THE APPLICATION OF MULTI-FREQUENCY GPR ANTENNA FOR IMAGING THE SHALLOW SUBSURFACE FEATURES IN THE YUSHU ACTIVE FAULT
-
摘要:
地质雷达技术具有操作性强、分辨率高、探测深度深、对地表环境无破坏和可重复探测等特点,在活断层探测中具有很大的优势。为验证综合多中心频率地质雷达天线探测活断层地下浅层结构效果,以民主村处发育的玉树活动断裂为研究对象,采用25 MHz、100 MHz、250 MHz和500 MHz中心频率的地质雷达天线对活断层浅层结构进行探测,并与探槽剖面进行效果对比。研究结果表明:低中心频率的地质雷达天线(25 MHz和100 MHz)可获取大范围内深度较深(约32 m)的活断层地下浅层结构的整体形态,从雷达图像上可识别出主断层分布范围、断层倾向及地下浅层结构等;而中高中心频率的地质雷达天线(250 MHz和500 MHz)则可获取局部范围内深度较浅(约3 m)的地下浅层结构,尤其是500 MHz天线。探测结果与地表构造地貌形态和探槽剖面地质构造一致,表明综合多中心频率地质雷达天线探测玉树活动断裂浅层结构的有效性和适用性,为活断层研究提供多尺度数据及方法支持。
Abstract:Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) has the characteristics of strong operability, high resolution, deep detection depth, no damage to the surface environment and repeatable detection, so it is widely-used in active fault detection. In order to assess the effects of GPR for imaging the shallow subsurface geometry in active fault, the 25 MHz, 100 MHz, 250 MHz and 500 MHz GPR frequency antenna were firstly conducted on the Minzhu site of the Yushu active fault zone for the fault detecting. Moreover, the multi-frequency GPR profiles were compared with the three trench section, which were excavated by the previous researches. The research results show that:the low GPR frequencies (25 MHz and 100 MHz) were applied to delineate an excellent general view of deformation zones at a much wider area and greater depth (up to 32 m). The distribution and the direction of the active fault and the horst structure can be deduced on the GPR profiles. The high GPR frequencies (250 MHz and 500 MHz) provided more detailed analysis of the shallow subsurface geometry within 3 m depth. The GPR results are consistent with the surface morphology and trench wall, and the result show that multi-frequency GPR antenna is valuable for imaging the shallow subsurface geometry of the Yushu acive fault, and also provide multi-scale data and method for active fault study.
-
Key words:
- GPR /
- the Yushu active fault /
- multi-frequency antenna /
- subsurface geometry
-

-
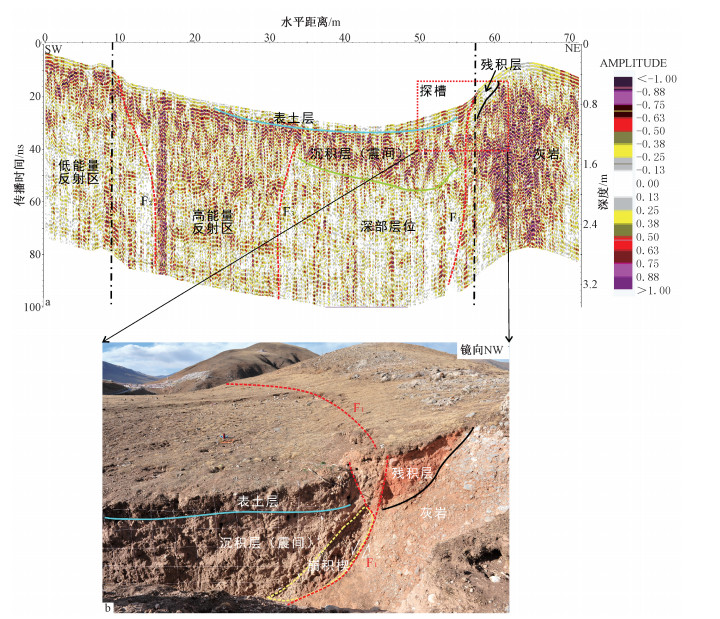
表 1 地质雷达剖面位置及天线采集参数
Table 1. The location and acquisition parameters of different GPR antennas
GPR测线剖面 开始位置经度/维度 结束位置经度/维度 剖面长度/m 天线类型 天线频率/MHz 道间距/m 时间窗口/纳秒 测线1 32.9871°/96.9990° 32.9886°/96.9998° 140 RTA 25 0.3 1750 测线2 32.9879°/96.9993° 32.9883°/97.0000° 71 RTA 100 0.1 553 测线3 32.9879°/96.9993° 32.9883°/97.0000° 71 屏蔽天线 250 0.05 160 测线4 32.9879°/96.9993° 32.9883°/97.0000° 71 屏蔽天线 500 0.02 80 -
邓起东, 陈立春, 冉勇康.活动构造定量研究与应用[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(4): 383-392. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.04.005
DENG Qidong, CHEN Lichun, RAN Yongkang. Quantitative studies and applications of active tectonics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(4): 383-392. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.04.005
李海兵, 司家亮, 潘家伟, 等.活动断裂的变形特征及其大地震复发周期的估算[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(12): 1968-1991. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.12.003
LI Haibing, SI Jialiang, PAN Jiawei, et al. Deformation feature of active fault and recurrence intervals estimation of large earthquake[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(12): 1968-1991. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.12.003
张培震, 邓起东, 张竹琪, 等.中国大陆的活动断裂、地震灾害及其动力过程[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2013, 43(10): 1607-1620. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201310005
ZHANG Peizhen, DENG Qidong, ZHANG Zhuqi, et al. Active faults, earthquake hazards and associated geodynamic processes in continental China[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2013, 43(10): 1607-1620. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201310005
吴中海.活断层的术语、研究进展及问题思考[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2018, 40(6): 706-726. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2018.06.002
WU Zhonghai. Active faults: Terminology, research advances, and thinking on some problems[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2018, 40(6): 706-726. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2018.06.002
邓起东.中国活动构造研究的进展与展望[J].地质论评, 2002, 48(2): 168-177. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2002.02.007
DENG Qidong. Advances and overview on researches of active tectonics in China[J]. Geological Review, 2002, 48(2): 168-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2002.02.007
朱坤静, 彭远黔, 周月玲.宁河-昌黎断裂基于浅层地震勘探资料研究[J].地震工程学报, 2019, 41(5): 1242-1250. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2019.05.1242
ZHU Kunjing, PENG Yuanqian, ZHOU Yueling. Research on the Ninghe-Changli fault based on data from shallow seismic exploration[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2019, 41(5): 1242-1250. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2019.05.1242
徐良鑫, 卞菊梅, 呼楠, 等.骊山山前断裂华清池以西段晚更新世以来的活动性[J].地震地质, 2019, 41(3): 561-575. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.03.002
XU Liangxin, BIAN Jumei, HU Nan, et al. The activity of western Lishan fault since the late Pleistocene[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2019, 41(3): 561-575. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.03.002
王志鹏, 刘江平, 易磊. 2D、3D高密度电法探测断层效果及其应用[J].科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(25): 75-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.25.011
WANG Zhipeng, LIU Jiangping, YI Lei. Effect and application of 2D and 3D high density resistivity method for fault detection[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(25): 75-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.25.011
CARBONEL D, RODRÍGUEZ-TRIBALDOS V, GUTIÉRREZ F G, et al. Investigating a damaging buried sinkhole cluster in an urban area (Zaragoza city, NE Spain) integrating multiple techniques: Geomorphological surveys, DInSAR, DEMs, GPR, ERT, and trenching[J]. Geomorphology, 2015, 229: 3-16. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.02.007
李征西, 曾昭发, 李恩泽, 等.地球物理方法探测活动断层效果和方法最佳组合分析[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2005, 35(S1): 109-114.
LI Zhengxi, ZENG Zhaofa, LI Enze, et al. The function of geophysical method in active fault detection and discuss of combining methods[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2005, 35(S1): 109-114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
刘澜波, 钱荣毅.探地雷达:浅表地球物理科学技术中的重要工具[J].地球物理学报, 2015, 58(8): 2606-2617. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkxxk201001003
LIU Lanbo, QIAN Rongyi. Ground penetrating radar: a critical tool in near-surface geophysics[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(8): 2606-2617. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkxxk201001003
张迪, 李家存, 吴中海, 等.地质雷达在活动断裂探测中的应用与进展[J].地质力学学报, 2016, 22(3): 733-746. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.03.027 http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20160327&journal_id=dzlxxb
ZHANG Di, LI Jiacun, WU Zhonghai, et al. Application and progress of ground penetrating radar in active fault detection[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 22(3): 733-746. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.03.027 http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20160327&journal_id=dzlxxb
MAURYA D M, CHOWKSEY V, TIWARI P, et al. Tectonic geomorphology and neotectonic setting of the seismically active South Wagad Fault (SWF), Western India, using field and GPR data[J]. Acta Geophysica, 2017, 65(6): 1167-1184. doi: 10.1007/s11600-017-0099-5
LUNINA O V, GLADKOV A S, GLADKOV A A. Surface and shallow subsurface structure of the Middle Kedrovaya paleoseismic rupture zone in the Baikal Mountains from geomorphological and ground-penetrating radar investigations[J]. Geomorphology, 2019, 326: 54-67. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.03.009
LIBERTY L M, HEMPHILL-HALEY M A, MADIN I P. The Portland Hills Fault: uncovering a hidden fault in Portland, Oregon using high-resolution geophysical methods[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 368(1-4): 89-103. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(03)00152-5
李建军, 张军龙.探地雷达在探测隐伏活动断层中的应用[J].地震, 2015, 35(4): 83-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2015.04.009
LI Jianjun, ZHANG Junlong. Application of GPR in surveying underlied active faults[J]. Earthquake, 2015, 35(4): 83-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2015.04.009
YAL#199;INER C Y, ALTUNEL E, BANO M, et al. Application of GPR to normal faults in the Büyük Menderes Graben, western Turkey[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 2013, 65: 218-227. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2012.05.011
ANCHUELA P, LAFUENTE P, ARLEGUI L, et al. Geophysical characterization of buried active faults: the Concud Fault (Iberian Chain, NE Spain)[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2016, 105(8): 2221-2239. doi: 10.1007/s00531-015-1283-y
ANDERSON K B, SPOTILA J A, HOLE J A. Application of geomorphic analysis and ground-penetrating radar to characterization of paleoseismic sites in dynamic alluvial environments: an example from southern California[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 368(1-4): 25-32. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(03)00148-3
张迪, 李家存, 吴中海, 等.探地雷达在探测玉树走滑断裂带活动性中的初步应用[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(1): 204-216. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.01.016
ZHANG Di, LI Jiacun, WU Zhonghai, et al. A preliminary application of ground penetrating radar to the detection of active faults along Yushu strike-slip faulted zone[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(1): 204-216. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.01.016
ERCOLI M, PAUSELLI C, FRIGERI A, et al. "Geophysical paleoseismology" through high resolution GPR data: a case of shallow faulting imaging in Central Italy[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2013, 90: 27-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2012.12.001
DUJARDIN J R, BANO M, SCHLUPP A, et al. GPR measurements to assess the Emeelt active fault's characteristics in a highly smooth topographic context, Mongolia[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2014, 198(1): 174-186. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggu130
LUNINA O V, GLADKOV A S, AFONKIN A M, et al. Deformation style in the damage zone of the Mondy fault: GPR evidence (Tunka basin, southern East Siberia)[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2016, 57(9): 1269-1282. doi: 10.1016/j.rgg.2016.08.012
CHRISTIE M, TSOFLIAS G P, STOCKLI D F, et al. Assessing fault displacement and off-fault deformation in an extensional tectonic setting using 3-D ground-penetrating radar imaging[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2009, 68(1): 9-16. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=25073fdcb997fce86d4bbaca024b84e9
ERCOLI M, PAUSELLI C, FRIGERI A, et al. 3-D GPR data analysis for high-resolution imaging of shallow subsurface faults: the Mt Vettore case study (Central Apennines, Italy)[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2014, 198(1): 609-621. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggu156
AZIZ A S, STEWART R R, GREEN S L, et al. Locating and characterizing burials using 3D ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) at the historic Mueschke Cemetery, Houston, Texas[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2016, 8: 392-405. doi: 10.1016/j.jasrep.2016.06.035
张迪, 吴中海, 李家存, 等.利用地面激光与地质雷达综合探测活断层浅层三维结构:以川西理塘毛垭坝盆地北缘正断层为例[J].地震地质, 2019, 41(2): 377-399. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.02.008
ZHANG Di, WU Zhonghai, LI Jiacun, et al. The delineation of three-dimensional shallow geometry of active fault based on TLS and GPR: a case study of an normal fault on the north margin of Maoyaba basin in Litang, western Sichuan province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2019, 41(2): 377-399. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.02.008
崔国柱, 李恩泽, 曾昭发.活动断层与地球物理方法[J].世界地质, 2003, 22(2): 185-190. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2003.02.016
CUI Guozhu, LI Enze, ZENG Zhaofa. Active fault and geophysical methods[J]. Global Geology, 2003, 22(2): 185-190. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2003.02.016
薛建, 黄航, 张良怀.探地雷达方法探测与评价长春市活动断层[J].物探与化探, 2009, 33(1): 63-66. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht200901017
XUE Jian, HUANG Hang, ZHANG Lianghuai. The application of the GPR method to detecting and estimating active faults in Changchun[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(1): 63-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht200901017
侯卫生, 陈国能, 庄文明, 等.西淋岗第四系断层探测及活动性评价[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(3): 925-931. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201103045
HOU Weisheng, CHEN Guoneng, ZHUANG Wenming, et al. Detection and activity estimation of quaternary fault in Xilingang Area[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(3): 925-931. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201103045
尹艳广, 施炜, 公王斌, 等.地质雷达探测技术在浅覆盖活动构造区填图中的应用:以宁夏青铜峡地区1:5万新构造与活动构造区填图为例[J].地质力学学报, 2017, 23(2): 214-223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.02.004 http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20170204&journal_id=dzlxxb
YIN Yanguang, SHI Wei, GONG Wangbin, et al. The application of Ground penetrating radar technology in geological mapping of shallow covered active tectonics region: a case study of 1: 50000 mapping of neotectonic zone and active tectonic zone in Qingtongxia area, Ningxia[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(2): 214-223. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.02.004 http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20170204&journal_id=dzlxxb
JOL H M. Ground penetrating radar theory and applications[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science, 2009.
曾昭发, 刘四新, 冯晅, 等.探地雷达原理与应用[M].北京:电子工业出版社, 2010.
ZENG Zhaofa, LIU Sixin, FENG Xuan, et al. The principle and application of ground penetrating radar[M]. Beijing: Electronics Industry Press, 2010. (in Chinese)
周荣军, 马声浩, 蔡长星.甘孜-玉树断裂带的晚第四纪活动特征[J].中国地震, 1996, 12(3): 250-260.
ZHOU Rongjun, MA Shenghao, CAI Changxing. Late quaternary active features of the Ganzi-Yushu Fault Zone[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 1996, 12(3): 250-260. (in Chinese with English abstract)
闻学泽, 徐锡伟, 郑荣章, 等.甘孜-玉树断裂的平均滑动速率与近代大地震破裂[J].中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(S1): 199-208. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd2003z1022
WEN Xueze, XU Xiwei, ZHENG Rongzhang, et al. Average slip-rate and recent large earthquake ruptures along the Garzê-Yushu fault[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2003, 46(S2): 276-288. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd2003z1022
李跃华, 吴中海, 叶培盛, 等.玉树断裂带左旋走滑活动标志及其几何学与运动学特征[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(9): 1410-1422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.09.010
LI Yuehua, WU Zhonghai, YE Peisheng, et al. The geomorphologic and geological marks of the active left-lateral strike-slip fault and the characteristics of geometry and kinematics along the Yushu fault zone in southeastern Tibet[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(9): 1410-1422. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.09.010
赵根模, 吴中海, 刘杰, 等.印度-欧亚板块碰撞变形区的大地震时空分布特征与迁移规律[J].地质力学学报, 2019, 25(3): 324-340. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190303&journal_id=dzlxxb
ZHAO Genmo, WU Zhonghai, LIU Jie, et al. The time space distribution characteristics and migration law of large earthquakes in the Indiam-Eurasian plate collision deformation area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(3): 324-340. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190303&journal_id=dzlxxb
闻学泽, 黄圣睦, 江在雄.甘孜-玉树断裂带的新构造特征与地震危险性估计[J].地震地质, 1985, 7(3): 23-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HY000001825567
WEN Xueze, HUANG Shengmu, JIANG Zaixiong. Neotectonic features of the Ganzi-Yushu fault zone and assessment of its earthquake risk[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1985, 7(3): 23-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HY000001825567
吴中海, 龙长兴, 范桃园, 等.青藏高原东南缘弧形旋扭活动构造体系及其动力学特征与机制[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(1):1-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.01.002
WU Zhonghai, LONG Changxing, FAN Taoyuan, et al. The arc rotational-shear active tectonic system on the southeastern margin of Tibetan Plateau and its dynamic characteristics and mechanism[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(1):1-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.01.002
周荣军, 闻学泽, 蔡长星, 等.甘孜-玉树断裂带的近代地震与未来地震趋势估计[J].地震地质, 1997, (2): 115-124.
ZHOU Rongjun, WEN Xunze, CHAI Changxing, et al. Recent earthquakes and assessment of seismic tendency on the Ganzi-Yushu Fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1997, (2): 115-124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
中国地震局灾害防御司.中国近代地震目录(公元1912年-1990年Ms≥4.7)[M].北京:中国科学技术出版社, 1999.
Disaster Prevention Division, China Earthquake Administration.China's modern earthquake catalog (From AD1912-AD1990 Ms≥4.7)[M]. Beijing:China Scientific and Technical Press, 1999. (in Chinese)
石学录, 姚家骏, 张博. 2010年玉树地震序列ML≥4.0事件震源机制解特征分析[J].地震工程学报, 2017, 39(1): 112-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2017.01.0112
SHI Xuelu, YAO Jiajun, ZHANG Bo. Focal mechanism solution analysis of ML≥4.0 earthquakes in the 2010 Yushu Earthquake sequence[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2017, 39(1): 112-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2017.01.0112
吴中海, 周春景, 冯卉, 等.青海玉树地区活动断裂与地震[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(4): 419-469. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.04.003
WU Zhonghai, ZHOU Chunjing, FENG Hui, et al. Active faults and earthquake around Yushu in eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(4): 419-469. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.04.003
李家存, 吴中海, 张铎, 等.青海玉树地区主要活动断裂的遥感影像解译及构造活动性[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(4): 535-550. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.04.010
LI Jiacun, WU Zhonghai, ZHANG Duo, et al. Remote sensing image interpretation and tectonic activity study of the main active faults in Yushu area, Qinghai Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(4): 535-550. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.04.010
BUSBY J P, MERRITT J W. Quaternary deformation mapping with ground penetrating radar[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 1999, 41(1): 75-91. doi: 10.1016/S0926-9851(98)00050-0
MAURYA D M, CHOUKSEY V, JOSHI P N, et al. Application of GPR for delineating the neotectonic setting and shallow subsurface nature of the seismically active Gedi Fault, Kachchh, western India[J]. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 2013, 10(3): 034006. doi: 10.1088/1742-2132/10/3/034006
-




 下载:
下载: