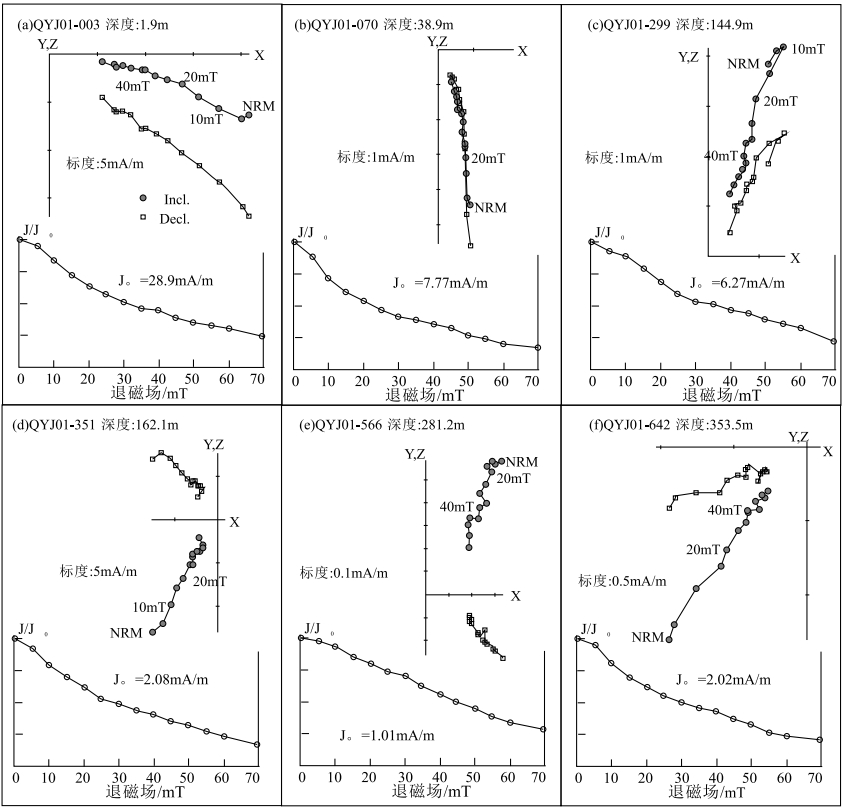
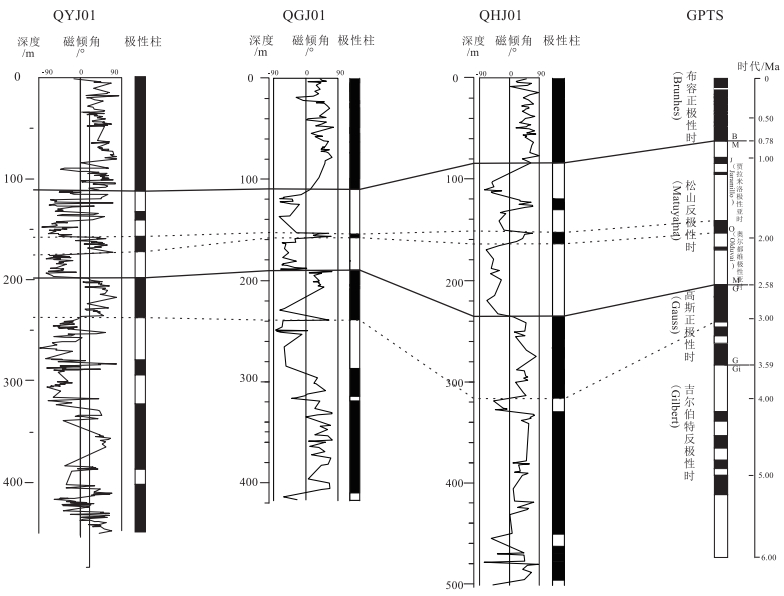
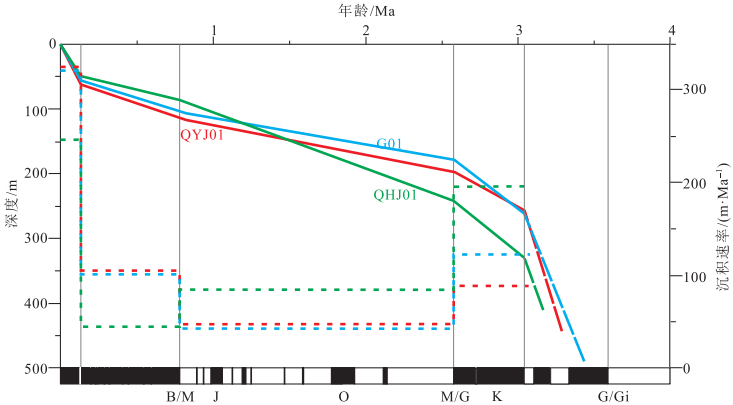
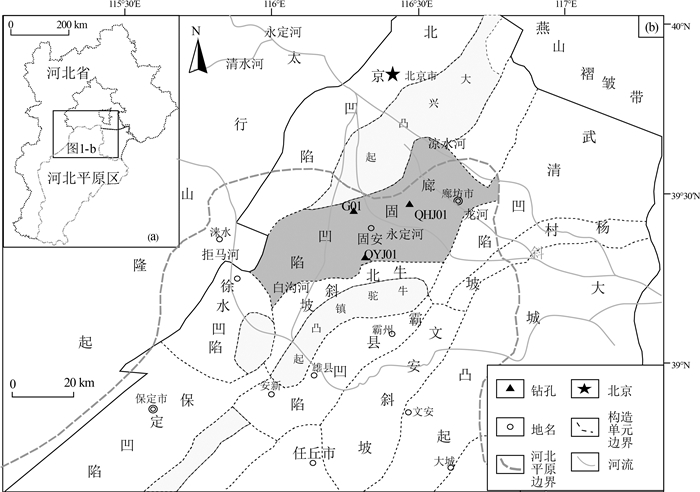
Chronostratigraphic division and sedimentary rate characteristics in the south alluvial plain of Yongding River
-
摘要:
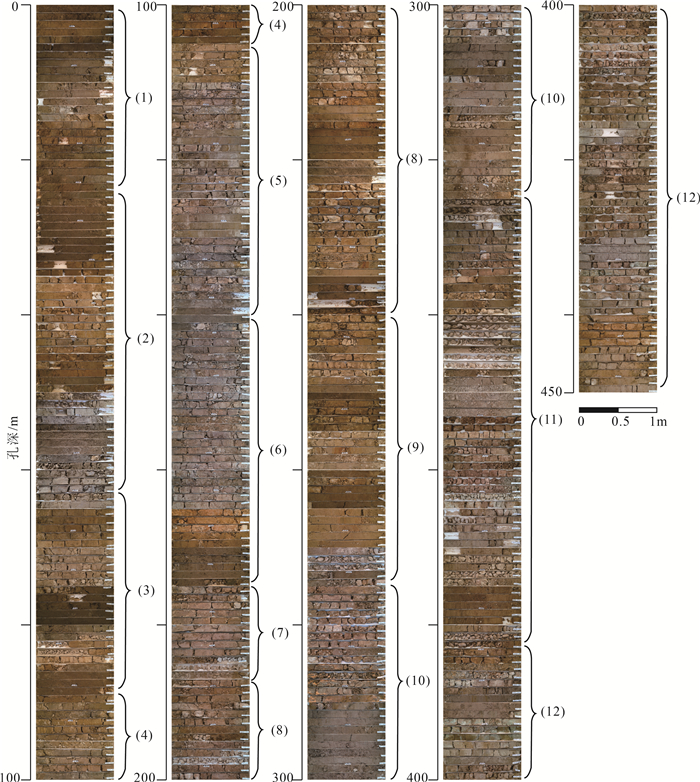
依据磁性地层和14C年代结果,结合岩性分层特征,对永定河冲积平原南部QYJ01年代地层进行划分,并综合QGJ01和QHJ01钻孔年代地层划分成果讨论沉积速率特征。将QYJ01钻孔的年代地层划分为上新统、下更新统、中更新统、上更新统和全新统,其对应孔深分别为198.1~450.9 m、111.5~198.1 m、88.65~111.5 m、23.7~88.65 m和0~23.7 m。综合分析永定河冲积平原南部第四纪代表钻孔QYJ01、QGJ01和QHJ01的沉积速率特征,发现永定河冲积平原南部晚新生代地层沉积中心经历了2次偏移,第1次是始于早更新世、在中更新世完成的沉积中心由中东部向南部偏移,第2次是在全新世完成的沉积中心由南部向中东部回迁。研究结果为永定河冲积平原区新构造运动的活动强度和时限研究及深覆盖区第四纪地层对比提供参考。
Abstract:Based on magnetostratigraphy and 14C dating, combined with stratification characteristics of strata, the stratigraphy of Quaternary in the southern alluvial plain of Yongding River was classified, and its sedimentary rate was discussed based on the stratigraphic classification results from boreholes QGJ01 and QHJ01.The chronostratigraphy of borehole QYJ01 is divided into Upper Pliocene, Lower Pleistocene, Middle Pleistocene, Upper Pleistocene and Holocene, the corresponding depth is 198.1~450.9 m, 111.5~198.1 m, 88.65~111.5 m, 23.7~88.65 m and 0~23.7 m, respectively.The sedimentary rate of Quaternary strata revealed by boreholes QYJ01, QGJ01 and QHJ01 were analyzed comprehensively.It is indicated that the sedimentary center of the late Cenozoic in the south alluvial plain of Yongding River experienced two migrations: the first was the migration of the sedimentary center from the east to the south in the Early Pleistocene and the second was the migration from the south to the east in the Holocene.This study provides some reference for the study of neotectonic activity intensity and time limit in Yoagding River alluvial plain and the division and correlation of Quaternary stratigraphy in deep covered area.
-

-
表 1 QYJ01钻孔14C测年结果
Table 1. 14C dating of borehole QYJ01
样品编号 实验室编号 岩性 深度/m 14C年代/a B.P. 树轮校正后年龄/cal.a B.P. 1σ 2σ 01 BA172277 粉砂质粘土 5.8 3480±35 3789 3681 02 BA172280 粘土质粉砂 32.8 30680±150 23555 23323 -
[1] Han L, Zhao B, Wu J, et al. An integrated approach for extraction of lithology information using the SPOT 6 imagery in a heavily Quaternary-covered region—North Baoji District of China[J]. Geological Journal, 2017, 53: 352-363.
[2] Arfai J, Franke D, Lutz R, , et al. Rapid Quaternary subsidence in the northwestern German North Sea[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 1-12.
[3] 吴富强, 江振寅, 周硕. 国内外风化壳覆盖区地质调查研究综述[J]. 中国地质调查, 2018, 5(6): 41-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201806006.htm
[4] 王强, 刘立军, 徐海振, 等. 华北平原第四系下限的再研究[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2003, 26(1): 52-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2003.01.009
[5] 全国地质委员会. 中国地层指南[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2001: 1-57.
[6] 刘东生, 施雅风, 王汝建, 等. 以气候变化为标志的中国第四纪地层对比表[J]. 第四纪研究, 2000, 20(2): 108-128. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2000.02.002
[7] 邱占祥. 泥河湾哺乳动物群与中国第四系下限[J]. 第四纪研究, 2000, 20(2): 142-154. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2000.02.004
[8] 劳金秀, 杨祝良, 于俊杰, 等. 江苏兴化ZK10孔第四纪多重地层研究[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(10): 1705-1714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.10.018 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20161018&flag=1
[9] 陈望和, 倪明云. 河北第四纪地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987: 1-179.
[10] 丁仲礼, 刘东生, 刘秀铭, 等. 250万年以来的37个气候旋回[J]. 科学通报, 1989, 19: 1494-1496. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1989.19.004
[11] 易亮, 姜兴钰, 田立柱, 等. 渤海盆地演化的年代学研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36: 1075-1087 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.05.05
[12] 刘嘉麒, 刘强. 中国第四纪地层[J]. 第四纪研究, 2000, 20(2): 129-141. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2000.02.003
[13] 王涛, 杨凯越, 李伟荣, 等. 城市浅层地下古河道表征——以广东省潼湖盆地第四纪地下古河道为例[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(10): 1729-1736. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20211016&flag=1
[14] 钱方. 中国第四纪大陆海侵层磁性地层学的初步研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1984, 4(3): 89-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198403009.htm
[15] 朱日祥, 李春景, 吴汉宁, 等. 中国黄土磁学性质与古气候意义[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1994, 24(9): 992-997. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK199409013.htm
[16] 刘立军, 徐海振, 崔秋苹, 等. 河北平原第四纪地层划分研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2010, 26(2): 54-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLGT201002013.htm
[17] Xu Q, Yang J, Yuan G, et al. Stratigraphic sequence and episodes of the ancient Huanghe Delta along the southwestern Bohai Bay since the LGM[J]. Marine Geology, 2015, 367: 69-82. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.05.008
[18] 蔡向民, 张磊, 郭高轩, 等. 北京平原地区第四纪地质研究新进展[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(3): 1055-1066. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201603027.htm
[19] 周毅, 郭高轩, 张磊, 等. 北京后沙峪凹陷的第四纪地层划分与构造演化[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(3): 1067-1075. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201603028.htm
[20] Lu Y C, Wang X L, Wintle A G. A new OSL chronology for dust accumulation in the last 130, 000?yr for the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Research, 2007, 67(1): 152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2006.08.003
[21] Sümegi P, Gulyás S, Molnár D, et al. New chronology of the best developed loess/paleosol sequence of Hungary capturing the past 1.1 Ma: Implications for correlation and proposed pan-Eurasian stratigraphic schemes[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 191: 144-166. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.04.012
[22] Lin Z Y, Han X B, Jin X L, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and paleoenvironmental significance of sediments from ANT29-P7-09 core in Prydz Bay, Antarctica[J]. China Geology, 2019, 2: 493-500.
[23] 朱首峰, 盛君. 第四系覆盖区地质调查中的物探方法研究[J]. 江苏科技信息, 2016, 3: 70-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJXY201603027.htm
[24] 蔡向民, 郭高轩, 栾英波, 等. 北京山前平原区第四系三维结构调查方法研究[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(7): 1047-1057. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.07.012
[25] 代鹏, 邓晓红, 王盛栋, 等. 河北平原区固安G01孔岩芯特征及第四纪地层划分[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(2): 399-407.
[26] 桂宝玲. 伸展盆地构造几何学、运动学——以渤海湾盆地廊固凹陷为例[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2011: 1-118.
[27] 刘国臣, 陆克政, 严俊君. 廊固凹陷构造特征及成因解析[J]. 地质论评, 1996, 42(sup): 83-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP1996S1012.htm
[28] Dunlop D J, Özdemir Ö. Rock magnetism: fundamentals and Frontiers[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1997: 1-573.
[29] 朱日祥, 邓成龙, 潘永信. 泥河湾盆地磁性地层定年与早期人类演化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(6): 922-944. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.06.008
[30] 张惠民, 张文治, Elston D P. 华北蓟县中、上元古界古地磁研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 1991, 34(5): 602-615. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1991.05.009
[31] Cande S C, Kent D V. Revised calibration of the geomagnetic polarity timescale for the Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1995, 100(B4): 6093-6095. doi: 10.1029/94JB03098
[32] 赵勇, 王强, 李瑞杰, 等. 北京平原区南部PGZ01孔第四纪地层划分及其环境意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(2): 167-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201802014.htm
[33] 代鹏, 王盛栋, 邓晓红, 等. 地球物理方法在厚覆盖区第四纪地层划分中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(6): 2143-2151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201906002.htm
[34] 赵勇, 李瑞杰, 魏波, 等. 北京大兴凸起南部PGZ05钻孔剖面第四纪磁性地层学研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(1): 56-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201901006.htm
[35] 胥勤勉, 袁桂邦, 张金起, 等. 渤海湾沿岸晚第四纪地层划分及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(8): 1352-1367. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201108010.htm
[36] 白凌燕, 张磊, 蔡向民, 等. 磁性地层年代对北京平原顺义断裂第四纪活动性的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(6): 1234-1242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.06.014
[37] 陈永胜, 王福, 田立柱, 等. 渤海湾西岸全新世沉积速率对河流供给的响应[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(10): 1582-1590. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.10.015 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20141015&flag=1
[38] Yi L, Deng C L, Tian L Z, et al. Plio-Pleistocene evolution of Bohai Basin (East Asia): demise of Bohai Paleolake and transition to marine environment[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 1-9. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0001-8
[39] 邓成龙, 郝青振, 郭正堂, 等. 中国第四纪综合地层和时间框架[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 48: 1-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201901015.htm
[40] 邵时雄, 安仲元, 韩书华. 河北平原新构造运动主要特征的分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1984, 4(4): 69-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198404009.htm
[41] 陈望和. 河北地下水[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1999: 1-539.
-



 下载:
下载: