Deformation sequences and ore-controlling structures of the Chanziping–Daping gold mining area in Hunan Province, China
-
摘要:
湖南铲子坪−大坪金矿区位于雪峰弧形构造带西南段,金矿脉主要呈北西西向—北北西向,其次为北北东向。尽管现有研究表明北东向断裂为导矿和容矿构造、北西向断裂为容矿构造,但对控矿断裂的性质和形成时代缺乏明确可靠的认识。文章根据对地表露头构造和矿化蚀变的观测、解析,结合区域构造特征、构造演化和测年资料等,厘定了铲子坪−大坪金矿区构造变形序列及其时代背景,确定了控矿构造类型及其属性。研究认为,研究区自早至晚经历了6期主要变形事件:志留纪晚期受到北西西向挤压,形成北北东走向的褶皱、板劈理和脆韧性剪切带;中三叠世晚期受到北北西向挤压,形成北西西向—北西向右行走滑断裂和剪切破裂、南北向左行剪切破裂、北西向和北北东向共轭剪切破裂、北东东向的逆断裂和叠加褶皱;晚三叠世早期受到南北向挤压,形成北西向—北北西向右行走滑断裂和剪切破裂、北北东向—北东向左行剪切破裂和断裂、北东东向左行膝折构造;中侏罗世晚期受到北西西—近东西向挤压,形成南北向—北北东向逆断裂、北西向—北西西向左行剪切破裂、北东向右行逆冲剪切破裂、北北东向—近南北向的破劈理、面理褶皱和石香肠;古近纪中晚期受到北东向挤压,形成北北东向—南北向右行剪切破裂和断裂、北东东向左行剪切破裂、北西向的逆断裂和破劈理;古近纪晚期—新近纪初期受到北西向挤压,形成北东向逆冲剪切破裂、北西西向右行剪切破裂。研究区北北东向矿脉形成于志留纪晚期和晚三叠世,北西西向—北北西向矿脉形成于晚三叠世晚期。志留纪晚期成矿与断裂运动导致的构造活化作用有关,晚三叠世晚期成矿与同期大规模花岗质岩浆活动有关。导矿构造主要为志留纪晚期北西西向挤压形成的北北东向大断裂即脆韧性剪切带。主要容矿构造为中三叠世晚期北北西向挤压形成的北西西向—北西向右行走滑断裂、晚三叠世早期南北向挤压形成的北西向—北北西向右行走滑断裂,其次为志留纪晚期北西西向挤压形成的北北东向脆韧性剪切带。
Abstract:The Chanziping–Daping gold deposit area is located in the southwest section of the Xuefeng arc-shaped structural belt, with mainly NWW-NNW-trending and secondary NNE-trending Au veins. Existing studies proposed the NE-trending faults as the ore-passing and ore-bearing structures and the NW-trending faults as the ore-bearing structures. However, there is no clear and reliable understanding of the nature and age of ore-controlling faults. Given this, the authors carried out detailed field observation and analysis of surface outcrop structures and mineralization alteration, and then combined with regional structural characteristics, tectonic evolutions, and dating data, determined the deformation sequences and their ages in the Chanziping–Daping gold deposit area, and determined the types and attributes of ore-controlling structures. The study suggests that the study area experienced six main deformation events from early to late: Regional NWW compression during the late Silurian which resulted in the NNE-trending folds, slaty cleavages and brittle-ductile shear zones; Regional NNW compression in the late Middle Triassic which caused the formation of NWW-to-NW-trending dextral strike-slip faults and shear fractures, NS-trending sinistral shear fractures, NW- and NNE-trending conjugate shear fractures, NEE-trending thrust faults and superimposed folds; Regional NS compression in the early Late Triassic which led to the development of NW-to-NNW-trending dextral strike-slip faults and shear fractures, NNE-to-NE-trending sinistral shear fractures and faults, and NEE-trending sinistral kinks; Regional NWW-to-near EW-compression in the late Middle Jurassic which resulted in the NS-to-NNE-trending thrust faults, NW-to-NWW-trending sinistral shear fractures, NE-trending dextral thrust shear fracture, NNE-to-near NS-trending fracture cleavages, foliation folds and boudins; Regional NE compression in the middle-late Paleogene which led to the development of NNE-to-NS-trending dextral shear fractures and faults, NEE-trending sinistral shear fractures, NW-trending thrust faults and fracture cleavages; Regional NW compression during the late Paleogene to early Neogene which led to the formation of NE-trending thrust shear fractures and NWW-trending dextral shear fractures. The NNE-trending mineral veins in the study area formed in the late Silurian and the late Late Triassic, and the NWW-to-NNW-trending mineral veins formed in the late Late Triassic. The mineralization in the late Silurian was associated with the tectonic activation caused by the fault movement, and the mineralization in the late Late Triassic was related to large-scale granitic magmatism in the same period. The ore-passing structures are mainly the large NNE-trending faults, namely the brittle-ductile shear zones formed by NWW- compression in the late Silurian. The main ore-bearing structures are the NWW-to-NW-trending dextral strike-slip faults formed by NNW compression in the late Middle Triassic, NW-to-NNW-trending dextral strike-slip faults formed by NS compression in the early Late Triassic, with next NNE-trending brittle-ductile shear zones formed by NWW compression in the late Silurian.
-

-
图 1 区域地质及锑−钨−金矿床分布图(据柏道远等,2021a修改)
Figure 1.
表 1 铲子坪—大坪金矿区构造变形序列
Table 1. Deformation sequences in Chanziping–Daping Au deposit area
时代 变形
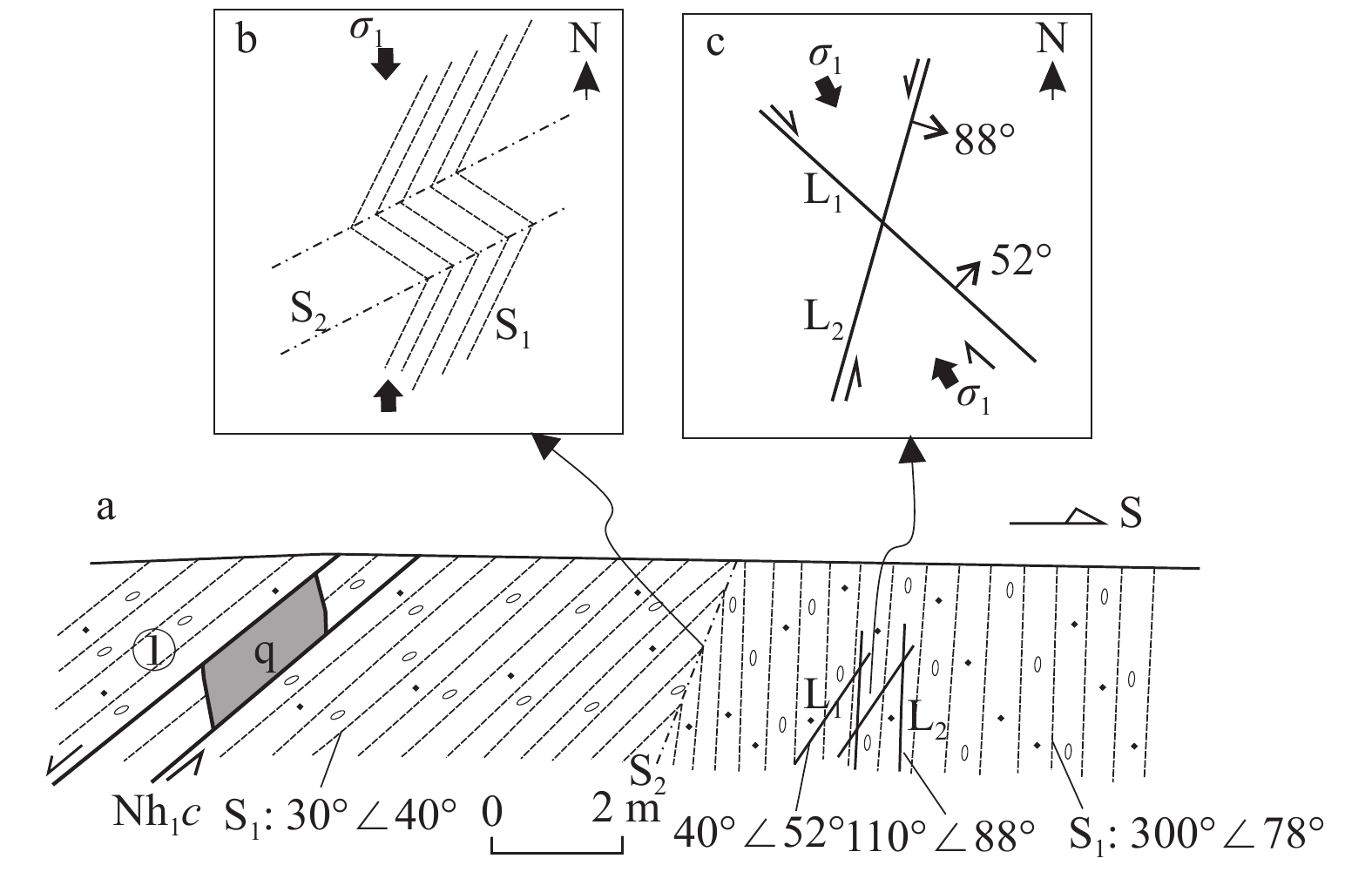
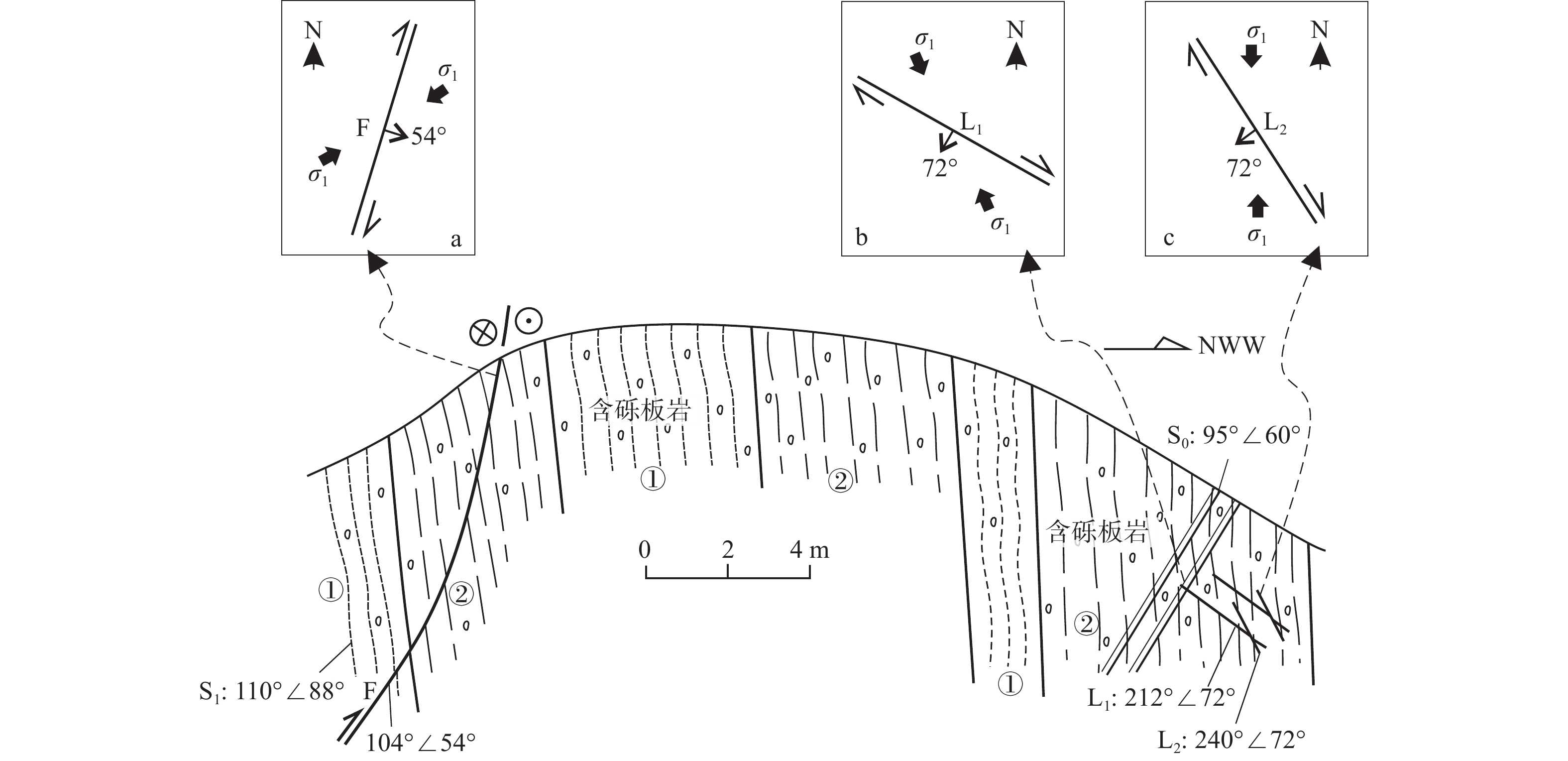
期次构造变形 实例 区域构造体制 形成构造动力背景 E3—N1 D6 NE向逆冲剪切破裂 D504 NW向挤压 菲律宾海板块与华南块体碰撞 NWW向右行剪切破裂 D504 E2—E3 D5 NNE向—SN向右行剪切破裂、断裂 D501(继承活动)、D504、D506、D510 NE向挤压 印度−欧亚板块碰撞导致亚洲东部形成右行走滑断裂 NEE向左行剪切破裂(切割石英脉) D508 NW向逆断裂 D505 NW向破劈理 D505 J2晚期 D4 NW向—NWW向左行剪切破裂 D501(继承性活动)、D507、D511 NWW—近EW向挤压 古太平洋板块(或伊泽奈崎板块)俯冲 SN向—NNE向逆断裂 D505 NE向右行逆冲剪切破裂 D510 NNE向—近SN向破劈理 D505、D508 NNE向—近SN向劈理褶皱或剪切面理褶皱 D505、D508 NNE向石英脉石香肠 D508 T3 D3 NW向—NNW向右行走滑断裂(含金矿)、剪切破裂 D504、D506;F7(图2a) SN向挤压 扬子及其以南各地块向北运移与中朝板块碰撞 NNE向—NE向左行剪切破裂、断裂 D504、D505、D510;F10(图2a) NEE向左行膝折构造 D503 T2晚期 D2 NWW向—NW向右行走滑断裂(含金矿)、剪切破裂 D501、D506、D507、D510;铲子坪含矿断裂等(图2a) NNW向挤压 中扬子板块与华夏板块的继发性陆内俯冲汇聚,以及秦岭−大别−苏鲁构造带碰撞造山 SN向左行剪切破裂 D501 NW向和NNE向共轭剪切破裂 D503 NEE向逆断裂 F4(图2a) NEE向叠加褶皱(使NNE向劈理变位为NW向) D505 S晚期 D1 区域NNE向褶皱 f1、f2、f3、f4(图2a) NWW向挤压 扬子与华夏陆内汇聚 NE向—NNE向板劈理(局部后期变位为NW向) D503、D504、D505、D506、D507、D508、D509、D510 NNE向脆韧性剪切带(含金矿)(局部后期变位为NW向) D503、D504、D505、D506、D508、D509;F2、F3、F5、F6等(图2a) -
[1] ALLEN M B, MACDONALD D I M, XUN Z, et al. , 1997. Early Cenozoic two-phase extension and Late Cenozoic thermal subsidence and inversion of the Bohai Basin, northern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 14(7-8): 951-972. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(97)00027-5
[2] BAI D Y, JIA B H, ZHONG X, et al. , 2012a. Potential genesis of the trending changes of Jinning Period and Caledonian structural lineamens in Middle-southern Hunan[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 18(2): 165-177. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] BAI D Y, JIA B H, ZHONG X, et al. , 2012b. Study on the deformation of Indosinian movement in Southeastern Hunan[J]. Geological Review, 58(1): 19-29. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] BAI D Y, JIANG W, ZHONG X, et al. , 2015. Mesozoic-Cenozoic structural deformation characteristics of Yuanling-Mayang Basin and regional tectonic setting[J]. Geology in China, 42(6): 1851-1875. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] BAI D Y, LI B, JIANG W, et al. , 2020. Tectonic framework controlling characteristics and dynamic mechanisms of main endogenous mineralization events in Hunan province, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 42(1): 49-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] BAI D Y, LI B, ZHOU C, et al. , 2021a. Gold mineralization events of the Jiangnan Orogen in Hunan and their tectonic settings[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 40(5): 897-922. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] BAI D Y, LI B, LI Y M, et al. , 2021b. Segmentation of the movement in Indosinian of the Changde-Anren fault in Hunan: constraints from granite[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 40(5): 173-187. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] BAI D Y, TANG F P, LI B, et al. , 2022. Summary of main mineralization events in Hunan province[J]. Geology in China, 49(1): 151-180. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] BAI D Y, LI B, WU M J, et al. , 2023a. Deformation sequences, ore-forming Epoch and attributes of ore-bearing structurals in the Zhazixi Sb-W deposit, Hunan province[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 47(2): 260-283. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] BAI D Y, LI B, JIN H, et al. , 2023b. Deformation sequences and ore-controlling structures of Au—Sb deposits in the Longshan area in central Hunan province[J]. Geological Review, 69(1): 88-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] BAI D Y, LI B, JIANG C, et al. , 2023c. Deformation sequences, metallogenic events and ore-controlling structures at Gutaishan Au-Sb deposit in central Hunan province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 42(2): 229-252. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] BAI D Y, WEN C H, HUANG J Z, et al. , 2023d. Mesozoic tectono-magmatic characteristics and their control on rare metal pegmatites in Mufushan area, northeastern Hunan[J]. Geological Review, 69(3): 855-880. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] CAO L, DUAN Q F, PENG S G, et al. , 2015a. Characteristics of fluid inclusions in the Chanziping gold deposit in western Hunan province and their geological implications[J]. Geology and Exploration, 51(2): 212-224. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] CAO L, DUAN Q F, PENG S G, et al. , 2015b. Characteristics and geological significance of stable isotopes in the Chanziping gold deposit of Xuefeng Mountains[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 31(2): 167-175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] CHEN M Y, 1996. Characteristics of alteration zone of NW structure in Chanziping gold deposit and its significance of research[J]. Hunan Geology, 15(2): 78-80, 84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] CHEN X, RONG J Y, 1999. From biostratigraphy to tectonics—with Ordovician and Silurian of South China as an example[J]. Geoscience, 13(4): 385-389. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] CHU Y, LIN W, FAURE M, et al. , 2019. Cretaceous episodic extension in the South China Block, East Asia: evidence from the Yuechengling Massif of central South China[J]. Tectonics, 38(10): 3675-3702,doi: 10.1029/2019TC005516.
[18] FU H H, TANG W G, TANG Y P, 2011. Re-understanding of Chanziping gold deposit ore-controlling factors and prospects analysis of deep side prospecting[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 25(2): 91-97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] GILDER S A, LELOUP P H, COURTILLOT V, et al. , 1999. Tectonic evolution of the Tancheng-Lujiang (Tan-Lu) fault via Middle Triassic to early Cenozoic paleomagnetic data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 104(B7): 15365-15390. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900123
[20] HALL R, 2002. Cenozoic geological and plate tectonic evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: computer-based reconstructions, model and animations[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 20(4): 353-431. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(01)00069-4
[21] HAO Y, LI S Z, JIN C, et al. , 2010. Galedonian structural characteristics and mechanism in Hunan-Jiangxi-Guangxi provinces[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 34(2): 166-180. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] HUANG J Z, SUN J, ZHOU C, et al. , 2020. Metallogenic regularity and resource potential of gold deposits of Hunan area in the Jiangnan Orogenic Belt, South China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 41(2): 230-252. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] Hunan Institute of Geological Survey, 2017. Regional geology of China, Hunan province[M]. Beijing: Geology Press. (in Chinese)
[24] LI B, XU D R, BAI D Y, et al. , 2022a. Characteristics of structural deformation and its tectonic setting in the Huishangang area, northern Xuefeng Orogen[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 46(1): 1-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] LI B, XU D R, BAI D Y, et al. , 2022b. Structural deformation, metallogenic Epoch and genetic mechanism of the Woxi Au-Sb-W deposit, western Hunan province, South China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 65(12): 2358-2384. doi: 10.1007/s11430-021-9978-0
[26] LI H Q, WANG D H, CHEN F W, et al. , 2008. Study on chronology of the Chanziping and Daping gold deposit in Xuefeng Mountains, Hunan province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 82(7): 900-905. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] LI J H, ZHANG Y Q, XU X B, et al. , 2014. SHRIMP U-Pb dating of zircons from the Baimashan Longtan super-unit and Wawutang granites in Hunan province and its geological implication[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 44(1): 158-175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] LI W, XIE G Q, MAO J W, et al. , 2018. Muscovite 40Ar/39Ar and in situ sulfur isotope analyses of the slate-hosted Gutaishan Au–Sb deposit, South China: implications for possible Late Triassic magmatic-hydrothermal mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 101: 839-853. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.08.006
[29] LI Z X, LI X H, 2007. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: a flat-slab subduction model[J]. Geology, 35(2): 179-182,doi: 10.1130/G23193A.1.
[30] LUO X Q, 1993. Tectonic metallogenesis of Chanziping gold deposit[J]. Hunan Geology, 12(3): 171-176. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] LUO X Q, 1996a. Mineralization and prospecting guide of Chanziping gold deposit in Hunan[J]. Hunan Geology, 15(1): 33-38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] LUO X Q, 1996b. Typomorphic characteristics and geological implications of minerals from the Chanziping gold deposit, Hunan province[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 15(2): 170-179, 169. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] LUO Z G, WANG Y J, ZHANG F F, et al. , 2010. LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb dating for Baimashan and Jintan Indosinian granitic plutons and its petrogenetic implications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 34(2): 282-290. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] LV Y J, PENG J T, CAI Y F, 2021. Geochemical characteristics, U-Pb dating of hydrothermal titanite from the Xingfengshan tungsten deposit in Hunan province and their geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 37(3): 830-846. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.03.12
[35] MENG X G, CHEN Z L, SHAO Z G, et al. , 2001. Ore-controlling structures and genesis in the Tongxi gold field in the central segment of the Xuefeng Mountains[J]. Regional Geology of China, 20(4): 404-410. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] QIU Y X, ZHANG Y C, MA W P, 1998. Tectonics and geological evolution of Xuefengintra-continental orogene, South China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 4(4): 432-443. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] SHU L S, ZHOU X M, 2002. Late Mesozoic tectonism of southeast China[J]. Geological Review, 48(3): 249-260. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] SHU L S, ZHOU X M, DENG P, et al. , 2004. Geological features and tectonic evolution of Meso-Cenozoic basins in southeastern China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(9-10): 876-884. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[39] SHU L S, ZHOU X M, DENG P, et al. , 2009. Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Southeast China Block: new insights from Basin analysis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 34(3): 376-391,doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.06.004.
[40] SHU L S, YAO J L, WANG B, et al. , 2021. Neoproterozoic plate tectonic process and Phanerozoic geodynamic evolution of the South China Block[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 216: 103596,doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103596.
[41] SU K M, LV S J, KONG L B, et al. , 2016. Geological characteristics, metallogenetic regularity and model of quartz vein type tungsten deposits in Chongyangping, Hunan province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 35(5): 902-912. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[42] WAN T F, ZHU H, 2002. Tectonics and environment change of Meso-Cenozoic in China continent and its adjacent areas[J]. Geoscience, 16(2): 107-120. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[43] WANG C, SHAO Y J, EVANS N J, et al. , 2020. Genesis of Zixi gold deposit in Xuefengshan, Jiangnan Orogen (South China): age, geology and isotopic constraints[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 117: 103301,doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103301.
[44] WANG J, LI S Z, JIN C, et al. , 2010. Dome-and-Basin pattern in central Hunan province: stages and genesis of fold superposition[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 34(2): 159-165. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[45] WANG Y L, CHEN Y C, WANG D H, et al. , 2012. Scheelite Sm-Nd dating of the Zhazixi W-Sb deposit in Hunan and its geological significance[J]. Geology in China, 39(5): 1339-1344. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[46] WEI D F, 1993. Source of ore-forming materials in Chanziping gold deposit and the geologic study of its mechanism of Formation[J]. Hunan Geology, 12(1): 29-34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[47] WEI D F, 1995. On discussion of geochemical anomaly model of Chanziping gold deposit, Qianyang County[J]. Hunan Geology, 14(4): 252-256. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[48] WU N J, BAI D Y, LI B, et al. , 2023. Deformation sequence and its constraints on the attributes of ore-controlling structures of Wangu gold deposit in northeast Hunan[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 43(2): 161-175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[49] XU D R, DENG T, CHI G X, et al. , 2017. Gold mineralization in the Jiangnan Orogenic Belt of South China: geological, geochemical and geochronological characteristics, ore deposit-type and geodynamic setting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 88: 565-618. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.004
[50] XU X B, ZHANG Y Q, JIA D, et al. , 2009. Early Mesozoic geotectonic processes in South China[J]. Geology in China, 36(3): 573-593. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[51] XU Z Y, LIN G, LIU C Y, et al. , 2004. A discussion on amalgamation course between the South China and North China blocks: evidences from deformational characters in the Jianghan superimposed Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 39(2): 284-295. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[52] YANG J, LUO P, LING Y X, et al. , 2021. Superimposed features and deformation mechanism of Early Mesozoic folds in the Sangzhi-Shimen area, northern Hunan[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 40(6): 43-54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[53] YIN A, HARRISON T M, 2000. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Xizang orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28: 211-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211
[54] ZHANG G W, GUO A L, DONG Y P, et al. , 2011. Continental geology, tectonics and dynamics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(3): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[55] ZHANG L, YANG L Q, GROVES D I, et al. , 2019. An overview of timing and structural geometry of gold, gold-antimony and antimony mineralization in the Jiangnan Orogen, southern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 115: 103173. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103173
[56] ZHANG L S, PENG J T, ZHANG D L, et al. , 2012. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Indosinian Dashenshan granite, western Hunan, South China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 36(1): 137-148. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[57] ZHANG L S, PENG J T, HU A X, et al. , 2014. Re-Os dating of molybdenite from Darongxi tungsten deposit in western Hunan and its geological implications[J]. Mineral Deposits, 33(1): 181-189. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[58] ZHANG Y Q, XU X B, JIA D, et al. , 2009. Deformation record of the change from Indosinian collision-related tectonic system to Yanshanian subduction-related tectonic system in South China during the Early Mesozoic[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(1): 234-247. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[59] ZHANG Y Q, DONG S W, LI J H, et al. , 2012. The new progress in the study of Mesozoic tectonics of South China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 33(3): 257-279. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[60] ZHAO J G, 2000. Existing state and distibution regular of Au in Chanziping gold deposit[J]. Hunan Geology, 19(3): 164-168. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[61] ZHENG Y D, WANG T, WANG X S, 2007. The maximum effective moment criterion (MEMC) and related geological structures[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(4): 49-60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[62] 柏道远, 贾宝华, 钟响, 等, 2012a. 湘中南晋宁期和加里东期构造线走向变化成因[J]. 地质力学学报, 18(2): 165-177.
[63] 柏道远, 贾宝华, 钟响, 等, 2012b. 湘东南印支运动变形特征研究[J]. 地质论评, 58(1): 19-29.
[64] 柏道远, 姜文, 钟响, 等, 2015. 湘西沅麻盆地中新生代构造变形特征及区域地质背景[J]. 中国地质, 42(6): 1851-1875.
[65] 柏道远, 李彬, 姜文, 等, 2020. 湖南省主要内生成矿事件的构造格局控矿特征及动力机制[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 42(1): 49-70.
[66] 柏道远, 李彬, 周超, 等, 2021a. 江南造山带湖南段金矿成矿事件及其构造背景[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 40(5): 897-922.
[67] 柏道远, 李彬, 李银敏, 等, 2021b. 湖南常德-安仁断裂印支期构造运动分段性: 来自花岗岩的约束[J]. 地质科技通报, 40(5): 173-187.
[68] 柏道远, 唐分配, 李彬, 等, 2022. 湖南省成矿地质事件纲要[J]. 中国地质, 49(1): 151-180.
[69] 柏道远, 李彬, 吴梦君, 等, 2023a. 湖南渣滓溪锑钨矿区变形序列、成矿时代及含矿构造属性[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 47(2): 260-283.
[70] 柏道远, 李彬, 金华, 等, 2023b. 湘中龙山地区变形序列及金锑矿控矿构造[J]. 地质论评, 69(1): 88-112.
[71] 柏道远, 李彬, 江灿, 等, 2023c. 湘中古台山金锑矿床变形序列、成矿事件及控矿构造[J]. 矿床地质, 42(2): 229-252.
[72] 柏道远, 文春华, 黄建中, 等, 2023d. 湘东北幕阜山地区中生代构造—岩浆特征及其对稀有金属伟晶岩的控制[J]. 地质论评, 69(3): 855-880.
[73] 曹亮, 段其发, 彭三国, 等, 2015a. 雪峰山铲子坪金矿床流体包裹体特征及地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 51(2): 212-224.
[74] 曹亮, 段其发, 彭三国, 等, 2015b. 雪峰山铲子坪金矿床稳定同位素特征及成矿地质意义[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 31(2): 167-175.
[75] 陈明扬, 1996. 铲子坪金矿北西向构造蚀变带特征及其研究意义[J]. 湖南地质, 15(2): 78-80, 84.
[76] 陈旭, 戎嘉余, 1999. 从生物地层学到大地构造学: 以华南奥陶系和志留系为例[J]. 现代地质, 13(4): 385-389.
[77] 符海华, 唐卫国, 汤亚平, 2011. 铲子坪金矿控矿因素再认识与深边部找矿远景分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 25(2): 91-97.
[78] 郝义, 李三忠, 金宠, 等, 2010. 湘赣桂地区加里东期构造变形特征及成因分析[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 34(2): 166-180.
[79] 湖南省地质调查院, 2017. 中国区域地质志·湖南志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
[80] 黄建中, 孙骥, 周超, 等, 2020. 江南造山带(湖南段)金矿成矿规律与资源潜力[J]. 地球学报, 41(2): 230-252.
[81] 李彬, 许德如, 柏道远, 等, 2022a. 雪峰造山带北段灰山港地区构造变形特征及其形成构造背景[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 46(1): 1-21.
[82] 李彬, 许德如, 柏道远, 等, 2022b. 湘西沃溪金-锑-钨矿床构造变形、成矿时代及成因机制[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 52(12): 2479-2505.
[83] 李华芹, 王登红, 陈富文, 等, 2008. 湖南雪峰山地区铲子坪和大坪金矿成矿作用年代学研究[J]. 地质学报, 82(7): 900-905. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.07.006
[84] 李建华, 张岳桥, 徐先兵, 等, 2014. 湖南白马山龙潭超单元、瓦屋塘花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 44(1): 158-175.
[85] 骆学全, 1993. 铲子坪金矿的构造成矿作用[J]. 湖南地质, 12(3): 171-176.
[86] 骆学全, 1996a. 湖南铲子坪金矿的成矿规律及找矿标志[J]. 湖南地质, 15(1): 33-38.
[87] 骆学全, 1996b. 湖南铲子坪金矿的矿物标型及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 15(2): 170-179, 169.
[88] 罗志高, 王岳军, 张菲菲, 等, 2010. 金滩和白马山印支期花岗岩体LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb定年及其成岩启示[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 34(2): 282-290.
[89] 吕沅峻, 彭建堂, 蔡亚飞, 2021. 湖南杏枫山钨矿床热液榍石的地球化学特征、U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 37(3): 830-846.
[90] 孟宪刚, 陈正乐, 邵兆刚, 等, 2001. 雪峰山中段桐溪金矿田控矿构造及成因[J]. 中国区域地质, 20(4): 404-410.
[91] 丘元禧, 张渝昌, 马文璞, 1998. 雪峰山陆内造山带的构造特征与演化[J]. 高校地质学报, 4(4): 432-443.
[92] 舒良树, 周新民, 2002. 中国东南部晚中生代构造作用[J]. 地质论评, 48(3): 249-260.
[93] 舒良树, 周新民, 邓平, 等, 2004. 中国东南部中、新生代盆地特征与构造演化[J]. 地质通报, 23(9-10): 876-884.
[94] 苏康明, 吕书君, 孔令兵, 等, 2016. 湖南崇阳坪地区石英脉型钨矿床的地质特征、成矿规律及成矿模式[J]. 矿床地质, 35(5): 902-912.
[95] 万天丰, 朱鸿, 2002. 中国大陆及邻区中生代-新生代大地构造与环境变迁[J]. 现代地质, 16(2): 107-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2002.02.001
[96] 王建, 李三忠, 金宠, 等, 2010. 湘中地区穹盆构造: 褶皱叠加期次和成因[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 34(2): 159-165.
[97] 王永磊, 陈毓川, 王登红, 等, 2012. 湖南渣滓溪W-Sb矿床白钨矿Sm-Nd测年及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 39(5): 1339-1344.
[98] 魏道芳, 1993. 铲子坪金矿成矿物质来源及成矿机理的地球化学研究[J]. 湖南地质, 12(1): 29-34.
[99] 魏道芳, 1995. 黔阳县铲子坪金矿地球化学异常模式探讨[J]. 湖南地质, 14(4): 252-256.
[100] 吴能杰, 柏道远, 李彬, 等, 2023. 湘东北万古金矿区变形序列及其对控矿构造属性的约束[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 43(2): 161-175.
[101] 徐先兵, 张岳桥, 贾东, 等, 2009. 华南早中生代大地构造过程[J]. 中国地质, 36(3): 573-593.
[102] 徐政语, 林舸, 刘池阳, 等, 2004. 从江汉叠合盆地构造形变特征看华南与华北陆块的拼贴过程[J]. 地质科学, 39(2): 284-295. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2004.02.015
[103] 杨俊, 罗鹏, 凌跃新, 等, 2021. 湘北桑植-石门一带早中生代褶皱叠加特征及变形机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 40(6): 43-54.
[104] 张国伟, 郭安林, 董云鹏, 等, 2011. 大陆地质与大陆构造和大陆动力学[J]. 地学前缘, 18(3): 1-12.
[105] 张龙升, 彭建堂, 张东亮, 等, 2012. 湘西大神山印支期花岗岩的岩石学和地球化学特征[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 36(1): 137-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.01.017
[106] 张龙升, 彭建堂, 胡阿香, 等, 2014. 湘西大溶溪钨矿床中辉钼矿Re-Os同位素定年及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 33(1): 181-189.
[107] 张岳桥, 徐先兵, 贾东, 等, 2009. 华南早中生代从印支期碰撞构造体系向燕山期俯冲构造体系转换的形变记录[J]. 地学前缘, 16(1): 234-247.
[108] 张岳桥, 董树文, 李建华, 等, 2012. 华南中生代大地构造研究新进展[J]. 地球学报, 33(3): 257-279.
[109] 赵建光, 2000. 铲子坪金矿床金的赋存状态及分布规律[J]. 湖南地质, 19(3): 164-168.
[110] 郑亚东, 王涛, 王新社, 2007. 最大有效力矩准则及相关地质构造[J]. 地学前缘, 14(4): 49-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.04.005
-




 下载:
下载: