The discovery of Early Cretaceous Hauterivian Ammonite Fauna in Bange area, northern Xizang and its constraints on the stratigraphic correlation of the Lower Cretaceous
-
摘要:
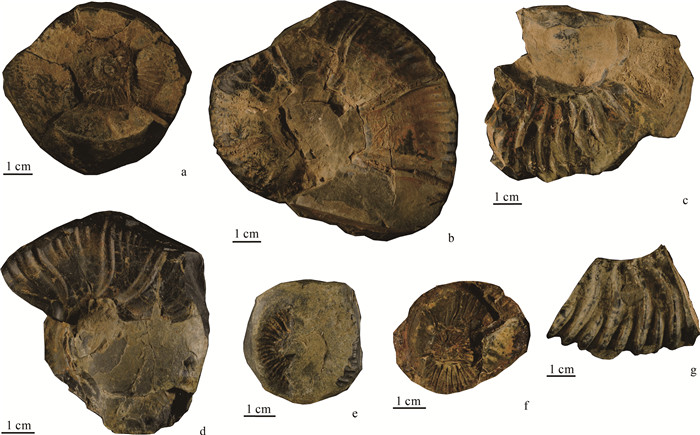
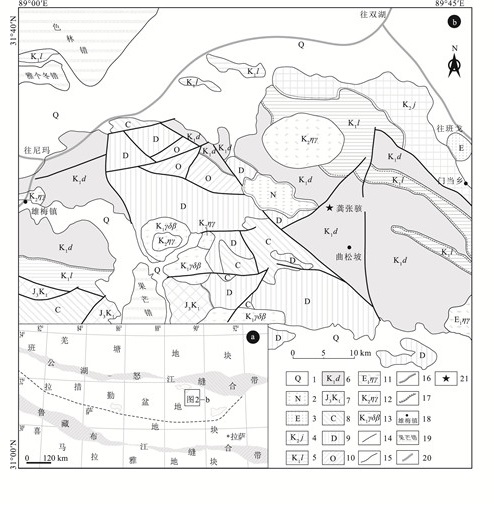
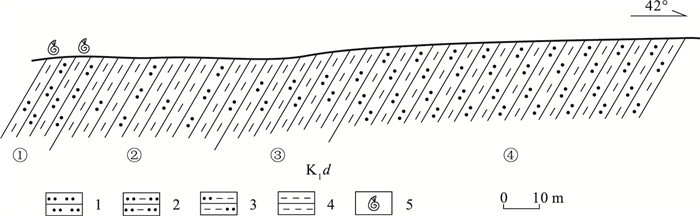
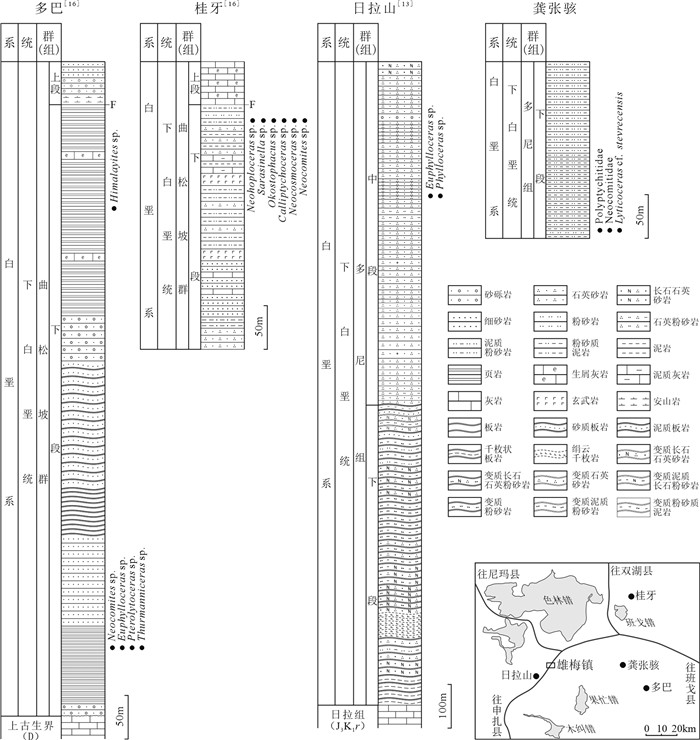
在藏北班戈地区多尼组中发现了早白垩世欧特里夫期菊石。这些菊石化石部分保存较完整,鉴定出2科和1种(比较种),包括多皱菊石科Polyptychitidae,新考米菊石科Neocomitidae,减退菊石比较种Lyticoceras cf.stevrecensis。对比发现,该化石组合可能具有较强的地方属性特征。其中,Lyticoceras cf.stevrecensis属于地方菊石亚科,是早欧特里夫期的典型分子,可以与特提斯域的喜马拉雅北部、巴基斯坦北部和西地中海等地区的菊石进行对比,填补了班戈地区Thurmanniceras - Sarasinella菊石组合的欧特里夫期空白,这对于该地区的下白垩统地层对比和重新认识措勤盆地的沉积构造演化可能具有重要的约束作用和指示意义。
Abstract:Recently, ammonites have been discovered in the Bange area of northern Xizang, which of the age is Early Cretaceous Hauterivian.The ammonite assemblages sampled in the Duoni Formation are of good preservation.Two families and one comparative species have been identified, including Polyptychitidae, Neocomitidae, Lyticoceras cf.Stevrecensis.By comparison and analysis with early studies, the ammonites have strong local attribute characteristics.Lyticoceras cf.stevrecensis is the typical species of the Early Hauterivian, which belongs to the subfamily Endemoceratinae, and can be compared with those faunas from the Northern Himalayas, Northern Pakistan and Western Mediterranean(South-East France)around the Tethys realm, even the North-Eastern Peri-Tethys.The discovery of ammonites extends the epoch of Thurmanniceras - Sarasinella to Early Hauterivian.These findings could be important foundations for the stratigraphic correlation study of the Lower Cretaceous, and for re-recognizing the sedimentary tectonic evolution in this area of Cuoqin Basin.
-
Key words:
- ammonites /
- Hauterivian /
- Early Cretaceous /
- Bange area /
- Cuoqin basin /
- geological survey engineering /
- Xizang
-

-
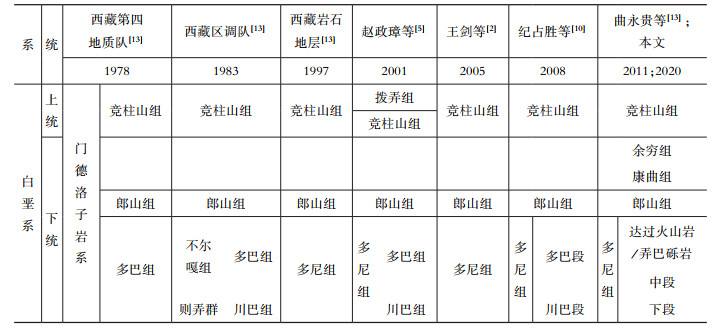
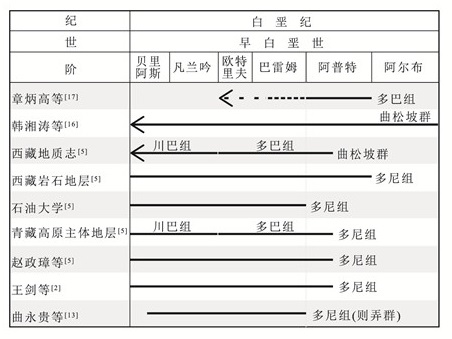
表 1 西藏班戈地区白垩系地层划分
Table 1. Stratigraphic chart of the Cretaceous in Bange area, Xizang
-
[1] 赵政璋, 李永铁, 叶和飞, 等. 青藏高原海相烃源层的油气生成[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000.
[2] 王剑, 谭富文, 李亚林, 等. 青藏高原重点沉积盆地油气资源潜力[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2005.
[3] 王剑, 丁俊, 王成善, 等. 青藏高原油气资源战略选区调查与评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009.
[4] 魏玉帅, 王成善, 李亚林, 等. 西藏措勤盆地中生界生储盖特征和含油气远景评价[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(10): 1575-1586. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.10.011 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20111011&flag=1
[5] 赵政璋, 李永铁, 叶和飞, 等. 青藏高原地层[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001.
[6] 纪占胜, 姚建新, 武桂春, 等. 西藏措勤县敌布错地区"下拉组"中发现晚三叠世诺利期高舟牙形石[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(1/2): 138-141. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060121&flag=1
[7] 纪占胜, 姚建新, 武桂春. 西藏冈底斯西段措勤地区海相三叠系的划分[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(8): 947-952. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.08.005 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200708154&flag=1
[8] 纪占胜, 姚建新, 武桂春. 关于藏北改则地区夏岗江植物群及其地层时代的修订意见[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(8): 953-959. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.08.006 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200708155&flag=1
[9] 武桂春, 姚建新, 纪占胜. 西藏冈底斯西段措勤地区三叠纪牙形石生物地层特征[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(8): 938-946. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.08.004 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200708153&flag=1
[10] 纪占胜, 姚建新, 武桂春. 西藏措勤盆地的上古生界—下古生界: 潜在的油气沉积建造[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(1): 36-63. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080104&flag=1
[11] 赵政璋, 李永铁, 叶和飞, 等. 青藏高原羌塘盆地石油地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000: 356-367.
[12] 林良彪, 伍新和. 西藏措勤盆地中生界石油地质条件分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2010, 32(4): 348-352. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.04.008
[13] 曲永贵, 王永胜, 段建祥, 等. 中华人民共和国区域地质调查报告(多巴区幅)[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2011: 1-273.
[14] Zhang K J, Xia B D, Wang G M, et al. Early Cretaceous stratigraphy, depositional environments, sandstone provenance, and tectonic setting of central Xizang, western China[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2004, 116(9/10): 1202-1222.
[15] 何国雄, 夏金宝. 藏北班戈一带早白至世早期菊石动物群[J]. 古生物学报, 1984, 23(6): 659-673. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX198406000.htm
[16] 韩湘涛, 伦珠加措, 李才. 藏北湖区班戈一带海相白垩系的划分[C]//青藏高原地质文集(3). 北京: 地质出版社, 1983: 194-211.
[17] 章炳高, 孙东立, 杨胜秋, 等. 关于藏北班戈、申扎地区白至系的新认识[J]. 地层学杂志, 1981, 5(4): 313-315. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ198104010.htm
[18] 张维忠, 陈寿铭, 曲红晔, 等. 西藏北部申扎地区的海相白垩系[J]. 吉林地质, 2008, 27(2): 5-7, 21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLDZ200802002.htm
[19] 王冠民. 西藏措勤盆地下白垩统多巴组沉积环境分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2000, 18(3): 349-354, 368. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200003004.htm
[20] 丁俊, 王剑, 王成善, 等. 青藏高原油气资源战略选区调查与评价图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009.
[21] 王冠民. 西藏措勤盆地构造沉积演化及含油气远景[J]. 石油学报, 2001, 22(1): 31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200101005.htm
[22] 宋全友, 王冠民. 西藏措勤盆地中、新生代岩相古地理特征[J]. 石油大学学报, 2002, 26(6): 7-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200206002.htm
[23] 阴家润. 西藏喜马拉雅晚侏罗世—早白垩世菊石群[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016: 1-308.
[24] Reboulet S, Klein J, Barragán R, et al. Report on the 3rd international meeting of the IUGS Lower Cretaceous AmmoniteWorking Group, the "Kilian Group"(Vienna, Austria, 15th April 2008)[J]. Cretaceous Research, 2009, 30: 496-502.
[25] Hancock J M. Ammonite scales for the Cretaceous System[J]. Cretaceous Research, 1991, 12: 259-291.
[26] Wright C W, Callomon J H, Howarth M K, Cretaceous Ammonoidea[C]//Brousius E, Hardesty J, Keim J, et al. Treatise on invertebrate paleontology, Part L. Mollusca 4(Revised). The Geological Society of America, Boulder. The University of Kansas Press, Lawrence. 1996: 362.
[27] Collignon M. Atlas du fossiles caractéristiques de Madagascar[J]. Fascicle 8(Berriassian, Valanginien, Hauterivien, Barremien), Service Geologique Tananarive, 1962: 176-214.
[28] Fatmi N A. Neocomian ammonites from northern areas of Pakistan[J]. Bulletin of the Brish Museum(Natural History), Geology, 1977, 28: 257-296.
[29] 刘桂芳, 王思恩. 西藏喜马拉雅区上侏罗统和下白垩统研究的新进展[J]. 地层古生物论文集, 1987, 17: 143-166. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ198700013010.htm
[30] Baraboshkin Y, Alekseev S, Kopaevich F. Cretaceous palaeogeography of the North-Eastern Peri-Tethys[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2003, 196: 177-208.
[31] 刘桂芳. 西藏拉萨、纳木湖地区早白垩世阿普第期菊石[J]. 古生物学报, 1988, 27(3): 382-389. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX198803011.htm
-



 下载:
下载: