Shallow and submarine identifications of gas hydrate in the Makran accretionary prism, northern Arabian Sea
-
摘要:
阿拉伯海北部的莫克兰增生楔是阿拉伯板块以低速、低角度俯冲到欧亚板块之下形成的主动陆缘构造,蕴藏着丰富的天然气水合物资源。依据2019年中国在莫克兰增生楔海域采集的高分辨率多道地震资料、浅地层剖面及多波束测深数据,并结合以往的调查成果,探讨莫克兰海域天然气水合物存在的浅表层识别标志。地震识别标志主要有似海底反射层(BSR)和振幅空白带2种标志,地形地貌标志包括海底麻坑、海底滑塌、丘状体、泥火山、冷泉系统等,水体标志主要为羽状流。在水深1000m和2900m的站位已分别钻获水合物样品。莫克兰增生楔丰富的水合物识别标志可能与低速、低角度的俯冲地质背景有关,使该区水合物存在指示兼具主动大陆边缘和被动大陆边缘的特征。综合研究区的异常标志分布特征,推测增生楔中部和西部的背斜脊及其附近区域是天然气水合物远景区。
Abstract:The Makran accretionary prism located in the northern Arabian Sea is formed by the subduction of the Arabian plate beneath the Eurasian plate in a northerly direction at low speed and low angle,and there are abundant gas hydrate resources in the accretionary prism. Based on the high-resolution multi-channel seismic data,sub-bottom profile and multi-beam echo sounding data acquired by China in 2019, combined with the former investigation results,this paper discusses the shallow and submarine identifications of gas hydrate in the Makran accretionary prism. The seismic identifications mainly include bottom simulating reflector(BSR)and acoustic blank zone. The topographic and geomorphic signs include submarine pockmark,submarine slump,mound,mud volcano and cold seeps system. The water body signs mainly is flare. Gas hydrate samples have been drilled at the stations with water depth of 1000 m and 2900 m respectively. The abundant hydrate identifications of Makran accretionary prism may be related to the low velocity and low angle subduction geological background,which makes the hydrate identifications in this area show the characteristics of active continental and passive continental margins. Based on the distribution characteristics of identifications in the study area,the anticlinal ridges and theiradjacent areas in the central and western parts of accretionary prism are the gas hydrates prospective areas.
-

-
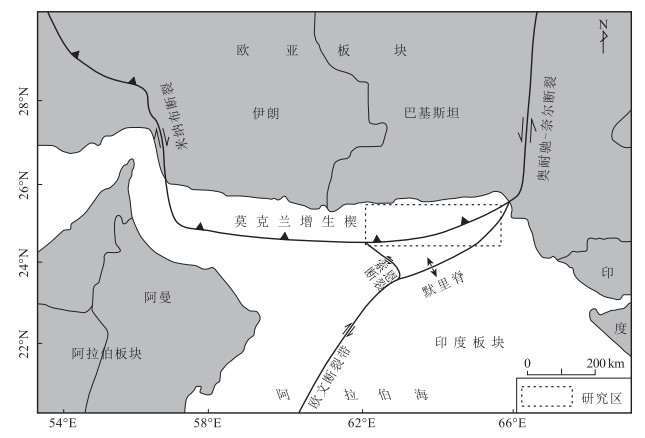
图 1 莫克兰增生楔大地构造位置(据Kukowski et al., 2001)
Figure 1.
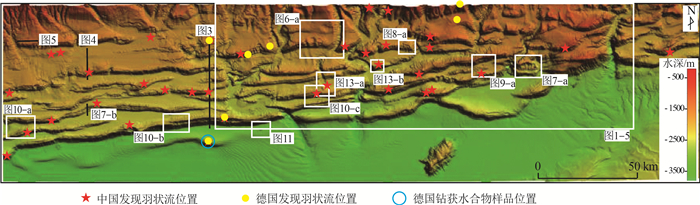
图 2 莫克兰增生楔构造图(图中德国发现羽状流位置和钻获水合物样品位置据Bohrmann et al., 2008)
Figure 2.
图 11 变形前缘的泥火山特征(地震剖面据Wiedicke et al., 2001)
Figure 11.
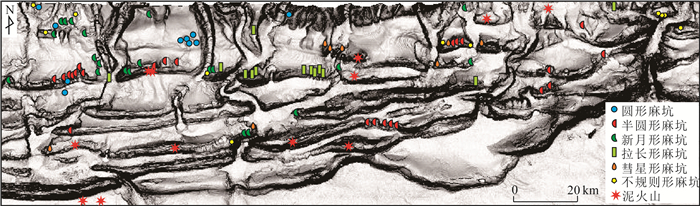
图 13 莫克兰增生楔羽状流现象(c、d据Bohrmann et al., 2008)
Figure 13.
图 14 莫克兰增生楔钻获的气泡状水合物样品(a)和片状水合物碎片(b) (据Bohrmann et al., 2008)
Figure 14.
表 1 主动大陆边缘主要水合物分布区的水合物存在指示(据胡高伟等,2020)
Table 1. Occurrence indicator of hydrate in major hydrate distribution areas of active continental margin
水合物分布区 水合物存在指示 日本Nankai海槽 存在大面积的BSR 南极海南设得兰海沟 沟-增生楔-弧前盆地序列发育、
存在BSR智利西海岸和智利三联点附近 增生楔浅部存在BSR 南太平洋秘鲁海沟增生楔 存在连续BSR Cascadia俯冲带及增生楔 增生楔顶部有明显的、
较连续的强反射层BSR台湾碰撞带西南近海增生楔 存在BSR 西北太平洋大陆边缘鄂霍茨克海 冷泉、泥底辟、泥火山 -
[1] Abid H, Moin R K, Nadeem A, et al. Mud diapirism induced structuration and implications for the definition and mapping of hydrocarbon traps in Makran accretionary prism, Pakistan[C]//Washington: AAPG/SEG International Conference & Exhibition, 2015: 13-16.
[2] Arthuron R S, Farah A, Ahmed W. The late Cretaceous-Cenozoic history of western Baluchistan, Pakistan-the northern margin of the Makran subduction complex[C]//Legett J K. Trench-Forearc geology. Special Publication Geological Society of London, 1982, 10: 373-385.
[3] Bohrmann G, Bahr A, Brinkmann F, et al. Cold seeps of the Makran subduction zone(continental margin of Pakistan): R/V Meteor cruise report M74/3: M74, Leg 3, Fujairah-Male, 30 October-28 November, 2007[M]. Berichte, Fachbereich Geowissenschaften, Universität Bremen, No. 266, 2008: 1-161.
[4] Byrne D E, Sykes L R, Davis D M. Great thrust earthquakes and aseismic slip along the plate boundary of the Makran subduction zone[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 1992, 97: 449-478. doi: 10.1029/91JB02165
[5] Campbell K A. Hydrocarbon seep and hydrothermal vent palaeoenvironments and palaeontology: past developments and future research directions[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeogeography, 2006, 232(2/4): 362-407.
[6] Delisle G, von Rad U, Andruleit H, et al. Active mud volcanoes on-and offshore eastern Makran, Pakistan[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2002, 91: 93-110. doi: 10.1007/s005310100203
[7] Demets C, Gordon R G, Argus D F. Geologically current plate motions[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2010, 181(1): 1-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04491.x
[8] Dillon W P, Lee M W, Felhaber K, et al. Gas hydrates on the Atlantic continental margin of the United States-Controls on the concentration[C]//Howell D G. The Feature of Energy Gases. U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1570, 1993: 313-330.
[9] Ellouz-Zimmermann N, Deville E, Müller C, et al. Impact of sedimentation on convergent margin tectonics: example of the Makran accretionary prism(Pakistan)[C]//Lacombe O, Roure F, Lavé J, et al. Thrust Belts and Foreland Basins. Springer, France Chapter, 2007, 17: 327-350.
[10] Ellouz-Zimmermann N, Lallemant S J, Castilla R, et al. Offshore frontal part of the Makran accretionary prism: the Chamak survey(Pakistan)[J]. Frontiers in Earth Sciences, 2007, 18: 351-366.
[11] Foucher J P, Westbrook G K, Boetius A, et al. Structure and drivers of cold seep ecosystems[J]. Oceanography, 2009, 22(1): 92-109. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2009.11
[12] Grando G, McClay K. Morphotectonics domains and structural styles in the Makran accretionary prism, offshore Iran[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2007, 196(1): 157-179.
[13] Gutscher M A, Westbrook G K. Great earthquakes in slow-subduction, low-taper margins[C]//Lallemand S, Funiciello F. Subduction Zone Geodynamics. Berlin: Springer-Verlag Berlin, 2009: 119-133.
[14] Holbrook W S, Hoskins H, Wood W T, et al. Methane hydrate and free gas on the Blake Ridge from vertical seismic profiling[J]. Science, 1996, 273: 1840-1843. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5283.1840
[15] Hovland M, Judd A G. Seabed pockmarks and seepages[M]. London: Graham & Trotman Ltd., 1988.
[16] Hovland M, Svensen H. Submarine pingoes: indicators of shallow gas hydrates in a pockmark at Nyegga, Norwegian Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 228: 15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2005.12.005
[17] Hovland M, Heggland R, Vries M H D, et al. Unit-pockmarks and their potential significance for predicting fluid flow[J]. Marine & Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27(6): 1190-1199.
[18] Judd A, Hovland M. Seabed Fluid Flow: The Impact on Geology, Biology and the Marine Environment[M]. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 2007.
[19] Kopp C, Fruehn J, Flueh E R, et al. Structure of the Makransubduction zone from wide-angle and reflection seismic data[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 329(1): 171-191.
[20] Kukowski N, Schillhorn T, Huhn K, et al. Morphotectonics and mechanics of the central Makran accretionary wedge off Pakistan[J]. Marine Geology, 2001, 173: 1-19. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(00)00167-5
[21] Kvenvolden K A, Lorenson T D. The global occurrence of natural gas hydrates[C]//Paull C K, Dillon W P. Natural Gas Hydrates: Occurrence, Distribution and Detection. USA: AGU Geophysical Monograph, 2001: 3-18.
[22] Majumdar U, Cook A E, Shedd W, et al. The connection between natural gas hydrate and bottom-simulating reflectors[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(13): 7044-7051. doi: 10.1002/2016GL069443
[23] Milkov A V. Worldwide distribution of submarine mud volcanoes and associated gas hydrates[J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 167(1): 29-42.
[24] Noguchi S, Shimoda N, Takano O, et al. 3-D internal architecture of methane hydrate-bearing turbidite channels in the eastern Nankai Trough, Japan[J]. Marine & Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28: 1817-1828.
[25] Paull C K, Normark W R, Ussler W, et al. Association among active seafloor deformation, mound formation, and gas hydrate growth and accumulation within the seafloor of the Santa Monica Basin, offshore California[J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 250: 258-275. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2008.01.011
[26] Pilcher R, Argent J. Mega-pockmarks and linear pockmark trains on the West African continental margin[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 244(1/4): 15-32.
[27] Platt J P, Leggett J K, Alam S. Slip vectors and fault mechanics in the Makran accretionary wedge, Southwest Pakistan[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1988, 93(7): 7955-7973.
[28] Römer M, Sahling H, Pape T, et al. Quantification of gas bubble emissions from submarine hydrocarbon seeps at the Makran continental margin(offshore Pakistan)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2012, 117(C10015): 1-19.
[29] Serié C, Huuse M, Schodt N H. Gas hydrate pingoes: Deep seafloor evidence of focused fluid flow on continental margins[J]. Geology, 2012, 40: 207-210.
[30] Shipley T H, Houston M H, Buffler R T, et al. Seismic evidence for widespread possible gas hydrate hotizons on continental slope and rises[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1979, 63(12): 2204-2213.
[31] Smith G L, McNeill L C, Henstock T J, et al. The structure and fault activity of the Makran accretionaryprism[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2012, 117: 1-17.
[32] Vanreusel A, Andersen A C, Boetius A, et al. Biodiversity of cold seep ecosystems along the European margins[J]. Oceanography, 2009, 22(1): 110-127. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2009.12
[33] Von Rad U, Berner U, Delisle G, et al. Gas and fluid venting at the Makran accretionary wedge off Pakistan[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2000, 20(1): 10-19. doi: 10.1007/s003670000033
[34] Webb K E, Hammer O, Lepland A, et al. Pockmarks in the inner Oslofjord, Norway[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2009, 29(2): 111-124. doi: 10.1007/s00367-008-0127-1
[35] Wiedicke M, Neben S, Spiess V. Mud volcanoes at the front of the Makran accretionary complex, Pakistan[J]. Marine Geology, 2001, 172: 57-73. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(00)00127-4
[36] Xu Z Z, Chen S Y, Yang S Q, et al. Identification signs and prospects of hydrate gas[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2007, 9(1): 84-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9620.2007.01.010
[37] Zhang Z, Deng X G, Yao H Q, et al. A preliminary study on geomorphological characteristics and genetic mechanism of pockmarks in the Makran accretionary prism, northern Arabian Sea[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2021, 41(3): 1-16.
[38] Zhang Z, He G W, Yao H Q, et al. Diapir structure and its constraint on gas hydrate accumulation in the Makran accretionary prism, offshore Pakistan[J]. China Geology, 2020, 3(4): 611-622. doi: 10.31035/cg2020049
[39] 樊栓狮, 关进安, 梁德青, 等. 天然气水合物动态成藏理论[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2007, 18(6): 819-826. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2007.06.009
[40] 方银霞, 高金耀, 黎明碧, 等. 冲绳海槽天然气水合物与地质构造的关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(1): 85-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ20050100E.htm
[41] 龚建明, 廖晶, 孙晶, 等. 巴基斯坦马克兰增生楔天然气水合物的主控因素[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(12): 10-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201612002.htm
[42] 龚建明, 廖晶, 张莉, 等. 印度洋北部马克兰增生楔泥火山分布及主控因素探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(5): 1025-1030. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201805015.htm
[43] 龚跃华, 杨胜雄, 王宏斌, 等. 南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物成藏特征[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(2): 210-216. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.02.003
[44] 胡高伟, 卜庆涛, 吕万军, 等. 主动、被动大陆边缘天然气水合物成藏模式对比[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(8): 45-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202008005.htm
[45] 匡增桂, 方允鑫, 梁金强, 等. 珠江口盆地东部海域高通量流体运移的地貌-地质-地球物理标志及其对水合物成藏的控制[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 48(8): 1033-1044. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201808006.htm
[46] 廖晶, 龚建明, 何拥军, 等. 马克兰增生楔地层层序及发育过程[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(4): 69-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201904008.htm
[47] 刘杰, 孙美静, 苏明, 等. 海底泥火山特征及其与天然气水合物的成矿关系[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(8): 53-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201508008.htm
[48] 沙志彬, 王宏斌, 张光学, 等. 底辟构造与天然气水合物的成矿关系[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(3): 283-288. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200503039.htm
[49] 王后金, 沙志斌, 梁劲. 南海神狐暗沙海区天然气水合物地震识别特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2013, 34(1): 83-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201301026.htm
[50] 张光学, 祝有海, 梁金强, 等. 构造控制型天然气水合物矿藏及其特征[J]. 现代地质, 2006, 20(4): 605-612. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200604011.htm
[51] 张伟, 梁金强, 苏丕波, 等. 双似海底反射层与天然气水合物成藏关系研究进展与展望[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(1): 29-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202001004.htm
[52] 张旭东, 尹成, 曾凡祥, 等. 南海北部陆坡聚集流体活动系统及其对天然气水合物成藏的指示意义[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(2/3): 280-286. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2021020309&flag=1
-



 下载:
下载: