Magmatism in the Early Triassic continental margin arc environment in the West Qinling mountains: Evidence from zircon U-Pb ages and geochemical characteristics of the Nazha pluton
-
摘要:
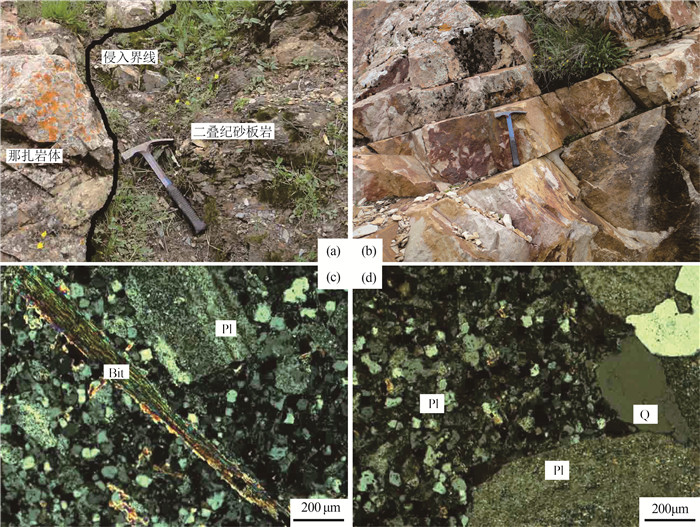
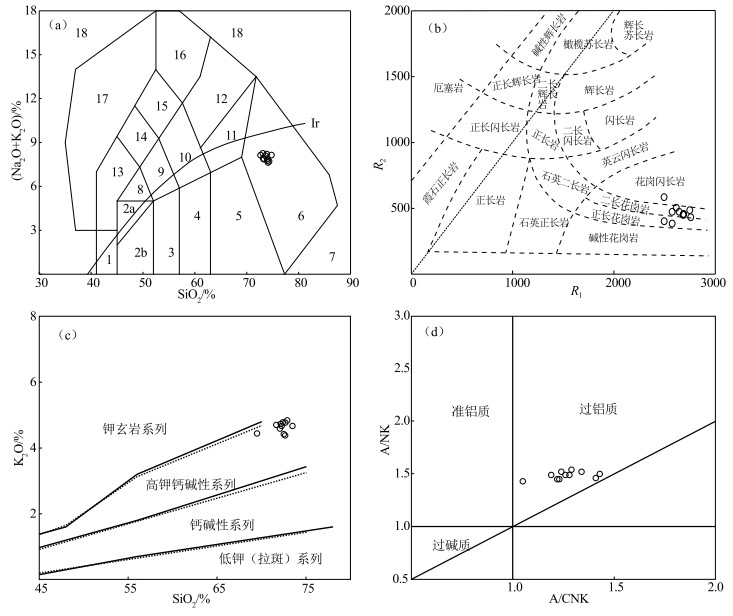
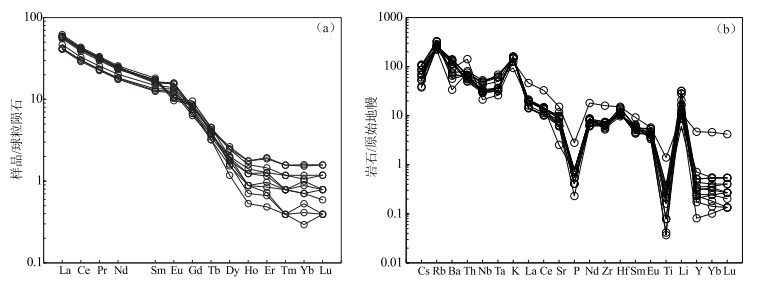
甘肃合作那扎岩体岩性为花岗斑岩。对岩体地质学、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及岩石地球化学特征进行研究, 探讨岩体的成因机制及构造意义, 为该地区印支期的构造演化提供新证据。岩石地球化学分析表明, SiO2含量为69.50%~73.48%, TiO2含量为0.008%~0.084%, CaO含量为0.22%~2.07%, Na2O含量为2.96%~3.40%, K2O含量为4.38%~4.84%, Al2O3含量为14.74%~16.19%, 铝饱和指数A/CNK值为1.49~1.91, >1.1, 里特曼指数σ为1.88~2.27, 属高钾钙碱性过铝质S型花岗岩。稀土元素总量为42.82×10-6~62.85×10-6, LREE/HREE值为16.55~24.19, 轻稀土元素含量相对富集, δEu值为0.79~1.41;高场强元素P、Ti相对亏损, Nb、Ta略有亏损, 大离子亲石元素和轻稀土元素Th、Rb、K相对富集。岩石地球化学特征显示, 那扎岩体起源于地壳变质砂岩和变质泥岩等物质部分熔融, Mg#值高(67~77), 稀土元素总量低, 成岩过程中有幔源组分的加入。花岗斑岩中获得LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为249.7±1.8 Ma, 形成于早印支期。结合区域地质背景, 认为研究区所在的西秦岭夏河—合作一带, 在早印支期处于地壳和岩石圈加厚的陆缘弧环境, 那扎岩体就是该阶段岩浆作用的产物。
Abstract:The lithology of Nazha pluton in Hezuo, Gansu Province is granite porphyry. Through the study of rock geology, LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age, and rock geochemistry, the genetic mechanism and tectonic significance of the Nazha pluton are explored, providing new evidences for the tectonic evolution of the Indosinian period in this region. The rock geochemical analysis of granite porphyry shows that the content of SiO2 is 69.50%~73.48%, the content of TiO2 is 0.008%~0.084%, the content of CaO is 0.22%~2.07%, the content of Na2O is 2.96%~3.40%, the content of K2O is 4.38%~4.84%, the content of Al2O3 is 14.74%~16.19%, the aluminum saturation index A/CNK value is 1.49 ~ 1.91(>1.1), and the Rittman index σ is 1.88~2.27. The result indicates the granite belonging to high potassium calc alkaline peraluminous S-type granite. Total rare earth element(ΣREE)content is 42.82×10-6~62. 85×10-6, LREE/HREE value is 16.55~24.19, light rare earth element is relatively enriched, and the δEu value is 0.79~1.41. High field strength elements P and Ti are relatively deficient, the Nb and Ta are slightly deficient, and large ion lithophile elements and light rare earth elements Th, Rb and K are relatively enriched. The geochemical characteristics of rocks show that the Nazha pluton originated from the partial melting of metamorphic sandstones and mudstones, with the high Mg# value (67~77), and the low total rare earth element content, with some. The mantle-derived components added during diagenesis. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age (250.4±1.0 Ma) was obtained from granite porphyry and formed in Early Indosinian period. Combined with the regional geological background, the author believes that the Xiahe-Hezuo area in West Qinling region was in the continental margin arc environment of crustal and lithosphere thickening during the Early Indosinian period, and the Nazha pluton is the product of the magmatism in this stage.
-

-
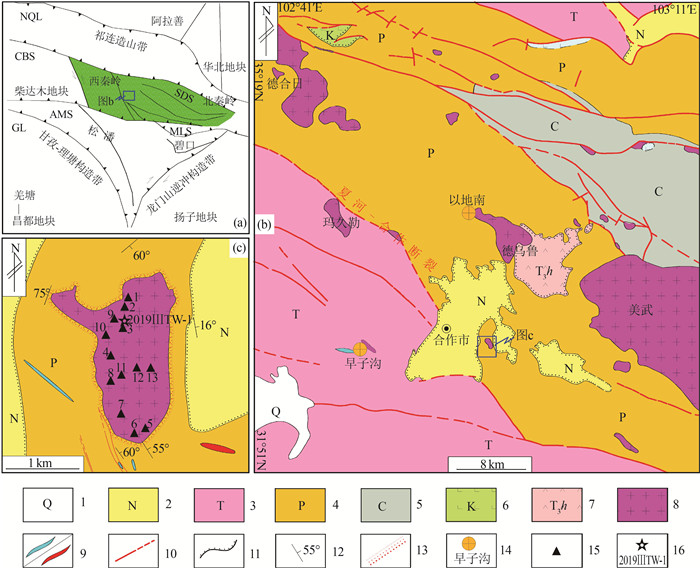
图 1 夏河—合作地区地质简图(a图据张国伟等, 1995修改)
Figure 1.
图 6 那扎岩体稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(稀土元素和微量元素标准化数据据Sun et al., 1989)
Figure 6.
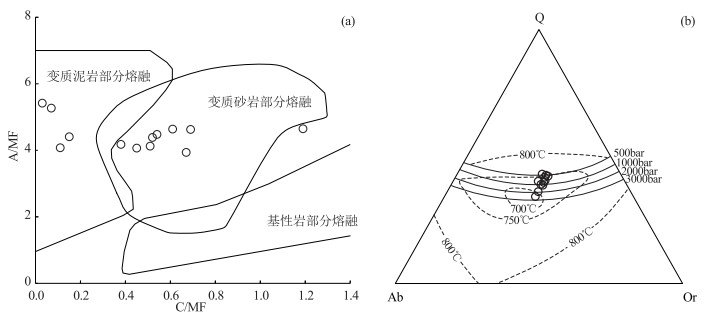
图 7 那扎岩体C/MF-A/MF图解(a, 底图据Alther et al., 2000)和Q-Ab-Or-H2O系相图(b, 底图据Tuttle et al., 1958)
Figure 7.
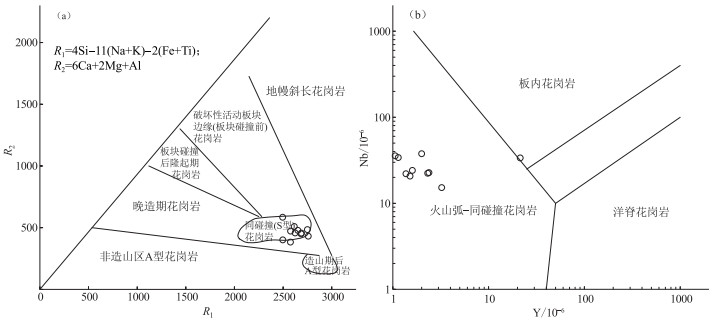
图 8 那扎岩体花岗岩R1-R2(a, 底图据Batchelor et al., 1985) 与Y-Nb构造环境判别图解(b, 底图据Pearce et al., 1984)
Figure 8.
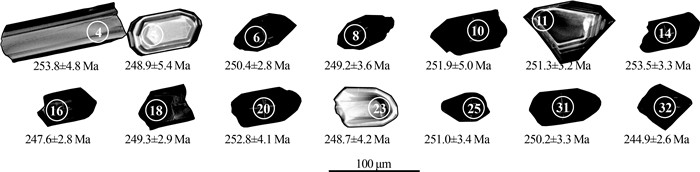
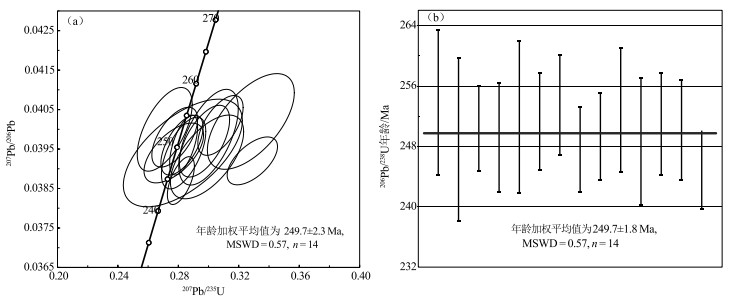
表 1 那扎岩体花岗斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb年龄测试结果
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb age of granite porphyry in Nazha pluton
测点号 元素含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 2σ 207Pb/235U 2σ 206Pb/238U 2σ 207Pb/206Pb 2σ 207Pb/235U 2σ 206Pb/238U 2σ 2019ⅢTW-1-4 11.1 90.8 244.0 0.37 0.0596 0.0034 0.3280 0.0190 0.0402 0.0008 500.0 130.0 286.0 14.0 253.8 4.8 2019ⅢTW-1-5 6.0 35.3 143.0 0.25 0.0530 0.0053 0.2830 0.0260 0.0394 0.0009 190.0 190.0 249.0 20.0 248.9 5.4 2019ⅢTW-1-6 43.7 204.2 1021.0 0.20 0.0518 0.0018 0.2824 0.0092 0.0396 0.0005 250.0 76.0 252.0 7.3 250.4 2.8 2019ⅢTW-1-8 56.8 282.6 1312.0 0.22 0.0519 0.0017 0.2835 0.0097 0.0394 0.0006 255.0 73.0 252.9 7.6 249.2 3.6 2019ⅢTW-1-10 63.7 235.0 1425.0 0.16 0.0539 0.0022 0.3000 0.0130 0.0398 0.0008 344.0 90.0 265.8 10.0 251.9 5.0 2019ⅢTW-1-11 34.9 272.0 783.0 0.35 0.0502 0.0019 0.2776 0.0100 0.0398 0.0005 212.0 80.0 248.7 7.9 251.3 3.2 2019ⅢTW-1-14 58.2 262.7 1277.0 0.21 0.0549 0.0018 0.3079 0.0099 0.0401 0.0005 385.0 71.0 272.1 7.7 253.5 3.3 2019ⅢTW-1-16 46.8 206.3 1116.0 0.18 0.0616 0.0022 0.3290 0.0110 0.0392 0.0004 641.0 75.0 289.3 9.0 247.6 2.8 2019ⅢTW-1-18 28.7 109.5 681.0 0.16 0.0510 0.0025 0.2770 0.0130 0.0394 0.0005 205.0 100.0 247.3 11.0 249.3 2.9 2019ⅢTW-1-20 29.0 119.2 722.0 0.17 0.0497 0.0022 0.2710 0.0120 0.0400 0.0007 156.0 95.0 243.0 9.6 252.8 4.1 2019ⅢTW-1-23 24.1 179.3 520.0 0.34 0.0547 0.0029 0.2990 0.0160 0.0393 0.0007 340.0 110.0 264.0 12.0 248.7 4.2 2019ⅢTW-1-25 78.7 339.9 1733.0 0.20 0.0533 0.0019 0.2973 0.0110 0.0397 0.0006 322.0 80.0 263.9 8.3 251.0 3.4 2019ⅢTW-1-31 57.1 251.9 1291.0 0.20 0.0515 0.0011 0.2835 0.0061 0.0396 0.0005 255.0 48.0 253.1 4.8 250.2 3.3 2019ⅢTW-1-32 66.2 298.3 1456.0 0.20 0.0527 0.0010 0.2817 0.0059 0.0387 0.0004 297.0 44.0 251.6 4.7 244.9 2.6 注: 样品测试由北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成(2019年) 表 2 那扎岩体花岗斑岩主量、微量及稀土元素测试结果
Table 2. The analytical results of major, trace and rare earth elements of granite porphyry in Nazha pluton
元素 GS01 GS02 GS03 GS05 GS06 GS07 GS08 GS10 GS11 GS12 GS13 SiO2 72.41 72.07 72.27 73.48 72.17 72.51 72.89 69.5 72.67 71.66 72.68 TiO2 0.035 0.009 0.017 0.084 0.077 0.048 0.054 0.008 0.062 0.045 0.047 Al2O3 16.19 15.18 14.95 15.08 15.48 15.01 15.46 14.74 15.00 15.08 15.01 Fe2O3 0.648 0.517 0.516 0.646 0.537 0.824 0.595 0.386 0.464 0.487 0.560 FeO 0.27 0.16 0.20 0.18 0.25 0.10 0.30 0.16 0.10 0.44 0.16 MnO 0.024 0.026 0.024 0.021 0.022 0.023 0.019 0.023 0.023 0.024 0.026 MgO 0.971 0.942 0.945 0.999 1.070 0.984 1.030 0.967 0.990 1.020 0.979 CaO 0.294 1.100 0.998 0.751 1.06 0.912 0.221 2.070 1.230 1.420 0.978 Na2O 3.40 3.34 3.20 2.96 3.01 3.21 3.26 3.35 3.11 3.06 3.00 K2O 4.78 4.59 4.67 4.67 4.73 4.42 4.84 4.44 4.38 4.70 4.77 P2O5 0.017 0.016 0.017 0.012 0.017 0.009 0.012 0.016 0.009 0.009 0.005 烧失量 1.38 2.03 1.76 1.69 1.92 1.98 1.38 4.54 2.20 2.20 2.00 总计 101.64 101.99 101.62 102.70 102.57 102.38 101.69 104.85 102.52 102.64 102.49 Mg# 66.99 72.87 71.72 70.05 72.23 67.58 68.73 77.26 77.32 67.43 72.44 Na2O+K2O 8.18 7.93 7.87 7.63 7.74 7.63 8.10 7.79 7.49 7.76 7.77 Na2O/K2O 0.71 0.73 0.69 0.63 0.64 0.73 0.67 0.75 0.71 0.65 0.63 σ 2.27 2.15 2.10 1.91 2.05 1.96 2.18 2.24 1.88 2.09 2.03 A/CNK 1.91 1.68 1.69 1.80 1.76 1.76 1.86 1.49 1.72 1.64 1.72 A/NK 1.50 1.56 1.45 1.55 1.54 1.49 1.48 1.43 1.58 1.52 1.56 Na2O/(Na2O+CaO) 0.92 0.75 0.76 0.80 0.74 0.78 0.94 0.62 0.72 0.68 0.75 MgO/(MgO+TFeO) 0.53 0.60 0.59 0.57 0.59 0.54 0.55 0.66 0.66 0.54 0.60 Li 51.3 26.3 45.6 26.4 44.8 16.9 33.0 51.0 21.5 19.0 9.8 Be 6.17 4.59 4.69 3.20 3.57 3.43 2.80 4.45 2.87 3.30 2.74 Cr 3.80 3.70 3.70 3.70 3.70 3.70 3.70 3.70 3.70 3.70 3.70 Co 9.80 9.10 12.50 8.70 7.70 8.30 8.10 6.40 7.90 9.10 8.70 Ni 1.70 1.70 1.70 1.70 1.70 1.70 1.70 1.70 1.70 1.70 1.70 Ga 21.9 22.7 21.6 21.5 21.6 22.4 22.1 24.4 21.5 22.0 21.4 Ge 0.35 0.47 0.72 0.78 0.65 0.96 0.79 1.18 1.00 0.48 0.88 Rb 210 204 206 164 167 159 174 140 151 166 164 Sr 193 130 183 199 208 134 188 54 130 249 130 Y 2.00 1.06 0.79 0.94 2.31 1.60 1.37 1.14 2.38 0.37 1.51 Zr 71.4 64.8 69.8 83.7 83.3 70.8 70.8 58.7 78.1 80.2 70.0 Nb 37.6 35.6 30.1 21.1 22.3 24.1 22.0 34.0 22.7 22.6 20.7 Cs 7.32 6.10 7.66 4.77 6.00 3.81 4.97 6.10 2.68 4.28 2.81 Ba 531 396 503 953 987 804 875 236 948 797 916 Hf 4.50 3.30 4.30 3.50 3.20 3.50 3.80 4.20 3.20 3.40 3.40 Ta 2.55 2.54 2.04 1.30 1.34 1.51 1.45 2.82 1.49 1.49 1.32 Th 6.86 5.73 5.18 5.64 5.75 4.88 4.69 6.42 5.60 4.31 4.21 F 900 800 840 900 800 700 870 820 780 940 670 Te 0.028 0.019 0.022 0.018 0.025 0.025 0.026 0.026 0.021 0.019 0.028 La 13.90 13.10 13.60 14.10 13.90 11.10 9.70 14.70 13.60 10.00 9.88 Ce 25.50 23.80 24.70 25.90 25.40 20.10 17.80 26.60 24.90 18.50 18.50 Pr 3.06 2.83 3.00 3.08 3.04 2.43 2.14 3.17 2.92 2.21 2.20 Nd 11.40 10.80 11.30 11.60 11.60 9.48 8.21 12.00 11.10 8.56 8.42 Sm 2.60 2.65 2.66 2.49 2.51 2.26 1.92 2.78 2.43 2.06 1.97 Eu 0.62 0.56 0.60 0.89 0.92 0.81 0.70 0.60 0.91 0.78 0.73 Gd 1.77 1.76 1.70 1.54 1.67 1.56 1.30 1.96 1.63 1.38 1.39 Tb 0.17 0.15 0.15 0.12 0.16 0.14 0.13 0.17 0.16 0.12 0.14 Dy 0.62 0.45 0.41 0.39 0.63 0.49 0.45 0.50 0.67 0.30 0.51 Ho 0.09 0.05 0.04 0.05 0.10 0.07 0.07 0.05 0.10 0.03 0.08 Er 0.24 0.12 0.11 0.14 0.31 0.21 0.19 0.16 0.32 0.08 0.21 Tm 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.01 0.02 Yb 0.20 0.09 0.07 0.12 0.27 0.18 0.17 0.12 0.26 0.05 0.15 Lu 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.01 0.02 ΣREE 60.23 56.38 58.36 60.46 60.59 48.89 42.82 62.85 59.08 44.09 44.22 LREE 57.08 53.74 55.86 58.06 57.37 46.18 40.47 59.85 55.86 42.11 41.70 HREE 3.15 2.64 2.50 2.40 3.22 2.71 2.35 3.00 3.22 1.98 2.52 LREE/HREE 18.12 20.36 22.34 24.19 17.82 17.04 17.22 19.98 17.35 21.27 16.55 (La/Yb)N 49.85 104.41 139.36 84.28 36.93 44.23 40.93 87.87 37.52 143.46 47.25 (La/Sm)N 3.36 3.11 3.22 3.56 3.49 3.09 3.18 3.33 3.52 3.05 3.16 (Gd/Yb)N 7.14 15.77 19.59 10.35 4.99 6.99 6.17 13.17 5.06 22.26 7.47 δEu 0.88 0.79 0.86 1.39 1.37 1.32 1.35 0.79 1.40 1.41 1.35 注:主量元素含量单位为%, 微量与稀土元素含量单位为10-6。A/CNK(摩尔比)=Al2O3/(CaO+Na2O+K2O);A/NK(摩尔比)=Al2O3(CaO+Na2O+K2O);δEu=[EuN/(Sm+Gd)N]1/2;测试单位:自然资源部兰州矿产资源检测中心, 2019年 -
[1] Ather R, Holl A, Hegner E, et al. High-potassium, calc-alkaline I-type plutonism in the European Variscides: northern Vosges (France)and northern Schwarzwald (Germany)[J]. Lithos, 2000, 50: 51-73. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00052-3
[2] Batchelor R A, Bowden P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985, (48): 43-55.
[3] De La Roche H, Leterrier J, Grandclaude P, et al. A classification of volcanic and plutonic rocks using R1-R2 diagram and major-element analyses-Its relationships with current nomenclature[J]. Chemical Geology, 1980, 29: 183-210. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(80)90020-0
[4] Jiang Y H, Jin G D, Liao S Y, et al. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on the origin of Late Triassic granitoids from the Qinling orogen, central China: Implications for a continental arc to continent-continent collision[J]. Lithos, 2010, 117: 183-197. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.02.014
[5] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al. Reappraisement and Refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15): 1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
[6] Luo B J, Zhang H F, Xun W C, et al. The Middle Triassic Meiwu Batholith, West Qinling, Central China: Implications for the Evolution of Compositional Diversity in a Composite Batholith[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2015, 56(6): 1139-1172. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egv032
[7] Maniar Pd, Piccoli Pm. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
[8] Mao J W, Qiu Y M, Goldfarb R J, et al. Geology, distribution and classification of gold deposits in the Western Qinling belt, Central China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2002, 37(3/4): 352-377.
[9] Middlemost A K. Magmas and magmatic rocks[M]. London: Longman, 1985: 1-266.
[10] Middlemost A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4): 215-224.
[11] Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25: 956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
[12] Peccerillo R, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contrib. Mineral Petrol, 1976, 58: 63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
[13] Qiu K F, Deng J. Petrogenesis of granitoids in the Dewulu skarn copper deposit: implications for the evolution of the Paleotethys ocean and mineralization in Western Qinling, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 90: 1078-1098. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.027
[14] Qiu K F, Yu H C. Nature and origin of Triassic igneous activity in the Western Qinling Orogen: the Wenquan composite pluton example[J]. International Geology Review, 2018, 60(2): 242-266. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2017.1334598
[15] Rapp R P, Shimizu N, Norman M D. et al. Reaction Between Slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge: Experimental constraints at 3.8 GPa[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 160(4): 335-356. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00106-0
[16] Sui J X, Li J W, We G, et al. The Dewulu reduced Au-Cu skarn deposit in the Xiahe-Hezuo district, West Qinling orogen, China: Implications for an intrusion-related gold system[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 80: 1230-1244. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.018
[17] Sun S, Mcdonough W. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[18] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust[J]. Review in Geophysics, 1995, 33: 241-265. doi: 10.1029/95RG00262
[19] Tuttle O F, Bowen N L. Origin of granite in the light of experimental studies in the system NaAlSi3O8-KAlSi3O8-SiO2-H2O[J]. Geological Society of America Memoirs, 1958, 74: 1-146.
[20] Yu H C, Guo C A, Qiu K F, et al. Geochronological and geochemical Constraints on the Formation of the Giant Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit, west Qinling, China[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(1): DOI: 10.3390/min9010037.
[21] 陈明辉, 郭素雄, 徐军伟, 等. 德乌鲁岩体内外接触带金多金属成矿区成岩成矿地质地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 矿产与地质, 2016, 30(4): 517-530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2016.04.001
[22] 代文军, 陈耀宇. 甘肃枣子沟金矿区中性岩脉与成矿关系[J]. 黄金, 2012, 33(1): 19-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ201201007.htm
[23] 第鹏飞. 西秦岭夏河-合作早子沟金矿床地球化学特征及成矿机制研究[D]. 兰州大学博士学位论文, 2018.
[24] 冯小明, 李注苍, 齐建宏. 西秦岭德乌鲁岩体成因及地质意义——来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2021, 40(2): 347-362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2021.02.012
[25] 冯益民, 曹宣铎, 张二朋, 等. 西秦岭造山带的演化、构造格局和性质[J]. 西北地质, 2003, (1): 1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2003.01.001
[26] 耿建珍, 黄雅琪, 姜桂鹏, 等. 西秦岭早子沟金锑矿床含矿英安斑岩年代学及其成因[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2019, 42(3): 166-173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2019.03.002
[27] 龚全胜, 代文军, 武雪梅. 西秦岭早子沟金矿含矿岩体地球化学特征及成因机制探讨[J]. 矿产勘查, 2019, 10(4): 854-862. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2019.04.016
[28] 何彤彤, 华永成, 逯文辉. 西秦岭德乌鲁-美武地区中生代岩体年代学、地球化学特征及与成矿关系研究[J]. 黄金, 2020, 41(7): 17-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ202007004.htm
[29] 贾儒雅, 王涛, 李康宁, 等. 西秦岭德乌鲁含矿岩体及其包体的岩石学成因和构造意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(5): 290-303. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2019.9.23
[30] 金维浚, 张旗, 何登发, 等. 西秦岭埃达克岩的SHRIMP定年及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(3): 959-966. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200503034.htm
[31] 靳晓野, 李建威, 隋吉祥, 等. 西秦岭夏河-合作地区德乌鲁杂岩体的侵位时代、岩石成因及构造意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2013, 35(3): 20-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2013.03.002
[32] 刘伯崇, 李康宁, 史海龙, 等. 西秦岭甘青交界一带晚三叠世火山岩岩石成因及构造指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(4): 704-717. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201804007.htm
[33] 骆必继, 张宏飞, 肖尊奇. 西秦岭印支早期美武岩体的岩石成因及其构造意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(3): 199-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201203022.htm
[34] 李春昱. 中国的板块构造轮廓[J]. 中国地质科学院院报, 1980, 2(1): 11-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB198000001.htm
[35] 路凤香, 桑隆康, 邬金华, 等. 岩石学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002.
[36] 李康宁, 贾儒雅, 李鸿睿, 等. 西秦岭甘肃夏河-合作地区与中酸性侵入岩有关的金铜多金属成矿系统及找矿预测[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(8): 1191-1203. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200807&flag=1
[37] 毛景文. 西秦岭地区造山型与卡林型金矿床[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2001, (1): 11-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200101003.htm
[38] 任纪舜, 姜春发, 张正坤, 等. 中国大地构造及其演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1980.
[39] 任纪舜, 张正坤, 牛宝贵, 等. 论秦岭造山带——中朝与扬子陆块的拼合过程[C]//叶连俊, 钱祥麟, 张国伟. 秦岭造山带学术讨论会论文选集. 西安: 西北大学出版社, 1991: 99-110.
[40] 韦萍, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 等. 西秦岭夏河花岗岩的地球化学、年代学及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(11): 3981-3992. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201311027.htm
[41] 肖庆辉, 邓晋福, 马大铨, 等. 花岗岩研究思维与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002.
[42] 闫臻. 西秦岭晚古生代弧前盆地沉积与成矿作用[D]. 中国科学院研究生院(地质与地球物理研究所)博士学位论文, 2002.
[43] 张德贤, 束正祥, 曹汇, 等. 西秦岭造山带夏河-合作地区印支期岩浆活动及成矿作用——以德乌鲁石英闪长岩和老豆石英闪长斑岩为例[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(5): 1257-1273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201505007.htm
[44] 张国伟, 张宗清, 董云鹏, 等. 秦岭造山带主要构造岩石地层单元的构造性质及其大地构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 1995, 11(2): 101-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199502000.htm
[45] 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 等. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001.
[46] 张国伟, 郭安林, 姚安平. 中国大陆构造中的西秦岭-松潘大陆构造结[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(3): 23-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200403004.htm
-



 下载:
下载: