Characteristics of ore minerals for the Changtuxili Ag-Pb-Zn-Mn deposit in the middle-southern segment of Da Hinggan Mountains and its constraints on the genesis of the deposit
-
摘要:
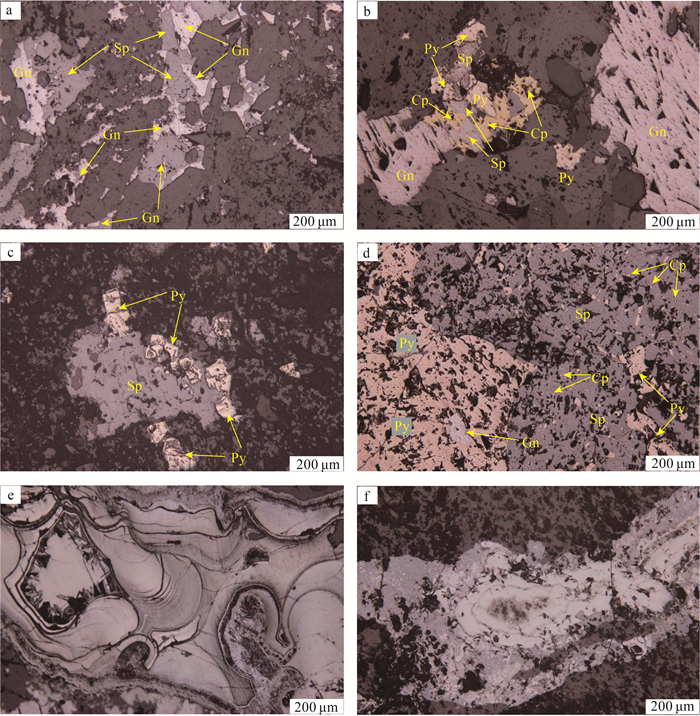
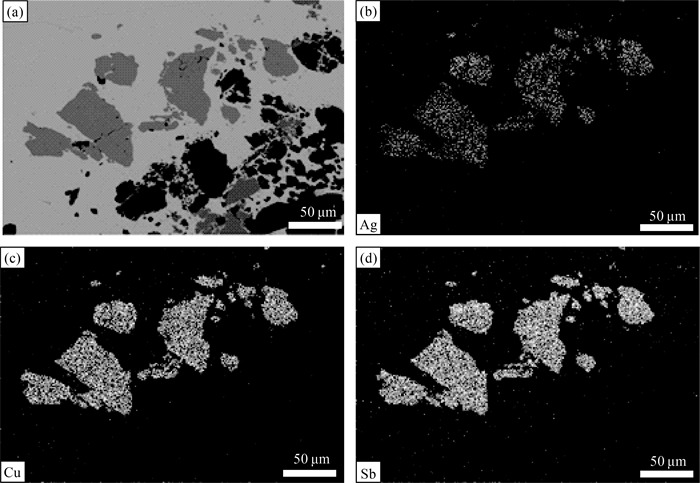
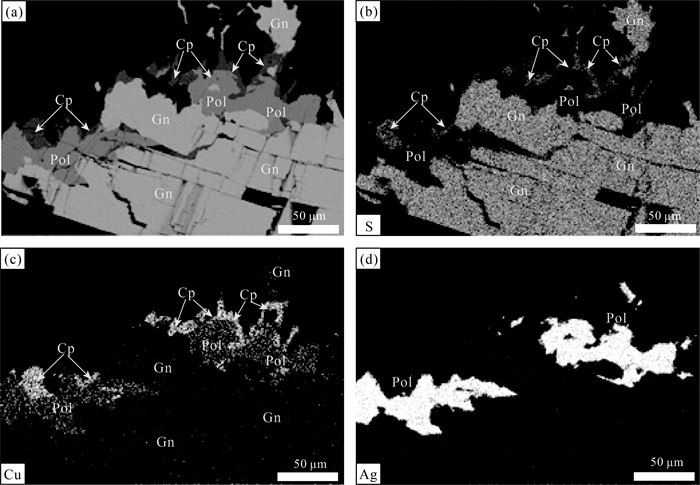
昌图锡力银铅锌锰矿是近年在大兴安岭成矿带中南段锡林浩特-霍林郭勒多金属成矿亚带上新发现的1处银铅锌多金属矿床。矿床中的主要矿物分析结果表明:矿床中的银矿物有银黝铜矿、硫锑铜银矿、深红银矿等, 主要以独立的银矿物分布于金属硫化物中;银黝铜矿的Ag含量为8.25%~13.11%, 平均为10.54%, Cu含量为27.65%~31.43%, 平均为29.64%, 面扫描图像显示Ag以类质同像的形式赋存于银黝铜矿中。硫锑铜银矿的Ag含量较高, 平均为68.99%, 主要分布于方铅矿的边缘及其裂隙中。闪锌矿的Fe含量为0.30%~0.38%, 平均为0.33%, 属于贫铁闪锌矿, Cd与Zn具有很好的相关性, 可作为寻找闪锌矿的地球化学标志。菱锰矿(MnCO3)为晚期低温石英-碳酸盐阶段的产物, 是主要的碳酸盐矿物;锰的氧化物主要为软锰矿及硬锰矿, 软锰矿呈环带结构、胶状构造。除Mn外, 同时也富集高品位Pb。综合分析昌图锡力矿床的矿物学特征及矿床地质特征, 认为该矿为浅成低温热液型银铅锌锰多金属矿床。
Abstract:The Changtuxili Ag-Pb-Zn-Mn deposit is a newly discovered polymetallic deposit in Xilinhaote-Huolinguole Pb-Zn-Ag-Cu-Mo polymetallic metallogenic subzone of the middle and southern Da Hinggan Mountains polymetallic metallogenic belt in recent years.In order to explore the mineral type, mineral occurrence state, and genesis of the Changtuxili deposit, the occurrence of silver minerals, sulfides and manganese minerals were studied by mineral phase observation and electron probe analysis.The silver minerals in the deposit are freibergite, polybasite, pyrargyrite, which are distributed as separate silver minerals in metal sulfides.The Ag content of freibergite ranges from 8.25% to 13.11%(10.54% on average), and the Cu content of freibergite ranges from 27.65% to 31.43%(29.64% on average).The element X-ray mappings show that Ag is present in freibergite in the form of isomorphism.The silver content of polybasite is relatively high(average 68.99%), mainly distributed in the edge of galena and its fissures, indicating that galena is an important silver-carrying mineral.The black manganese cap is a geological sign for finding Ag-Pb-Zn deposits.Sphalerite belongs to low iron sphalerite, and the content is 0.30%~0.38%, with an average value of 0.33%.Cd has a good correlation with Zn in sphalerite and can be used as a geochemical marker for sphalerite prospecting.Rhodochrosite is the product of late low-temperature quartz-carbonate stage.MnCO3 is the main mineral component and rhodochrosite belongs to hydrothermal genesis.Manganese oxides are mainly pyrolusite and psilomelane.Pyrolusite shows ring and colloidal structure, and it enriches high-grade Pb and Zn besides Mn.Comprehensive analysis of the mineralogical characteristics and ore geological characteristics of the Changtuxili deposit, which is considered to be a hypothermal hydrothermal Ag-Pb-Zn-Mn polymetallic deposit.
-

-
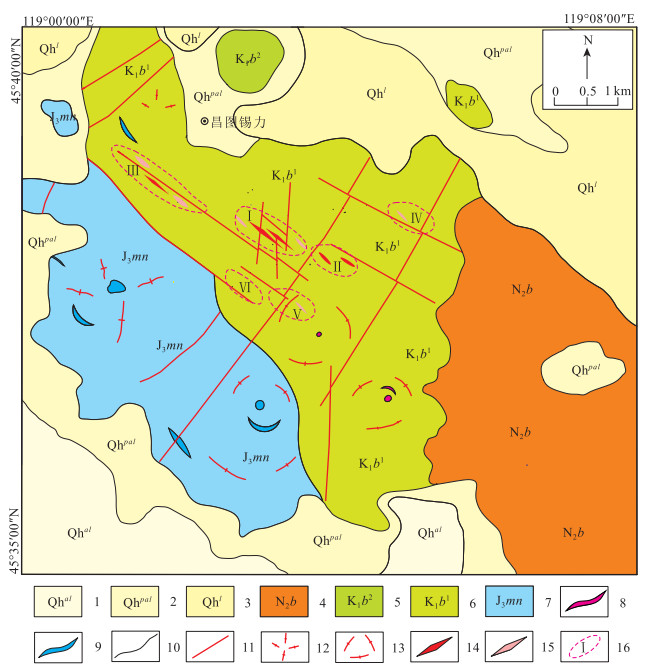
图 2 昌图锡力矿区地质图(据参考文献[16]修改)
Figure 2.
表 1 昌图锡力矿床矿物共生组合与生成顺序
Table 1. Paragenetic assemblage and sequence of hydrothermal minerals in the Changtuxili deposit
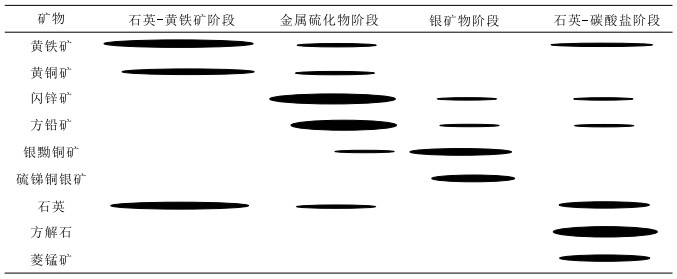
表 2 昌图锡力矿床单矿物电子探针分析结果
Table 2. EMPA results of polymetallic mineralization in the Changtuxili deposit
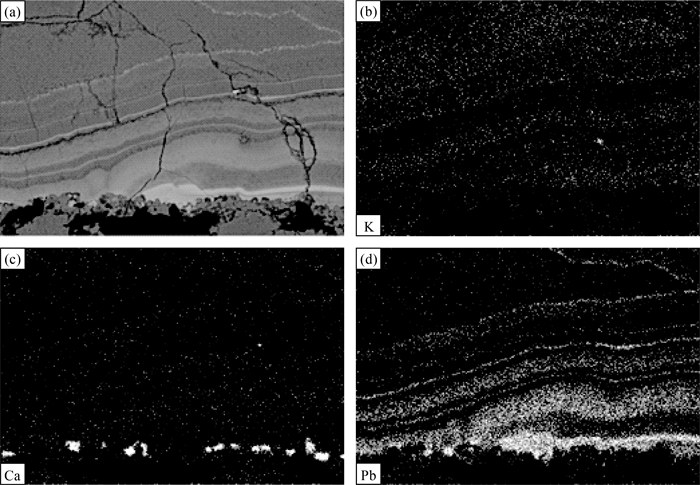
% 矿物 分析点号 Pb Zn Fe Co Ni Cu Ge S Sb Cd Ag As 总计 方铅矿 ZK126G-1 85.83 0.03 - - 0.03 - 0.07 13.28 - - - - 99.23 ZK126G-2 84.93 - 0.36 0.01 - 0.13 - 13.12 - - 0.01 - 98.57 ZK126G-3 86.90 - 0.05 0.01 - 0.15 - 13.25 - - - - 100.36 ZK153G-1 87.63 0.06 0.04 0.01 0.02 0 0.01 13.31 - - 0.03 - 101.07 ZK153G-2 85.92 0.01 0.37 - - 0.27 0.01 13.20 0.01 - - - 99.78 ZK153G-3 85.23 0.01 0.28 0.02 - 0.25 0.02 13.20 0.00 - 0.01 - 99.00 闪锌矿 ZK126S-1 - 66.14 0.34 - 0.02 - - 32.68 0.03 0.63 - 0.03 100.03 ZK126S-2 - 66.85 0.34 - 0.03 0.06 - 32.50 - 0.68 - - 100.53 ZK126S-3 - 67.20 0.31 - - - 0.04 32.32 - 0.51 - - 100.39 ZK153S-1 0.02 66.87 0.30 - 0.01 - - 32.70 - 0.38 - - 100.30 ZK153S-2 0.08 65.76 0.38 - 0.02 - 0.01 32.62 0.01 0.34 - - 99.32 ZK153S-3 0.04 66.18 0.30 - 0.02 - - 32.93 - 0.34 - 0.02 99.88 银黝铜矿 ZK153A-1 0.43 5.24 1.84 - - 30.79 - 24.01 28.35 - 9.49 0.13 100.30 ZK153A-2 0.47 5.96 0.46 - - 31.43 - 24.36 28.16 - 8.25 0.12 99.22 ZK153A-3 0.39 5.52 1.27 - 0.01 31.39 - 24.15 27.75 - 8.40 0.34 99.22 ZK159A-1 0.58 5.31 0.56 - 0.01 27.65 - 23.82 26.23 - 13.11 1.09 98.36 ZK159A-2 0.77 6.14 0.34 - 0.02 28.68 - 23.88 25.54 - 11.53 1.66 98.56 ZK159A-3 0.76 6.90 0.18 - - 27.87 - 23.86 26.20 - 12.43 1.26 99.45 硫锑铜银矿 ZK164A-1 0.29 - 0.00 - - 8.34 - 16.05 9.73 - 66.74 0.44 101.59 ZK164A-2 0.21 - 0.07 - - 8.14 - 15.41 9.15 - 66.94 0.40 100.31 ZK164A-3 0.28 0.03 0.00 - 0.02 8.40 - 15.63 9.44 - 66.85 0.50 101.15 ZK166A-1 0.71 - 0.20 - 0.00 5.28 - 15.88 3.82 - 70.54 3.68 100.12 ZK166A-2 0.43 - 0.05 - - 5.45 - 15.56 3.60 - 70.40 3.99 99.48 ZK166A-3 0.57 - 0.16 - - 4.70 - 13.70 4.98 - 72.47 2.51 99.12 深红银矿 ZK85A-1 0.08 - 0.00 - - - - 17.56 22.05 - 59.72 0.06 99.47 ZK85A-2 0.18 - 0.01 - - - - 17.13 22.37 - 59.28 0.09 99.06 表 3 昌图锡力矿床中菱锰矿组成
Table 3. Compositions of rhodoch rosite of the Changtuxili deposit
分析点号 组分/分子比 MnCO3 FeCO3 CaCO3 MgCO3 ZK01-1 0.942 0.038 0.012 0.008 ZK01-2 0.943 0.036 0.018 0.003 ZK01-3 0.948 0.031 0.015 0.006 ZK53-1 0.927 0.045 0.021 0.007 ZK53-2 0.925 0.048 0.026 0.001 ZK53-3 0.928 0.042 0.023 0.007 表 4 昌图锡力矿床中氧化锰组成
Table 4. Compositions of manganese oxide of the Changtuxili deposit
% 分析点号 K2O CaO TiO2 PbO MgO MnO FeO ZnO 总计 ZK01-01 0.28 0.18 0.01 23.51 0 58.10 0.25 0.82 83.14 ZK01-02 1.57 0.43 0 0.78 0.02 74.73 0.34 1.44 79.32 ZK37401-01 0.34 0.77 0.01 0.08 0.08 74.67 0.73 0.91 77.59 ZK37401-02 0.43 0.86 0 0.10 0.10 69.70 1.05 1.07 73.33 -
[1] 刘建明, 张锐, 张庆洲.大兴安岭地区的区域成矿特征[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(1) :269-277. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.01.024
[2] 葛文春, 吴福元, 周长勇, 等. 兴蒙造山带东段斑岩型Cu、Mo矿床成矿时代及其地球动力学意义[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(20) : 2407-2417. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074x.2007.20.012
[3] 武新丽, 毛景文, 周振华, 等. 大兴安岭中南段布敦化铜矿床H-O-S-Pb同位素特征及成矿指示[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(6) : 1812-1829. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.06.026
[4] Zeng Q D, Liu J M, Yu C M, et al. Metal deposits in the Hinggan Mountains, NE China: styles, characteristics and exploration potential[J]. International Geology Review, 2011, 53(7) : 846-878. doi: 10.1080/00206810903211492
[5] 陈良, 张达, 狄永军, 等. 大兴安岭中南段区域成矿规律初步研究[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2009, 24(4) : 267-281. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK200904001.htm
[6] 张万益, 聂凤军, 刘妍, 等. 内蒙古东乌旗阿尔哈达铅-锌-银矿床硫和铅同位素研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2007, 37(5) : 868-877. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200705003.htm
[7] 江思宏, 聂凤军, 刘翼飞, 等. 内蒙古拜仁达坝及维拉斯托银多金属矿床的硫和铅同位素研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(1) : 101-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2010.01.010
[8] 刘翼飞, 樊志勇, 蒋胡灿, 等. 内蒙古维拉斯托-拜仁达坝斑岩-热液脉状成矿体系研究[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(12), 2373-2385. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201412016.htm
[9] 匡永生, 郑广瑞, 卢民杰, 等. 内蒙古赤峰市双尖子山银多金属矿床的基本特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2014, 33(4) : 847-856. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2014.04.014
[10] 陈永清, 黄静宁, 卢映祥, 等. 中缅毗邻区金腊Pb-Zn-Ag多金属矿田元素, 稳定同位素和流体包裹体地球化学[J]. 地球科学, 2009, 34(4) : 585-594. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2009.04.003
[11] 何鹏, 郭硕, 张天福, 等. 大兴安岭中南段扎木钦铅锌银多金属矿床成矿物质来源及矿床成因: 来自S、Pb同位素的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(12) : 3597-3610. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201812010.htm
[12] 江彪, 武广, 陈毓川, 等. 内蒙古巴林左旗双尖子山银多金属矿床微量稀土元素特征及其矿床成因制约[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 92(4), 769-786. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-9515.2008.04.006
[13] 刘铭涛, 陈向平, 王居松, 等. 内蒙古大井铜多金属矿床流体包裹体研究及成矿作用探讨[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2019, 44(3) : 194-201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2019.03.005
[14] 金若时, 刘永顺, 张跃龙, 等. 大兴安岭中南段昌图锡力锰、银、铅、锌多金属矿床的发现及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(7) : 1268-1275. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.07.016 https://www.cgsjournals.com/article/id/6153fec4ed73f876a05b5fd0
[15] 郑全波, 苏航, 何鹏, 等. 内蒙古昌图锡力地区锰银铅锌多金属矿的找矿标志[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2019, 42(1) : 39-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ201901005.htm
[16] 何鹏, 张跃龙, 苏航, 等. 综合找矿方法在内蒙古昌图锡力锰银铅锌矿勘查中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2018, 54(3) : 65-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201803007.htm
[17] Jahn B M, Wu F Y, Chen B. Grantitoids of the central Asian orogenic belt and continental growth in the Phanerozoic. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh[J]. Earth Sciences, 2000, 91: 181-193.
[18] 任纪舜, 牛宝贵, 刘志刚. 软碰撞、叠覆造山和多旋回缝合作用[J]. 地学前缘, 1999, 6(3) : 85-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY199903010.htm
[19] Ouyang H G, Wu X L, Mao J W, et al. The nature and timing of ore formation in the Budunhua Copper Deposit, southern great Xingan range: evidence from geology, fluid inclusions, and U-Pb and Re-Os geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 63: 238-251. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.05.016
[20] 赵一鸣. 大兴安岭及其邻区铜多金属矿床成矿规律与远景评价[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1997: 125-144.
[21] 聂凤军, 温银维, 赵元艺, 等. 内蒙古白音查干银多金属矿化区地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 矿床地质, 2007, 26(2) : 213-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.02.008
[22] 牛树银, 孙爱群, 王宝德, 等. 内蒙古大井铜锡多金属矿成矿物质来源及成矿作用探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2008, 35(4) : 714-724. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.04.016
[23] 毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 等. 中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(1) : 169-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200501018.htm
[24] 潘小菲, 王硕, 侯增谦, 等. 内蒙古道伦达坝铜多金属矿床特征研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(3) : 402-410. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200903014.htm
[25] 周振华, 吕林素, 冯佳睿, 等. 内蒙古黄岗夕卡岩型锡铁矿床辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(3) : 667-679. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201003003.htm
[26] 张帮禄, 张连昌, 冯京, 等. 西昆仑玛尔坎苏地区奥尔托喀讷什大型碳酸锰矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 地质论评, 2018, 64(2) : 361-377. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201802007.htm
[27] 王璞, 潘兆橹, 翁玲宝. 系统矿物学(上、中、下册) [M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1982.
[28] Sharp T G, Buseck P R. The distribution of Ag and Sb in Galena: Inclusions Versus Solid Solution[J]. American Mineralogist, 1993, 78(1/2) : 85-95.
[29] 胡耀国, 李朝阳, 廖震文, 等. 贵州银厂坡银矿床银矿物特征及其赋存状态[J]. 矿物学报, 2000, 20(2) : 150-159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200002008.htm
[30] 郑榕芬, 毛景文, 高建京. 河南熊耳山沙沟银铅锌矿床中硫化物和银矿物的矿物学特征及其意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(6) : 715-726. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200606007.htm
[31] 唐燕文, 谢玉玲, 李应栩, 等. 浙江安吉多金属矿床金银赋存状态及银矿物特征研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(3) : 393-402. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201203010.htm
[32] 王静纯, 余大良. 我国氧化矿石银的赋存状态研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2006, 25(2) : 129-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200602003.htm
[33] 赵留喜, 孙亚光, 余丽秀. 中国锰银矿资源分布及特性[J]. 中国矿业, 2009, 18(7) : 16-18.
[34] 范晨子, 王玲. 河北相广锰银矿床中两种层状锰氧化物的矿物学研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2015, 35(4) : 522-528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201504017.htm
[35] 叶霖, 刘铁庚. 银和锰之间可能存在的联系[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2000, 19(4) : 303-304. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200004035.htm
[36] 韩仲文, 郭天威. 中国银矿床的主要地质特征[J]. 中国地质, 1990, (7) : 21-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI199007011.htm
[37] 张百胜. 官地银金矿床氧化带划分的试验研究及物相锰在贫硫化物型银矿床中的应用[J]. 矿产与地质, 1998, 12(5) : 318-323. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD805.005.htm
[38] 陈百友, 王增润, 彭省临, 等. 云南澜沧老厂红土型银锰矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2002, 26(1) : 86-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200201014.htm
[39] 黄民智, 唐绍华. 大厂锡矿石学概论[J]. 北京: 科学技术出版社, 1998: 21-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199001011.htm
[40] 黄典豪. 热液脉型铅-锌-银矿床富铁闪锌矿中硫化物包裹体成因探讨[J]. 矿床地质, 1999, 18(3) : 244-252. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ903.006.htm
[41] 钟日晨, 杨永飞, 石英霞, 等. 内蒙古拜仁达坝银多金属矿区矿石矿物特征及矿床成因[J]. 中国地质, 2008, 35(6) : 1274-1285. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200806025.htm
[42] 张天福, 郭硕, 辛后田, 等. 大兴安岭南段维拉斯托高分异花岗岩体的成因与演化及其对Sn-(Li-Rb-Nb-Ta) 多金属成矿作用的制约[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 44(1) : 248-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201901019.htm
[43] 姚敬劬. 我国沉积碳酸盐型锰矿中菱锰矿的成分特征[J]. 矿物学报, 1991, 11(l) : 13-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB199101002.htm
[44] 何鹏, 郭硕, 张阔, 等. 大兴安岭中南段昌图锡力银铅锌锰多金属矿床成矿物质来源及矿床成因: 来自S-Pb-C-O同位素的制约[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(8) : 2037-2054. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201908014.htm
[45] 吴福元, 葛文春, 孙德有, 等. 中国东部岩石圈减薄研究中的几个问题[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(3) : 51-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200303005.htm
[46] 翟德高, 刘家军, 王建平, 等. 内蒙古甲乌拉大型矿床稳定同位素地球化学研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(2) : 214-225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201302030.htm
[47] 翟德高, 刘家军, 李俊明, 等. 内蒙古维拉斯托斑岩型锡矿床成岩、成矿时代及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2016, 35(5) : 1011-1022. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201605009.htm
[48] 李俊建, 付超, 唐文龙, 等. 内蒙古东乌旗沙麦钨矿床的成矿时代[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(4) : 524-530. https://www.cgsjournals.com/article/id/dztb_20160405
[49] 梁小龙, 孙景贵, 邱殿明, 等. 大兴安岭西坡比利亚谷银铅锌多金属矿床成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(3) : 781-799. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202003009.htm
[50] 田杰鹏, 李俊建, 宋立军, 等. 华北地区锰矿成矿规律初探[J]. 华北地质, 2021, 44(3) : 58-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ202103007.htm
-



 下载:
下载: