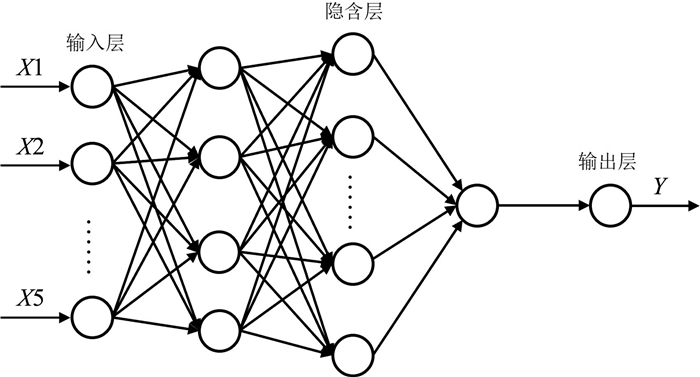
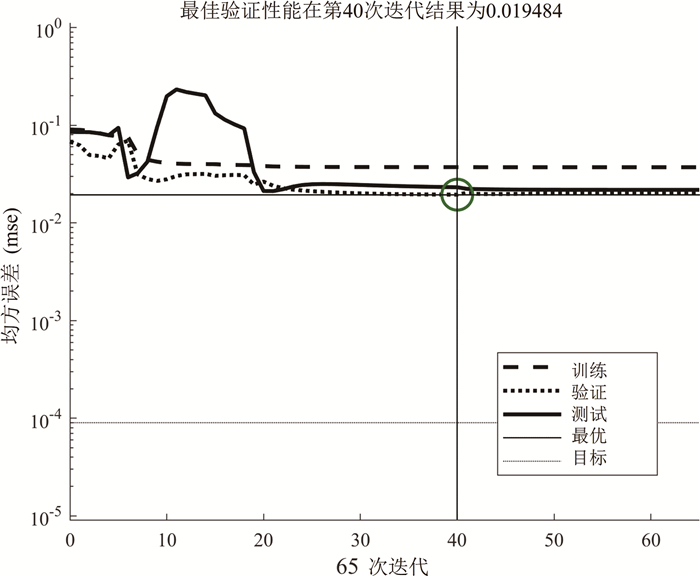
Research on landslide sliding distance prediction model based on multiple nonlinear regression and BP neural network
-
摘要:
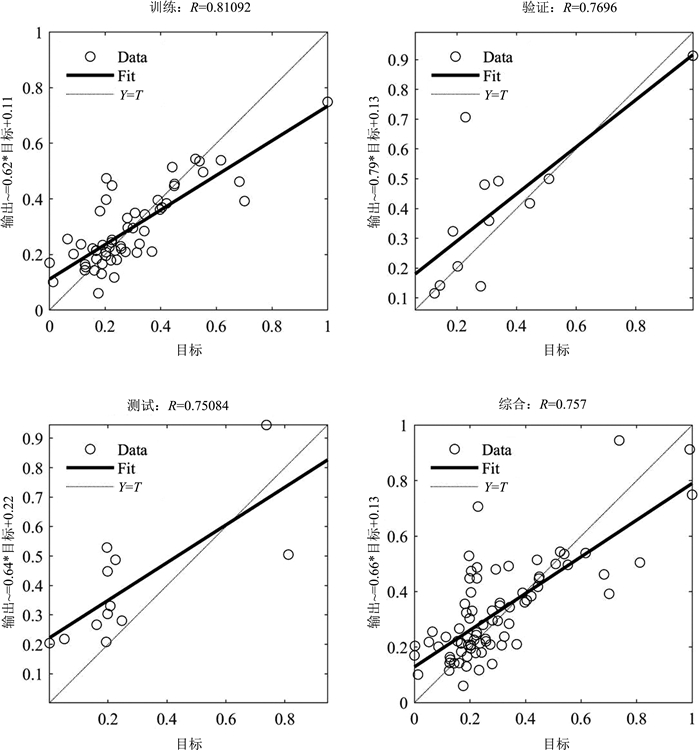
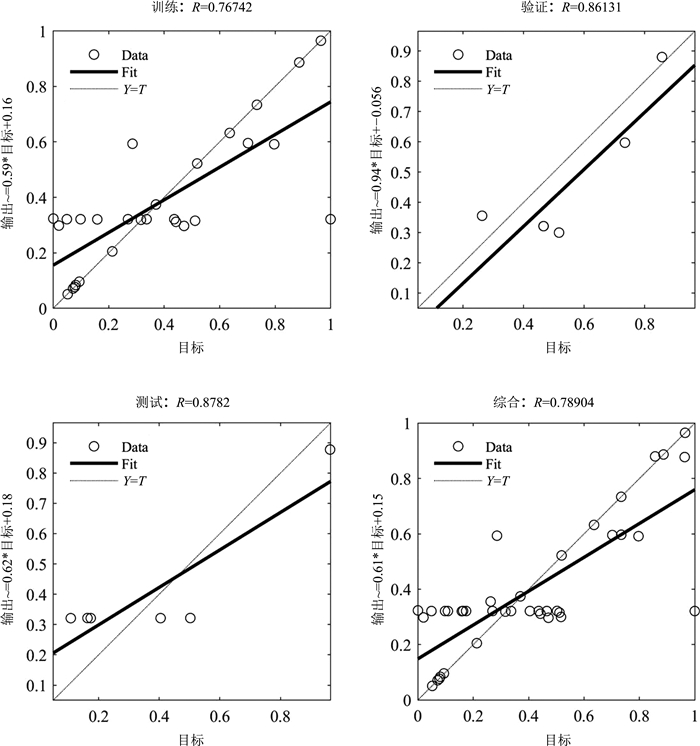
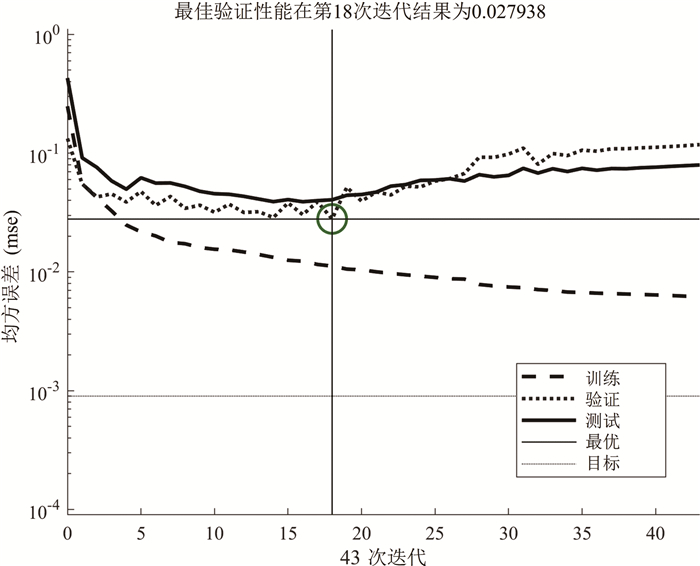
滑坡灾害严重威胁着人类的生命财产安全, 对土地资源造成了一定影响。滑坡滑动距离直接表明了滑坡的冲击、堆积范围大小, 是估算滑坡受灾面积、评估滑坡潜在风险的重要参数, 也是滑坡防灾减灾工作中需要重点关注的指标。为了更准确高效地预测滑坡危害范围, 分别采用多元非线性回归和BP神经网络2种模型对影响滑坡滑动距离的因子进行了评估和建模, 并对天水地区的滑坡实例进行研究。研究结果表明, 2种模型均可用于滑坡滑动距离的预测。相较而言, BP神经网络的预测结果与实际情况有更高的拟合度, 准确性更高。
Abstract:Landslide disasters seriously threaten the safety of human life and property and have a certain impact on land resources. The landslide sliding distance directly indicates the impact and accumulation range size of landslides, which is an important parameter for estimating the affected area of landslides and assessing the potential risk of landslides and is also an indicator that needs to be focused on in landslide prevention and mitigation work. In order to predict the landslide hazard range more accurately and efficiently, this paper uses the theories of multivariate nonlinear regression and BP neural network to estimate the sliding distance of the landslide, respectively. And to study examples of landslides in the Tianshui region, the results show that both models can be used to predict landslide. Compared with the actual results, the BP neural network has a higher degree of fit and accuracy.
-

-
表 1 滑坡样本信息
Table 1. Landslide sample information
滑坡类型 序号 面积(S)/m2 滑坡高差(ΔH)/m 滑坡平面形态 剖面曲率 实测水平滑动距离/m 地震型滑坡 1 3714.65 49.00 8.57 -0.16 114.08 2 4340.20 67.00 0.67 0.01 123.17 3 3682.84 37.00 0.24 -0.13 103.61 4 3083.52 23.00 1.50 -0.07 92.85 5 2591.62 10.00 9.80 -0.14 78.32 6 205537.00 96.15 2.40 0.01 579.50 7 46081.19 117.55 2.78 0.04 266.49 8 2230.50 5.00 5.38 -0.01 71.59 9 1521.04 5.00 2.50 0.66 65.05 10 2021.91 8.00 3.90 -0.52 67.43 降雨型滑坡 1 364142.40 195.31 2.66 -0.00 848.98 2 69610.23 84.35 7.10 0.61 378.90 3 293670.00 139.79 2.78 -0.44 751.93 4 246494.90 143.72 9.41 0.01 664.15 5 232660.70 148.89 2.64 0.09 798.40 6 205327.20 134.00 2.93 0.06 674.40 7 192072.60 229.52 4.02 -0.13 658.76 8 153099.00 169.30 9.80 -0.32 560.31 9 129207.60 333.89 4.39 -0.25 568.51 10 85299.35 213.01 5.39 0.09 402.65 表 2 单因素滑坡要素线性相关计算结果
Table 2. Calculation results of the linear correlation of single factor landslide elements
降雨型滑坡 地震型滑坡 相关方程 相关系数 相关方程 相关系数 滑坡前后缘高差(ΔH) y=25.38x0.5654 0.4702 y=0.011x2-0.9985x + 306.08 0.6266 滑坡面积(S) y = 0.4344x0.5997 0.8357 y = 1.6571x0.4771 0.8312 滑坡坡度(i) 0.0536 0.0328 斜坡等价摩擦系数(μ=H/L) 0.0588 0.1272 滑坡平面形态(长宽比γ) y= 99.602x + 557.27 0.5752 y=379.5x+432.76 0.5378 地形地貌(平面曲率K) 0.5170 0.1490 植被覆盖 0.3870 0.0900 表 3 多元相关系数
Table 3. Multiple correlation coefficient
模型 R R2 调整后R2 标准差 德宾-沃森 地震诱发 0.980a 0.960 0.957 49.037 2.077 降雨诱发 0.901a 0.812 0.806 114.208 1.625 表 4 非线性回归模型检验结果
Table 4. Nonlinear regression model test results
滑坡类型 序号 实测水平滑动距离/m 模型计算得滑动距离/m 误差 地震 1 114.0800 100.4163 11.98% 2 123.1700 108.7141 11.74% 3 103.6100 96.7813 6.59% 4 92.8500 86.4384 6.91% 5 78.3200 75.7050 3.34% 6 579.5030 602.0008 3.88% 7 266.4900 246.2345 7.60% 8 71.5850 69.0334 3.56% 9 65.0480 58.7377 9.70% 10 67.4300 67.8396 0.61% 降雨 1 848.9849 911.8369 7.40% 2 378.9010 366.0614 3.39% 3 751.9303 813.8553 8.24% 4 664.1453 744.9368 12.16% 5 798.3964 723.7249 9.35% 6 674.3973 676.9118 0.37% 7 658.7645 662.6150 0.58% 8 560.3139 583.3253 4.11% 9 568.5081 545.4595 4.05% 10 402.6479 426.6198 5.95% 表 5 BP神经网络模型模型检验结果
Table 5. BP neutral network model test results
滑坡类型 序号 实测水平滑动距离/m 模型计算得滑动距离/m 误差 滑坡类型 序号 实测水平滑动距离/m 模型计算得滑动距离/m 误差 地震 1 601.1812 613.0617 1.98% 降雨 1 422.6054 419.8734 -0.65% 2 776.7570 783.4776 0.87% 2 522.1985 512.9397 -1.77% 3 675.6853 607.7622 -10.05% 3 204.6307 205.0255 0.19% 4 541.9784 545.0218 0.56% 4 280.4112 278.6681 -0.62% 5 638.5164 594.7821 -6.85% 5 318.2101 319.4857 0.40% 6 627.1131 577.6841 -7.88% 6 362.5568 365.213 0.73% 7 1132.0020 1034.372 -8.62% 7 182.6633 178.6214 -2.21% 8 790.7921 787.0566 -0.47% 8 293.9445 296.3856 0.83% 9 761.6214 733.1141 -3.74% 9 379.9835 413.9774 8.95% 10 669.9125 647.8153 -3.30% 10 254.1331 264.9736 4.27% 表 6 平均相对误差
Table 6. Average relative error
滑坡类型 多元非线性回归模型 BP神经网络模型 地震 6.59% 4.43% 降雨 5.56% 2.06% -
[1] 钟秀梅, 李伟利, 袁中夏, 等. 地震作用下天水市区滑坡危险区划研究[J]. 国际地震动态, 2019, (8) : 118-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJZT201908096.htm
[2] 王鼐, 王兰民, 王谦, 等. 黄土高原地震作用下黄土滑坡滑距预测方法[J]. 地震工程学报, 2016, 38(4) : 533-540. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2016.04.0533
[3] Mahaboob B, Venkateswarlu B, Mokeshrayalu G, et al. A different approach to estimate nonliner regression model using numerical methods[C]//Materials Science & Engineering Conference Series. Materials Science and Engineering Conference Series, 2017.
[4] 张保生, 纪昌明, 陈森林. 多元线性回归和神经网络在水库调度中的应用比较研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2004, (7) : 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNSD200407011.htm
[5] 吴玮江. 天水市滑坡泥石流灾害[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2003, (5) : 75-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200305017.htm
[6] 白晓华, 马金辉, 冯乐涛, 等. 基于GIS的天水市滑坡危险性评价[J]. 甘肃地质, 2008, 17(4) : 72-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ200804015.htm
[7] 孟华君, 姜元俊, 张树轩, 等. 汶川地震前后都江堰山区滑坡滑动距离影响因素变化分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 2017, 23(6) : 904-913. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201706011.htm
[8] 王念秦, 张倬元, 王家鼎. 一种典型黄土滑坡的滑距预测方法[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, (1) : 111-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ200301030.htm
[9] 黄发明, 殷坤龙, 蒋水华, 等. 基于聚类分析和支持向量机的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(1) : 156-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201801016.htm
[10] 李秀珍, 孔纪名. "5 · 12" 汶川地震诱发滑坡的滑动距离预测[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2010, 42(5) : 243-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLH201005037.htm
[11] 刘盈, 赵方. 基于多元非线性回归和BP神经网络的长春花形态指标生长模型的比较[J]. 上海农业学报, 2019, 35(6) : 64-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHLB201906013.htm
[12] 辛大欣, 王长元, 肖峰. BP神经网络在回归分析中的应用研究[J]. 西安工业学院学报, 2002, (2) : 129-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGY200202007.htm
[13] 徐辉, 潘萍, 宁金魁, 等. 多元线性回归与神经网络模型在森林地上生物量遥感估测中的应用[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2018, (1) : 63-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBLY201801012.htm
[14] 张保生, 纪昌明, 陈森林. 多元线性回归和神经网络在水库调度中的应用比较研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2004, (7) : 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNSD200407011.htm
[15] 曹朋, 郝蒙蒙, 王佳佳. 基于多元线性回归与BP神经网络的矿井瓦斯预测模型应用[J]. 煤炭技术, 2011, (11) : 91-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTJS201111040.htm
[16] 周越, 曾昭发, 唐海燕, 等. 公路勘察中滑坡体的地球物理特征与分析——以张榆线公路勘察为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2021, 51(2) : 638-644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202102028.htm
-



 下载:
下载: