The historical evolution law and planning enlightenment of China's geographical pattern
-
摘要:
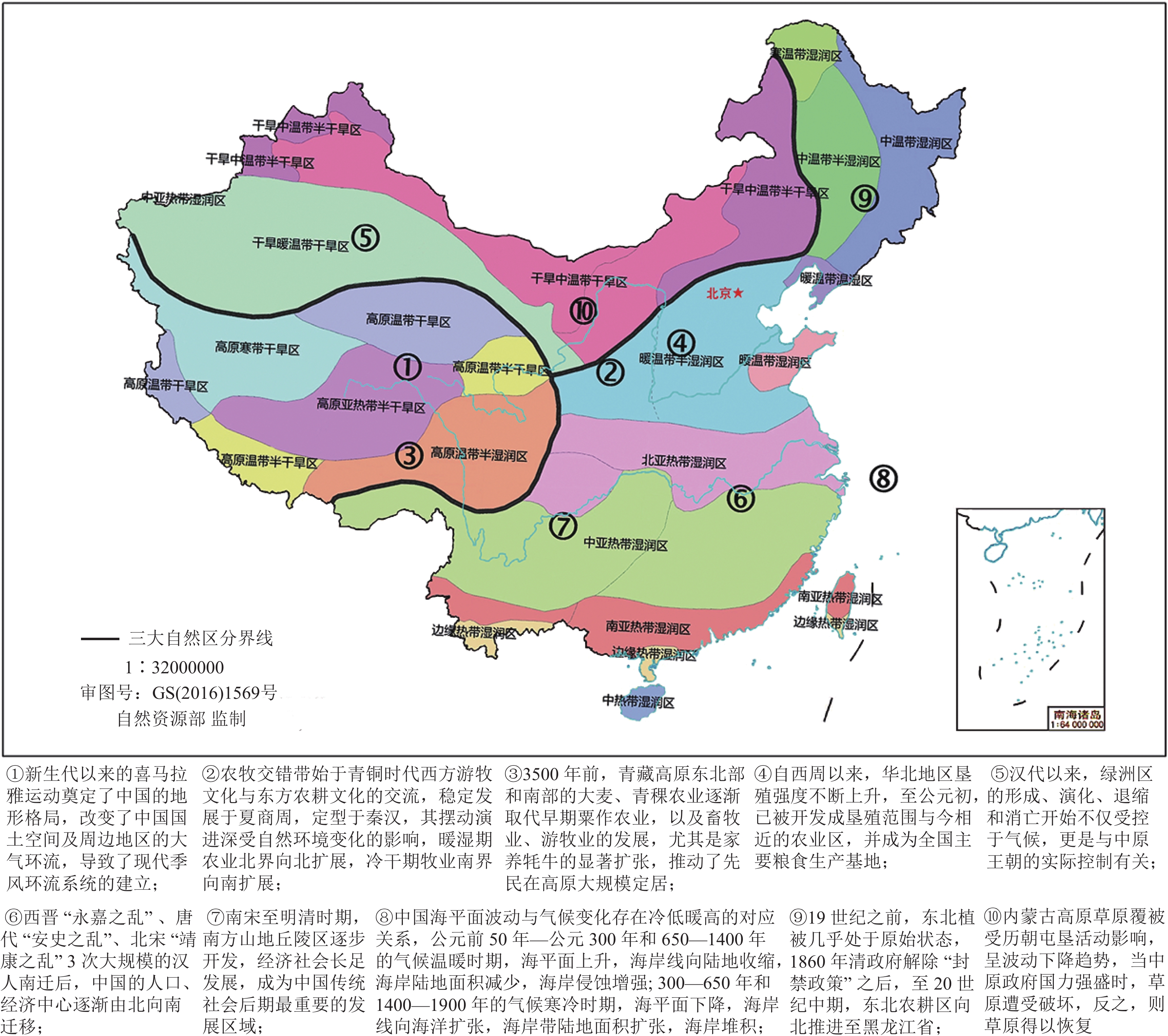
以历史逻辑回溯千年以来的自然地理格局演变规律,能够更好地支撑以行政逻辑凝练提出中国广袤国土未来发展的政策建议。通过对大量文献进行综述,总结归纳各区带的独特自然环境基础和历史演化规律,从而基于历史、科学和行政逻辑提出国土空间规划的政策建议。中国现代地理格局是经过地质时期几十亿年的演化,以及历史时期上万年的人类活动刻画而最终形成的。在地质时期的地质构造、季风运动、江河形塑等作用下,中国陆域分异出了东部季风区、西北干旱—半干旱区、青藏高原区三大自然区,以及农牧交错带、海岸带两大过渡缝合带,历史时期人类因地制宜所形成迥异的生产生活方式,更是不断改造着国土空间结构,使各区带形成了独特的区域演化历史。通过对各区带的演变过程和规律进行了详细阐述和总结,由此提出了遵从自然生态限制和历史发展规律,保持自然生态系统和人类生态系统合理搭配及相互之间物质能量畅通交流,以及优化区域过渡带等国土空间开发保护格局的建议。
Abstract:Tracing the evolution of the natural geographical pattern over the past thousand years by historical logic can better support policy recommendations for the future development of China’s territory condensed by administrative logic. We reviewed a large number of literature and summarized the unique natural environmental foundations and historical evolution laws of each region and zone, in order to propose policy recommendations for national spatial planning by historical, scientific, and administrative logic. We found that the modern geographical pattern of China has been formed by the billions years of evolution over geological period and ten thousand years of human activities over historical period. Under the influence of geological structures, monsoon movements, and river shaping during geological period, China’s land has differentiated into 3 natural regions (Eastern Monsoon Region, Northwest Arid−semiarid Region, Tibetan Plateau) and 2 transition zones (Farming−pastoral Zone, Coastal Zone). In historical period, humans have formed distinct production and lifestyle patterns tailored to local conditions, continuously transforming the spatial structure of the country, and thus forming each region’s and zone’s unique regional evolutionary histories. And we provided a detailed explanation and summary of the evolution process and laws in each region and zone, thus proposing suggestions for the national territory developing and protecting, such as following the natural ecological restriction and historical development law, maintaining the reasonable combination and material−energy exchange between natural and human ecosystem, and optimizing spatial pattern in transition zones.
-

-
[1] Chen Q G. 2018. Revisiting the "Hu Huanyong Line" and the pastoral−agricultural boundary[J]. Grassland Science, 35(3): 669−676 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] Fan J, Wang Y F. 2019. Changes in China's economic geography over the past 40 years and regional coordinated development in the new era[J]. Economic Geography, 39(1): 1−7 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Fang X Q. 1999. The decline of primitive agriculture and the formation of the pastoral−agricultural boundary in northern China from an agroclimatic perspective[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 14(3): 212−218 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Fang X Q, He F N, Wu Z L, et al. 2021. Basic characteristics of the expansion of China's cultivated area and changes in the rate of reclamation over the past 2000 years[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 76(7): 1732−1746 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Fang X Q, Zhao W Y, Zhang C P, et al. 2020. Methods for assessing the reliability of global historical LUCC datasets and case studies[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 50(7): 1009−1020 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] Fang Y K. 1989. Forty years of agricultural reclamation in Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Science and Technology, (6): 46−49(in Chinese).
[7] Ge J X. 1985. Population geography of the Western Han Dynasty[M]. Beijing: People's Publishing House(in Chinese).
[8] Ge Q S. 2011. Climate changes in Chinese dynasties [M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
[9] Ge Q S, Liu H L, Zheng J Y, et al. 2013. Climate change and social development in China over the past 2000 years[J]. Acta Naturae, 35(1): 9−21 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[10] Han D L. 1999. Progress in the study of Chinese oases[J]. Science of Geography, 19(4): 313−319 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Han M L. 1999. General history of agriculture in the Liao and Jin dynasties [M]. Beijing: Social Sciences Academic Press (in Chinese).
[12] Han M L. 2012. Historical agricultural geography of China [M]. Beijing: Peking University Press: 433−434 (in Chinese).
[13] Han M L. 2015. Fifteen lectures on the historical geography of China [M]. Beijing Peking University Press: 1−17 (in Chinese).
[14] He C F, Hu X Q. 2019. Evolution of China's industrial geography since the reform and opening up in 1978[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 74(10): 1962−1979 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] He F N, Ge Q S, Dai J H, et al. 2007. Changes in China's forests over the past 300 years[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, (1): 30−40 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] He B T. 2020. Population and related issues from the early Ming Dynasty to 1953 [M]. Beijing: Zhonghua Book Company: 203 (in Chinese).
[17] Hou X Y, Liu J, Song Y, et al. 2016. Ecological environmental impact and policy recommendations of the development and utilization of the mainland China coastline[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 31(10): 1143−1150 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Jia D, Li Y K, Fang X Q. 2018. Complexity of factors influencing the spatiotemporal distribution of archaeological settlements in Northeast China over the past millennium[J]. Quaternary Research, 89(2): 413−424. doi: 10.1017/qua.2017.112
[19] Jin F J, Chen Z. 2019. Evolution and patterns of China's transportation geography since the reform and opening up in 1978[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica (English Edition), 74(10): 1941−1961 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Jin S M, Hou G L, Chen X L, et al. 2022. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of human activities on the Tibetan Plateau since the last glacial period and their causes[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 42(1): 223−235(in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Li B G, Liu Z, Huang F, et al. 2021. Consolidating the black soil grain basket to ensure national food security[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 36(10): 1184−1193 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Li S C, He F N, Zhang X Z. 2016. A spatially explicit reconstruction of cropland cover in China from 1661 to 1996[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 16(2): 417−428. doi: 10.1007/s10113-014-0751-4
[23] Lin Z H, Mo X G. 2011. Changes in agricultural systems and the evolution of agricultural production environment in the Huang−Huai−Hai Plain during historical times[J]. Research of Farmland Water Consumption, 19(5): 1072−1079 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Lu X Q, Dong Q. 2010. Historical process and spatial distribution of economic development in southern mountainous areas[J]. Chinese Historical Geography, 25(4): 31−46 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Niu F Q, Feng Z M, Liu H. 2018. Review and prospect of methods for evaluating the carrying capacity of resources and environment[J]. Resources Science, 40(4): 655−663 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Wan T F, Zhu H. 2002. Mesozoic−Cenozoic tectonics and environmental changes in mainland China and adjacent areas[J]. Modern Geology, 16(2): 107−120(in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Wang M D. 2008. From the Yellow River era to the canal era [M]. Chengdu: Bashu Publishing House (in Chinese).
[28] Wang S M. 2010. Research on the spread of American crops in China and their impact [M]. Beijing: China Three Gorges Press (in Chinese).
[29] Wen P H. 2021. Response of human activities on the Ordos Plateau to environmental changes during the Holocene [D]. Doctoral Dissertation of Lanzhou University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Wu N, Liu Z G. 1998. Discussion on the causes of the geographical pattern of subalpine forest meadow vegetation in the eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Environmental Biology, 4(3): 290−297 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Wu Z L, Fang X Q, Jia D, et al. 2020. Reconstruction of cropland cover using historical literature and settlement relics in farming areas of Shangjing Dao during the Liao Dynasty around 1100 AD[J]. The Holocene, 30(11): 1516−1527. doi: 10.1177/0959683620941293
[32] Xie Z R, Yuan L W. 2012. A brief discussion on the volatility of Holocene sea−level changes and its environmental significance[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 32(6): 1065−1077 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Xu N. 2019. Monitoring global coastline changes from 1987 to 2016 using Landsat imagery[D]. Doctoral Dissertation of Tsinghua University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Yin Y H. 2003. Sedimentation and land creation rates of the modern Yellow River Delta coast[J]. Marine Geology Dynamics, (7): 13−18,37−38 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Ye Y, Fang X Q, Ren Y Y, et al. 2009. Changes in cropland coverage in Northeast China over the past 300 years[J]. Science China (D Series: Earth Sciences), 39(3): 340−350 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] You L Y, Yang J C. 2013. Chinese geomorphology [M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
[37] Yu K F. 2012. South China coral reefs and their records and responses to Holocene environmental changes[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 42(8): 1160−1172 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Zhang C M, Weng S X, Bao J G. 2019. The geographical pattern of China's tourism development since the reform and opening up in 1978[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 74(10): 1980−2000 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Zhang H, Fan Z L. 1998. The impact of climate change and human activities on the evolution of oases in the Tarim Basin[J]. Chinese Deserts, (4): 14−19 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[40] Zhang L S. 2012. Ancient Geography of China: The Formation of China's Natural Environment [M]. Beijing: Science Press: 306−359 (in Chinese) .
[41] Zhao H T. 2017. Discovery and scientific significance of the ancient coastline relics at Qixinggang, Guangzhou[J]. Tropical Geography, 37(4): 610−619 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[42] Zheng D, Yao T D. 2004. Uplift of the Tibetan Plateau and its environmental effects [M]. Beijing: Science Press: 165−275 (in Chinese) .
[43] Zheng J Y, Wen Y J, Fang X Q. 2020. Some characteristics of climate and land cover changes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River over the past 2000 years[J]. Resources Science, 42(1): 3−19 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[44] Zheng J Y, Hao Z X, Zhang X Z, et al. 2014. Drought and flood patterns of warm and cold periods in eastern China over the past 2000 years[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59(30): 2964−2971 (in Chinese with English abstract) . doi: 10.1360/N972014-00393
[45] Editorial Board of "Geology of China". 1999. Geology of China [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1−53 (in Chinese) .
[46] Zhu S G. 1994. Vegetation changes in the North China Plain during historical times[J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 22(4): 79−85 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[47] Zou Y L. 1995. Shift of the northern pastoral−agricultural boundary and climate warm−cold changes during the Ming and Qing periods. Journal of Fudan University (Social Sciences Edition), (1): 25−33 (in Chinese with English abstract) .
[48] Zou Y L, Zhang X G. 2013. Historical natural geography of China [M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
[49] 陈全功. 2018. 再谈“胡焕庸线”及农牧交错带[J]. 草业科学, 35(3): 669−676. doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2017-0139
[50] 樊杰, 王亚飞. 2019. 40年来中国经济地理格局变化及新时代区域协调发展[J]. 经济地理, 39(1): 1−7.
[51] 方修琦. 1999. 从农业气候条件看我国北方原始农业的衰落与农牧交错带的形成[J]. 自然资源学报. 14(3): 212−218.
[52] 方修琦, 何凡能, 吴致蕾, 等. 2021. 过去2000年中国农耕区拓展与垦殖率变化基本特征[J]. 地理学报, 76(7): 1732−1746. doi: 10.11821/dlxb202107012
[53] 方修琦, 赵琬一, 张成鹏, 等. 2020. 全球历史LUCC数据集数据可靠性的评估方法及评估案例[J]. 中国科学, 50(7): 1009−1020.
[54] 方英楷. 1989. 新疆农垦四十年[J]. 新疆农垦科技, (6): 46−49.
[55] 葛剑雄. 1985. 西汉人口地理[M]. 北京: 人民出版社.
[56] 葛全胜. 2011. 中国历朝气候变化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
[57] 葛全胜, 刘浩龙, 郑景云, 等. 2013. 中国过去2000年气候变化与社会发展[J]. 自然杂志, 35(1): 9−21.
[58] 韩德林. 1999. 中国绿洲研究之进展[J]. 地理科学, 19(4): 313−319. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.1999.04.005
[59] 韩茂莉. 1999. 辽金农业通史[M]. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社.
[60] 韩茂莉. 2012. 中国历史农业地理[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社: 433−434.
[61] 韩茂莉. 2015. 中国历史地理十五讲[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社: 1−17.
[62] 贺灿飞, 胡绪千. 2019. 1978年改革开放以来中国工业地理格局演 变[J]. 地理学报, 74(10): 1962−1979. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201910002
[63] 何凡能, 葛全胜, 戴君虎, 等. 2007. 近300年来中国森林的变迁[J]. 地理学报, (1): 30−40.
[64] 何炳棣. 2020. 明初以降人口及其相关问题1368—1953[M]. 北京: 中华书局: 203.
[65] 侯西勇, 刘静, 宋洋, 等. 2016. 中国大陆海岸线开发利用的生态环境影响与政策建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 31(10): 1143−1150.
[66] 金凤君, 陈卓. 2019. 1978年改革开放以来中国交通地理格局演变与规律[J]. 地理学报: 英文版, 74(10): 1941−1961.
[67] 金孙梅, 侯光良, 陈晓良, 等. 2022. 青藏高原末次冰消期以来人类活动的时空演化特征及其原因探讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 42(1): 223−235.
[68] 李保国, 刘忠, 黄峰, 等. 2021. 巩固黑土地粮仓保障国家粮食安全[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 36(10): 1184−1193.
[69] 林忠辉, 莫兴国. 2011. 历史时期黄淮海平原农作制度变迁与农业生产环境演变[J]. 农田耗水研究, 19(5): 1072−1079.
[70] 鲁西奇, 董勤. 2010. 南方山区经济开发的历史进程与空间展布[J]. 中国历史地理论丛, 25(4): 31−46.
[71] 牛方曲, 封志明, 刘慧. 2018. 资源环境承载力评价方法回顾与展望[J]. 资源科学, 40(4): 655−663.
[72] 万天丰, 朱鸿. 2002. 中国大陆及邻区中生代—新生代大地构造与环境变迁[J]. 现代地质, 16(2): 107−120.
[73] 王明德. 2008. 从黄河时代到运河时代[M]. 成都: 巴蜀书社: 1−390.
[74] 王思明. 2010. 美洲作物在中国的传播及其影响研究[M]. 北京: 中国三峡出版社: 44.
[75] 温鹏辉. 2021. 鄂尔多斯高原全新世人类活动对环境变迁的响应[D]. 兰州大学博士学位论文.
[76] 吴宁, 刘照光. 1998. 青藏高原东部亚高山森林草甸植被地理格局的成因探讨[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 4(3): 290−297.
[77] 谢志仁, 袁林旺. 2012. 略论全新世海面变化的波动性及其环境意 义[J]. 第四纪研究, 32(6): 1065−1077.
[78] 徐南. 2019. 利用美国陆地卫星监测1987—2016年全球海岸线变 化[D]. 清华大学博士学位论文.
[79] 尹延鸿. 2003. 现代黄河三角洲海岸的冲淤及造陆速率[J]. 海洋地质动态, (7): 13−18, 37−38.
[80] 叶瑜, 方修琦, 任玉玉, 等. 2009. 东北地区过去300年耕地覆盖变 化[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 39(3): 340−350.
[81] 尤联元, 杨景春. 2013. 中国地貌[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
[82] 余克服. 2012. 南海珊瑚礁及其对全新世环境变化的记录与响应[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 42(8): 1160−1172.
[83] 张城铭, 翁时秀, 保继刚. 2019. 1978年改革开放以来中国旅游业发展的地理格局[J]. 地理学报, 74(10): 1980−2000.
[84] 张宏, 樊自立. 1998. 气候变化和人类活动对塔里木盆地绿洲演化的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, (4): 14−19.
[85] 张兰生. 2012. 中国古地理: 中国自然环境的形成[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 306−359.
[86] 赵焕庭. 2017. 广州七星岗古海岸遗迹的发现及其科学意义[J]. 热带地理, 37(4): 610−619.
[87] 郑度, 姚檀栋. 2004. 青藏高原隆升与环境效应[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 165−275.
[88] 郑景云, 文彦君, 方修琦. 2020. 过去2000年黄河中下游气候与土地覆被变化的若干特征[J]. 资源科学, 42(1): 3−19.
[89] 郑景云, 郝志新, 张学珍, 等. 2014. 中国东部过去2000年百年冷暖的旱涝格局[J]. 科学通报, 59(30): 2964−2971.
[90] 《中国地质学》扩编委员会. 1999. 中国地质学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1−53.
[91] 朱士光. 1994. 历史时期华北平原的植被变迁[J]. 陕西师大学报(自然科学版), 22(4): 79−85.
[92] 邹逸麟. 1995. 明清时期北部农牧交错带的推移和气候暖寒变化[J]. 复旦大学学报(社会科学版), (1): 25−33.
[93] 邹逸麟, 张修桂. 2013. 中国历史自然地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
-



 下载:
下载: