR对各硝酸盐来源贡献率进行计算。
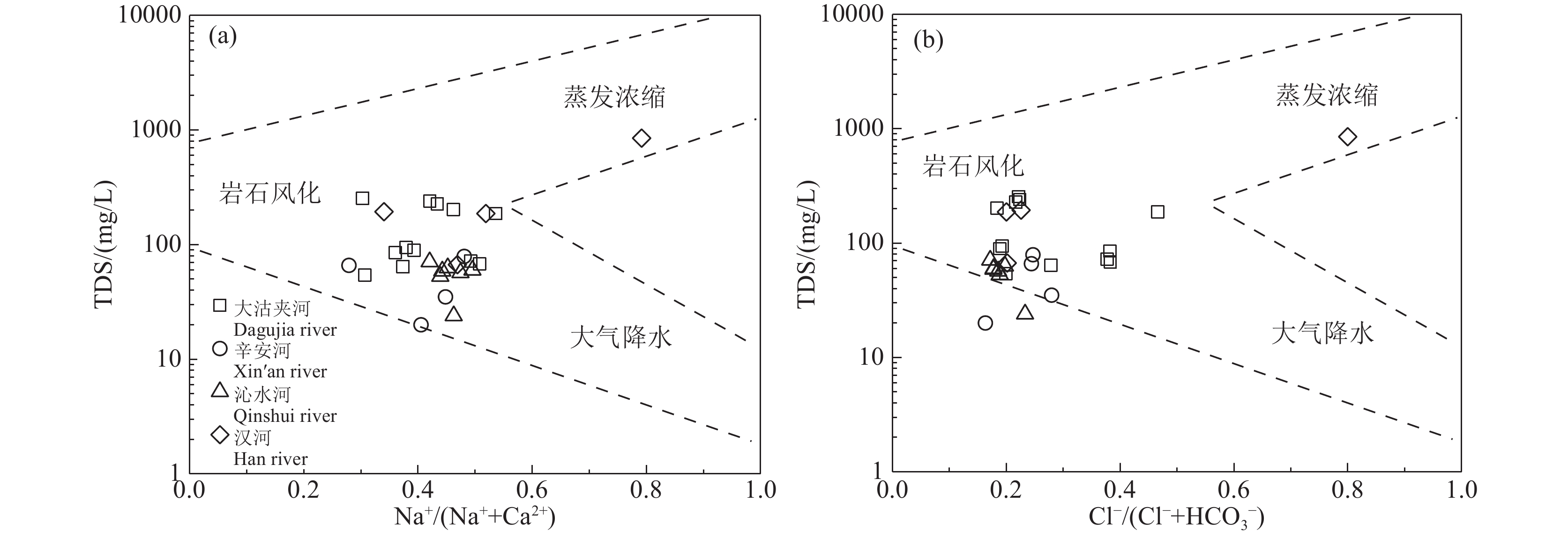
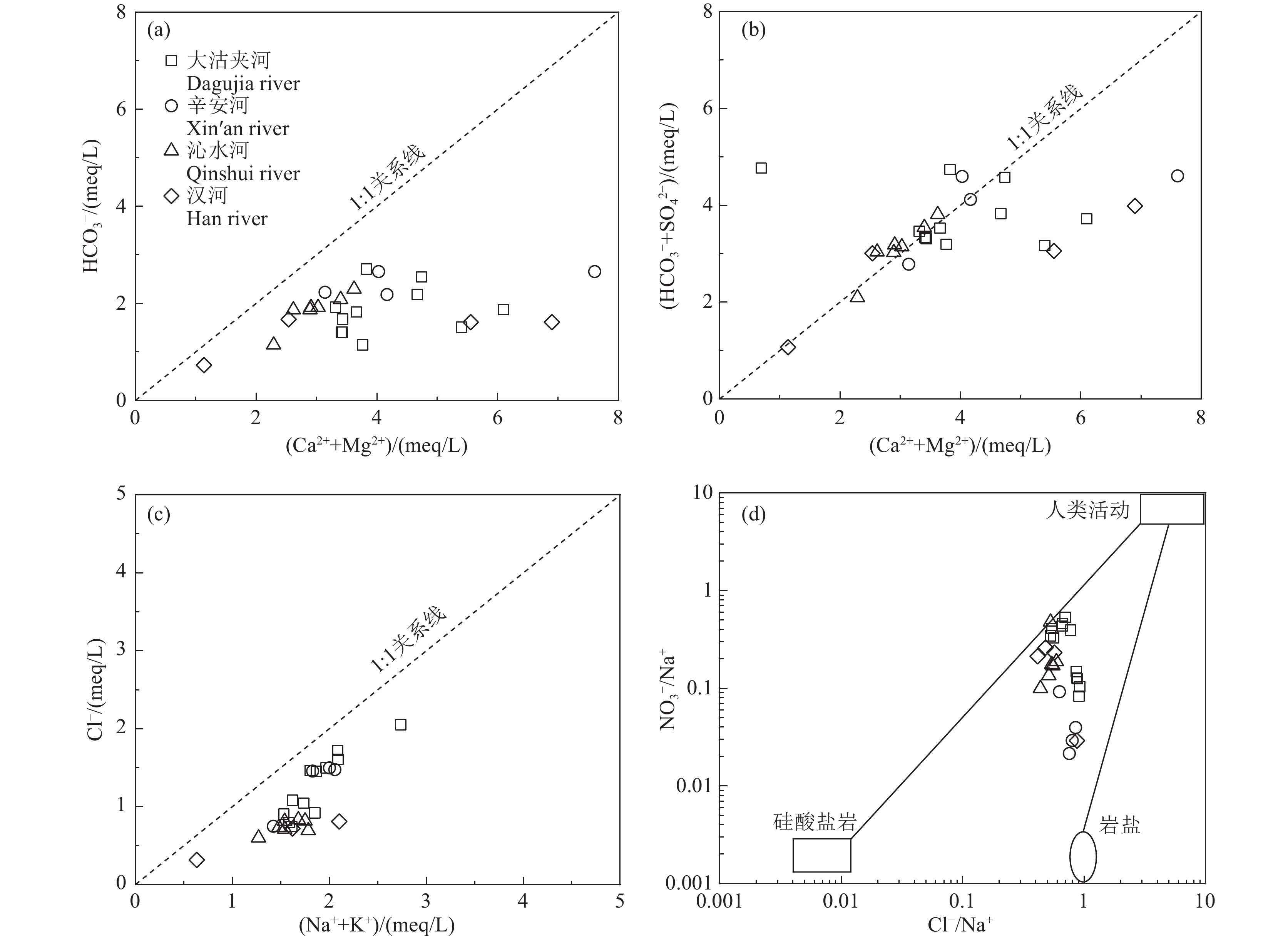
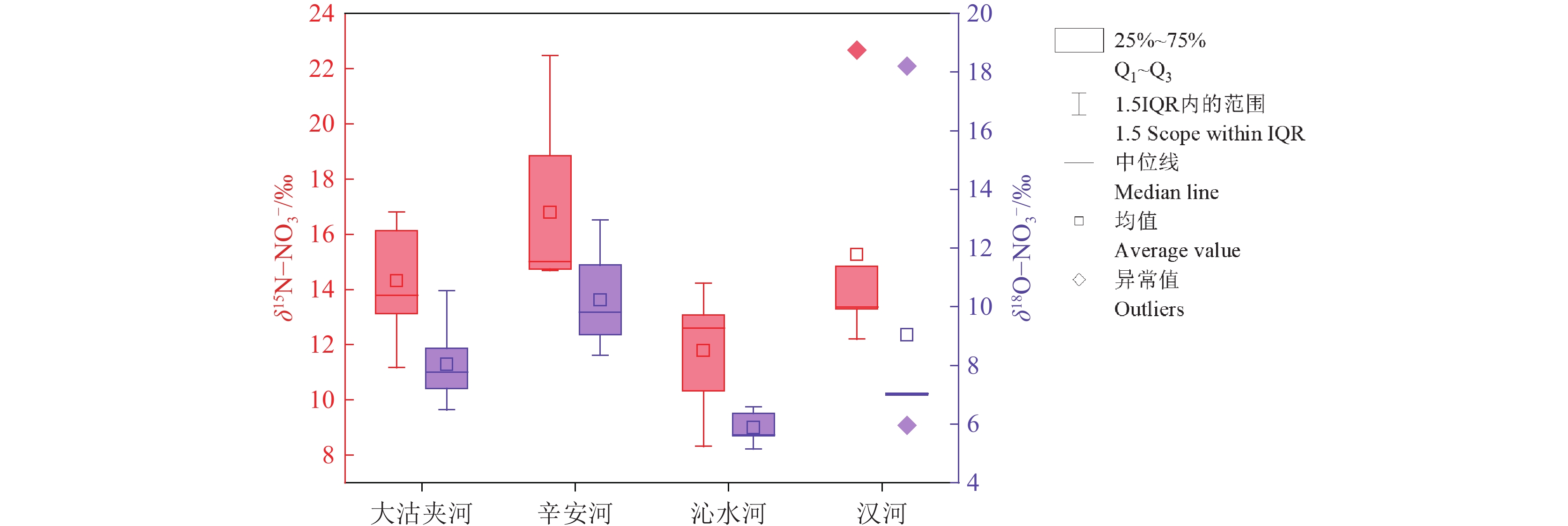
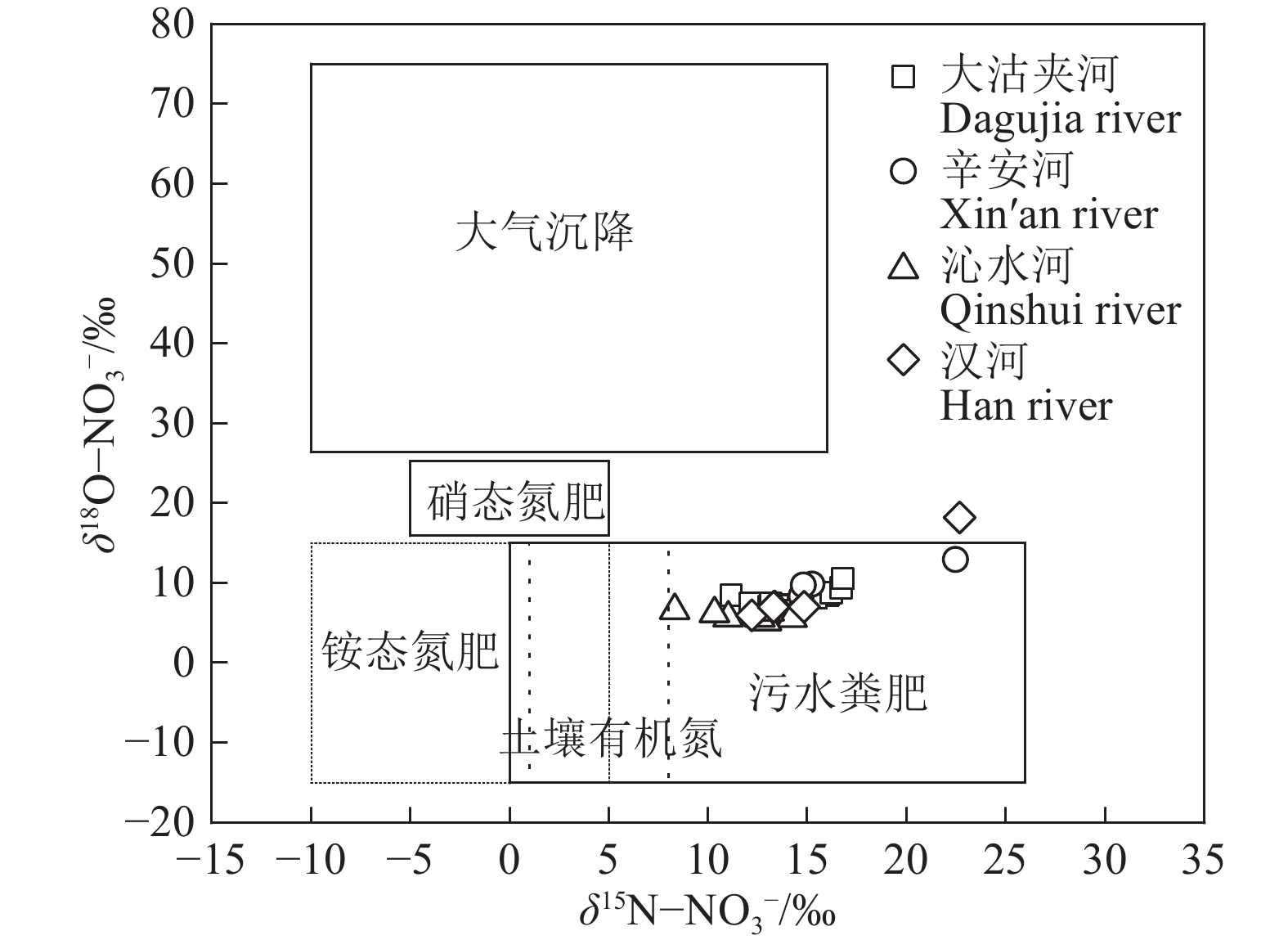
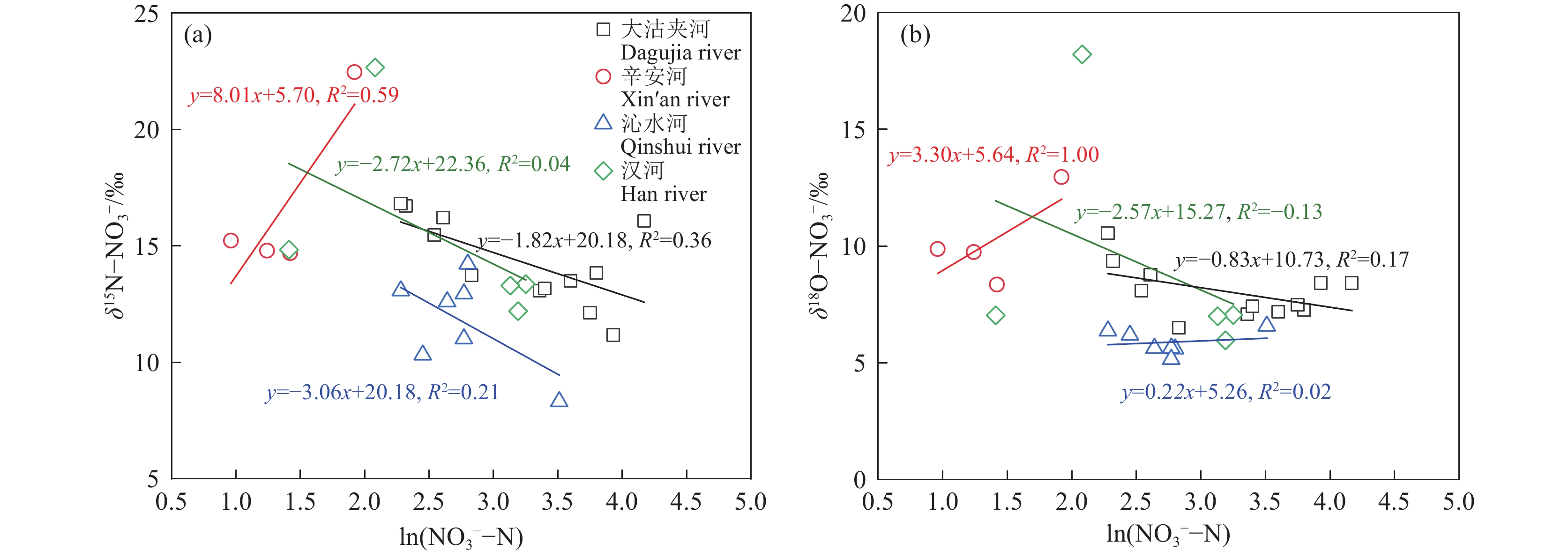
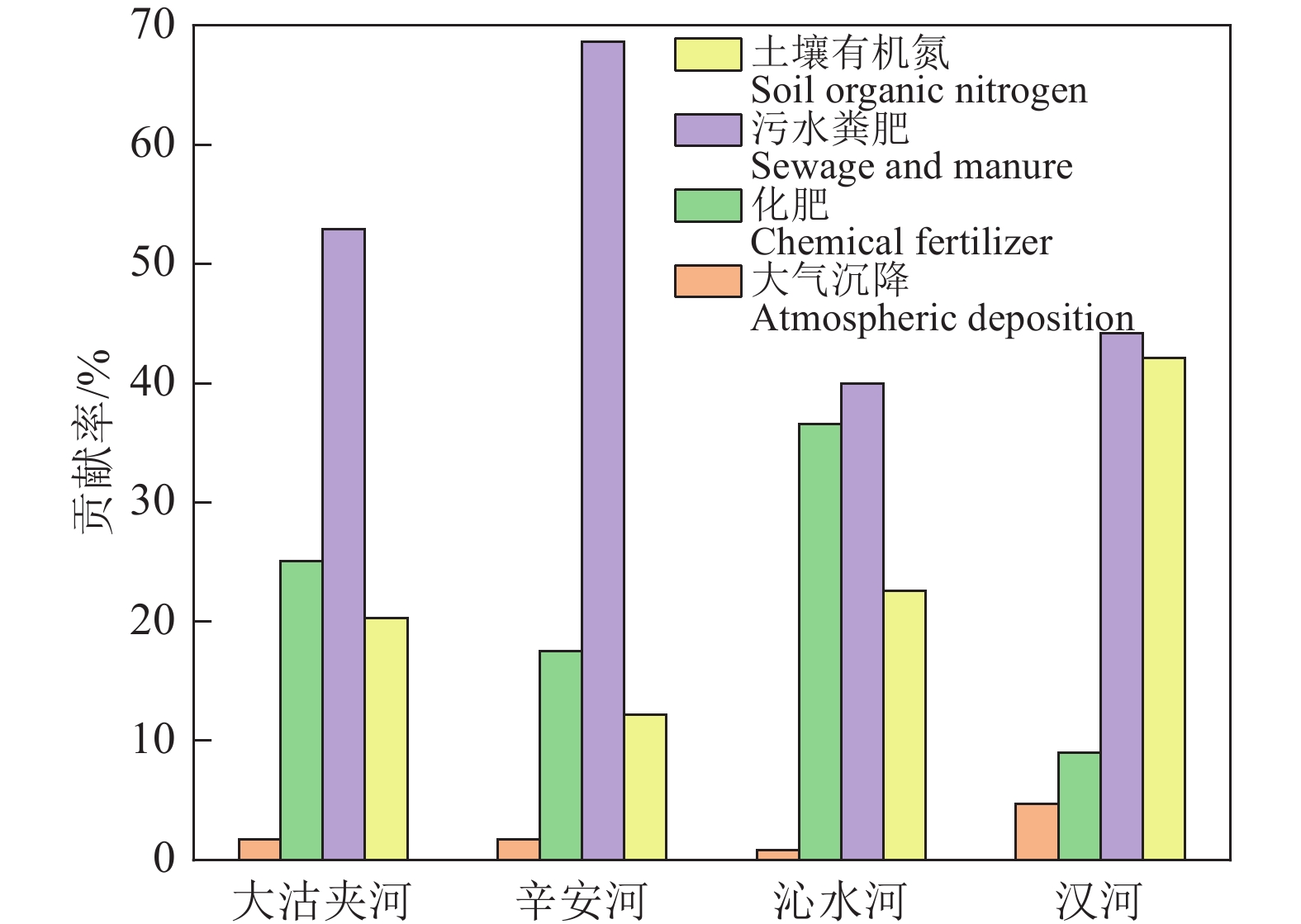
研究结果 (1)研究区地表水呈弱碱性,NO3−−N浓度远高于NH4+−N和NO2−−N浓度,为研究区地表水主要氮素污染物,仅辛安河NO3−−N浓度符合国家规定的生活饮用水卫生标准限值10 mg/L;(2)研究区地表水硝酸盐转化过程以硝化作用为主,反硝化作用不明显;(3)MixSIAR模型输出结果显示,研究区地表水各硝酸盐源的贡献率依次为污水粪肥(51.1%)>土壤有机氮(23.9%)>化肥(22.9%)>大气沉降(2.1%)。
结论 总体上,研究区地表水硝酸盐来源以污水粪肥贡献率最大,其次是土壤有机氮和化肥。人为输入产生的污水粪肥是研究区硝酸盐污染的主要来源,因此减少污水粪肥对各河流的排放是控制污染的关键。
Abstract:This paper is the result of environmental geological survey engineering.
Objective Nitrate pollution in surface water is a global environmental issue, therefore identifying the source and transformation of nitrate is fundamental to improving water quality.
Methods To accurately identify the sources and transformation processes of nitrate in surface water in north of Yantai city, hydrochemistry and dual isotopes of nitrate nitrogen−oxygen technologies were used to sample and analyze surface water from different river basins, including Dagujia River, Xin'an River, Qinshui River, and Han River. And the Bayesian isotopes mixing model MixSIAR was also used to calculate the contribution rates of various nitrate sources.
Results (1) The surface water in the study area is weakly alkaline, with NO3−−N concentration significantly higher than NH4+−N and NO2−−N concentrations, making NO3−−N is the primary nitrogen pollutant in the surface water of the study area. Only the NO3−−N concentration in Xin'an River (NO3−−N<10 mg/L) fell within the national health standard for drinking water. (2) Nitrification dominates the nitrate transformation process in the surface waters in the study area, while denitrification playing a negligible role. (3) The output results of the MixSIAR model show that the contribution rates of nitrate sources in surface water in the study area are as follows: sewage and manure (51.1%)>soil organic nitrogen (23.9%)>chemical fertilizer (22.9%)>atmospheric deposition (2.1%).
Conclusions Overall, sewage and manure have the highest contribution rate to nitrate sources in surface water in the study area, followed by soil organic nitrogen and chemical fertilizer. Sewage and manure from anthropogenic inputs are the main sources of nitrate pollution in the study area. Therefore, reducing discharge of sewage and manure into rivers is key to controlling pollution.
-

-
表 1 烟台北部地表水水化学参数及硝酸盐氮氧同位素组成
Table 1. Chemical parameters and nitrate isotopes of surface water in study area
河流 范围 pH TDS CODcr HCO3− SO42− Cl− Ca2+ Na+ Mg2+ K+ (NO3−−N) (NH4+−N) (NO2−−N) (δ15N−NO3−) (δ18O−NO3−) 大沽夹河
(n=12)最大值 9.2 254.0 8.00 292.0 114.0 72.6 138.0 61.1 40.0 9.37 64.7 0.363 1.530 16.81 10.54 最小值 7.5 54.0 0.80 69.8 74.0 26.3 37.6 31.4 13.3 3.07 9.7 0.009 0.081 11.17 6.49 中位数 8.8 91.5 4.90 112.5 90.1 44.9 49.0 37.2 18.5 7.13 29.4 0.085 0.495 13.79 7.77 平均值 8.6 136.3 4.70 126.9 89.5 45.1 59.7 39.0 20.4 7.01 30.1 0.118 0.593 14.32 8.04 标准差 0.5 74.8 2.19 56.7 10.9 14.1 28.5 7.6 6.4 2.0 17.3 0.100 0.480 1.80 1.09 辛安河
(n=4)最大值 8.6 79.0 6.72 162.0 93.7 53.1 116.0 44.9 22.1 9.0 6.8 0.113 1.910 22.47 12.96 最小值 8.1 20.0 3.04 133.0 26.5 26.5 40.2 27.4 13.8 4.1 2.6 0.017 0.080 14.69 8.35 中位数 8.2 50.5 3.40 149.0 93.2 52.0 47.5 41.3 21.0 4.7 3.8 0.030 0.118 15.02 9.81 平均值 8.3 50.0 4.14 148.3 76.7 45.9 62.8 38.7 19.5 5.6 4.3 0.047 0.556 16.80 10.23 标准差 0.2 23.6 1.50 13.8 29.0 11.2 30.9 6.8 3.3 2.0 1.6 0.039 0.780 3.28 1.69 沁水河
(n=7)最大值 7.8 71.0 4.64 140.0 72.8 29.5 48.0 36.5 14.9 9.3 33.5 0.271 1.430 14.23 6.58 最小值 7.1 24.0 1.12 69.8 45.6 21.2 30.2 26.0 9.5 5.4 9.8 0.021 0.072 8.32 5.15 中位数 7.5 59.0 3.68 117.0 58.9 26.0 38.3 31.9 12.4 6.4 16.0 0.119 0.108 12.61 5.63 平均值 7.5 55.3 3.52 114.1 60.0 26.3 38.8 32.3 12.5 6.8 16.8 0.112 0.306 11.79 5.88 标准差 0.2 13.8 1.03 20.1 8.5 2.8 5.6 3.2 1.7 1.2 7.2 0.077 0.461 1.87 0.47 汉河
(n=5)最大值 7.93 852.0 4.80 152.0 1701.0 13115.0 402.0 4811.0 955.0 394.0 25.8 0.180 1.430 22.67 18.21 最小值 7.47 67.0 0.32 44.4 16.3 11.2 14.5 12.8 5.0 2.9 4.1 0.060 0.089 12.20 5.96 中位数 7.86 190.5 2.40 98.4 69.4 28.7 76.9 45.0 14.6 5.7 22.9 0.110 0.488 13.36 7.03 平均值 7.74 325.0 2.40 99.0 393.0 2714.7 122.5 1039.0 204.7 85.7 17.0 0.120 0.587 15.27 9.05 标准差 0.19 308.4 1.43 34.1 654.7 5202.2 142.4 1888.7 375.3 154.3 9.1 0.044 0.457 3.79 4.60 注:pH无量纲,(δ15N−NO3−)、(δ18O−NO3−) 单位为‰,其余单位为mg/L。 表 2 硝酸盐来源氮、氧同位素组成
Table 2. Summary of the δ15N−NO3− and δ18O−NO3− values of various nitrate sources
来源 δ15N−NO3− δ18O−NO3− 文献 平均值±标准偏差 平均值±标准偏差 大气沉降 4.6±3.9 54±13.2 Ren et al., 2024 化肥 0.9±2.0 3.0±1.4 Mu et al., 2024 土壤有机氮 3.8±1.8 −2.7±4.4 Zhang et al., 2022 污水粪肥 11.5±1.2 5.6±1.4 Chen et al., 2023 -
[1] Adelana M S, Heaven W M, Dresel E P, Giri K, Holmberg M, Croatto G, Webb J. 2020. Controls on species distribution and biogeochemical cycling in nitrate−contaminated groundwater and surface water, southeastern Australia[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 726: 138426. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138426
[2] Biddau R, Dore E, Pelo S D, Lorrai M, Botti P, Testa M, Cidu R. 2023. Geochemistry, stable isotopes and statistic tools to estimate threshold and source of nitrate in groundwater (Sardinia, Italy)[J]. Water Research, 232: 119663. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2023.119663
[3] Chen Qiao, Dai Wei, Sun Lin, Song Zhaojun, Zhang Chunrong. 2016. Geo−chemical characteristic analysis of seawater mixture in estuary of Jiahe River, Yantai City, China[J]. Earth and Environment, 44(5): 534−541 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Chen R D, Hu Q H, Shen W Q, Guo J X, Yang L, Yuan Q Q, Lu X M, Wang L C. 2023. Identification of nitrate sources of groundwater and rivers in complex urban environments based on isotopic and hydro−chemical evidence[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 871: 162026. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162026
[5] Chen X, Jiang C L, Zheng L G, Dong X L Chen Y C, Li C. 2020. Identification of nitrate sources and transformations in basin using dual isotopes and hydrochemistry combined with a Bayesian mixing model: Application in a typical mining city[J]. Environmental Pollution, 267: 115651. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115651
[6] Ding Jingtao, Xi Beidou, Xu Qigong, Gao Rutai, Lu Yi, Huang Jian, Liu Hongliang. 2013. Application of stable isotope on nitrate pollution researches of surface water[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 25(5): 617−627 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18307/2013.0501
[7] Fan Zujin, Wei Xing, Zhou Yulin, Chen Meng’en, Shen Jiwei, Li Jiawen. 2023. Analysis of nitrate sources and transformation processes in shallow groundwater in typical mountainous agricultural area[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 36(10): 1946−1956 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Guo Linzhen, Xue Dongmei, Wang Zhongliang. 2016. Research progress of stable isotopes of nitrogen and oxygen in nitrate of surface water[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 44(10): 57−59, 91 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Guo Z F, Yan C Z, Wang Z S, Xu F F, Yang F. 2020. Quantitative identification of nitrate sources in a coastal peri−urban watershed using hydrogeochemical indicators and dual isotopes together with the statistical approaches[J]. Chemosphere, 243: 125364. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125364
[10] Hu J, Pan M Y, Han T H, Zhuang Z, Cao Y N, Yang K L, Li Y L, Liu W G. 2021. Identification of nitrate sources in the Jing River using dual stable isotopes, Northwest China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(48): 68633−68641. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-15380-6
[11] Kendall C, Elliot E M, Wankel S D. 2007. Chapter 12. Tracing Anthropogenic Inputs of Nitrogen to Ecosystems. Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science[M]. Blackwell PUB.
[12] Kim S H, Lee D H, Kim M S, Rhee H P, Hur J, Shin K H. 2023. Systematic tracing of nitrate sources in a complex river catchment: An integrated approach using stable isotopes and hydrological models[J]. Water Research, 235: 119755. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2023.119755
[13] Li Huanwei, Zhao Guangju, Li Ming, Mu Xingmin, Tian Peng. 2023. Identification of nitrate source of surface water in a typical peri−urban watershed in the tableland of the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Environmental Science, 44(2): 761−769 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Li Zhenghong, Li Yasong, Hao Qichen, Li Jianfeng, Zhu Yuchen. 2021. Characteristics, genesis and treatment measures of NO3 type groundwater in Xiamen, Fujian Province[J]. Geology in China, 48(5): 1441−1452 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Li Z W, Wang S L, Nie X D, Sun Y Z, Ran F W. 2022. The application and potential non−conservatism of stable isotopes in organic matter source tracing[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 838: 155946. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155946
[16] Lorette G, Sebilo M, Buquet D, Lastennet R, Denis A, Peyraube N, Charriere V, Studer J C. 2022. Tracing sources and fate of nitrate in multilayered karstic hydrogeological catchments using natural stable isotopic composition (δ15N−NO3− and δ18O−NO3−): Application to the Toulon karst system (Dordogne, France)[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 610: 127972. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127972
[17] Lu M, Yue F J, Wang X D, Liu Z H, Shi Z Y, Zhang P. 2023. Identify nitrogen transport paths and sources contribution in karst valley depression area using isotopic approach[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 337: 117751. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117751
[18] Matiatos I, Wassenaar L I, Monteiro L R, Venkiteswaran J J, Gooddy D C, Boeckx P, Sacchi E, Yue F J, Michalski G, Alonso−Hernandez C, Biasi C, Bouchaou L, Edirisinghe N V, Fadhullah W, Fianko J R, Garcia−Moya A, Kazakis N, Li S L, Luu M T N, Priyadarshanee S, Re V, Rivera D S, Romanelli A, Sanyal P, Tamooh F, Trinh D A, Walters W, Walters N. 2021. Global patterns of nitrate isotope composition in rivers and adjacent aquifers reveal reactive nitrogen cascading[J]. Communications Earth & Environment, 2(1): 52.
[19] Ma Zhaohu, Wang Lei, Wang Dongliang, Yu Long. 2012. Evaluation and analysis on the quality of the sea water adjacent to the Yantai Xin'an River estuary[J]. Ludong University Journal (Natural Science Edition), 28(4): 364−369 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Meng Zhilong, Yang Yonggang, Qin Zuodong, Jiao Wentao. 2017. Isotopic tracing for nitrate pollution process of water body in the lower reaches of Fenhe River[J]. China Environmental Science, 37(3): 1066−1072 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Mu J L, Ding S, Liu S M, Song G D, Ning X Y, Zhang X T, Xu W Q, Zhang H M. 2024. Multiple isotopes decipher the nitrogen cycle in the cascade reservoirs and downstream in the middle and lower Yellow River: Insight for reservoir drainage period[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 918: 170625. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170625
[22] Parnell A C, Inger R, Bearhop S, Jackson A L. 2010. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too much variation[J]. Plos One, 5(3): 9672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009672
[23] Pyrgaki K, Kelepertzis E, Argyraki A, Boeckx P, Botsou F, Dassenakis E. 2022. Identification of sources and transformations of nitrate in Cr(VI)−impacted alluvial aquifers by a hydrogeochemical and δ15N−NO3− and δ18O−NO3− isotopes approach[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(38): 57703−57719. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-19837-0
[24] Ren Kun, Pan Xiaodong, Peng Cong, Liang Jiapeng, Zeng Jie, Gan Mingwei, Zhang Hua, Wei Liangshuai. 2022. Identification of nitrate sources of groundwaters in the Zhaotong basin using hydrochemistry, nitrogen and oxygen isotopes and its impact on the environment[J]. Geology in China, 49(2): 409−419 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Ren X W, Yue F J, Tang J H, Li C, Li S L. 2024. Nitrate transformation and source tracking of rivers draining into the Bohai Sea using a multi−tracer approach combined with an optimized Bayesian stable isotope mixing model[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 463: 132901.
[26] Saka D, AduGyamfi J, Skrzypek G, Antwi E O, Heng L, TorresMartínez J A. 2023. Disentangling nitrate pollution sources and apportionment in a tropical agricultural ecosystem using a multi−stable isotopes model[J]. Environmental Pollution, 328: 121589. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121589
[27] Singh B, Craswell E. 2021. Fertilizers and nitrate pollution of surface and ground water: An increasingly pervasive global problem[J]. SN Applied Sciences, 3: 518. doi: 10.1007/s42452-021-04521-8
[28] Tao Lanchu, Cun Dexin, Tu chunlin, Ma Yiqi, Liu Zhennan, Yin Linhu, He Chengzhong, Pang Long, Zhang Qidao. 2023. Hydrochemical characteristics and control factors of surface water in Kuaize River basin at the upper Pearl River[J]. Environmental Science, 44(11): 6025−6037 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Wang Qibin, Tan Yang. 2020. Investigation and analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus content in surface water around Yantai in Shandong Province of China[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 26(12): 87−90 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Wang Shihui, Ma Yukun, Shen Zhenyao. 2021. Identification of nitrate source in receiving water with dual isotopes NO3− (δ15(N) and δ18(O))[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 57(1): 36−42 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Wang Youzhi. 2020. Study on comprehensive evaluation of geological environment quality based on analytic hierarchy process—Take the Dagu Clip River basin in Yantai City as an example[J]. Ground Water, 42(5): 161−163, 280 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Wei Yinghuai, Hu Minpeng, Chen Dingjiang. 2024. Nitrate pollution characteristics and its quantitative source identification of major river systems in China[J]. Environmental Science, 45(2): 755−767 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Xing Meng, Liu Weiguo. 2016. Nitrate source proportional contributions in the Chanhe and Bahe rivers—Using its isotopic ratios in combination with a Bayesian isotope mixing mode[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 7(1): 27−36 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Xue D M, Botte J, Baets B D, Accoe F, Nestler A, Taylor P, Cleemput O V, Berglund M, Boeckx P. 2008. Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface− and groundwater[J]. Water Research, 43(5): 1159−1170.
[35] Xu Qifeng, Xia Yun, Li Shujian, Wang Wanzhou, Li Zhi. 2023. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and source analysis of nitrate in surface water of Wuding River basin[J]. Environmental Science, 44(6): 3174−3183 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Xu Zhiwei, Zhang Xinyu, Ren Yufen, Sun Xiaomin, Wang Xiaoke, Wang Shengzhong. 2012. Spatial changes and sources of nitrate in Beijing urban ecosystem surface water[J]. Environmental Science, 33(8): 2569−2573 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Yang Yifan, Liu Yaojun, Tian Liang, Nie Xiaodong, Peng Bo, Li Zhongwu. 2024. Identification of nitrate source in polder surface water by nitrogen and oxygen isotopes[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 37(2): 326−335 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Zhang J, Cao M D, Jin M G, Huang X, Zhang Z X, Kang F X. 2022. Identifying the source and transformation of riverine nitrates in a karst watershed, North China: Comprehensive use of major ions, multiple isotopes and a Bayesian model[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 246: 103957. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2022.103957
[39] Zhang Xin, Zhang Yan, Bi Zhilei, Shan Zexuan, Ren Lijiang, Li Qi. 2020. Distribution and source analysis of nitrate in surface waters of China[J]. Environmental Science, 41(4): 1594−1606 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Zhang Yali, Zhang Yizhang, Zhang Yuan, Liu Xiangchao, Ma Shuqin, Tang Changyuan, Liu Sisi, Sun Lihui. 2014. Characteristics and potential sources of nitrate pollution in surface water and groundwater systems in Taizihe River basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco−Agriculture, 22(8): 980−986 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] 陈桥, 戴维, 孙琳, 宋召军, 张春荣. 2016. 烟台夹河河口海水混合过程的地球化学特征研究[J]. 地球与环境, 44(5): 534−541.
[42] 丁京涛, 席北斗, 许其功, 高如泰, 卢义, 黄健, 刘鸿亮. 2013. 稳定同位素技术在地表水硝酸盐污染研究中的应用[J]. 湖泊科学, 25(5): 617−627. doi: 10.18307/2013.0501
[43] 范祖金, 魏兴, 周育琳, 陈蒙恩, 申纪伟, 李佳文. 2023. 典型山地农业区浅层地下水硝酸盐来源及转化过程解析[J]. 环境科学研究, 36(10): 1946−1956.
[44] 郭林臻, 薛冬梅, 王中良. 2016. 地表水硝酸盐的氮氧稳定同位素研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 44(10): 57−59, 91.
[45] 李欢玮, 赵广举, 李明, 穆兴民, 田鹏. 2023. 黄土高塬沟壑区典型城郊流域地表水硝酸盐来源示踪[J]. 环境科学, 44(2): 761−769.
[46] 李政红, 李亚松, 郝奇琛, 李剑锋, 朱玉晨. 2021. 福建厦门市硝酸型地下水特征、成因及其治理措施建议[J]. 中国地质, 48(5): 1441−1452. doi: 10.12029/gc20210510
[47] 马兆虎, 王磊, 王东亮, 喻龙. 2012. 烟台市辛安河口邻近海域水质评价及分析[J]. 鲁东大学学报(自然科学版), 28(4): 364−369.
[48] 孟志龙, 杨永刚, 秦作栋, 焦文涛. 2017. 汾河下游流域水体硝酸盐污染过程同位素示踪[J]. 中国环境科学, 37(3): 1066−1072.
[49] 任坤, 潘晓东, 彭聪, 梁嘉鹏, 曾洁, 甘明伟, 张华, 魏良帅. 2022. 氮氧同位素和水化学解析昭通盆地地下水硝酸盐来源及对环境的影响[J]. 中国地质, 49(2): 409−419. doi: 10.12029/gc20220205
[50] 陶兰初, 寸得欣, 涂春霖, 马一奇, 刘振南, 尹林虎, 和成忠, 庞龙, 张七道. 2023. 珠江源块泽河流域地表水水化学特征及控制因素[J]. 环境科学, 44(11): 6025−6037.
[51] 王祺斌, 谭扬. 2020. 烟台周边地表水中氮磷含量状况调查与分析[J]. 天津农业科学, 26(12): 87−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6500.2020.12.022
[52] 王诗绘, 马玉坤, 沈珍瑶. 2021. 氮氧稳定同位素技术用于水体中硝酸盐污染来源解析方面的研究进展[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 57(1): 36−42.
[53] 王有智. 2020. 基于层次分析法的地质环境质量综合评价研究—以烟台市大沽夹河流域为例[J]. 地下水, 42(5): 161−163, 280.
[54] 韦英怀, 胡敏鹏, 陈丁江. 2024. 我国主要河流水系硝态氮污染特征及定量源解析[J]. 环境科学, 45(2): 755−767.
[55] 邢萌, 刘卫国. 2016. 浐河、灞河硝酸盐端元贡献比例—基于硝酸盐氮、氧同位素研究[J]. 地球环境学报, 7(1): 27−36. doi: 10.7515/JEE201601004
[56] 徐奇峰, 夏云, 李书鉴, 王万洲, 李志. 2023. 无定河流域地表水硝酸盐浓度的时空分布特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 44(6): 3174−3183.
[57] 徐志伟, 张心昱, 任玉芬, 孙晓敏, 王效科, 王升忠. 2012. 北京城市生态系统地表水硝酸盐污染空间变化及其来源研究[J]. 环境科学, 33(8): 2569−2573.
[58] 杨忆凡, 刘窑军, 田亮, 聂小东, 彭博, 李忠武. 2024. 氮氧同位素解析堤垸地表水硝酸盐来源[J]. 环境科学研究, 37(2): 326−335.
[59] 张鑫, 张妍, 毕直磊, 山泽萱, 任丽江, 李琦. 2020. 中国地表水硝酸盐分布及其来源分析[J]. 环境科学, 41(4): 1594−1606.
[60] 张亚丽, 张依章, 张远, 刘相超, 马淑芹, 唐常源, 刘思思, 孙丽慧. 2014. 太子河流域地表水和地下水硝酸盐污染特征及来源分析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 22(8): 980−986.
-




 下载:
下载: