Avoidance distance and influence range of active faults: A case study of Litang fault
-
摘要:
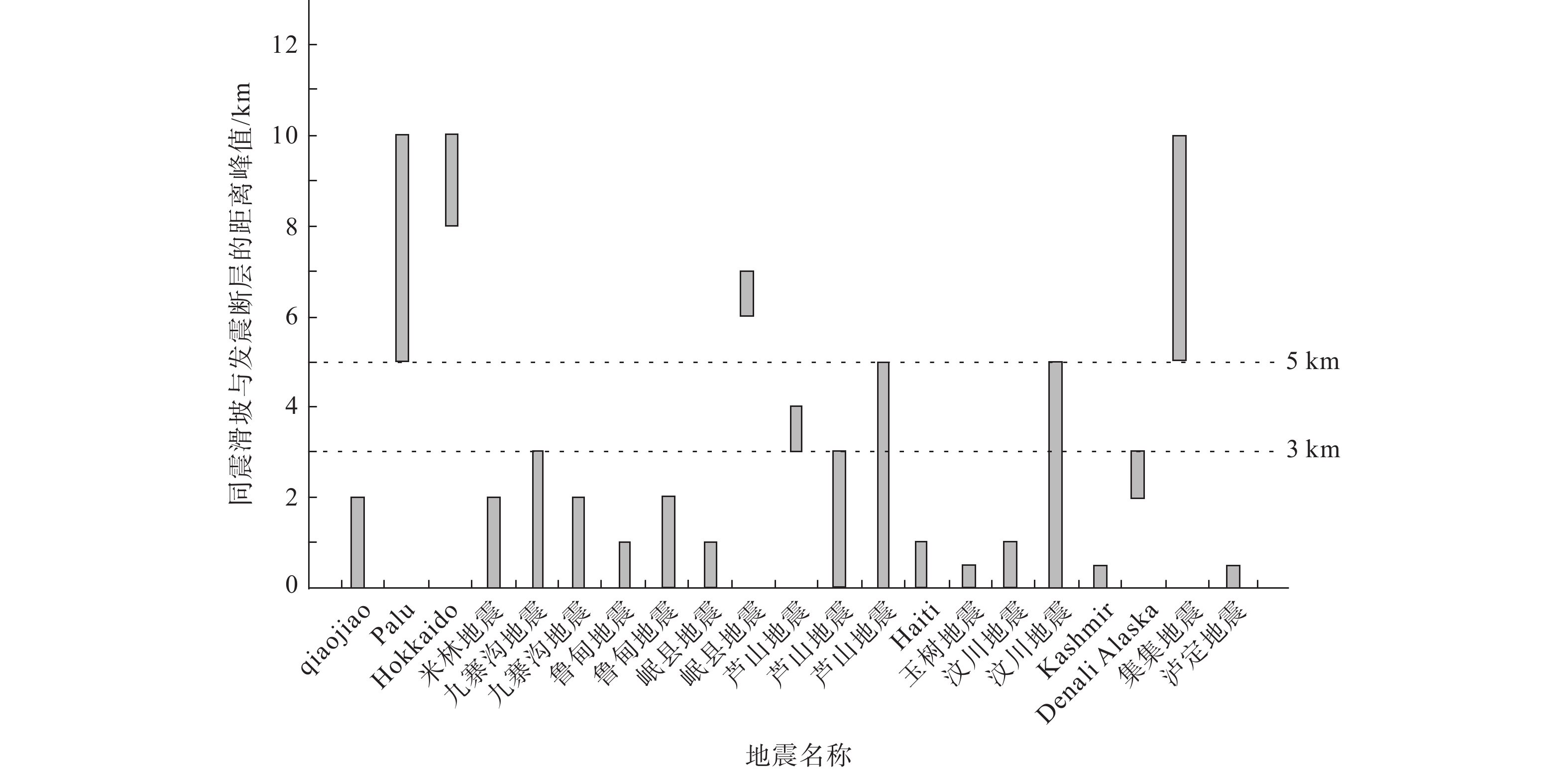
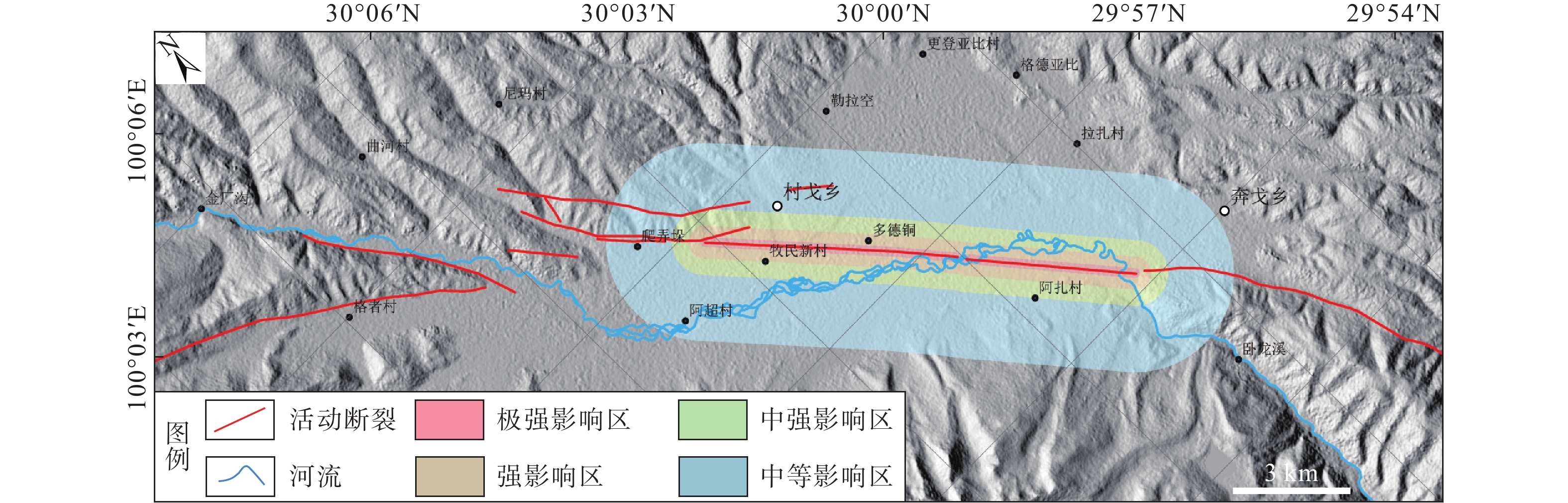
活动断层除引发强震外,还会引起工程错断、蠕滑变形和诱发地质灾害,严重威胁重大工程规划建设和安全运营。在同震地表破裂资料统计的基础上,建立了不同性质活动断层的避让距离,讨论了影响不同出露区断层避让距离的因素,以及活动断层带极强、强、中强和中等影响区范围。研究结果认为正断层上盘的避让距离不小于30 m,下盘不小于15 m;逆断层上盘避让距离不小于45 m,下盘不小于15 m;走滑断层避让距离不小于30 m。同时,基于遥感解译、野外调查、断层剖面和浅层地震勘探等资料,分析了青藏高原理塘断裂带理塘段(理塘断裂)的避让距离与影响范围。研究结果显示:理塘断裂为全新世活动断层,运动性质以走滑运动为主兼有正断分量,其上盘避让距离为30 m,下盘避让距离为15 m。理塘断裂的极强、中强、强和中等活动影响区分别为154 m、154~500 m、500~1000 m和1000~3000 m,研究结果可为区域重大工程规划建设和国土空间管控提供基础资料。
Abstract:Objective Active faults can not only trigger strong earthquakes, but also cause engineering breaks, creep deformation, and geological disasters, which seriously threaten the planning, construction, and safe operation of major projects.
Methods In this study, based on the statistics of coseismic surface ruptures, the avoidance distances of faults with different properties and the ranges of extremely strong, strong, less strong, and moderately affected areas of active fault zones are established. Remote sensing, a geological survey, dislocation landforms, and shallow seismic exploration were used to analyze, the avoidance distance and affected area of the Litang fault on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.
Conclusion This study concludes that the hanging wall and footwall avoidance distances of normal faults are not less than 30 m and 15 m, respectively; the hanging wall and footwall avoidance distances of thrust faults are not less than 45 m and 15 m, respectively; the avoidance distance of strike-slip faults is not less than 30 m. The Litang fault is mainly characterized by strike-slip with normal fault components, and its hanging-wall avoidance distance is 30 m and its footwall avoidance distance is 15 m. The extremely strong, strongly, less strong, and moderately affected areas of the Litang fault zones are 154 m, 154-500 m, 500-1000 m, and 1000-3000 m, respectively. [Significance] The research provides basic data for the planning and construction of major projects and the spatial control of the national land.
-
Key words:
- active faults /
- avoidance distances /
- influence range /
- Litang fault /
- Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
-

-
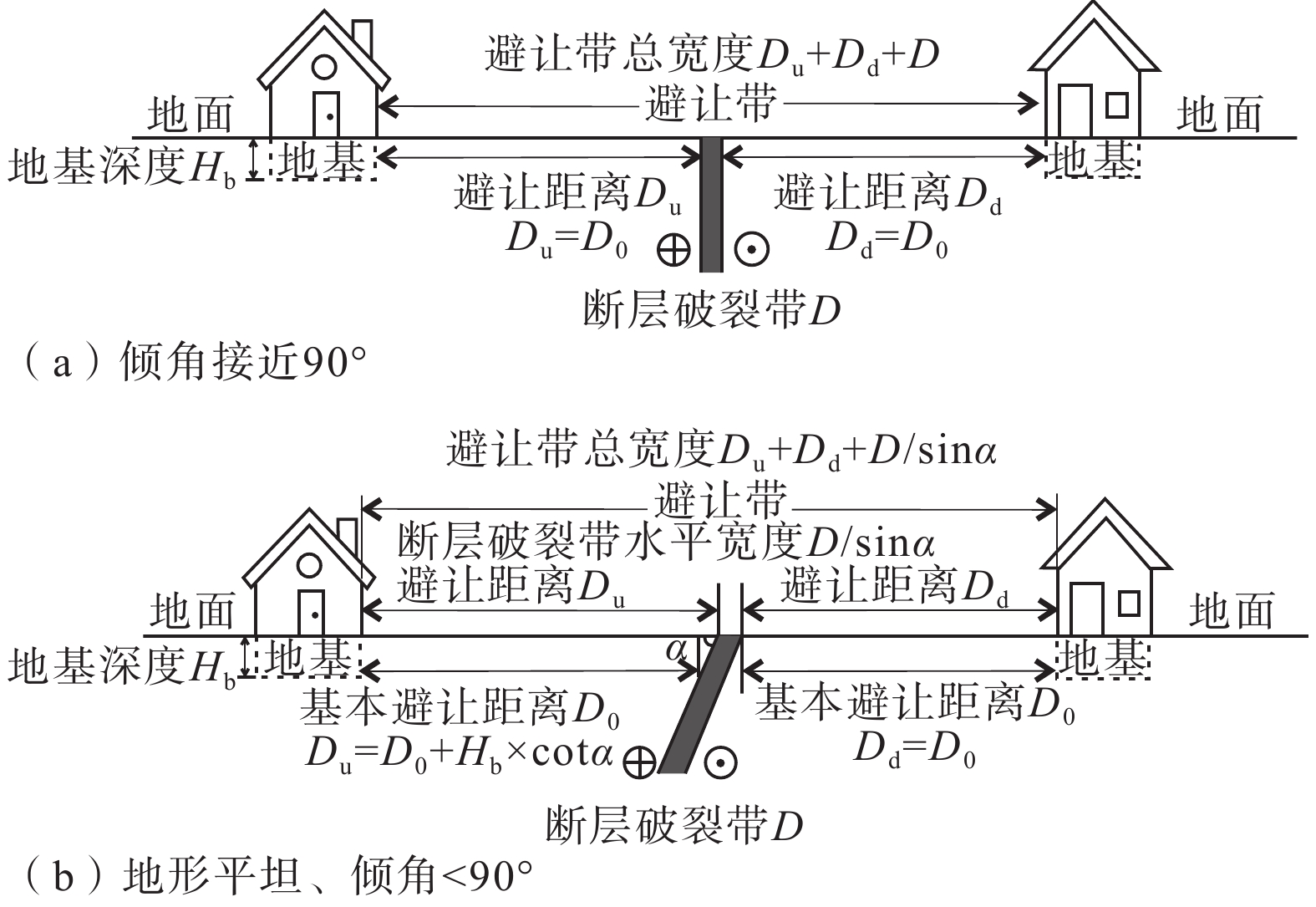
图 2 走滑断层上、下盘避让距离及计算方法示意图(《活动断层避让》征求意见稿,2019)
Figure 2.
-
[1] BAI Y J, NI H Y, GE H, 2019. Advances in research on the geohazard effect of active faults on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(6): 1116-1128. (in Chinese with English abstract
[2] BOUCKOVALAS G. 2006. ETC-12: geothchnical evaluation and application of the seismic eurocode EC8[J]. National Technical University, Greece, 2006: 55-64.
[3] CAI L W, HUANG Y, HE J, et al., 2022. Earthquake damage and enlightenment from traffic system in 2022 Qinghai Menyuan MS6.9 earthquake[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 42(4): 8-16. (in Chinese with English abstract
[4] CHEN G H, XU X W, ZHENG R Z, et al., 2008. Quantitative analysis of the co-seismic surface rupture of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan, China along the Beichuan-Yingxiu fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30(3): 723-738. (in Chinese with English abstract
[5] CHEN G H, LI Z W, XU X W, et al., 2022. Co-seismic surface deformation and late Quaternary accumulated displacement along the seismogenic fault of the 2021 Madoi M7.4 earthquake and their implications for regional tectonics[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 65(8): 2984-3005. (in Chinese with English abstract
[6] CHEN Y M, WANG L M, DAI W, et al., 2004. The frozen soils and devastating characteristics of west Kunlun Mountains pass MS8.1 earthquake area in 2001[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 20(2): 161-169. (in Chinese with English abstract
[7] CHEVALIER M L, LELOUP P H, REPLUMAZ A, et al., 2016. Tectonic-geomorphology of the Litang fault system, SE Tibetan Plateau, and implication for regional seismic hazard[J]. Tectonophysics, 682: 278-292. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.05.039
[8] European Committee for Standardization Eurocode8: Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance, 2003.
[9] GAI H L, YAO S H, YANG L P, et al., 2021. Characteristics and causes of coseismic surface rupture triggered by the “5.22”MS 7.4 Earthquake in Maduo, Qinghai, and their significance[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(6): 899-912. (in Chinese with English abstract
[10] GAO S P, 2021. Late Quaternary paleoseismology and faulting behavior of the internal and western boundary faults of Northwest Sichuan Subblock[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese with English abstract
[11] GONG Z, LI H B, TANG F T, et al., 2023. Fault zone scale, fault zone structure and historical activity of the Yanyuan segment of the Lijiang-Xiaojinhe fault[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 97(7): 2111-2125. (in Chinese with English abstract
[12] GUO T T, 2013. A study on Wenchuan earthquake disasters and the safety distance from active faults[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese with English abstract
[13] GUO T T, XU X W, YU G H, et al., 2017. Research history and current situation of active faults and their avoidance zone width[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 32(5): 1893-1900. (in Chinese with English abstract
[14] HE X L, XU C, XU X W, et al., 2022. Advances on the avoidance zone and buffer zone of active faults[J]. Natural Hazards Research, 2(2): 62-74 doi: 10.1016/j.nhres.2022.05.001
[15] HE Z T, MA B Q, LI Y S, et al., 2012. Width and hanging Wall effect of surface rupture caused by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 48(6): 886-894. (in Chinese with English abstract
[16] LAN H X, ZHANG N, LI L P, et al., 2021. Risk analysis of major engineering geological hazards for Sichuan-Tibet Railway in the phase of feasibility study[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 29(2): 326-341. (in Chinese with English abstract
[17] LI B, YIN Y P, TAN C X, et al., 2022. Geo-safety challenges against the site selection of engineering projects in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(6): 907-918. (in Chinese with English abstract
[18] LI C Y, YE J Q, XIE F R, et al., 2008. Characteristics of the surface rupture zone of the MS8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, China along the segment north to Beichuan[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30(3): 683-696. (in Chinese with English abstract
[19] LI C Y, WEI Z Y, 2009. Representative patterns of coseismic deformation along surface rupture north to Beichuan city of 2008 Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 29(3): 416-425. (in Chinese with English abstract
[20] LI H B, WANG Z X, FU X F, et al., 2008. The surface rupture zone distribution of the Wenchuan earthquake (MS8.0) happened on May 12th, 2008[J]. Geology in China, 35(5): 803-813. (in Chinese with English abstract
[21] LI H B, PAN J W, SUN Z M, et al., 2021. Continental tectonic deformation and seismic activity: a case study from the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(1): 194-213. (in Chinese with English abstract
[22] LI J N, HAN Z J, LUO J H, et al., 2021. Characteristics and implications of seismic activity around Minshan active block in eastern margin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(6): 1459-1484. (in Chinese with English abstract
[23] LI W L, 2019. Distribution pattern and post-earthquake effect of coseismic landslides of strong earthquakes[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract
[24] LI W Q, CHEN J, YUAN Z D, et al., 2011. Coseismic surface ruptures of multi segments and seismogenic fault of the tashkorgan earthquake in Pamir, 1895[J]. Seismology and Geology, 33(2): 260-276. (in Chinese with English abstract
[25] LIU F S, WU Z H, ZHANG Y Q, et al., 2014. New progress and prospects of neotectonics and active tectonics synthetical study on eastern edge Qinghai-Xizang plateau[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 33(4): 403-418. (in Chinese with English abstract
[26] LIU X L, XIA T, LIU J, et al., 2022. Distributed characteristics of the surface deformations associated with the 2021 MW7.4 Madoi earthquake, Qinghai, China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 44(2): 461-483. (in Chinese with English abstract
[27] PAN J W, BAI M K, LI C, et al., 2021. Coseismic surface rupture and seismogenic structure of the 2021-05-22 Maduo (Qinghai) MS7.4 earthquake[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(6): 1655-1670. (in Chinese with English abstract
[28] PAN J W, LI H B, CHEVALIER M L, et al., 2020. A newly discovered active fault on the Selaha-Kangding segment along the SE Xianshuihe fault: the South Mugecuo fault[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(11): 3178-3188. (in Chinese with English abstract
[29] PENG J B, XU N X, ZHANG Y S, et al., 2022. The framework system for geosafety research[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 30(6): 1798-1810. (in Chinese with English abstract
[30] RAN Y K, CHEN L C, 2004. Active tectonic research for seismic safety evaluation of long-line engineering sites in China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 26(4): 733-741. (in Chinese with English abstract
[31] REN J J, XU X W, ZHANG S M, et al., 2017. Tectonic transformation at the eastern termination of the Eastern Kunlun fault zone and seismogenic mechanism of the 8 August 2017 Jiuzhaigou MS7.0 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(10): 4027-4045. (in Chinese with English abstract
[32] REN J J, XU X W, ZHANG S M, et al., 2018. Surface rupture of the 1933 M7.5 Diexi earthquake in eastern Tibet: implications for seismogenic tectonics[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 212(3): 1627-1644. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggx498
[33] SUN X Z, XU X W, CHEN L C, et al., 2012. Surface rupture features of the 2010 Yushu earthquake and its tectonic implication[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(1): 155-170. (in Chinese with English abstract
[34] TAN X B, XU X W, YU G H, et al., 2015. The application of 3D laser scanning technology in surface rupture survey of the normal fault: an example of the 2008 MS7.3 Yutian earthquake[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 10(3): 491-500. (in Chinese with English abstract
[35] TANG C, VAN WESTEN C J, 2018. Atlas of Wenchuan-Earthquake geohazards: analysis of co-seismic and post-seismic geohazards in the area affected by the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake[M]. Beijing: Science Press.
[36] TANG R C, HAN W B, 1993. Active faults and earthquakes in Sichuan[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press. (in Chinese)
[37] TWISS R J, MOORES E M, 2007. Structural geology[M]. 2nd ed. New York: W. H. Freeman: 61-90.
[38] WANG E, BURCHFIEL B C, 2000. Late Cenozoic to Holocene deformation in southwestern Sichuan and adjacent Yunnan, China, and its role in formation of the southeastern part of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. GSA Bulletin, 112(3): 412-423.
[39] WANG F W, CHENG Q G, HIGHLAND L, et al., 2009. Preliminary investigation of some large landslides triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Landslides, 6(1): 47-54. doi: 10.1007/s10346-009-0141-z
[40] WANG H, LI H B, SI J L, et al., 2013. The relationship between the internal structure of the Wenchuan earthquake fault zone and the uplift of the Longmenshan[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(6): 2048-2060. (in Chinese with English abstract
[41] WANG T, 2020. Research on setback distance of strip-foundation under surface rupture in strong earthquakes[D]. Sanhe: Institute of Disaster Prevention. (in Chinese with English abstract
[42] WANG Z J, DANG G M, ZHANG R B, et al., 2002. Styles and characteristics of the surface rupture of the west Kunlun Mountains earthquake with MS8.1[J]. Platean Earthquake Research, 14(1): 17-25. (in Chinese with English abstract
[43] WU J F, 2009. Study on setback distance from surface rupture for Post-Wenchuan earthquake reconstruction[D]. Harbin: Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese with English abstract
[44] WU Q, LI H B, CHEVALIER M L, et al., 2021. Rock characteristics, internal structure and physical-chemical properties of Qianning segment in Xianshuihe fault zone[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 37(10): 3204-3224. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.10.14
[45] WU Z H, 2019. The definition and classification of active faults: history, current status and progress[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 40(5): 661-697. (in Chinese with English abstract
[46] WU Z H, 2022. Active faults and engineering applications I: definition and classification[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 44(6): 922-947. (in Chinese with English abstract
[47] WU Z M, SHEN T J M, CAO Z Q, et al., 1990. The surface ruptures of Danxung (Tibet) earthquake(M=8) in 1411[J]. Seismology and Geology, 12(2): 98-108. (in Chinese with English abstract
[48] Xu C, Xu X W, Yao X, et al., 2014. Three (nearly) complete inventories of landslides triggered by the May 12, 2008 Wenchuan Mw 7.9 earthquake of China and their spatial distribution statistical analysis[J]. Landslides, 11(3): 441-461. doi: 10.1007/s10346-013-0404-6
[49] XU C, 2015. Utilizing coseismic landslides to analyze the source and rupturing process of the 2014 Ludian earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 23(4): 755-759. (in Chinese with English abstract
[50] XU X W, YU G H, MA W T, et al., 2002. Evidence and methods for determining the safety distance from the potential earthquake surface rupture on active fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 470-483. (in Chinese with English abstract
[51] XU X W, WEN X Z, YU G H, et al., 2005. Average slip rate, earthquake rupturing segmentation and recurrence behavior on the Litang fault zone, western Sichuan province, China[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 48(8): 1183-1196. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/04yd0072
[52] XU X W, 2006. Active faults, associated earthquake disaster distribution and policy for disaster reduction[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 1(1): 7-14. (in Chinese with English abstract
[53] XU X W, YU G H, MA W T, et al., 2008a. Rupture behavior and deformation localization of the Kunlunshan earthquake (MW7.8) and their tectonic implications[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 51(10): 1361-1374. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1007/s11430-008-0099-z
[54] XU X W, WEN X Z, YE J Q, et al., 2008b. The MS8.0 Wenchuan earthquake surface ruptures and its seismogenic structure[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30(3): 597-629. (in Chinese with English abstract
[55] XU X W, GUO T T, LIU S Z, et al., 2016. Discussion on issues associated with setback distance from active fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 38(3): 477-502. (in Chinese with English abstract
[56] XU X W, CHEN G H, 2018. Discussion and suggestions on active fault avoidance[J]. City and Disaster Reduction(1): 8-13. (in Chinese)
[57] YU G H, XU X W, CHEN G H, et al., 2009. Relationship between the localization of earthquake surface ruptures and building damages associated with the Wenchuan 8.0 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(12): 3027-3041. (in Chinese with English abstract
[58] YUAN L X, 2005. The mechanism of loess landslide caused by earthquake in Haiyuan of Ningxia[D]. Xian: Northwest University. (in Chinese with English abstract
[59] ZANG W J, 2017. Damage to highway tunnels caused by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 54(2): 17-25. (in Chinese with English abstract
[60] ZHANG J Y, BO J S, YUAN Y F, et al., 2012. Review of research on active fault and its setback[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 21(2): 9-18. (in Chinese with English abstract
[61] ZHANG K Q, WU Z H, ZHOU C J, et al., 2020. Paleoearthquake events and inhomogeneous activity characteristics in the Benge-Cunge section of the Litang fault zone in the western Sichuan province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(4): 1295-1303. (in Chinese with English abstract
[62] ZHANG X B, YANG Z, ZHONG N, et al., 2024. Late Quaternary activity and paleoearthquake recurrence characteristics of the Litang fault in western Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 98(7): 2084-2100. (in Chinese with English abstract
[63] ZHANG Y S, SUN P, SHI J S, et al., 2010. Investigation of rupture influenced zones and their corresponding safe distances for reconstrution after 5.12 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 18(3): 312-319. (in Chinese with English abstract
[64] ZHANG Y S, GUO C B, YAO X, et al., 2016. Research on the geohazard effect of active fault on the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 37(3): 277-286. (in Chinese with English abstract
[65] ZHANG Y Z, REPLUMAZ A, WANG G C, et al., 2015. Timing and rate of exhumation along the Litang fault system, implication for fault reorganization in Southeast Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 34(6): 1219-1243. doi: 10.1002/2014TC003671
[66] ZHAO G H, 2014. Study on fault activity and tectonic geomorphology of Litang Fault within the Sichuan-Yunnan Blocks[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract
[67] ZHAO J S, WU J F, SHI L J, et al., 2009. Setback distance determination in reconstruction along the trace of surface rupture caused by MS8.0 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 29(6): 96-101. (in Chinese with English abstract
[68] ZHENG W J, LI C Y, WANG W T, et al., 2008. Trench logs of earthquake scarp of the MS8.0 Wenchuan earthquake in the segment north of Beichuan[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30(3): 697-709. (in Chinese with English abstract
[69] ZHONG N, 2017. Earthquake and provenance analysis of the lacustrine sediments in the upper reaches of the Min River during the Late Pleistocene[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese with English abstract
[70] ZHOU C J, WU Z H, ZHANG K Q, et al., 2015. New chronological constraint on the co-seismic surface rupture segments associated with the Litang Fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 37(2): 455-467. (in Chinese with English abstract
[71] ZHOU Q, XU X W, YU G H, et al., 2008. Investigation on widths of surface rupture zones of the M8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan province, China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30(3): 778-788. (in Chinese with English abstract
[72] ZHOU Q, XU X W, YU G H, et al., 2008. Investigation on widths of surface rupture zones of the M8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan province, China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30(3): 778-788. (in Chinese with English abstract
[73] ZHUANG J Q, PENG J B, XU C, et al., 2018. Distribution and characteristics of loess landslides triggered by the 1920 Haiyuan Earthquake, Northwest of China[J]. Geomorphology, 314: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.04.012
[74] 白永健,倪化勇,葛华,2019. 青藏高原东南缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究现状[J]. 地质力学学报,25(6):1116-1128. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.06.095
[75] 蔡丽雯,黄勇,何静,等,2022. 2022年青海门源6.9级地震交通系统震害与启示[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,42(4):8-16.
[76] 陈桂华,徐锡伟,郑荣章,等,2008. 2008年汶川MS8.0地震地表破裂变形定量分析:北川-映秀断裂地表破裂带[J]. 地震地质,30(3):723-738. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2008.03.011
[77] 陈桂华,李忠武,徐锡伟,等,2022. 2021年青海玛多M7.4地震发震断裂的典型同震地表变形与晚第四纪断错累积及其区域构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报,65(8):2984-3005. doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0873
[78] 陈永明,王兰民,代炜,等,2004. 2001年昆仑山口西8.1级地震区的冻土及地震破坏特征[J]. 中国地震,20(2):161-169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2004.02.006
[79] 翠川三郎. 1995. 连锁灾害的发生机制与实态追踪[C]. 科学朝日,紧急增刊:15-18.
[80] 邓起东,1984. 断层性状、盆地类型及其形成机制[J]. 地震科学研究(3):56-64.
[81] 盖海龙,姚生海,杨丽萍,等,2021. 青海玛多“5·22”MS 7.4级地震的同震地表破裂特征、成因及意义[J]. 地质力学学报,27(6):899-912. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.06.073
[82] 高帅坡,2021. 川西北次级块体内部及其西边界断裂的晚第四纪活动习性[D]. 北京:中国地震局地质研究所.
[83] 龚正,李海兵,唐方头,等,2023. 丽江-小金河断裂盐源段断裂带规模、断裂带结构及其历史活动性[J]. 地质学报,97(7):2111-2125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.07.002
[84] 郭婷婷,2013. 汶川地震震害与活动断层“避让带”宽度的分析研究[D]. 北京:中国地震局地质研究所.
[85] 郭婷婷,徐锡伟,于贵华,等,2017. 活动断层及其“避让带”宽度的研究历史与现状[J]. 地球物理学进展,32(5):1893-1900. doi: 10.6038/pg20170504
[86] 何仲太,马保起,李玉森,等,2012. 汶川地震地表破裂带宽度与断层上盘效应[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版),48(6):886-894.
[87] 兰恒星,张宁,李郎平,等,2021. 川藏铁路可研阶段重大工程地质风险分析[J]. 工程地质学报,29(2):326-341.
[88] 李滨,殷跃平,谭成轩,等,2022. 喜马拉雅东构造结工程选址面临的地质安全挑战[J]. 地质力学学报,28(6):907-918. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222819
[89] 李传友,叶建青,谢富仁,等,2008. 汶川MS8.0地震地表破裂带北川以北段的基本特征[J]. 地震地质,30(3):683-696. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2008.03.008
[90] 李传友,魏占玉,2009. 2008年汶川MS8.0地震北川以北段地表破裂变形的主要样式[J]. 第四纪研究,29(3):416-425. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2009.03.003
[91] 李海兵,王宗秀,付小方,等,2008. 2008年5月12日汶川地震(MS8.0)地表破裂带的分布特征[J]. 中国地质,35(5):803-813. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.05.002
[92] 李海兵,潘家伟,孙知明,等,2021. 大陆构造变形与地震活动:以青藏高原为例[J]. 地质学报,95(1):194-213.
[93] 李佳妮,韩竹军,罗佳宏,等,2021. 青藏高原东缘岷山活动地块周缘的地震活动特征与启示[J]. 地震地质,43(6):1459-1484. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.06.007
[94] 李为乐,2019. 典型强震同震地质灾害分布规律及后效应研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学.
[95] 李文巧,陈杰,袁兆德,等,2011. 帕米尔高原1895年塔什库尔干地震地表多段同震破裂与发震构造[J]. 地震地质,33(2):260-276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.02.002
[96] 李勇,李永昭,张毅,等,2006. 青藏高原东缘大陆动力学过程与地质响应[M]. 北京:地质出版社.
[97] 刘凤山,吴中海,张岳桥,等,2014. 青藏高原东缘新构造与活动构造研究新进展及展望[J]. 地质通报,33(4):403-418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.04.002
[98] 刘小利,夏涛,刘静,等,2022. 2021年青海玛多MW7.4地震分布式同震地表裂缝特征[J]. 地震地质,44(2):461-483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.02.012
[99] 潘家伟,白明坤,李超,等,2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多MS7.4地震地表破裂带及发震构造[J]. 地质学报,95(6):1655-1670. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.06.001
[100] 潘家伟,李海兵,CHEVALIER M L,等,2020. 鲜水河断裂带色拉哈—康定段新发现的活动断层:木格措南断裂[J]. 地质学报,94(11):3178-3188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.11.002
[101] 彭建兵,徐能雄,张永双,等,2022. 论地质安全研究的框架体系[J]. 工程地质学报,30(6):1798-1810.
[102] 冉勇康,陈立春,2004. 中国长线工程场地地震安全性评价工作中的活动构造问题[J]. 地震地质,26(4):733-741. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2004.04.019
[103] 任俊杰,徐锡伟,张世民,等,2017. 东昆仑断裂带东端的构造转换与2017年九寨沟MS7.0地震孕震机制[J]. 地球物理学报,60(10):4027-4045. doi: 10.6038/cjg20171029
[104] 孙鑫喆,徐锡伟,陈立春,等,2012. 2010年玉树地震地表破裂带典型破裂样式及其构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报,55(1):155-170. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.01.015
[105] 谭锡斌,徐锡伟,于贵华,等,2015. 三维激光扫描技术在正断层型地表破裂调查中的应用:以2008MS7.3于田地震为例[J]. 震灾防御技术,10(3):491-500. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20150302
[106] 唐荣昌,韩渭宾,1993. 四川活动断裂与地震[M]. 北京:地震出版社.
[107] 王焕,李海兵,司家亮,等,2013. 汶川地震断裂带结构特征与龙门山隆升的关系[J]. 岩石学报,29(6):2048-2060.
[108] 王拓,2020. 强震地表破裂下条形基础避让距离研究[D]. 三河:防灾科技学院.
[109] 王赞军,党光明,张瑞斌,等,2002. 昆仑山口西8.1级地震地表破裂的类型与性质[J]. 高原地震,14(1):17-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-586X.2002.01.004
[110] 吴景发,2009. 汶川地震灾后重建断层避让距离研究[D]. 哈尔滨:中国地震局工程力学研究所.
[111] 吴琼,李海兵,CHEVALIER M L,等,2021. 鲜水河断裂带乾宁段岩石特征与内部结构及其物理-化学性质[J]. 岩石学报,37(10):3204-3224. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.10.14
[112] 吴中海,2019. 活断层的定义与分类:历史、现状和进展[J]. 地球学报,40(5):661-697. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2019.051001
[113] 吴中海,2022. 活断层与工程应用I:定义与分类[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,44(6):922-947.
[114] 吴章明,申屠炯明,曹忠权,等,1990. 1411年西藏当雄南8级地震地表破裂[J]. 地震地质,12(2):98-108.
[115] 许冲,2015. 利用同震滑坡分析2014年鲁甸地震震源性质与破裂过程[J]. 工程地质学报,23(04):755-759.
[116] 徐锡伟,于贵华,马文涛,等,2002. 活断层地震地表破裂“避让带”宽度确定的依据与方法[J]. 地震地质,24(4):470-483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.001
[117] 徐锡伟,闻学泽,于贵华,等,2005. 川西理塘断裂带平均滑动速率、地震破裂分段与复发特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学),(6):540-551.
[118] 徐锡伟,2006. 活动断层、地震灾害与减灾对策问题[J]. 震灾防御技术,1(1):7-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2006.01.002
[119] 徐锡伟,于贵华,马文涛,等,2008a. 昆仑山地震(MW7.8)破裂行为、变形局部化特征及其构造内涵讨论[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学),(7):785-796.
[120] 徐锡伟,闻学泽,叶建青,等,2008b. 汶川MS8.0地震地表破裂带及其发震构造[J]. 地震地质,30(3):597-629.
[121] 徐锡伟,郭婷婷,刘少卓,等,2016. 活动断层避让相关问题的讨论[J]. 地震地质,38(3):477-502. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.03.001
[122] 徐锡伟,陈桂华,2018. 活动断层避让问题探讨与建议[J]. 城市与减灾(1):8-13.
[123] 于贵华,徐锡伟,陈桂华,等,2009. 汶川8.0级地震地表变形局部化样式与建筑物破坏特征关系初步研究[J]. 地球物理学报,52(12):3027-3041. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.12.012
[124] 袁丽侠,2005. 宁夏海原地震诱发黄土滑坡的形成机制研究:以西吉地区地震诱发黄土滑坡为例[D]. 西安:西北大学.
[125] 臧万军,2017. 汶川地震公路隧道震害规律研究[J]. 现代隧道技术,54(2):17-25.
[126] 张建毅,薄景山,袁一凡,等,2012. 活动断层及其避让距离研究综述[J]. 自然灾害学报,21(2):9-18.
[127] 张克旗,吴中海,周春景,等,2020. 川西理塘断裂带奔戈-村戈段古地震事件及其非均匀性活动特征[J]. 地质学报,94(4):1295-1303. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.04.018
[128] 张献兵,杨镇,钟宁,等,2024. 川西理塘断裂晚第四纪活动性及古地震复发特征[J]. 地质学报,98(7):2084-2100.
[129] 张永双,孙萍,石菊松,等,2010. 汶川地震地表破裂影响带调查与建筑场地避让宽度探讨[J]. 工程地质学报,18(3):312-319. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.03.004
[130] 张永双,郭长宝,姚鑫,等,2016. 青藏高原东缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究[J]. 地球学报,37(3):277-286. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.03.03
[131] 赵国华,2014. 川滇块体内理塘断裂活动性及其构造地貌研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学.
[132] 赵纪生,吴景发,师黎静,等,2009. 汶川地震地表破裂周围建筑物重建的避让距离[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,29(6):96-101.
[133] 郑文俊,李传友,王伟涛,等,2008. 汶川8.0级地震陡坎(北川以北段)探槽的记录特征[J]. 地震地质,30(3):697-709. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2008.03.009
[134] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部,2010. 建筑抗震设计规范(GB50011—2010). 北京:中国建筑工业出版社.
[135] 中国地震局地壳应力研究所,2019. 《活动断层避让》(征求意见稿)[R]. 北京:中国地震局地壳应力研究所.
[136] 钟宁,2017. 岷江上游晚更新世湖相沉积的古地震及物源分析[D]. 北京:中国地震局地质研究所.
[137] 周春景,吴中海,张克旗,等,2015. 川西理塘活动断裂最新同震地表破裂形成时代与震级的重新厘定[J]. 地震地质,37(2):455-467. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.02.009
[138] 周庆,徐锡伟,于贵华,等,2008. 汶川8.0级地震地表破裂带宽度调查[J]. 地震地质,30(3):778-788. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2008.03.016
-




 下载:
下载: