Pan-lake during the late Pleistocene in the source area of the Yellow River and its significance
-
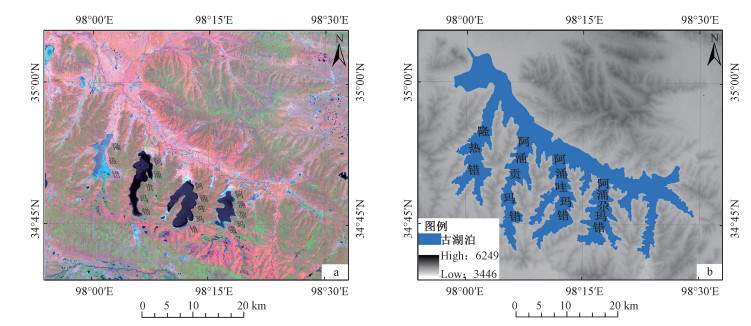
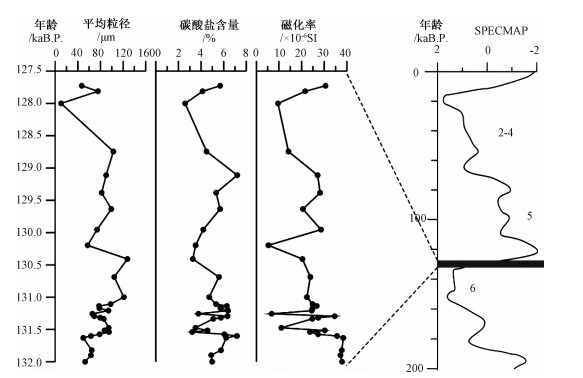
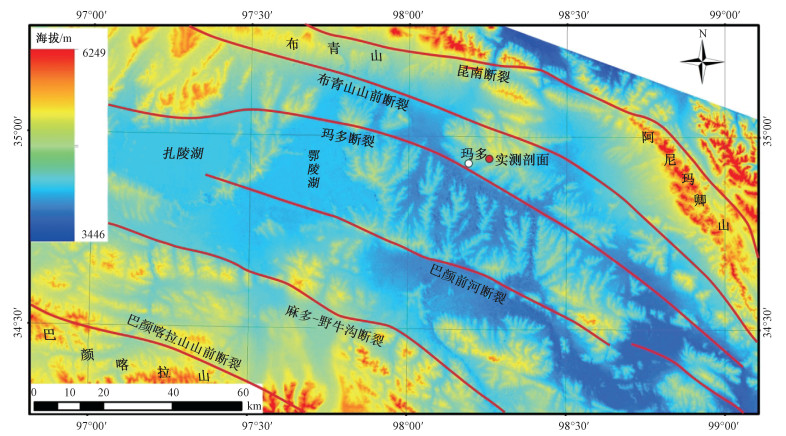
摘要: 通过青海玛多湖相地层剖面沉积特征,结合ESR样品年代测试结果,分析认为黄河源地区在13万年左右的晚更新世时期发生过湖泛事件。湖泛时期,玛多"四姐妹湖"相互连通,形成一个面积巨大的湖泊,约是现今"四姐妹湖"总面积的4.1倍。玛多地区此次湖泛事件与深海氧同位素MIS 6(Marine isotope stages 6)向MIS 5(Marine isotope stages 5)转变时期相对应,显示出青藏高原气候变化与全球气候变化密切相关,然而黄河源地区湖相地层对全球气候变化反应更敏感,记录的气候转换时间早于其他地区。玛多剖面湖相地层剖面沉积物的粒度、碳酸盐、磁化率分析表明,在132±10~128±12 ka年间,黄河源地区湖相沉积可分为9个阶段,表明青藏高原在MIS 6向MIS 5转变时期的气候变化是一个波动上升过程。13万年左右,黄河源地区大面积的湖相地层结束沉积,认为由于青藏高原共和运动,下游的多石峡被切开,湖水突然外泄所形成。Abstract: According to the sedimentary characteristics and the results of ESR dating of the lacustrine strata profile in Maduo County, Qinghai Province, the pan-lake event had occurred in the source area of the Yellow River during the late Pleistocene period at about 130 kaB.P.. During the pan-lake period, the four lakes in Maduo County connected with each other, and formed one huge lake whose area was 4.1 times bigger than the total area of the present four lakes. The pan-lake event in the Maduo area coincided with the transition of deep sea oxygen isotope from MIS 6 to MIS 5, which shows that the climate change on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is closely related to the global climate change. As the lacustrine strata in the source area of the Yellow River were more sensitive to the global climate change, it recorded the climate change earlier than other areas did. The analysis of the grain size, carbonate and magnetic susceptibility of the sediments in the Maduo lacustrine strata profile shows 9 stages of the lacustrine sediments during the period of 132±10~128±12 ka, indicating a fluctuating and rising process of climate change on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in transition from MIS 6 to MIS 5. A large area of lacustrine sedimentation in the source area of the Yellow River ended at about 130 kaB.P. This may be the result of the regional tectonic activities of Gonghe Movement which cut through the Duoshixia gorge in the lower reaches, causing a suddenly leak out of the lake water.
-

-
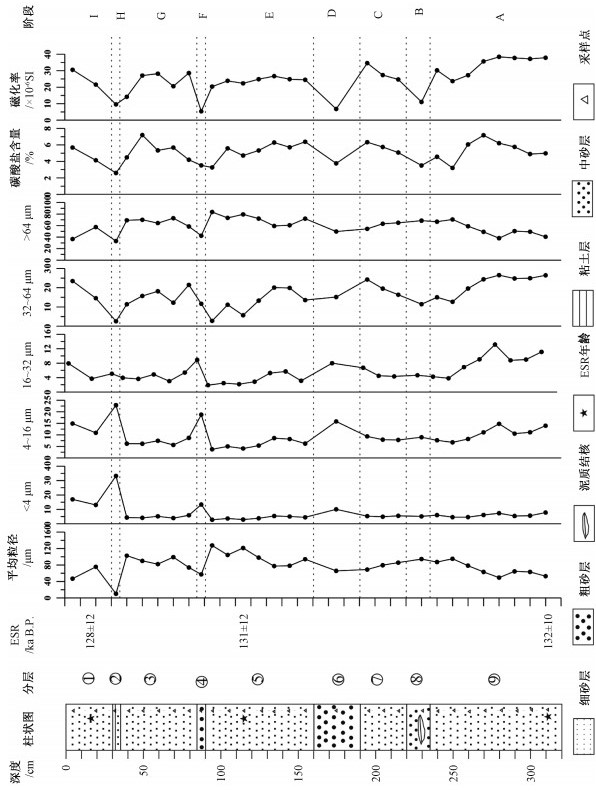
上覆:表土层 0.30~0.40 m ①褐红色细砂层 30 cm ②褐红色中砂层,中夹小砾石 5 cm ③褐红色细砂层 50 cm ④褐黄色含砾中粗砂层,砾石呈薄片状 5 cm ⑤褐黄色含砾细砂层,夹铁锈色条带,见水平层理、斜层理,产状250°∠30° 70 cm ⑥褐红色含砾粗砂层,砾石棱角状、次棱角状,大小在0.5~1 cm 30 cm ⑦褐红色含细砾细砂层,砾石砾径约2 mm左右 30 cm ⑧灰白色含砾中砂层,中含粗砂层透镜体,砾石薄片状,见交错层理 15 cm ⑨褐红色细砂层,夹青灰色条带,局部见砂包泥现象,含螺化石 85 cm ———未见底——— 表 1 黄河源地区玛多剖面湖相沉积物ESR测年结果
Table 1. ESR dating of lacustrine sediments of the Maduo profile, the source area of the Yellow River
样品编号 深度/cm 古剂量/Gy 年剂量/mGy 年龄/kaB.P. 2010P1-3ESR/B18 60 295.4 2.301 128±12 2010P1-2ESR/B17 130 367.7 2.813 131±12 2010P1-1ESR/B16 320 750.4 5.671 132±10 注:由成都理工大学ESR实验室梁兴中教授测定 表 2 黄河源地区玛多剖面岩性与中值粒径、磁化率、碳酸盐含量变化
Table 2. Variations of median particle diameter, susceptibility and carbonate content with lithology in lacustrine strata of Maduo county, the source area of the Yellow River
分段 深度/cm 岩性 中值粒径/μm 磁化率/×10-6 SI 碳酸盐含量/% I 0~30 褐红色细砂层 49.44~95.10 23.68~38.42 3.21~7.18 H 30~35 褐红色中砂层 94.49~94.49 11.03~11.03 3.51~3.51 G 35~85 褐红色细砂层 68.93~85.81 24.72~34.60 5.08~6.33 F 85~90 褐黄色含砾中粗砂层 65.73~65.73 6.77~6.77 3.76~3.76 E 90~160 褐黄色含砾细砂层 77.48~127.66 20.37~26.71 3.27~6.38 D 160~190 褐红色含砾粗砂层 57.20~57.20 5.33~5.33 3.52~3.52 C 190~220 褐红色含细砾细砂层 74.00~102.73 14.17~28.59 4.20~7.20 B 220~235 灰白色含砾中砂层 10.31~10.31 9.57~9.57 2.59~2.59 A 235~320 褐红色细纱层 46.89~75.60 21.58~30.56 4.14~5.69 -
BARD E, HAMELIN B, FAIRBANKS R G, 1990. U/Th ages obtained by mass spectrometry in corals from Barbados[J]. Chemical Geology, 84(1-4):157-158. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(90)90196-E
BLUSZCZ A, GOSLAR T, HERCMAN H, et al., 1988. Comparison of TL, ESR and 14C dates of speleothems[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 7(3-4):417-421. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(88)90039-X
CAI M T, YE P S, YANG X C, et al., 2018. Evolution of sedimentary environment in the North Hetao Basin since 344ka[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(2):253-262. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb201802013
CAMPBELL C, 1998. Late Holocene lake sedimentology and climate change in southern Alberta, Canada[J]. Quaternary Research, 49(1):96-101. doi: 10.1006/qres.1997.1946
CHEN J A, WAN G J, 1999. Sediment particle size distribution and its environmental significance in Lake Erhai, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 19(2):175-182. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwxb199902008
CHEN J A, WAN G J, HUANG R G, 1999. Study of sediment particle sizes in lake Chenghai, Yunnan province[J]. Advances in Environmental Science, 7(4):76-82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN J A, WAN G J, TANG D G, et al., 2000. Recent climate changes recorded by sediment grain sizes and isotopes in Erhai Lake[J]. Progress in Natural Sciences, 10(3):253-259. (in Chinese) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJY200001009.htm
CHENG J, JIANG M Z, ZAN L H, et al., 2005. Progress in research on the quaternary geology in the source area of the Yellow River[J]. Geoscience, 19(2):239-246. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz200502012
CHENG J, ZHANG X J, TIAN M Z, et al., 2006. Quaternary geology and ecological environment in the source area of the Yellow River[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House:1-193. (in Chinese)
CHENG S P, DENG Q D, MIN W, et al., 1998. Yellow river and quaternary tectonic movements of the Ordos Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences(3):238-248. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1046-j.1365-3121.2002.00350.x/
DING Z L, SUN J M, LIU D S, 1999. A sedimentological proxy indicator linking changes in loess and deserts in the Quaternary[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 42(2):146-152. doi: 10.1007/BF02878513
GASSE F, ARNOLD M, FONTES J C, et al., 1991. A 13, 000-year climate record from western Tibet[J]. Nature, 353(6346):742-745. doi: 10.1038/353742a0
HAN J E, YU J, ZHU D G, et al., 2011. The palaeoenvironmental evolution of the Yellow River headwater basin in Qinghai Province since Early Pleistocene[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(12):1941-1949. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201112019
HAN J E, YU J, SHAO Z G, et al., 2013a. Fluvio-lacustrine facies sedimentary stratigraphy of Yellow River source during late cenozoic and its environment[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House:1-134. (in Chinese)
HAN J E, SHAO Z G, ZHU D G, et al., 2013b. Characteristics of river terraces and formation of the Yellow River in the source region of Yellow River[J]. Geology in China, 40(5):1531-1541. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201305018
HAN J E, ZHU D G, YU J, et al., 2013c. Characteristics of environmental proxies of lacustrine stratum in Youyun and the reflection of Paleoenvironmental changes in Yellow River source region[J]. Geoscience, 27(2):269-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz201302004
HIRONS K R, THOMPSON R, 1986. Palaeoenvironmental application of magnetic measurements from Inter-Drumlin Hollow Lake sediments near Dungannon, Co. Tyrone, Northern Ireland[J]. Boreas, 15(2):117-135. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1111-j.1502-3885.1986.tb00075.x/
HU S Y, WANG S M, APPEL E, et al., 2000. Environmental mechanism of magnetic susceptibility changes of lacustrine sediments from Lake Hulun, China[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 43(5):534-540. doi: 10.1007/BF02875315
IMBRIE J, HAYS J D, MARTINSON D G, et al., 1984. The orbital theory of Pleistocene climate: Support from a revised chronology of the marine δ18O record[M]//BERGER A, IMBRIE J, HAYS J, et al. Milankovitch and climate, Part 1. Hingham: Riedel: 269-305.
JIANG F C, FU J L, WANG S B, et al., 2013. Discussion on the epoch of lacustrine strata in Togtoh, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 19(1):1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb201301001
JIANG Q F, LIU X Q, SHEN J, 2006. Grain-size characteristics of Wulungu lake sediments and its palaeoclimate and palaeoenvironment implication[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 24(6):877-882. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LEI Y B, ZHANG C J, SHANG H M, et al., 2006. The grain size characteristics of Ximencuo lake core in the northeast Tibet Plateau and its environmental significance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 26(3):31-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200603005
LI B Y, 2000. The last greatest lakes on the Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 55(2):174-182. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlxb200005005
LI C A, YIN H F, YU W Q, 2000. Evolution of drainage systems and its developing trend in connection with tectonic uplift of eastern Kunlun Mt[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 45(20):1904-1908. doi: 10.1007/BF02886304
LI J J, FANG X M, VAN DER VOO R, et al., 1997. Magnetostratigraphic dating of river terraces:Rapid and intermittent incision by the Yellow River of the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau during the quaternary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 102(B5):10121-10132. doi: 10.1029/97JB00275
LI S J, OU R K, ZHU Z Y, et al., 1998. A Carbonate content record of Late Quaternary climate and environment changes from lacustrine core TS95 in Tianshuihai Lake Basin, Northwestern Qinghai-Xizang(Tibet) Plateau[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 10(2):58-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18307/1998.0210
LIANG X Z, TONG Y F, 1996. A method of paleodose exploration[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 18(S1):27-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600551097
LU Y C, 1981. Pleistocene climatic cycles and variation of CaCO3 contents in a loess profile[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica(2):122-131. (in Chinese with English abstract)
MA Z J, WANG Y P, ZHANG Y P, 2001. Study on the recent deformation and dynamics of the lithosphere of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press. (in Chinese)
PAN B T, SU H, LIU X F, et al., 2007. River terraces of the Yellow River and their genesis in eastern Lanzhou Basin during last 1.2Ma[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 27(2):172-180. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj200702002
PENG Y J, XIAO J L, NAKAMURA T, et al., 2005. Holocene East Asian monsoonal precipitation pattern revealed by grain-size distribution of core sediments of Daihai Lake in Inner Mongolia of north-central China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 233(3-4):467-479. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.022
QIN J M, YUAN D X, LIN Y S, et al., 2001. Records of high-resolution climate events from stalagmites since 160000a B.P. in Guangxi and Guizhou Provinces, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 8(1):99-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200101013
RAO Z G, CHEN F H, WANG H B, et al., 2006. Eastern Asian summer monsoon variation during MIS 5e as recorded by paleosol S1 at Jiuzhoutai loess section[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 26(2):103-111. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200602014
TAN H B, MA H Z, ZHANG X Y, 2003. Study on carbonates and its record for environmental changes[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 11(4):20-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
THOMPSON L G, MOSLEY-THOMPSON E, DAVIS M E, et al., 1989. Holocene-Late Pleistocene climatic ice core records from Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science, 246(4929):474-477. doi: 10.1126/science.246.4929.474
WANG J B, ZHU L P, 2002. Grain-size characteristics and their paleo-environmental significance of Chen Co Lake sediments in southern Tibet[J]. Progress in Geography, 21(5):459-467. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlkxjz200205007
WANG S M, FENG M, 1991. Environmental change recorded in the Daihai Lake and its relationship with the change in strength of the southeast monsoon[J]. Science in China (Series B)(7):759-768. (in Chinese)
WANG Y F, 1993. Lacustrine carbonate chemical sedimentation and climatic-environmental evolution:A case study of Qinghai Lake and Daihai Lake[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 24(1):31-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
XIAO J L, PORTER S C, AN Z S, et al., 1995. Grain size of quartz as an indicator of winter monsoon strength on the Loess Plateau of central China during the last 130, 000 Yr[J]. Quaternary Research, 43(1):22-29. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0033589485710034
YANG J Q, CUI Z J, YI C L, et al., 2004. The influencing factors and environmental significance of magnetic susceptibility in the Glacio-Lacustrinal sediments on the Diancang Mountains, Yunnan Province[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 24(5):591-597. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj200405017
YANG X C, CAI M T, YE P S, et al., 2018. Late Pleistocene paleolake evolution in the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Quaternary International, 464:386-395. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2017.11.047
ZHAN T, ZENG F M, XIE Y Y, et al., 2018. Grain size characteristics of Tianhengshan core and their indications for stratigraphic division in the eastern part of the Northeast plain of China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(4):515-521. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlxxb201804009
ZHANG J W, JIN M, CHEN F H, et al., 2003. High-resolution precipitation variations in the Northeast Tibetan Plateau over the last 800 years documented by sediment cores of Qinghai Lake[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(14):1451-14566. doi: 10.1360/02wd0271
ZHANG P G, FAN X Z, HUO J J, 2003. Environment designating singification of magnetic parameters[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 34(3):301-304, 308. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tylgdxxb200303021
ZHANG Y F, ZHANG J P, XU J M, et al., 1998. The Palaeoclimatic evolution of the Yellow River source area since 130 ka BP[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 4(4):69-75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHENG M P, YUAN H R, ZHAO X T, et al., 2006. The Quaternary Pan-lake (Overflow) Period and Paleoclimate on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(2):169-180. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHU D G, SHAO Z G, MENG X G, et al., 2009. The distribution and characteristics of lacustrine sedimentation from ancient high level lake at the north foot of Mt. Bayankala, Qinghai, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(5):549-555. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200905002
蔡茂堂, 叶培盛, 杨星辰, 等, 2018.河套盆地北部344 ka以来沉积环境演化[J].地质力学学报, 24(2):253-262. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180212&flag=1
陈敬安, 万国江, 1999.云南洱海沉积物粒度组成及其环境意义辨识[J].矿物学报, 19(2):175-182. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1999.02.008
陈敬安, 万国江, 黄荣贵, 1999.云南程海沉积物粒度研究[J].环境科学进展, 7(4):76-82. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199900271674
陈敬安, 万国江, 唐德贵, 等, 2000.洱海近代气候变化的沉积物粒度与同位素记录[J].自然科学进展, 10(3):253-259. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZKJZ200003010.htm
程捷, 姜美珠, 昝立宏, 等, 2005.黄河源区第四纪地质研究的新进展[J].现代地质, 19(2):239-246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.02.012
程捷, 张绪教, 田明中, 等, 2006.黄河源区第四纪地质与生态环境[M].北京:地质出版社:1-193.
程绍平, 邓起东, 闵伟, 等, 1998.黄河晋陕峡谷河流阶地和鄂尔多斯高原第四纪构造运动[J].第四纪研究(3):238-248. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.03.007
丁仲礼, 孙继敏, 孙东生, 1998.联系沙漠-黄土演变过程中耦合关系的沉积学指标[J].中国科学(D辑), 29(1):82-87. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd199901013
韩建恩, 余佳, 朱大岗, 等, 2011.青海黄河源盆地早更新世以来环境演变[J].地质通报, 30(12):1941-1949. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.12.019
韩建恩, 余佳, 邵兆刚, 等, 2013a.黄河源晚新生代河湖相沉积与环境[M].北京:地质出版社:1-134.
韩建恩, 邵兆刚, 朱大岗, 等, 2013b.黄河源区河流阶地特征及源区黄河的形成[J].中国地质, 40(5):1531-1541. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201305018
韩建恩, 朱大岗, 余佳, 等, 2013c.黄河源地区优云湖相地层环境代用指标反映的古环境变化[J].现代地质, 27(2):269-277. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz201302004
蒋复初, 傅建利, 王书兵, 等, 2013.内蒙古托克托湖相地层时代讨论[J].地质力学学报, 19(1):1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2013.01.001 http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130101&flag=1
蒋庆丰, 刘兴起, 沈吉, 2006.乌伦古湖沉积物粒度特征及其古气候环境意义[J].沉积学报, 24(6):877-882. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.06.014
类延斌, 张成君, 尚华明, 等, 2006.青藏高原东北部希门错湖岩心粒度特征及其环境意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 26(3):31-38. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200603005
李炳元, 2000.青藏高原大湖期[J].地理学报, 55(2):174-182. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2000.02.005
李长安, 殷鸿福, 于庆文, 1999.东昆仑山构造隆升与水系演化及其发展趋势[J].科学通报, 44(2):211-213. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.02.023
李世杰, 区荣康, 朱照宇, 等, 1998. 24万年来西昆仑山甜水海湖岩芯碳酸盐含量变化与气候环境演化[J].湖泊科学, 10(2):58-65.
梁兴中, 童运福, 1996.古剂量勘查技术[J].物探化探计算技术, 18(S1):27-30. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600551097
卢演俦, 1981.黄土地层中CaCO3含量变化与更新世气候旋回[J].地质科学(2):122-131. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1981-DZKX198102002.htm
马宗晋, 汪一鹏, 张燕平, 2001.青藏高原岩石圈现今变动与动力学[M].北京:地震出版社.
潘保田, 苏怀, 刘小丰, 等, 2007.兰州东盆地最近1.2Ma的黄河阶地序列与形成原因[J].第四纪研究, 27(2):172-180. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.02.002
覃嘉铭, 袁道先, 林玉石, 等, 2001.黔桂地区最近16万年高分辨率石笋记录的气候事件[J].地学前缘, 8(1):99-105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.01.013
饶志国, 陈发虎, 汪海斌, 等, 2006.九州台古土壤S1记录的末次间冰期东亚夏季风变化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 26(2):103-111. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200602014
谭红兵, 马海州, 张西营, 2003.碳酸盐研究与其记录的环境变化[J].盐湖研究, 11(4):20-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-858X.2003.04.003
王君波, 朱立平, 2002.藏南沉错沉积物的粒度特征及其古环境意义[J].地理科学进展, 21(5):459-467. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6301.2002.05.007
王苏民, 冯敏, 1991.内蒙古岱海湖泊环境变化与东南季风强弱的关系[J].中国科学B辑(7):759-768. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1991-JBXK199107012.htm
王云飞, 1993.青海湖、岱海的湖泊碳酸盐化学沉积与气候环境变化[J].海洋与湖沼, 24(1):31-36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1991-JBXK199107012.htm
杨建强, 崔之久, 易朝露, 等, 2004.云南点苍山冰川湖泊沉积物磁化率的影响因素及其环境意义[J].第四纪研究, 24(5):591-597. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.05.017
詹涛, 曾方明, 谢远云, 等, 2018.东北平原东部天恒山钻孔的粒度特征及其对地层划分的指示[J].地质力学学报, 24(4):515-521. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180409&flag=1
张家武, 金明, 陈发虎, 等, 2004.青海湖沉积岩芯记录的青藏高原东北部过去800年以来的降水变化[J].科学通报, 49(1):10-14. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.01.002
张普纲, 樊行昭, 霍俊杰, 2003.磁性参数的环境指示意义[J].太原理工大学学报, 34(3):301-304, 308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9432.2003.03.021
张玉芳, 张俊牌, 徐建明, 等, 1998.黄河源区距今13万年来古气候演化[J].地质力学学报, 4(4):69-75. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19980449&flag=1
郑绵平, 袁鹤然, 赵希涛, 等, 2006.青藏高原第四纪泛湖期与古气候[J].地质学报, 80(2):169-180. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200602001
朱大岗, 邵兆刚, 孟宪刚, 等, 2009.青海巴颜喀拉山北麓古高位湖相沉积的分布与特征[J].地质通报, 28(5):549-555. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.05.002
-



 下载:
下载: