Mica 40Ar-39Ar isotopic chronology of Bizigou and Nanhegou copper deposit in Zhongtiao Mountain region, Shanxi Province, and its constraint on metallogenic tectonic setting
-
摘要:
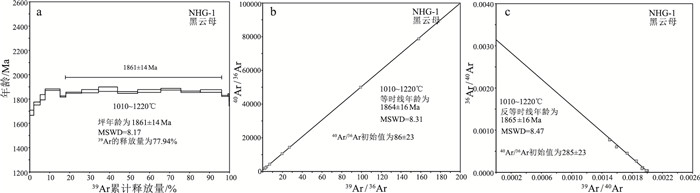
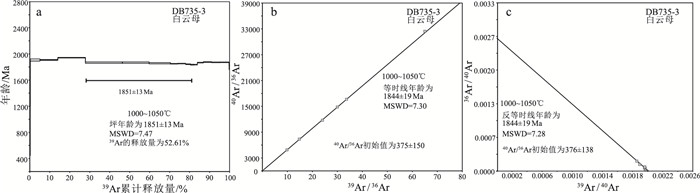
篦子沟、南河沟铜矿床位于华北克拉通中部造山带南缘,是山西中条山地区胡篦型铜矿的典型代表,因严格受地层控制,呈层状、似层状产出,也被认为是沉积岩型层状铜矿床。这些矿床的成矿年龄仍未被精确测定,成矿时代长期存在争议。在矿床学研究的基础上,对篦子沟、南河沟铜矿内与矿化有关的蚀变黑云母开展了高精度的40Ar-39Ar测年。获得篦子沟铜矿床黑云母40Ar-39Ar坪年龄为1825 ± 13 Ma(MSWD=8.86),对应的等时线年龄为1820 ± 13Ma(MSWD=5.67),反等时线年龄为1820 ± 13 Ma(MSWD=5.63);南河沟黑云母40Ar-39Ar坪年龄为1861 ± 14 Ma(MSWD=8.17),对应的等时线年龄为1864 ± 16 Ma(MSWD=8.31),反等时线年龄为1865 ± 16 Ma(MSWD =8.47)。2个矿床的成矿年龄在误差范围内一致,表明胡篦型铜矿热液期矿化年龄限定在1850 Ma左右。此年龄与中部造山带约1.85 Ga峰期变质和退变质作用时间一致,综合已有研究成果推测,该期成矿事件与碰撞造山事件耦合。区域上,在侵入中条群的基性岩内发育含矿石英脉,对脉内与硫化物伴生的白云母进行40Ar-39Ar定年,获得其坪年龄1851 ± 13 Ma(MSWD=7.47),对应的等时线年龄为1844 ± 19 Ma(MSWD=7.30),反等时线年龄为1844 ± 19 Ma(MSWD=7.28),说明基性岩内的含矿石英脉与矿区内的热液期矿化为同一地质事件的产物,印证了碰撞造山过程中产生的变质流体广泛作用于区域各地质体,且影响范围广泛。
Abstract:The Bizigou and Nanhegou copper deposits are located in the southern margin of the Trans-North China Orogen of the North China Craton.They are typical of the Hubi type copper deposits in the Zhongtiao Mountain area of Shanxi Province.Because they are controlled by strata and like stratified, they are also considered as the sediment-hosted stratiform copper deposits.However, the mineralization age of these deposits has not been determined and remain controversial.In this paper, high-precision 40Ar-39Ar dating of mica in Bizigou and Nanhegou copper deposits was carried out.The plateau age of Bizigou copper deposit sample was 1825 ± 13 Ma(MSWD=8.86), and the corresponding isochron age was 1820 ± 13 Ma(MSWD=5.67), inverse isochron age of 1820 ± 13 Ma(MSWD =5.63).The samples from Nanhegou copper deposit obtained plateau age of 1861 ± 14 Ma(MSWD=8.17), the corresponding isochron age is 1864 ± 16 Ma(MSWD=8.31), and the inverse isochron age is 1865 ± 16 Ma(MSWD= 8.47).The mineralization ages of the two deposits are consistent within the error range, indicating that the hydrothermal mineralization time of the Hubi type copper deposit is limited to ca.1850 Ma.This age is consistent with the peak metamorphism and retrometamorphism of ca.1.85 Ga in the Trans-North China Orogen.After that, it was found ore bearing quartz veins were developed in the mafic rocks of Zhongtiao Group.40Ar-39Ar dating of muscovite associated with sulfide in veins obtained the plateau age of 1851 ± 13 Ma(MSWD= 7.47), the corresponding isochron ages of 1844 ± 19 Ma(MSWD= 7.30)and inverse isochron ages of 1844 ± 19 Ma(MSWD= 7.28), indicating that the mineralization is the product of the same geological event as the hydrothermal mineralization in the mining area.It is proved that metamorphic hydrothermal fluid widely acted on geological bodies throughout the region during the collision orogeny.
-

-
表 1 篦子沟铜矿黑云母40Ar/39Ar阶段升温测年数据
Table 1. 40Ar/39Ar stepwise heating analytical data for biotite from the Bizigou copper deposit
T/℃ 36Ar[fA] 37Ar[fA] 38Ar[fA] 39Ar[fA] 40Ar[fA] 40(r)/39(k) 40Ar(r)/% 39Ar(k)/% 年龄/Ma 2σ 800 176.69583 0.000000 36.50807 30.6123 67116.21 486.81277 22.20 1.91 1832 52 840 92.04321 0.000000 19.80003 38.4186 46725.32 508.25295 41.79 2.40 1882 30 880 50.57066 0.000000 20.61411 172.1045 102693.61 509.85963 85.45 10.74 1885.5 7.8 980 21.44286 66.750257 16.91062 205.6011 112053.42 514.33801 94.35 12.82 1895.7 9.8 1020 19.67498 0.000000 15.17454 178.7073 95857.73 503.85685 93.93 11.15 1871.6 6.2 1090 57.88834 0.000000 33.20047 335.4301 180910.60 488.33723 90.54 20.92 1835.4 6.8 1120 12.13816 0.000000 18.43790 255.5425 128499.68 488.80957 97.21 15.94 1836.5 5.3 1150 8.10220 0.000000 16.24498 240.7596 118507.76 482.27536 97.98 15.02 1821.0 3.8 1180 1.07863 0.000000 6.96763 105.7083 51211.25 481.43828 99.38 6.59 1819.0 4.1 1210 0.17933 0.000000 1.69050 27.8751 13496.72 482.28008 99.61 1.74 1821.0 5.0 1240 0.99908 0.000000 0.69618 10.5787 5433.65 485.72934 94.57 0.66 1829.2 7.7 1400 3.55914 0.000000 0.66327 1.7329 1944.94 515.43722 45.92 0.11 1898 43 表 2 南河沟铜矿黑云母40Ar/39Ar阶段升温测年数据
Table 2. 40Ar/39Ar stepwise heating analytical data for biotite from the Nanhegou copper deposit
T/℃ 36Ar[fA] 37Ar[fA] 38Ar[fA] 39Ar[fA] 40Ar[fA] 40(r)/39(k) 40Ar(r)/% 39Ar(k)/% 年龄/Ma 2σ 830 73.83705 0.00000 14.72764 39.4528 38567.6 424.52253 43.43 2.02 1687 22 860 52.17596 0.00000 11.17139 62.3765 43778.1 454.65584 64.78 3.19 1764 12 890 88.03006 0.00000 17.61674 48.3965 49039.0 475.77527 46.95 2.48 1815 22 920 71.23406 0.00000 17.06537 145.6097 94135.9 501.92783 77.64 7.45 1877.1 5.9 980 12.25865 0.00000 3.40258 57.2300 30985.5 478.11929 88.31 2.93 1820.9 4.6 1010 42.87751 0.00000 11.56203 154.1373 88390.9 491.24955 85.66 7.89 1852.1 4.8 1040 92.97176 67.87742 21.30473 165.2197 109539.5 496.89904 74.92 8.45 1865 13 1070 76.36794 216.13466 18.24138 186.1223 116213.3 503.69451 80.59 9.52 1881 18 1100 29.05731 0.00000 9.87440 196.6160 105293.6 491.85293 91.84 10.06 1853.5 7.5 1130 11.65506 0.00000 7.23272 226.6876 116192.4 497.36828 97.03 11.60 1866 12 1160 7.28902 0.00000 5.26340 195.9159 100811.9 503.56868 97.86 10.03 1880.9 7.0 1190 1.20144 0.00000 3.93210 190.7202 94653.9 494.43091 99.62 9.76 1859.6 6.1 1220 2.08648 0.00000 4.62702 207.6087 103852.4 497.25665 99.41 10.63 1866 11 1250 1.31157 0.00000 1.41558 61.3139 29824.9 480.10337 98.70 3.14 1825.6 4.7 1300 2.00591 0.00000 0.49516 11.6520 6226.9 483.53157 90.48 0.60 1833.8 9.8 1400 3.61588 0.00000 0.63980 4.9203 3307.1 454.97528 67.69 0.25 1764 21 表 3 基性岩内石英硫化物脉中白云母40Ar/39Ar阶段升温测年数据
Table 3. 40Ar/39Ar stepwise heating analytical data for muscovite from the sulfides-bearing quartz veins in basic rock
T/℃ 36Ar[fA] 37Ar[fA] 38Ar[fA] 39Ar[fA] 40Ar[fA] 40(r)/39(k) 40Ar(r)/% 39Ar(k)/% 年龄/Ma 2σ 800 192.49119 0.000000 35.23279 8.1862 58186.8 159.48477 2.24 0.23 823 377 860 182.24442 20.265783 36.34226 170.8720 142391.4 518.20823 62.18 4.90 1908 15 950 62.43436 0.000000 16.92114 310.7092 179613.2 518.69200 89.73 8.91 1908.9 5.8 970 88.84845 0.000000 24.61812 482.0375 283437.2 533.52739 90.74 13.82 1942.3 4.5 1000 67.70976 0.000000 21.04461 643.7855 342349.7 500.69218 94.15 18.45 1868 11 1010 32.33111 0.000000 11.97875 467.8146 243796.0 500.71095 96.08 13.41 1868 10 1020 5.73966 0.000000 5.98579 371.6080 186383.5 496.99038 99.09 10.65 1859 10 1030 3.83061 0.000000 2.24855 127.8202 64188.6 493.31844 98.24 3.66 1850.3 4.4 1040 4.65581 0.000000 2.47282 138.1459 69678.5 494.42010 98.02 3.96 1852.9 4.6 1050 3.63382 0.000000 1.64754 86.0923 43276.1 490.19353 97.52 2.47 1842.9 4.3 1060 3.03562 0.000000 1.21217 60.1632 30213.1 487.27011 97.03 1.72 1836.0 6.0 1080 3.26425 0.000000 1.36329 59.4172 29920.7 487.33156 96.78 1.70 1836.2 4.3 1120 2.26651 0.000000 1.80064 104.1546 52818.1 500.67696 98.73 2.99 1867.5 4.5 1140 3.15040 0.000000 2.48257 145.1779 74117.0 504.10790 98.74 4.16 1875.4 5.3 1170 2.98468 0.000000 2.30369 143.1514 72817.8 502.51077 98.79 4.10 1871.7 5.1 1200 2.73909 0.000000 1.87604 107.2493 54743.5 502.88105 98.52 3.07 1872.6 4.5 1240 4.11148 0.000000 1.38814 54.4692 28616.6 503.06264 95.75 1.56 1873.0 4.3 1400 19.53027 0.000000 3.55394 7.6203 9340.3 468.37206 38.21 0.22 1791 29 -
[1] 庞雪娇. 山西中条山南和沟、老宝滩铜矿床矿化富集规律及矿床成因探讨[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2010: 10-26.
[2] 张晗. 山西中条山北段古元古代铜矿成矿作用[D]. 吉林大学博士学位论文, 2012: 35-78.
[3] 《中条山铜矿地质》编写组. 中条山铜矿地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1978: 1-184.
[4] 陶铨. 中条山前寒武纪地层的时代[J]. 中国地质科学院天津地质矿产研究所所刊, 1985: 12.
[5] 孙海田, 葛朝华, 冀树楷. 中条山地区前寒武纪地层同位素年龄及其意义[J]. 中国区域地质, 1990, 3: 237-248. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD199003005.htm
[6] 孙大中, 李惠民, 林源贤, 等. 中条山前寒武纪年代学、年代构造格架和年代地壳结构模式的研究[J]. 地质学报, 1991, (3): 216-231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199103001.htm
[7] 胡维兴. 关于中条山胡-篦型铜矿床成矿期和成矿时代问题[J]. 华北地质矿产杂志, 1994, (2): 161-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDZ402.002.htm
[8] 黄典豪, 杜安道, 吴澄宇, 等. 华北地台钼(铜)矿床成矿年代学研究——辉钼矿铼-锇年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 1996, (4): 78-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ604.008.htm
[9] 谭少华. 山西中条山胡-篦型铜矿床成矿地质条件与矿床成因[J]. 西南工学院学报, 1997, (2): 60-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNGX199702012.htm
[10] 李文光. 山西省中条山铜矿带胡-篦型矿床成矿构造特征研究[D]. 中南大学硕士学位论文, 2007: 20-36.
[11] 薛昊日. 山西中条山桐木沟、篦子沟铜矿床地质特征及成矿模式研究[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2010: 45-69.
[12] 张亮, 李碧乐, 张晗, 等. 山西中条山桐木沟铜矿床辉钼矿的铼-锇测年及地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2013, 32(4): 740-746. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2013.04.011
[13] 黄维平, 孙丰月, 张晗, 等. 山西中条山胡篦型铜矿床岩石地球化学特征[J]. 世界地质, 2013, 32(2): 212-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2013.02.003
[14] 王子维. 中条地区胡家峪铜矿床地质特征及成矿动力学背景[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2014: 26-35.
[15] Jiang Y, Niu H, Bao Z, et al. Fluid evolution of the Paleoproterozoic Hujiayu copper deposit in the Zhongtiaoshan region: evidence from fluid inclusions and carbon-oxygen isotopes[J]. Precambrian Research, 2014, 255: 734-747. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.08.007
[16] Qiu Z J, Fan H R, Liu X, et al. Fluid inclusion and carbon-oxygen isotope studies of the Hujiayu Cu deposit, Zhongtiao Mountains, China: Implications for syn-metamorphic copper remobilization[J]. Acta Geol. Sin., 2015, 89(3): 726-745. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12475
[17] Qiu Z J, Fan H R, Liu X. Mineralogy, chalcopyrite Re-Os geochronology and sulfur isotope of the Hujiayu Cu deposit in the Zhongtiao Mountains, North China Craton: Implications for a Paleoproterozoic metamorphogenic copper mineralization[J]. Ore Geol. Rev., 2016, 78: 252-267. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.04.007
[18] Qiu Z J, Fan H R, Liu X. Metamorphic P-T-t evolution of Paleoproterozoic schist-hosted Cu deposits in the Zhongtiao Mountains, North China Craton: Retrograde ore formation during sluggish exhumation[J]. Precambrian Research, 2017, 300: 59-77. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.08.014
[19] 耿艳光, 简伟, 李洪英, 等. 中条山篦子沟铜矿辉钼矿铼-锇同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(5): 1405-1418. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201705006.htm
[20] Zhao G C, Wilde S A, Cawood P A, et al. Archean blocks and their boundaries in the North China Craton: lithological, geochemical, structural and P-T path constraints and tectonic evolution[J]. Precambrian Research, 2001, 107: 45-73. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00154-6
[21] Zhao G C, Sun M, Wilde S A, et al. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: Key issues revisited[J]. Precambrian Research, 2005, 136: 177-202. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002
[22] Zhao G C, Cawood P A, Wilde S A, et al. Metamorphism of basement rocks in the Central Zone of the North China Craton: Implications for Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution[J]. Precambrian Research, 2000, 103: 55-88. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00076-0
[23] Wilde S A, Zhao G C, Sun M. Development of the North China Craton during the Late Archaean and its final amalgamation at 1.8 Ga: Some speculations on its position within a global Palaeoproterozoic supercontinent[J]. Gondwana Research, 2002, 5: 85-94. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70892-3
[24] Kröner A, Wilde S A, Li J H, et al. Age and evolution of a Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic upper to lower crustal section in the Wutaishan /Hengshan /Fuping terrain of northern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2005, 24: 577-595. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.01.001
[25] Kröner A, Wilde S A, Zhao G C, et al. Zircon geochronology and metamorphic evolution of mafic dykes in the Hengshan Complex of northern China: Evidence for late Palaeoproterozoic extension and subsequent high-pressure metamorphism in the North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2006, 146: 45-67. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.01.008
[26] Wilde S A, Zhao G C. Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2005, 24: 519-522. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.06.004
[27] Zhang J, Zhao G C, Li S Z, et al. Deformation history of the Hengshan Complex: Implications for the tectonic evolution of the Trans-North China Orogen[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2007, 29: 933-949. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2007.02.013
[28] Trap P, Faure M, Lin W, et al. Late Paleoproterozoic(1900-1800Ma)nappe stacking and polyphase deformation in the Hengshan-Wutaishan area: Implications for the understanding of the Trans-North-China belt, North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2007, 156: 85-106. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.03.001
[29] Trap P, Faure M, Lin W, et al. Contrasted tectonic styles for the Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: Evidence for a similar to 2.1Ga thermal and tectonic event in the Fuping Massif[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2008, 30: 1109-1125. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2008.05.001
[30] Wang J, Wu Y B, Gao S, et al. Zircon U-Pb and trace element data from rocks of the Huai'an Complex: New insights into the Late Paleoproterozoic collision between the Eastern and Western blocks of the North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2010, 178: 59-71. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2010.01.007
[31] 白瑾, 余致信, 戴凤岩, 等. 中条山前寒武纪地质[M]. 天津: 天津科学技术出版社, 1997: 1-143.
[32] 张瑞英. 华北克拉通南部中条山地区涑水杂岩的组成与演化[D]. 西北大学博士学位论文, 2015: 36-48.
[33] 孙大中, 胡维兴. 中条山前寒武纪年代构造格架和年代地壳结构[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. 1993: 31-45.
[34] 李秋根, 刘树文, 王宗起, 等. 中条山绛县群碎屑锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(6): 1359-1368. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200806020.htm
[35] 刘玄, 范宏瑞, 邱正杰, 等. 中条山地区绛县群和中条群沉积时限: 夹层斜长角闪岩SIMS锆石U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(6): 1564-1572. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201506006.htm
[36] Liu C H, Zhao G C, Sun M, et al. U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotope geochemistry of detrital zircons from the Zhongtiao Complex: Constraints on the tectonic evolution of the Trans-North China Orogen[J]. Precambrian Research, 2012, 222/223: 159-172. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.08.007
[37] 梅华林. 中条山早元古代变质岩石的PTt轨迹和构造演化[J]. 地质论评, 1994, 40(1): 36-47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1994.01.005
[38] Sun D Z, Hu W X, Tang M. Origin of Late Archean and Early Proterozoic rocks and associated mineral deposits from theZhongtiao Mountains, East-Central China[J]. Precambrian Research, 1990, 47(3/4): 287-306. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/030192689090043P
[39] 陈文, 张彦, 金贵善, 等. 青藏高原东南缘晚新生代幕式抬升作用的Ar-Ar热年代学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(4): 867-872. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200604010.htm
[40] 张彦, 陈文, 陈克龙, 等. 成岩混层(I/S)Ar-Ar年龄谱型及39Ar核反冲丢失机理研究——以浙江长兴地区P-T界线粘土岩为例[J]. 地质论评, 2006, 52(4): 556-561. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.04.015
[41] Brenan J M, Cherniak D J, Rose L A. Diffusion of osmium in pyrrhotite and pyrite: Implications for closure of the Re-Os isotopic system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 180(3/4): 399-413. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X00001655
[42] Peng J T, Zhou M F, Hu R Z, et al. Precise molybdenite Re-Os and mica Ar-Ar dating of the Mesozoic Yaogangxian tungsten deposit, central Nanling district, South China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2006, 41(7): 661-669. doi: 10.1007/s00126-006-0084-4
[43] Yuan S D, Peng J T, Shen N P, et al. 40Ar-39Ar isotopic dating of the Xianghualing Sn-polymetallic orefield in southern Hunan, China and its geological implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinca, 2007, 81(2): 278-286. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2007.tb00951.x
[44] 袁顺达, 侯可军, 刘敏. 安徽宁芜地区铁氧化物-磷灰石矿床中金云母Ar-Ar定年及其地球动力学意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(3): 797-808. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201003013.htm
[45] Purdy J W, Jäger E. K-Ar Ages on Rocks Forming Minerls from the Central Alps[C]//Memorie degli Istituti di Geologiae Mineralogia dell'Universita di Padova, 1976, 30: 1-321.
[46] 袁顺达, 张东亮, 双燕, 等. 湘南新田岭大型钨钼矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素测年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(1): 27-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201201005.htm
[47] 华杉, 薛生升. 40Ar/~39Ar同位素体系及其在地质中的应用[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2013, 27(2): 204-210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1211.2013.02.020
[48] Selley D, Broughton D, Scott R, et al. A new look at the geology of the Zambian Copperbelt[C]//Hedenquist J W, Thompson J F H, Goldfarb R J, et al. Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume, 2005: 965-1000.
[49] Volodin R N, Chechetkin V S, Bogdanov, et al. The Udokan cupriferous sandstones deposit(eastern Siberia)[J]. Geol. Ore Dep., 1994, 36: 1-25.
[50] Sawlowicz Z. REE and their relevance to the development of the Kupferschiefer copper deposit in Poland[J]. Ore Geol. Rev., 2013, 55: 176-186. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.06.006
[51] Richards J P, Krogh T E, Spooner E T C. Fluid inclusion characteristics and U-Pb rutile age of late hydrothermal alteration and veining at the Musoshi stratiform copper deposit, Central African Copper Belt, Zaire[J]. Economic Geology, 1988, 83: 118-139. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.83.1.118
[52] Guo J H, O'Brien P J, Zhai M G. High-pressure granulites in the Sanggan area, North China Craton: Metamorphic evolution, P-T paths and geotectonic significance[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2002, 20: 741-756. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1314.2002.00401.x
[53] Guo J H, Sun M, Chen F K, et al. Sm-Nd and SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of high-pressure granulites in the Sanggan area, North China Craton: Timing of Paleoproterozoic continental collision[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2005, 24: 629-642. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.01.017
[54] Liu S W, Pan Y M, Li J H, et al. Geological and isotopic geochemical constraints on the evolution of the Fuping Complex, North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2002, 117: 41-56. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00063-3
[55] Liu S W, Pan Y M, Xie Q L, et al. Archean geodynamics in the Central Zone, North China Craton: Constraints from geochemistry of two contrasting series of granitoids in the Fuping and Wutai complexes[J]. Precambrian Research, 2004, 130: 229-249. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2003.12.001
[56] Liu S W, Pan Y M, Xie Q L, et al. Geochemistry of the Paleoproterozonic Nanying granitic gneisses in the Fuping Complex: Implications for the tectonic evolution of the Central Zone, North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2005, 24: 643-658. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.10.010
[57] Liu S W, Zhao G C, Wilde S A, et al. Th-U-Pb monazite geochronology of the Luliang and Wutai complexes: Constraints on the tectonothermal evolution of the Trans-North China Orogen[J]. Precambrian Research, 2006, 148: 205-224. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.04.003
[58] Kusky T M, Li J H. Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2003, 22: 383-397. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00071-3
[59] Wang Y J, Fan W M, Zhang Y H, et al. Geochemical 40Ar /39Ar geochronological and Sr-Nd isotopic constraints on the origin of Paleoproterozoic mafic dikes from the southern Taihang Mountains and implications for the ca. 1800Ma event of the North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2004, 135: 55-77. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.07.005
[60] Wang Y J, Zhao G C, Fan W M, et al. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology and geochemistry of Paleoproterozoic mafic dykes from western Shandong Province: Implications for back-arc basin magmatism in the Eastern Block, North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2007, 154: 107-124. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.12.010
[61] Wu F Y, Zhao G C, Wilde S A, et al. Nd isotopic constraints on crustal formation in the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2005, 24: 523-545. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.10.011
[62] Li J H, Kusky T M. A Late Archean foreland fold and thrust belt in the North China Craton: Implications for early collisional tectonics[J]. Gondwana Research, 2007, 12: 47-66. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2006.10.020
[63] Guan H, Sun M, Wilde S A, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Fuping Complex: Implications for formation and assembly of the North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2002, 113: 1-18. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(01)00197-8
[64] Zhao G C, Wilde S A, Cawood P A, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages of the Fuping Complex: Implications for late Archean to Paleoproterozoic accretion and assembly of the North China Craton[J]. American Journal of Science, 2002, 302: 191-226. doi: 10.2475/ajs.302.3.191
[65] 刘超辉, 刘福来, 赵国春. 华北克拉通中部造山带早元古代盆地演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(9): 2770-2784. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201209009.htm
[66] Zhang J, Zhao G C, Li S Z, et al. Polyphase deformation of the Fuping Complex, Trans-North China Orogen: Structures, SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2009, 31: 177-193. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2008.11.008
[67] Selley D, Broughton D, Scott R, et al. A new look at the geology of the Zambian Copperbelt[C]//Hedenquist J W, Thompson J F H, Goldfarb R J, et al. Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume, 2005: 965-1000.
[68] Meng X Y, Richards J, Mao J W. The Tongkuangyu Cu Deposit, Trans-North China Orogen: A Metamorphosed Paleoproterozoic Porphyry Cu Deposit[J]. Economic Geology, 2020, 115, 51-77. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.4693
① 叶会寿, 李洪英, 毕珉锋, 等.《重要矿种关键问题调查与矿产地质专题填图试点》项目内部报告.2018.
-




 下载:
下载: