Quantitative analysis of mineralization-alteration index and deep prospecting significance of Qilinchang Pb-Zn deposit in Huize, northeastern Yunnan
-
摘要:
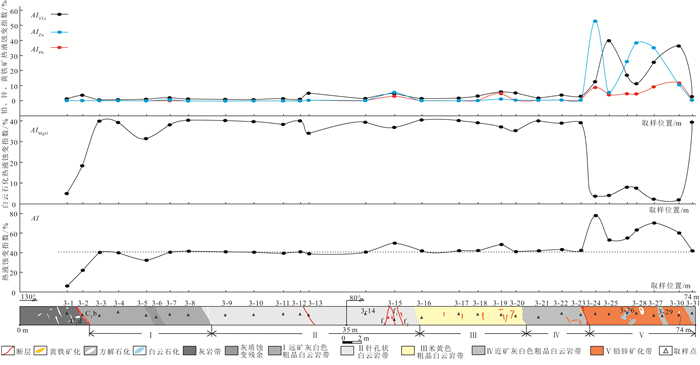
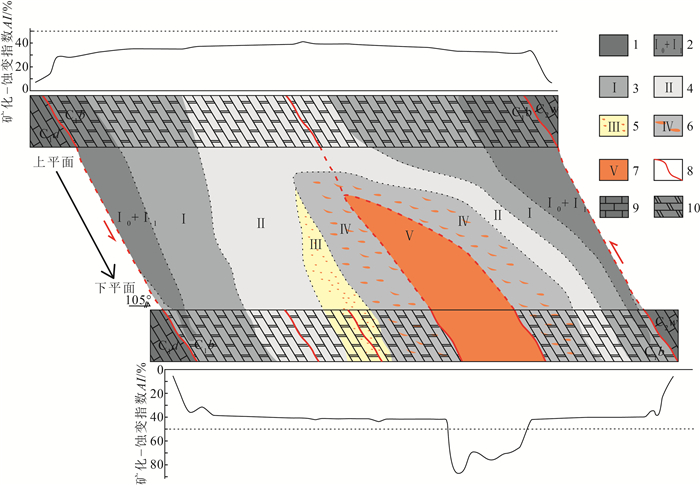
会泽超大型铅锌矿是滇东北铅锌多金属矿集区最具代表性的矿床之一。为了有效地提取和区分不同矿化-蚀变分带内铅锌矿化、黄铁矿化、白云石化等矿化-蚀变信息, 以麒麟厂1249 m中段典型剖面为例, 应用大比例尺蚀变岩相学填图方法, 基于矿化-蚀变岩的热液蚀变指数与迁入元素增长指数的定量分析, 对比和剖析了矿化蚀变类型与各矿化-蚀变带的岩石组成、结构构造等特征。结果表明, 该矿床主要的蚀变类型为白云石化、方解石化和黄铁矿化, 主要矿化为闪锌矿化、方铅矿化。以矿体为中心, 从矿体下盘围岩→矿体→矿体上盘围岩, 矿化-蚀变分带呈现出远矿浅灰色粗晶白云岩带(Ⅰ)→针孔状白云岩带(Ⅱ)→米黄色粗晶白云岩带(Ⅲ)→近矿灰白色粗晶白云岩带(Ⅳ)→铅锌矿化带(Ⅴ)→近矿灰白色粗晶白云岩带(Ⅳ)的变化规律。TFe、CaO、MgO、Pb、Zn在不同的矿化蚀变分带内均保持迁入富集状态, 其中TFe、Pb和Zn迁入富集明显; 矿化-蚀变指数值和迁入元素增长指数与矿化蚀变分带在空间上具有一致性, Ⅴ带呈现的矿化蚀变指数值(AI、AITFe及AIPb+Zn)最高, 而AIMgo值最低, 明显区别于其他蚀变带; 从Ⅰ带至Ⅴ带, 迁入元素增长指数(ZZn、ZPb及ZTFe)总体呈增长趋势, 且Ⅴ带的ZTFe、ZPb及ZZn值明显高于围岩。矿化蚀变指数研究揭示了热液蚀变作用与成矿的关系, 亦证实了空间上矿化蚀变分带的规律性, 对于同类矿床深部勘探具有指导意义。
Abstract:The giant Huize Pb-Zn deposit is the most representative deposit of Pb-Zn polymetallic ore concentration area in northeastern Yunnan.In order to effectively extract and distinguish the mineralization-alteration information such as lead-zinc mineralization, pyritization and dolomitization in different mineralization-alteration zones, using large scale alteration petrographical mapping method, taking the typical levels of 1249 m as an example, to analyze the levels' mineralization-alteration types, altered rock composition, structure and other characteristics base on quantitative analysis of hydrothermal alteration index and growth index of element transfer-in.The results show that the main alteration types are dolomitization, calcitization and pyritization.Mineralization mainly are sphalerite and galena.Taking the ore body as the center, from footwall rock of ore body to ore body to hanging wall rock of ore body, the mineralization-alteration zoning shows that grayish white coarse-grained crystalline dolomite which is far from the orebody(Ⅰ), coarse-grained dolomite with pinholes(Ⅱ), beige coarse-grained crystalline dolomite(Ⅲ), grayish white coarse-grained crystalline dolomite which is closed to the orebody(Ⅳ), orebody(Ⅴ)and grayish white coarse-grained crystalline dolomite which is closed to the orebody(Ⅳ).The element TFe, CaO, MgO, Pb, and Zn in the different mineralization alteration zones almost keep transfer-in.Among them, the element TFe, Pb and Zn are the most obvious.Moreover, the quantitative calculation results of the mineralized alteration rocks' mineralization alteration index and the growth index of the elements transfer-in are consistent with the mineralization alteration zone in space.The values of alteration index(AI), TFe's alteration index(AITFe), and(Pb+Zn)'s alteration index(AIPb+Zn)are the highest in the Ⅴ zone while the value of MgO's alteration index(AIMgO)is the lowest, clearly distinguished from other alteration zones; The values of Zn, Pb and TFe's growth index of element transfer-in(ZZn, ZPb and ZTFe)are generally increasing from Ⅰ zone to Ⅴ zone, and the values of ZZn, ZPb and ZTFe are significantly higher than those in surrounding rock.The study of mineralization alteration index reveals the relationship between hydrothermal alteration and mineralization, and also proves the rationality of spatial mineralization alteration zoning, which has guiding significance for deep exploration of similar deposits.
-

-
图 1 会泽铅锌矿区地质简图[14]
Figure 1.
表 1 会泽麒麟厂1249 m中段3号出矿道主量元素及Pb、Zn含量
Table 1. The results of major element and Pb-Zn element of No.3 withdrawal tunnel in the 1249 m level adit of the Huize deposit
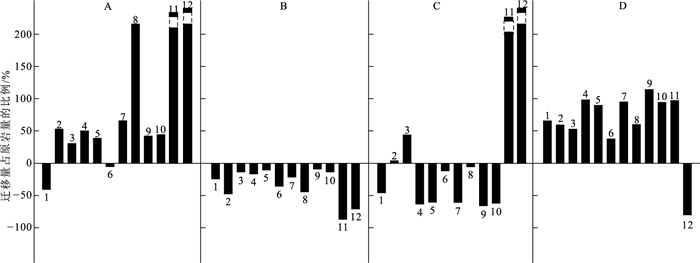
样品编号 SiO2/% Al2O3/% TFe2O3/% CaO/% MgO/% K2O/% Na2O/% MnO/% P2O5/% TiO2/% 烧失量/% 总计/% Zn/10-6 Pb/10-6 蚀变分带 未蚀变(6) 1.87 0.38 0.55 29.87 20.65 0.13 0.06 0.02 0.04 0.02 46.13 99.72 37.38 8.46 Ⅵ Ⅰ 3-3 0.81 0.30 0.25 30.65 20.84 0.06 0.07 0.02 0.04 0.01 46.55 99.60 2.80 53.64 3-4 0.57 0.22 0.32 30.98 20.63 0.05 0.07 0.03 0.04 0.01 47.03 99.95 92.10 34.26 3-5 0.67 0.43 0.44 35.18 16.74 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.03 0.01 46.06 99.74 222.30 98.50 3-7 1.35 0.96 0.93 29.86 20.29 0.19 0.09 0.07 0.04 0.02 45.78 99.58 3000.00 390.20 3-8 0.43 0.12 0.56 30.08 21.22 0.05 0.06 0.04 0.03 0.01 46.98 99.58 399.35 192.45 Ⅱ 3-9 0.38 0.07 0.40 30.50 21.11 0.05 0.06 0.02 0.04 0.01 47.19 99.83 85.80 53.23 3-10 0.55 0.17 0.36 30.86 20.90 0.05 0.07 0.02 0.04 0.01 47.24 100.27 64.90 29.48 3-11 1.03 0.58 0.64 30.63 20.23 0.10 0.07 0.02 0.04 0.03 46.32 99.69 200.20 108.40 3-12 1.12 0.25 0.46 30.30 20.98 0.07 0.06 0.02 0.04 0.01 46.89 100.20 61.00 5.00 3-14 0.30 0.16 0.64 30.56 20.78 0.05 0.06 0.05 0.04 0.01 46.87 99.52 137.70 62.10 Ⅲ 3-16 0.15 0.05 0.69 30.09 21.41 0.05 0.06 0.03 0.03 0.06 47.19 99.81 109.80 75.11 3-17 0.31 0.11 0.89 29.97 21.39 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.03 0.01 46.82 99.68 236.60 80.00 3-18 0.30 0.14 1.63 29.59 21.24 0.05 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.01 46.60 99.70 409.85 242.00 3-19 1.23 0.77 3.33 25.79 21.49 0.14 0.06 0.11 0.03 0.04 43.78 96.77 5300.00 26300.00 3-20 2.70 2.25 2.84 27.82 19.79 0.46 0.09 0.08 0.03 0.06 43.62 99.74 2000.00 1800.00 Ⅳ 3-21 0.28 0.14 0.88 29.85 21.27 0.05 0.06 0.04 0.03 0.01 46.85 99.46 1000.00 374.30 3-22 0.60 0.36 2.05 28.84 21.34 0.05 0.07 0.06 0.04 0.01 46.13 99.55 1300.00 635.20 3-23 0.61 0.35 1.55 29.36 21.18 0.05 0.07 0.05 0.03 0.02 46.37 99.64 1500.00 367.60 3-29 1.74 1.37 1.48 29.95 19.41 0.27 0.06 0.06 0.04 0.04 44.89 99.31 2800.00 881.60 注:样品分析在西北有色金属地研测试中心进行;表中“(6)”为样品数;Ⅵ—未蚀变白云岩;Ⅰ—远矿浅灰色粗晶白云岩带;Ⅱ—针孔状白云岩带;Ⅲ—米黄色粗晶白云岩带;Ⅳ—近矿灰白色粗晶白云岩带;在铅锌含量两列中,超过0.5%的样品含量,已换算成10-6 表 2 会泽麒麟厂1249中段3号出矿道各蚀变带化学成分迁移计算
Table 2. The results of chemical composition migration in different alteration zones of the No. 3 withdrawal tunnel in the 1249 m level adit in the Huize deposit
蚀变岩 未蚀变白云岩 未蚀变白云岩→远矿浅灰色粗晶白云岩 远矿浅灰色粗晶白云岩→针孔状粗晶白云岩 针孔状粗晶白云岩→米黄色粗晶白云岩 米黄色粗晶白云→近矿灰白色粗晶白云岩 化学成分 含量 含量 Ti加入(+)带出(-) Ti/%(迁移量/原岩量) 含量 Ti加入(+)带出(-) Ti/%(迁移量/原岩量) 含量 Ti加入(+)带出(-) Ti/%(迁移量/原岩量) 含量 Ti加入(+)带出(-) Ti/%(迁移量/原岩量) SiO2/% 1.87 0.77 -0.77 -41.19 0.68 -0.19 -24.59 0.94 -0.31 -46.08 0.81 +0.62 66.41 Al2O3/% 0.38 0.41 +0.20 53.71 0.25 -0.20 -48.13 0.67 0.01 4.84 0.55 +0.40 60.18 TFe2O3/% 0.55 0.50 +0.17 30.95 0.50 -0.07 -14.36 1.88 +0.23 45.13 1.49 +1.01 53.78 CaO/% 29.87 31.35 +15.25 51.05 30.57 -5.23 -16.70 28.65 -19.46 -63.67 29.50 +28.41 99.16 MgO/% 20.65 19.94 +8.05 38.97 20.80 -2.17 -10.89 21.06 -12.64 -60.76 20.80 +19.17 91.02 K2O/% 0.13 0.09 -0.01 -6.12 0.07 -0.03 -36.01 0.15 -0.01 -12.01 0.11 +0.06 38.59 Na2O/% 0.06 0.07 +0.04 66.25 0.06 -0.02 -21.81 0.06 -0.04 -61.17 0.06 +0.06 96.26 MnO/% 0.02 0.04 +0.04 217.21 0.03 -0.02 -44.95 0.06 0.00 -5.59 0.05 +0.04 61.12 P2O5/% 0.04 0.04 +0.02 42.84 0.04 0.00 -9.31 0.03 -0.02 -66.39 0.04 +0.04 115.66 烧失量/% 46.13 46.48 +20.77 45.02 46.90 -6.41 -13.79 45.60 -29.23 -62.31 46.06 +43.49 95.37 Zn/10-6 37.38 743.31 +1032.38 2761.56 109.92 -649.40 -87.37 1611.25 +514.63 468.18 1650.00 +1580.21 98.07 Pb/10-6 8.46 153.81 +212.90 2516.63 51.64 -109.69 -71.32 5699.42 +2157.54 4177.88 564.68 -4607.22 -80.84 表 3 会泽麒麟厂1249 m中段3号出矿道岩石矿化-蚀变指数
Table 3. The results of alteration index of the No.3 withdrawal tunnel in the 1249 m level adit in the Huize deposit
样品号 岩(矿)石 AI AIMgO AITFe AIPb AIZn AI均值 矿化-蚀变带 3-1 灰岩 6.02 4.90 1.12 0.00 0.00 6.02 / 3-3 灰白色粗晶白云岩 40.34 39.84 0.49 0.01 0.00 38.91 远矿浅灰色粗晶白云岩带 3-4 39.93 39.31 0.60 0.01 0.02 3-5 32.32 31.43 0.83 0.02 0.04 3-7 40.45 38.06 1.75 0.07 0.56 3-8 41.52 40.35 1.06 0.04 0.08 3-9 灰色—浅灰白色针孔状粗晶白云岩 41.01 40.22 0.76 0.01 0.02 40.50 针孔状粗晶白云岩带 3-10 40.40 39.69 0.69 0.01 0.01 3-11 39.63 38.35 1.22 0.02 0.04 3-12 40.89 40.00 0.88 0.00 0.01 3-14 40.60 39.36 1.21 0.01 0.03 3-16 米黄色粗晶白云岩 41.77 40.44 1.30 0.01 0.02 43.07 米黄色粗晶白云岩带 3-17 41.87 40.15 1.67 0.02 0.04 3-18 42.24 39.12 3.00 0.04 0.08 3-19 48.35 37.13 5.75 4.54 0.92 3-20 41.14 35.38 5.08 0.32 0.36 3-21 灰白色粗晶白云岩 41.93 40.02 1.65 0.07 0.19 42.34 近矿灰白色粗晶白云岩带 3-22 43.01 38.92 3.74 0.12 0.24 3-23 42.30 39.10 2.86 0.07 0.28 3-31 42.12 39.39 2.61 0.04 0.08 3-24 矿石 77.65 3.63 12.55 8.70 52.77 63.20 铅锌矿化带 3-25 52.89 4.07 39.77 3.70 5.35 3-26 55.12 8.02 16.86 4.38 25.86 3-28 63.16 7.57 11.37 4.35 38.33 3-27 70.31 2.29 25.34 9.13 35.08 3-30 60.06 1.89 36.25 11.56 10.36 3-2 断层泥 21.91 18.33 3.49 0.02 0.08 21.91 / 3-13 断层泥 38.97 34.00 4.82 0.06 0.09 38.97 / 3-15 碎粒(斑)岩 49.69 36.93 4.50 2.82 5.44 49.69 / 表 4 会泽麒麟厂矿区1249中段3号出矿道迁入元素的增长指数
Table 4. The values of growth index of element transfer-in of the No.3 withdrawal tunnel in the 1249 m level adit in the Huize deposit
样品号 岩(矿)石 ZTFe ZCaO ZMgO ZZn ZPb 矿化蚀变带 3-1 灰岩 0.22 0.33 0.03 0.10 0.52 / 3-3 灰白色粗晶白云岩 0.76 1.68 1.65 0.12 10.40 远矿浅灰色粗晶白云岩带 3-4 0.95 1.71 1.64 4.05 6.66 3-5 1.30 1.91 1.31 9.64 18.88 3-7 1.63 0.96 0.94 77.10 44.31 3-8 1.69 1.68 1.72 17.83 37.98 3-9 灰-浅灰白色针孔状粗晶白云岩 1.21 1.70 1.70 3.81 10.45 针孔状粗晶白云岩带 3-10 1.10 1.72 1.68 2.88 5.79 3-11 0.73 0.64 0.61 3.34 8.00 3-12 1.27 1.53 1.53 2.46 0.89 3-14 1.94 1.71 1.68 6.15 12.25 3-16 米黄色粗晶白云岩 0.34 0.27 0.28 0.80 2.42 米黄色粗晶白云岩带 3-17 2.75 1.71 1.76 10.78 16.10 3-18 5.05 1.69 1.75 18.67 48.71 3-19 2.76 0.39 0.47 64.57 1415.91 3-20 1.50 0.27 0.28 15.48 61.56 3-21 灰白色粗晶白云岩 2.67 1.67 1.72 44.66 73.86 近矿灰白色粗晶白云岩带 3-22 6.24 1.61 1.72 58.05 125.35 3-23 2.92 1.02 1.06 41.54 44.98 3-31 4.35 1.69 1.74 19.55 41.42 3-24 矿石 27.84 0.39 0.21 17195.20 12520.01 铅锌矿化带 3-25 45.32 0.14 0.12 895.35 2739.16 3-26 38.33 1.15 0.48 8636.32 6461.29 3-28 24.01 0.97 0.43 10881.94 12520.01 3-27 21.64 0.04 0.05 4806.53 2409.02 3-30 67.19 0.12 0.09 2819.56 13908.88 3-2 断层泥 0.06 0.01 0.01 0.20 0.24 / 3-13 断层泥 0.26 0.03 0.05 0.73 1.97 / 3-15 碎粒(斑)岩 7.98 1.47 1.74 1416.61 3240.71 / -
[1] 韩润生, 刘丛强, 黄智龙, 等. 论云南会泽富铅锌矿床成矿模式[J]. 矿物学报, 2001, 21(4): 674-680. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2001.04.018
[2] 黄智龙, 李文博, 张振亮, 等. 云南会泽超大型铅锌矿床成因研究中的几个问题[J]. 矿物学报, 2004, 24(2): 105-111. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2004.02.002
[3] Zhou C, Zhou C. The Source of Metals in theQilinchang Zn-Pb Deposit, Northeastern Yunnan, China: Pb-Sr Isotope Constraints[J]. Economic Geology, 2001, 96(3): 583-598. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.96.3.583
[4] 黄智龙, 陈进, 刘丛强, 等. 峨眉山玄武岩与铅锌矿床成矿关系初探——以云南会泽铅锌矿床为例[J]. 矿物学报, 2001, 21(4): 681-688. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2001.04.019
[5] 黄智龙, 李文博, 陈进, 等. 云南会泽超大型铅锌矿床构造带方解石稀土元素地球化学[J]. 矿床地质, 2003, 22(2): 199-207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2003.02.012
[6] 黄智龙, 李文博, 陈进, 等. 云南会泽超大型铅锌矿床C、O同位素地球化学[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2004, 28(1): 53-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2004.01.008
[7] Zhao D, Han R, Wang L, et al. Genesis of theLehong large zinc-lead deposit in northeastern Yunnan, China: Evidences from geological characteristics and C-H-O-S-Pb isotopic compositions[J]. Ore Geology Reviews. 2021, 135: 104219. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104219
[8] Zhao D, Han R, Ren T, et al. Geology, C-O-S-Pb isotopes, and their implications for the ore genesis of theXiaohe carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb deposit in northeastern Yunnan, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry. 2022, 142: 105306. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105306
[9] 柳贺昌, 林文达. 滇东北铅锌银矿床规律研究[M]. 昆明: 云南大学出版社, 1999.
[10] 韩润生, 邹海俊, 刘鸿. 构造地球化学、勘查地球化学——滇东北铅锌银矿床成矿规律及构造地球化学找矿[J]. 云南地质, 2006, 25(4): 382-384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2006.04.002
[11] 韩润生, 胡煜昭, 王学琨, 等. 滇东北富锗银铅锌多金属矿集区矿床模型[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(2): 280-294. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201202008.htm
[12] 韩润生, 王峰, 胡煜昭, 等. 会泽型(HZT)富锗银铅锌矿床成矿构造动力学研究及年代学约束[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2014(4): 758-771. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2014.04.003
[13] 于晓飞, 吕志成, 孙海瑞, 等. 全国整装勘查区成矿系统研究与矿产勘查新进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(5): 1261-1288. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202005002.htm
[14] 韩润生. 构造成矿动力学及隐伏矿定位预测: 以云南会泽超大型铅锌(银、锗)矿床为例[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006.
[15] 王奖臻, 李朝阳, 李泽琴, 等. 川滇地区密西西比河谷型铅锌矿床成矿地质背景及成因探讨[J]. 地球与环境, 2001, 29(2): 41-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200102006.htm
[16] 张长青. 中国川滇黔交界地区密西西比型(MVT)铅锌矿床成矿模型[D]. 中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2008.
[17] 李文博, 黄智龙, 陈进, 等. 会泽超大型铅锌矿床成矿时代研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2004, 24(2): 112-116. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2004.02.003
[18] 张长青, 毛景文, 刘峰, 等. 云南会泽铅锌矿床粘土矿物K-Ar测年及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2005, 24(3): 317-324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.03.011
[19] 赵冻, 韩润生, 王加昇, 等. 滇东北矿集区小河铅锌矿床构造解析及其控矿模式[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(3): 345-362. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202003007.htm
[20] 田光礼, 陈守余, 董凯, 等. 甘肃白银厂折腰山VMS矿床蚀变带元素迁移及定量计算[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(1): 80-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201901006.htm
[21] 艾金彪, 马生明, 朱立新, 等. 安徽马头斑岩型钼铜矿床蚀变带常量元素迁移规律及其定量计算[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(6): 1262-1274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.06.012
[22] 吴德海, 夏菲, 潘家永, 等. 粤北棉花坑铀矿床热液蚀变与物质迁移研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(9): 2745-2764. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201909008.htm
[23] 赵冻, 韩润生, 任涛, 等. 滇东北大型矿集区乐红大型铅锌矿床矿化蚀变分带模式[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2016, 35(6): 1258-1269. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.06.016
[24] 陈随海, 韩润生, 申屠良义, 等. 滇东北矿集区昭通铅锌矿区蚀变岩分带及元素迁移特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2016, 46(3): 711-721. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201603009.htm
[25] 韩润生, 王雷, 方维萱, 等. 初论云南易门地区凤山铜矿床刺穿构造岩-岩相分带模式[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(4): 495-504. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.04.006 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110405&flag=1
[26] 韩润生, 陈进, 李元, 等. 云南会泽麒麟厂铅锌矿床构造地球化学及定位预测[J]. 矿物学报, 2001, 21(4): 667-673. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2001.04.017
[27] Han R S, Chen J, Wang F, et al. Analysis of metal-element association halos within fault zones for the exploration of concealed ore-bodies-A case study of theQilinchang Zn-Pb-(Ag-Ge) deposit in the Huize mine district, northeastern Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 159(11): 62-78.
[28] 文德潇, 韩润生, 吴鹏, 等. 云南会泽HZT型铅锌矿床蚀变白云岩特征及岩石-地球化学找矿标志[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(1): 235-245. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.019
[29] 张可清, 杨勇. 蚀变岩质量平衡计算方法介绍[J]. 地质科技情报, 2002, 21(3): 104-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2002.03.021
[30] Gresens R L. Composition-volume relationships of metasomatism[J]. Chemical Geology, 1967, 2(67): 47-65.
[31] 周永章, 涂光炽, Chown E H, 等. 热液围岩蚀变过程中数学不变量的寻找及元素迁移的定量估计——以广东河台金矿田为例[J]. 科学通报, 1994, 39(11): 1026-1028. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199411019.htm
[32] Haeussinger H, Okrusch M, Scheepers D. Geochemistry of premetamorphic hydrothermal alteration of metasedimentary rocks associated with the Gorob massive sulfide prospect, Damara Orogen, Namibia[J]. Economic Geology, 1993, 88(1): 72-90. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.88.1.72
[33] 王雷, 韩润生, 黄建国, 等. 云南易门凤山铜矿床59#矿体分布区断裂构造地球化学特征及成矿预测[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2010, 34(2): 233-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2010.02.009
[34] 韩润生, 吴鹏, 张艳, 等. 西南特提斯川滇黔成矿区富锗铅锌矿床成矿理论研究新进展[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(2): 554-573. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.02.014
[35] 王明志, 韩润生, 张艳. 成矿构造体系对铅锌成矿系统的控制作用——以会泽富锗铅锌矿床为例[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(10): 3008-3023. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.015
[36] 韩润生, 李波, 倪培, 等. 闪锌矿流体包裹体显微红外测温及其矿床成因意义——以云南会泽超大型富锗银铅锌矿床为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2016, 46(1): 91-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201601009.htm
[37] 李孜腾, 韩润生, 闫庆文. 会泽超大型富锗银铅锌矿床矿化-蚀变分带规律及构造的控制作用[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(02): 316-330. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201702009.htm
[38] 林成贵, 程志中, 吕志成, 等. 甘肃省早子沟金矿原生晕分带特征及深部找矿预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(1): 70-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202001006.htm
[39] 刘建民, 赵国春, 徐刚, 等. 辽东半岛金矿成矿作用与深部资源勘查[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2021, 51(6): 1613-1635. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202106001.htm
-




 下载:
下载: