Geochronology, Petrogenesis and Tectonic Significance of Zhanhongshan Peraluminous Rhyolite Porphyry in Gouli Area, Eastern Section of East Kunlun
-
摘要:
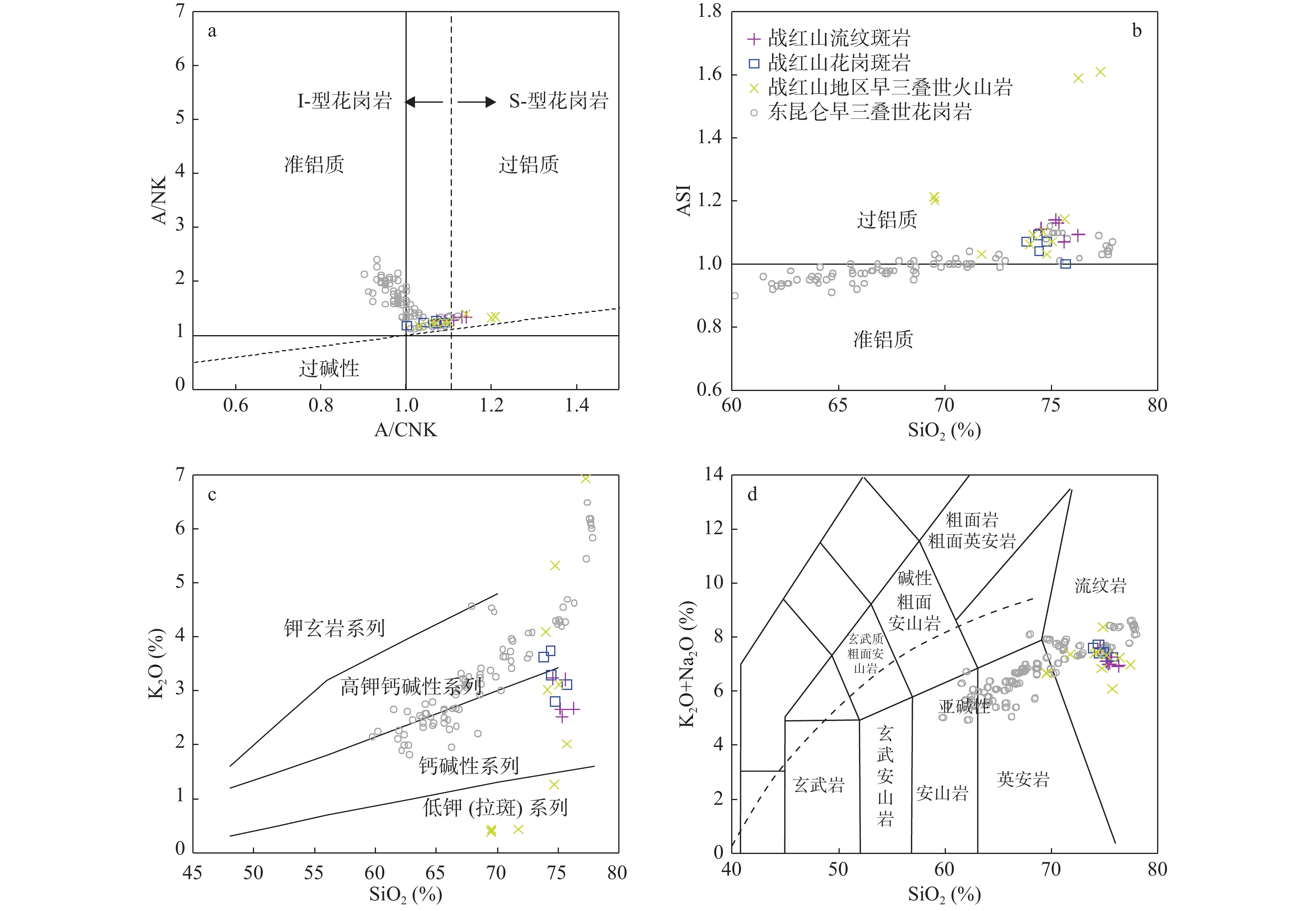
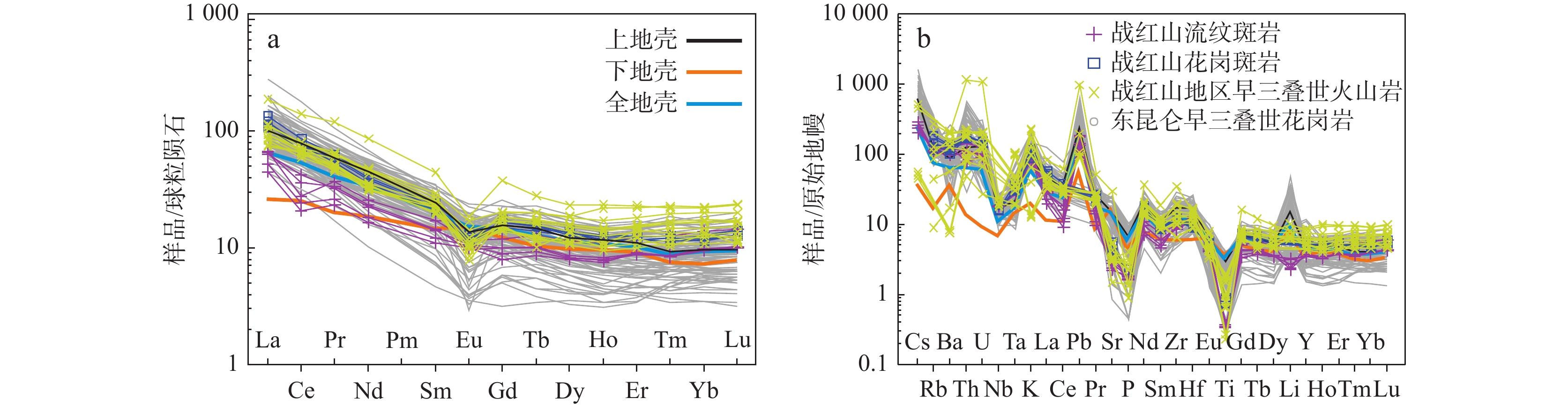
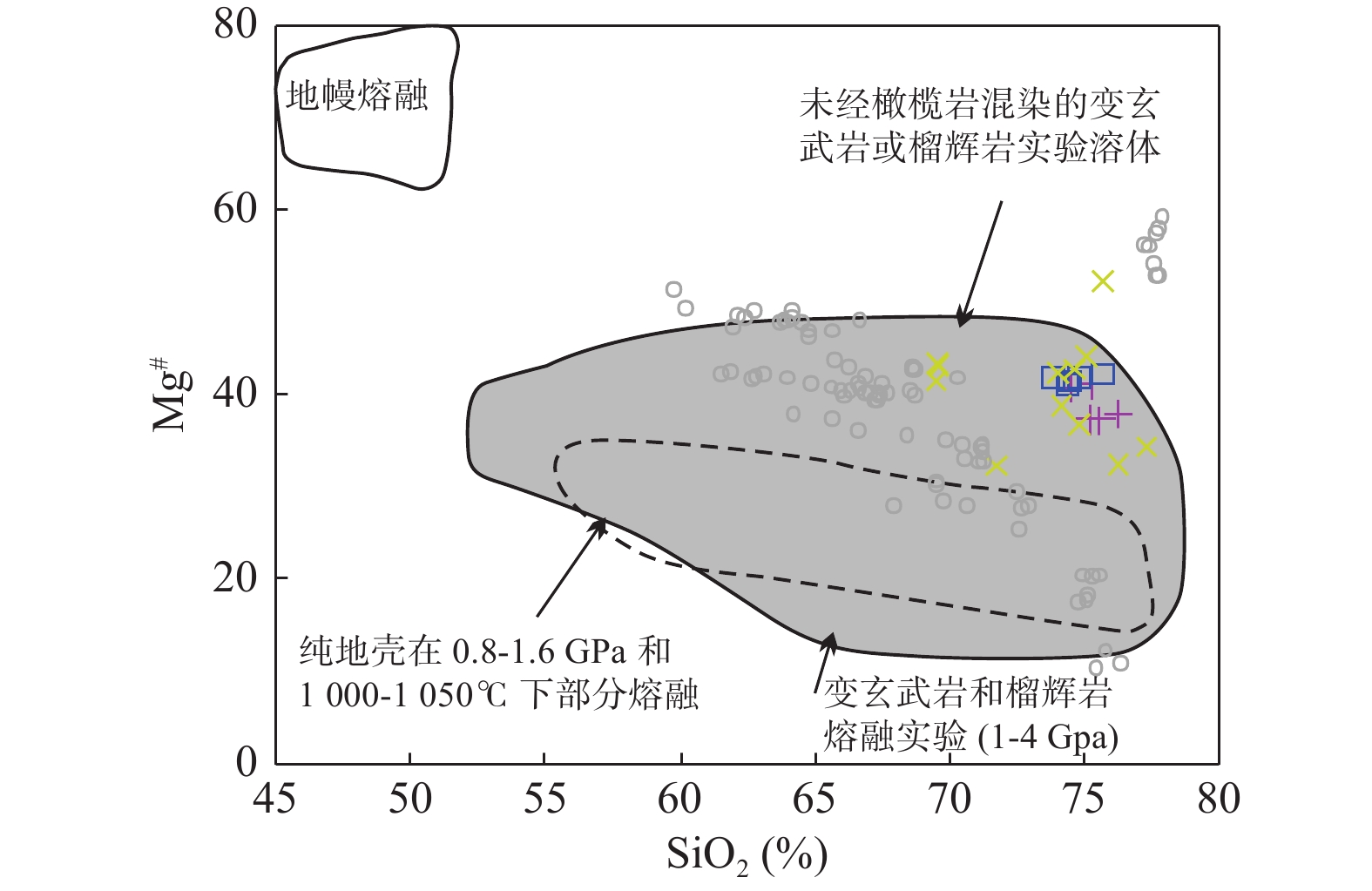
东昆仑三叠纪花岗质岩石的研究主要集中于具I型花岗岩特征的大型花岗岩基,而对少量出露的过铝质花岗岩研究较少。东昆仑造山带东段沟里地区战红山花岗斑岩LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb同位素定年结果显示,战红山流纹斑岩的结晶年龄为(245±1)Ma。战红山流纹斑岩具有高Si(SiO2=74.50%~75.59%)、富Na(Na2O=4.04%~4.06%),高Na2O/K2O值(1.26~1.76)和铝饱和指数(A/CNK=1.07~1.14),呈弱过铝质−过铝质中钾−高钾钙碱性系列。岩石稀土含量较低,轻、重稀土元素分馏明显,Eu具轻微的负异常和正异常(δEu=0.80~1.06);富集Ba、Rb、Th、K、U等大离子亲石元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Nd、P、Ti等高场强元素,εHf(t)同位素主体呈富集特征(εHf(t)=-4.7~+0.9)。战红山过铝质流纹斑岩具I型花岗岩特征,为早期俯冲洋壳经过幔源岩浆的底侵和外来流体的加入部分熔融的结果。战红山流纹斑岩具弧岩浆岩地球化学特征,结合东昆仑造山带东段岩浆岩分布以及沉积地层特征显示,早三叠世东昆仑地区处于古特提斯洋的俯冲阶段。
Abstract:The study of Triassic granitic rocks in East Kunlun mainly focuses on the large granite batholith with the characteristics of I−type granite, while the study of a small amount of peraluminous granite is less. The LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Pb dating of The Zhanhongshan rhyolite porphyry shows that the crystallization age of the Zhanhongshan rhyolite porphyry is 245±1 Ma. The Zhanhongshan rhyolite porphyry is characterized by high silica (SiO2=74.50%~75.59%), rich Na (Na2O=4.04%~4.06%), high Na2O/K2O ratio (1.26~1.76), and aluminum saturation index (A/CNK=1.07~1.14), which indicate weak peraluminous medium potassium and high potassium calc−alkaline series. The rocks is characterized by low REE content with obvious fractionation of LREE and HREE, slight negative and positive Eu anomalies (δEu=0.80~1.06), also enrichment of LILE and depletion of HFSE. They have enriched Hf isotopic compositions with εHf (t) isotope values of −4.7~+0.9. It is concluded that the peraluminous Zhanhongshan rhyolite porphyry has the characteristics of I−type granite, which is the result of the underplating of the subducted oceanic crust through mantle−derived magma and partial melting with the addition of foreign fluid, and has arc magmatic geochemical characteristics. Combined with the previous data, the study shows that the East Kunlun area was in the subduction stage of the Paleo−Tethys ocean in the Early Triassic.
-
Key words:
- Eastern Kunlun /
- peraluminous granite /
- petrogenesis /
- geochemistry /
- early Triassic.
-

-
图 4 战红山流纹斑岩A/CNK–A/NK图解(a)(据Maniar et al.,1989)、SiO2–ASI图解(b)(据Frost et al.,2001)、SiO2–K2O图解(c)(据Rollinson,1993)和SiO2–ALK分类命名图解(d)(据Wilson,1989)
Figure 4.
图 6 战红山流纹斑岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)(标准化值据Boynton,1984)和原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun et al.,1989)
Figure 6.
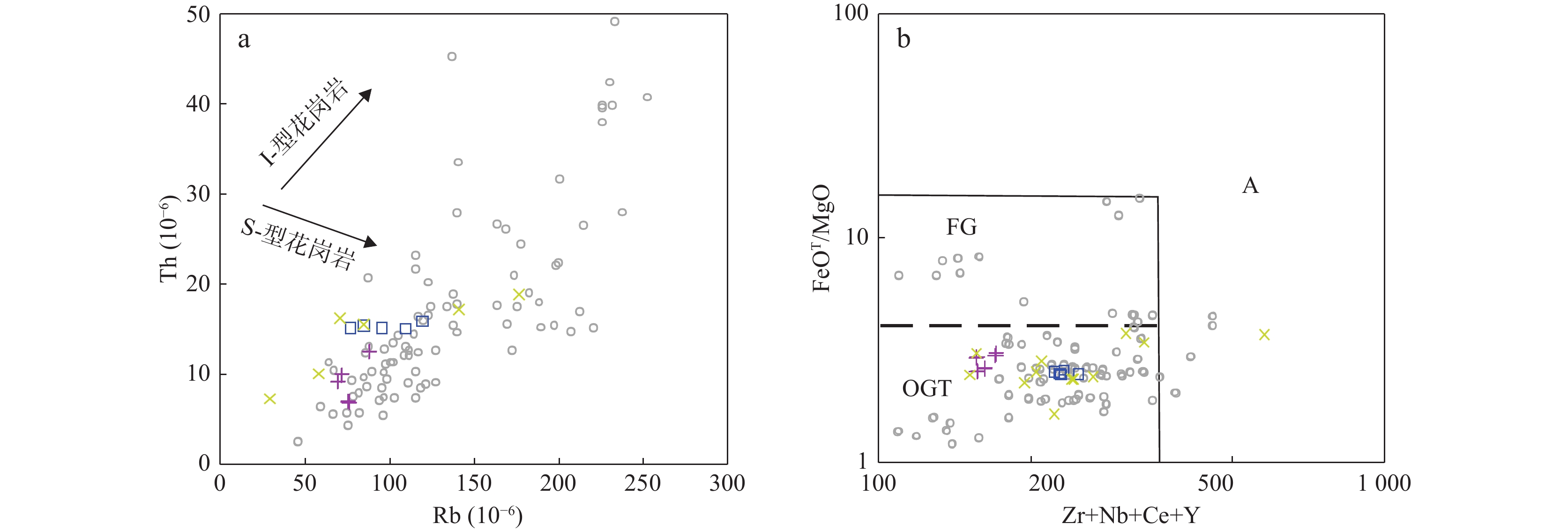
图 7 战红山流纹斑岩Rb–Th图解(a)和(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)–FeOT/MgO图解(b)(据Whalen et al., 1987)
Figure 7.
图 11 战红山流纹斑岩Y–Sr/Y图(a)和YbN–(La/Yb)N图(b)(底图据Castillo et al.,2006)
Figure 11.
表 1 战红山流纹斑岩LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1. LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Pb isotopic data for the Zhanhongshan rhyolite porphyry
测点 含量(10–6) Th/U 同位素比值 年龄(Ma) 谐和度 Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1b 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 1 78.34 542.90 1907.85 0.28 0.0491 0.0017 0.2638 0.0093 0.0389 0.0005 154 79 246 3 238 7 96% 2 37.07 383.19 549.67 0.70 0.0535 0.0028 0.2857 0.0143 0.0388 0.0005 350 117 245 3 255 11 96% 3 54.07 388.64 1207.20 0.32 0.0524 0.0023 0.2820 0.0120 0.0391 0.0005 302 102 247 3 252 10 98% 4 43.32 284.07 973.25 0.29 0.0525 0.0023 0.2811 0.0125 0.0387 0.0005 306 128 245 3 251 10 97% 5 80.34 613.89 1766.08 0.35 0.0491 0.0020 0.2626 0.0103 0.0388 0.0004 154 93 245 2 237 8 96% 6 26.34 204.87 601.44 0.34 0.0537 0.0027 0.2877 0.0148 0.0387 0.0005 367 118 245 3 257 12 95% 7 75.59 638.77 1396.56 0.46 0.0515 0.0020 0.2744 0.0097 0.0389 0.0005 265 89 246 3 246 8 99% 8 149.43 1223.27 3122.62 0.39 0.0528 0.0018 0.2812 0.0094 0.0387 0.0005 317 76 245 3 252 7 97% 9 94.39 663.10 2305.14 0.29 0.0505 0.0018 0.2709 0.0099 0.0389 0.0004 217 83 246 3 243 8 99% 10 33.10 226.67 795.31 0.29 0.0457 0.0025 0.2424 0.0125 0.0388 0.0005 – – 245 3 220 10 89% 11 76.66 640.53 1510.44 0.42 0.0530 0.0018 0.2824 0.0088 0.0387 0.0004 328 78 245 2 253 7 96% 12 77.67 528.41 1679.16 0.31 0.0551 0.0016 0.2953 0.0091 0.0388 0.0005 417 65 246 3 263 7 93% 13 20.49 157.49 473.73 0.33 0.0588 0.0031 0.3167 0.0166 0.0390 0.0007 561 115 246 4 279 13 87% 14 48.60 300.47 1286.35 0.23 0.0536 0.0023 0.2885 0.0135 0.0390 0.0006 354 98 247 4 257 11 95% 15 76.30 570.41 1647.07 0.35 0.0493 0.0017 0.2639 0.0087 0.0388 0.0004 161 80 246 3 238 7 96% 16 42.59 324.98 793.87 0.41 0.0572 0.0033 0.3063 0.0167 0.0389 0.0005 502 132 246 3 271 13 90% 17 318.24 441.11 838.71 0.53 0.0571 0.0023 0.3063 0.0122 0.0389 0.0004 494 61 246 3 271 9 90% 18 595.32 645.40 1419.72 0.45 0.0518 0.0017 0.2770 0.0093 0.0387 0.0005 280 71 245 3 248 7 98% 19 534.47 474.48 804.99 0.59 0.0507 0.0022 0.2711 0.0117 0.0388 0.0004 233 102 245 3 244 9 99% 20 654.52 502.77 556.83 0.90 0.0487 0.0023 0.2621 0.0122 0.0389 0.0004 200 111 246 3 236 10 96% 21 398.32 230.52 498.49 0.46 0.0508 0.0019 0.2723 0.0099 0.0388 0.0005 232 87 245 3 245 8 99% 22 583.59 299.31 654.19 0.46 0.0498 0.0019 0.2673 0.0101 0.0389 0.0005 183 117 246 3 241 8 97% 23 801.29 347.04 603.13 0.58 0.0496 0.0020 0.2659 0.0104 0.0387 0.0004 176 127 245 2 239 8 97% 24 796.78 264.83 402.38 0.66 0.0589 0.0036 0.3174 0.0202 0.0386 0.0005 561 133 244 3 280 16 86% 25 9185.75 156.34 167.38 0.93 0.8916 0.0197 28.1135 0.5696 0.2271 0.0019 – – 1320 10 3423 20 11% 26 1238.64 991.84 1269.06 0.78 0.0704 0.0025 0.3808 0.0147 0.0389 0.0005 939 73 246 3 328 11 71% 27 222.43 229.62 634.08 0.36 0.0514 0.0026 0.2752 0.0131 0.0388 0.0004 257 115 245 3 247 10 99% 28 321.80 449.12 1212.88 0.37 0.0538 0.0020 0.2892 0.0108 0.0388 0.0005 365 88 246 3 258 8 95% 29 74.12 146.14 388.29 0.38 0.0580 0.0078 0.3105 0.0373 0.0396 0.0006 532 494 250 4 275 29 90% 30 439.00 791.84 1040.54 0.76 0.1672 0.0053 1.1517 0.0461 0.0494 0.0009 2529 54 311 6 778 22 14% 注:–表示无数据。 表 2 战红山流纹斑岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10−6)分析结果
Table 2. Major (%) and trace element (10−6) compositions for the Zhanhongshan rhyolite porphyry
样品 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO MgO CaO Na2O K2O MnO TiO2 P2O5 LOI Li Be Sc V Cr Co Ni Cu ZHS-1 75.17 13.54 1.26 0.36 0.42 0.93 4.43 2.67 0.04 0.07 0.04 1.32 5.37 1.99 8.51 5.30 2.92 0.59 1.02 2.49 ZHS-2 75.59 12.89 1.25 0.36 0.41 1.03 4.04 3.21 0.04 0.08 0.04 1.31 3.82 1.96 6.45 4.23 1.98 0.70 0.95 3.40 ZHS-3 76.24 12.67 1.26 0.41 0.43 0.95 4.25 2.67 0.05 0.08 0.04 1.26 4.50 1.85 6.62 4.00 2.44 0.62 0.83 2.67 ZHS-4 74.50 13.59 1.33 0.36 0.51 0.84 4.36 3.24 0.04 0.08 0.04 1.33 5.16 1.96 9.42 4.17 4.47 0.59 1.79 2.39 ZHS-5 75.31 13.41 1.14 0.36 0.45 1.01 4.46 2.53 0.04 0.08 0.04 1.43 3.70 1.95 8.75 4.70 1.72 0.82 0.63 2.47 样品 Zn Ga Rb Sr Zr Nb Mo In Cs Ba Hf Ta W Tl Pb Bi Th U Y La ZHS-1 22.1 13.8 71.5 66.9 105 13.7 0.74 0.03 2.15 880 3.98 1.18 0.95 0.65 10.2 0.25 9.83 2.20 16.3 19.7 ZHS-2 22.1 13.2 87.8 79.4 111 13.4 0.71 0.03 1.65 893 4.14 1.13 1.34 0.70 13.4 0.15 12.4 2.76 22.8 20.8 ZHS-3 21.3 12.9 75.0 50.0 110 13.3 0.75 0.03 2.33 952 4.05 1.11 1.31 0.61 13.2 0.17 6.83 2.06 16.1 13.8 ZHS-4 20.1 13.6 75.9 47.4 112 13.8 0.66 0.03 1.90 929 4.12 1.14 0.91 0.67 9.86 0.24 6.76 2.00 16.4 16.2 ZHS-5 17.9 13.6 69.3 59.8 96.4 13.0 0.75 0.02 1.98 709 3.65 1.14 1.13 0.53 8.33 0.15 9.11 2.17 17.4 20.4 样品 Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Mg# A/CNK δEu (La/Yb)N (Gd/Yb)N Nb/Ta Tzr ZHS-1 34.0 3.93 13.4 2.73 0.77 2.59 0.47 2.65 0.55 1.89 0.27 1.96 0.32 43.7 1.14 0.87 6.79 1.07 11.57 762 ZHS-2 22.2 4.44 15.3 3.35 0.84 3.06 0.61 3.67 0.79 2.63 0.41 2.88 0.46 43.6 1.07 0.79 4.85 0.86 11.89 762 ZHS-3 16.7 2.79 9.80 2.13 0.73 2.06 0.41 2.56 0.54 1.88 0.28 2.02 0.33 44.3 1.09 1.05 4.59 0.82 12.05 763 ZHS-4 19.6 3.17 10.8 2.34 0.76 2.28 0.44 2.60 0.57 1.83 0.28 1.97 0.33 47.3 1.11 0.99 5.55 0.93 12.10 764 ZHS-5 29.2 4.04 13.7 2.77 0.70 2.61 0.48 2.73 0.59 1.85 0.28 2.01 0.33 47.6 1.13 0.79 6.83 1.05 11.45 754 注:Mg# = 100×[Mg2+(Mg2++Fe2+)]; δEu=EuN/(SmN×GdN)1/2;Tzr(℃)=12 900/[LnDz+0.85M+2.95]-273.15, M=(2Ca+K+Na)/(Si×Al)(Watson et al.,1983)。 表 3 战红山流纹斑岩锆石原位Hf同位素组成
Table 3. In–situ Hf isotopic compositions of zircon for the Zhanhongshan rhyolite porphyry
样品 176Hf/177Hf 1σ 176Yb/177Hf 1σ 176Lu/177Hf' 1σ εHf(t) TDM T2DM BQSCN-2-01 0.282654 0.000021 0.05 0.00 0.001750 0.000003 0.9 864 1211 BQSCN-2-02 0.282593 0.000022 0.04 0.00 0.001523 0.000005 −1.2 946 1345 BQSCN-2-03 0.282542 0.000019 0.06 0.00 0.002058 0.000019 −3.0 1033 1462 BQSCN-2-04 0.282614 0.000020 0.06 0.00 0.001969 0.000007 −0.5 928 1304 BQSCN-2-05 0.282621 0.000019 0.07 0.00 0.002233 0.000009 −0.3 923 1289 BQSCN-2-06 0.282599 0.000021 0.04 0.00 0.001344 0.000009 −1.0 933 1331 BQSCN-2-07 0.282602 0.000024 0.07 0.00 0.002397 0.000007 −1.0 955 1333 BQSCN-2-08 0.282567 0.000020 0.11 0.00 0.003283 0.000044 −2.4 1032 1422 BQSCN-2-09 0.282550 0.000018 0.06 0.00 0.002011 0.000018 −2.8 1021 1446 BQSCN-2-10 0.282525 0.000020 0.05 0.00 0.001711 0.000016 −3.6 1048 1498 BQSCN-2-11 0.282616 0.000020 0.07 0.00 0.002157 0.000010 −0.5 929 1301 BQSCN-2-12 0.282523 0.000019 0.04 0.00 0.001431 0.000004 −3.7 1043 1501 BQSCN-2-13 0.282563 0.000021 0.06 0.00 0.001894 0.000010 −2.3 999 1416 BQSCN-2-14 0.282495 0.000020 0.07 0.00 0.002239 0.000006 −4.8 1107 1570 BQSCN-2-15 0.282581 0.000020 0.07 0.00 0.002238 0.000010 −1.7 982 1379 -
陈国超, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑洪水川地区科科鄂阿龙岩体锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(2): 178–196 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.02.004
CHEN Guochao, PEI Xianzhi, LI Ruibao, et al. Zircon U-Pb Geochronology Geochemical Characteristics and Geological Sinificance of Cocoe A'Long Quartz Diorites Body from the Hongshuichuan Area in East Kunlun[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(2): 178–196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.02.004
陈国超, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑古特提斯后碰撞阶段伸展作用: 来自晚三叠世岩浆岩的证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(4): 191–208
CHEN Guochao, PEI Xianzhi, LI Ruibao, et al. Lithospheric extersion of the post-collision stage of the Paleo-Tethys oceanic system in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt: insights from Late Triassic plutons[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(4): 191–208.
陈国超, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑造山带东段晚古生代—早中生代构造岩浆演化与成矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(4): 33–48
CHEN Guochao, PEI Xianzhi, LI Ruibao, et al. Late Palaeozoic-Early Mesozoic tectonic-magmatic evolution and mineralization in the eastern section of the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2020, 27(4): 33–48.
陈能松, 孙敏, 王勤燕, 等. 东昆仑造山带昆中带的独居石电子探针化学年龄: 多期构造变质事件记录[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(11): 1297–1306 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.11.014
CHEN Nengsong, SUN Min, WANG Qinyan, et al. EMP chemical ages of monazites from Central Zone of the eastern Kunlun Orogen: Records of multi-tectonometamorphic events[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(11): 1297–1306. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.11.014
陈有炘, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑造山带东段元古界小庙岩组的锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(3): 510–521 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.03.013
CHEN Youxin, PEI Xianzhi, LI Ruibao, et al. Zircon U-Pb Age of Xiaomiao Formation of Proterozoic in the Eastern Section of the East Kunlun Orogenic Bel[J]. Geoscience, 2011, 25(3): 510–521. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.03.013
邓红宾, 何龙, 姚波, 等. 东昆仑造山带低山头二长花岗岩形成时代及岩石地球化学特征[J]. 西北地质, 2018, 51(4): 60–69 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2018.04.008
DENG Hongbin, HE Long, YAO Bo, et al. Formation Age and Geochemical Characteristics of Dishantou Monzonitic Granite in Estern Kunlun Orogenic Belt[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2018, 51(4): 60–69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2018.04.008
邓文兵, 裴先治, 刘成军, 等. 东昆仑东段香日德地区察汗陶勒盖正长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(5): 687–699 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.05.006
DENG Wenbin, PEI Xianzhi, LIU Chengjun, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of the Chahantaolegai syenogranites in Xiangride area of East Kunlun and its geological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2016, 35(5): 687–699. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.05.006
付彦文, 薛万文, 王涛, 等. 青海东昆南构造带战红山地区中酸性火山岩的发现及其地质特征[J]. 矿物岩石, 2019, 39(4): 78–85 doi: 10.19719/j.cnki.1001-6872.2019.04.09
FU Yanwen, XUE Wanwen, WANG Tao, et al. Discovery and geological characteristics of Intermediate acid volcanic rocks in the Zhanhongshan area, East Kunnan tectonic belt, Qinghai[J]. Journal Mineralogy Petrology, 2019, 39(4): 78–85. doi: 10.19719/j.cnki.1001-6872.2019.04.09
郭安林, 张国伟, 孙延贵, 等. 阿尼玛卿蛇绿岩带OIB和MORB 的地球化学及空间分布特征: 玛积雪山古洋脊热点构造证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2007, 36(7): 618–629.
GUO Anlin, ZHANG Guowei, SUN Yangui, et al. Geochemistry and spatial distribution of OIB and MORB in A'nyemaqen ophiolite zone: Evidence of Majixueshan ancient ridgecentered hotspot[J]. Science in China(Series D), 2007, 50(2): 197–208.
何凡, 宋述光. 东昆仑金水口地区格林威尔期超高温麻粒岩[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(4): 1030–1040 doi: 10.18654/2095-8927/004
HE Fan and SONG Shuguang. The Grenvillian⁃aged UHT granulite in Jinshuikou region, East Kunlun Orogenic Belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(4): 1030–1040. doi: 10.18654/2095-8927/004
李积清, 张鑫利, 王涛, 等. 东昆仑战红山地区花岗斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及岩石地球化学特征[J]. 西北地质, 2021, 54(1): 30–40
LI Jiqing, ZHANG Xinli, WANG Tao, et al. Zircon U-Pb Dating and Geochemical Characteristics of Granite Porphyry in Zhanhongshan Area, East Kunlun[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2021, 54(1): 30–40.
李瑞保, 裴先治, 李佐臣, 等. 东昆仑东段晚古生代—中生代若干不整合面特征及其对重大构造事件的响应[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(5): 244–254
LI Ruibao, PEI Xianzhi, LI Zuochen, et al. Geological characteristics of Late Palaeozoic-Mesozoic unconformities and their response to some significant tectonic events in eastern part of Eastern Kunlun[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(5): 244–254.
李瑞保, 裴先治, 李佐臣, 等. 东昆仑东段下三叠统洪水川组沉积序列与盆地构造原型恢复[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(12): 2302–2314 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.12.016
LI Ruibao, PEI Xianzhi, LI Zuochen, et al. The depositional sequence and prototype basin for Lower Triassic Hongshuichuan Formation in the eastern segment of East Kunlun Mountains[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(12): 2302–2314. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.12.016
李瑞保, 裴先治, 李佐臣, 等. 东昆仑东段古特提斯洋俯冲作用—乌妥花岗岩体锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(11): 3399–3421.
LI Ruibao, PEI Xianzhi, PEI Lei, et al. The Early Triassic Andean-type Halagatu granitoids pluton in the East Kunlun orogen, northern Xizang Plateau: Response to the northward subduction of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Gondwana Research, 2018, 62, 212–226.
罗照华, 柯珊, 曹永清, 等. 东昆仑印支晚期幔源岩浆活动[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(6): 292–297 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.06.003
LUO Zhaohua, KE Shan, CAO Yongqing, et al. Indosinian mantle-derived magmatism in the East Kunlun[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2002, 21(6): 292–297. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.06.003
马昌前, 熊富浩, 尹烁, 等. 造山带岩浆作用的强度和旋回性: 以东昆仑古特提斯花岗岩类岩基为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(12): 3555–3568
MA Changqian, XIONG Fuhao, YIN Shuo, et al. Intensity and cyclicity of orogenic magmatism: An example form a Paleo-Tethyan granitoid batholith, Eastern Kunlun, northern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(12): 3555–3568.
莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 等. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长[J]. 高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3): 403–414 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.010
MO Xuanxue, LUO Zhaohua, DENG Jinfu, et al. Granitoids and Crustal Growth in the East-Kunlun Orogenic Belt[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2007, 13(3): 403–414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.010
裴先治, 胡楠, 刘成军, 等. 东昆仑南缘哥日卓托地区马尔争组砂岩碎屑组成、地球化学特征与物源构造环境分析[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(2): 307–323
PEI Xianzhi, HU Nan, LIU Chengjun, et al. Detrital Composition, Geochemical Characteristics and Provenance Analysis for the Maerzheng Formation Sandstone in Gerizhuotuo Area, Southern Margin of East Kunlun Region[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(2): 307–323.
裴先治, 李瑞保, 李佐臣, 等. 东昆仑南缘布青山复合增生型构造混杂岩带组成特征及其形成演化过程[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(12): 4498–4520
PEI Xianzhi, LI Ruibao, LI Zuochen, et al. Composition Feature and Formation Process of Buqingshan Composite Accretionary Mélange Belt in Southern Margin of East Kunlun Orogen[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(12): 4498–4520.
钱兵, 高永宝, 李侃, 等. 新疆东昆仑于沟子地区与铁-稀有多金属成矿有关的碱性花岗岩地球化学、年代学及Hf同位素研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(9): 2508–2520
QIAN Bing, GAO Yongbao, LI Kan, et al. Zircon- U-Pb-Hf isotopes and whole rock geochemistry constraints on the petrogenesis of iron-rare metal mineralization related alkaline granite intrusive rock in Yugouzi area, eastern Kunlun, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinca, 2015, 31(9): 2508–2520.
王珂, 王连训, 马昌前, 等. 东昆仑加鲁河中三叠世含石榴石二云母花岗岩的成因及地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(2): 400–418
WANG Ke, WANG Lianxun, MA Changqian, et al. Petrogenesis and Geological Implications of the Middle Triassic Garnet-Bearing Two-Mica Granite from Jialuhe Region, East Kunlun[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(2): 400–418.
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007a, 23(2): 185–220 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.02.001
WU Fuyuan, LI Xianhua, ZHENG Yongfei, et al. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007a, 23(2): 185–220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.02.001
吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007b, 23(6): 1217–1238 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.001
WU Fuyuan, LI Xianhua, YANG Jinhui, et al. Discussions on the petrogenesis of granite[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007b, 23(6): 1217–1238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.001
吴福元, 刘小驰, 纪伟强, 等. 高分异花岗岩的识别与研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017, 47(7): 745–765
WU Fuyuan, LIU Xiaochi, JI Weiqiang, et al. Highly fractionated granites: Recognition and research[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2017, 47(7): 745–765.
吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16): 1589–604.
WU Yuanbao and ZHENG Yongfei. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(16): 1589–1604.
殷鸿福, 张克信. 东昆仑造山带的一些特点[J]. 地球科学, 1997, 22(4): 339–342 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.1997.04.001
YIN Hongfu and ZHANG Kexin. Characteristics of the Eastern Kunlun Orogenic belt[J]. Earth Science, 1997, 22(4): 339–342. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.1997.04.001
于淼, 丰成友, 何书跃, 等. 祁漫塔格造山带——青藏高原北部地壳演化窥探[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(4): 703–723 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.04.001
YU Miao, FENG Chengyou, HE Shuyue, et al. The Qiman Tagh Orogen as A Window to the Crustal Evolution of the Northern Xizang Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(4): 703–723. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.04.001
余能, 金巍, 葛文春, 等. 东昆仑金水口过铝花岗岩的地球化学研究[J]. 世界地质, 2005, 24(2): 123–128 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2005.02.004
YU Neng, JIN Wei, GE Wenchun, et al. Geochemical study on peraluminous granite from Jinshuikou in East Kunlun[J]. Global Geology, 2005, 24(2): 123–128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2005.02.004
袁洪林, 吴福元, 高山, 等. 东北地区新生代侵入体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定与稀土元素成分分析[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(14): 1511–1520 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.14.008
YUAN Honglin, WU Fuyuan, GAO Shan, et al. U-Pb age determination of zircon from Cenozoic intrusions in northeast China and analysis of rare earth elements[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(14): 1511–1520. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.14.008
张新远, 李五福, 欧阳光文, 等. 东昆仑东段青海战红山地区早三叠世火山岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(5): 631–641 doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2020.05.004
ZHANG Xinyuan, LI Wufu, OUYANG Guangwen, et al. The discovery of Early Triassic volcanic rocks in Zhanhongshan area of Qinghai Province in the eastern section of East Kunlun Mountain and its geological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2020, 39(5): 631–641. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2020.05.004
张照伟, 钱兵, 王亚磊, 等. 东昆仑夏日哈木镍成矿赋矿机理认识与找矿方向指示[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(3): 153–168 doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2020.03.013
ZHANG Zhaowei, QIAN Bing, WANG Yalei, et al. Understanding of the Metallogenic Ore-Bearing Mechanism and Its Indication of Prospecting Direction in Xiarihamu Magmatic Ni-Co Sulfide Deposit, East Kunlun Orogenic Belt [J]. Northwestern China, 2020, 53(3): 153–168. doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2020.03.013
赵旭, 付乐兵, 魏俊浩, 等. 东昆仑按纳格角闪辉长岩体地球化学特征及其对古特提斯洋演化的制约[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(2): 354–370
ZHAO Xu, FU Lebing, WEI Junhao, et al. Geochemical Characteristics of Annage Hornblende Gabbro from East Kunlun Orogenic Belt and Its Constraints on Evolution of Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(2): 354–370.
Altherr F F, Holl A, Hegner E, et al. High-Potassium, Calc-Alkaline I-Type Plutonism in the European Variscides: Northern Vosges (France) and Northern Schwarzwald (Germany)[J]. Lithos, 2000, 50: 51–73.
Anderson T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1–2): 59–79.
Annen C, Blundy J D and Sparks R S J. The genesis of intermediate and silicic magmas in deep crustal hot zones[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2006, 47(3): 505–539. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egi084
Barbarin B. Mafic magmatic enclaves and mafic rocks associated with some granitoids of the central Sierra Nevada batholith, California: nature, origin, and relations with the hosts[J]. Lithos, 2005, 80: 155–177. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.05.010
Bonin B. A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 2007, 97: 1–29. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.12.007
Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies. In: Henderson P, ed. Rare earth element geochemistry[J]. Amsterdam Elsevier, 1984: 63–114.
Cashman K V, Sparks R S J and Blundy J D. Vertically extensive and unstable magmatic systems: a unified view of igneous processes[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6331): eaag3055. doi: 10.1126/science.aag3055
Castillo P R. An overview of adakites petrogenesis[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51: 257–268. doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-0257-7
Castro A. Tonalite-granodiorite suites as cotectic systems: A review of experimental studies with applications to granitoid petrogenesis[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 124: 68–95. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.05.006
Castro A. A non-basaltic experimental cotectic array for calc-alkaline batholiths[J]. Lithos, 2021, 382–383: 105929.
Chapman J B, Runyon S E, Shields J E, et al. The North American Cordilleran Anatectic Belt[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2021, 215: 103576. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103576
Chappell B W, White A J R and Wyborn D. The importance of residual source material (restite) in granite petrogenesis[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1987, 28(6): 11–38.
Chappell B W and White A J R. I-and S-type granites in the Lachland Fold Belt[J]. Mineralogy Magazine Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences, 1992, 83: 1–26. doi: 10.1017/S0263593300007720
Chappell B W and White A J. Two contrasting granite types: 25 years later[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2001, 48(4): 489–499. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-0952.2001.00882.x
Chappell B W, Bryant C J and Wyborn D. Peraluminous I-type granites[J]. Lithos, 2012, 153: 142–153. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.07.008
Chauvel C, Lewin E, Carpentier M, et al. Role of recycled oceanic basalt and sediment in generating the Hf-Nd mantle array[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1: 64–67. doi: 10.1038/ngeo.2007.51
Chen J J, Wei J H, Fu L B, et al. Multiple sources of the Early Mesozoic Gouli batholith. Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt. , northern Xizang Plateau: Linking continental crustal growth with oceanic subduction[J]. Lithos, 2017, 292–293: 161–178.
Clemens J D and Stevens G. The enigmatic sources of I-type granites: The peritectic connexion[J]. Lithos, 2011, 126: 174–181. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.07.004
Clemens J D, Stevens G. What controls chemical variation in granitic magmas?[J]. Lithos, 2012, 134–135: 317–329.
Clemens J D, Stevens G and Bryan S E. Conditions during the formation of granitic magmas by crustal melting–hot or cold; drenched, damp or dry?[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 200: 102982. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102982
Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to south–eastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80: 189–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00374895
Collins W J, Huang H Q and Jiang X Y. Water-fluxed crustal melting produces Cordilleran batholiths[J]. Geology, 2016, 44, G37398.1.
Collins W J, Murphy J B, Johnson T E, et al. Critical role of water in the formation of continental crust[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2020, 13, 331–338. doi: 10.1038/s41561-020-0573-6
Corfu F, Hanchar J M, Hoskin P W O, et al. Atlas of zircon textures[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 53(1): 469–500. doi: 10.2113/0530469
Dong Y P, He D F, Sun S S, et al. Subduction and Accretionary Tectonics of the East Kunlun Orogen, Western Segment of the Central China Orogenic System[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 186: 231–261. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.12.006
Frost C D, Bell J M, Frost B R, et al. Crustal growth by magmatic underplating: isotopic evidence from the northern Sherman batholith[J]. Geology, 2001, 29: 515–518.
Gao P, Zheng Y F, Zhao Z F. Experimental melts from crustal rocks: a lithochemical constraint on granite petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2016, 266: 133–157.
Guo X Z, Jia Q Z, Lv X B, et al. The Permian Sn metallogenic event and its geodynamic setting in East Kunlun, NW China: Evidence from zircon and cassiterite geochronology, geochemistry, and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopes of the Xiaowolong skarn Sn deposit[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 118: 103370. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103370
Huang H, Niu Y L, Nowell G, et al. Geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic belt, northern Xizang Plateau: implications for continental crust growth through syn-collisional felsic magmatism[J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 370: 1–18. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.01.010
Hawkesworth C J and Kemp A I S. Evolution of the continental crust[J]. Nature, 2006, 443: 811–817. doi: 10.1038/nature05191
Jackson M D, Blundy J and Sparks R S J. Chemical differentiation, cold storage and remobilization of magma in the Earth’s crust[J]. Nature, 2018, 564: 405–409. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0746-2
Kemp A I S, Hawkesworth C J, Foster G L, et al. Magmatic and crustal differentiation history of granitic rocks from Hf-O isotopes in zircon [J]. Science, 2007, 315: 980–983.
Lee C T A and Bachmann O. How important is the role of crystal fractionation in making intermediate magmas? Insights from Zr and P systematics[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2014, 393: 266–274. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.02.044
Lee C T A and Morton D M. High silica granites: terminal porosity and crystal settling in shallow magma chambers[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 409: 23–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.10.040
Li R B, Pei X Z, Li Z C, et al. Late Silurian to Early Devonian volcanics in the East Kunlun orogen, northern Xizang Plateau: Record of postcollisional magmatism related to the evolution of the Proto-Tethys Ocean[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 2020a, 140: 101780. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2020.101780
Li Y J, Wei J H, Santosh M, et al. Anisian granodiorites and mafic microgranular enclaves in the eastern Kunlun Orogen, NW China: Insights into closure of the eastern Paleo–Tethys[J]. Geological Journal, 2020b, 55(9): 1–21.
Li Z C, Pei X Z, Bons P D, et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the early-middle triassic subduction-related granite in the eastern segment of East Kunlun: evidences from petrology, geochemistry, and zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopes [J]. International Geology Review, 2022, 22(5): 698-721.
Ludwig K R. Isoplot 3.0: A Geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003, 1–70.
Maniar P D and Piccoli P M . Tectonic discrimination in of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 1: 635–643.
Patiño Douce A E and Harris N. Experimental constraints on Himalayan anatexis[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998, 39(4): 689–710. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.4.689
Patiño Douce A E. What do experiments tell us about the relative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of the granitic magmas[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1999, 168(1): 55–75. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1999.168.01.05
Petford N and Atherton M. Na-rich partial melts from newly underplated basaltic crust: The Cordillera Blanca batholith, Peru[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37(6): 1491–1521. doi: 10.1093/petrology/37.6.1491
Rapp R P. Amphibole-out phase boundary in partially melted metabasalt, its control over liquid fraction and composition, and source permeability[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1995a, 100(B8): 15601–15610. doi: 10.1029/95JB00913
Rapp R P and Watson E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt an 8–32 kbar: implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995b, 36(4): 891–31. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
Rollinson H R. Using geochemical data: evaluation, presentation, interpretation[M]. Longman Group UK Ltd, New York, 1993: 1–352.
Rudnick R L, Gao S. Composition of the continental crust[M]. In: Treatise on Geochemistry. volume 3. Elsevier, 2003: 1–64.
Shao F L, Niu Y L, Liu Y, et al. Petrogenesis of Triassic granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, northern Xizang Plateau and their tectonic implicationsa[J]. Lithos, 2017, 282: 33–44.
Stern C R and Kilian R. Role of the subducted slab, mantle wedge and continental crust in the generation of adakites from the Andean Austral Volcanic Zone[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1996, 123: 263–281. doi: 10.1007/s004100050155
Sisson T W, Ratajeski K, Hankins W B, et al. Voluminous granitic magmas from common basaltic sources[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2005, 148: 635–661. doi: 10.1007/s00410-004-0632-9
Song K, Ding Q F, Zhang Q, et al. Zircon U–Pb geochronology, Hf isotopes, and whole‐rock geochemistry of Hongshuihe Early to Middle Triassic quartz diorites and granites in the Eastern Kunlun Orogen, NW China: Implication for petrogenesis and geodynamics[J]. Geological Journal, 2019, 55(2): 1–22.
Sun S S and McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. In: Sunders AD, Norry MJ, Magmatism in the Ocean Basins, Geological Society Special Publication, 1989: 313–345.
Thompson A B. Fluid-absent metamorphism[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1983, 140: 533–547. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.140.4.0533
Villaros A, Stevens G and Buick I S. Tracking S-type granite from source to emplacement: clues from garnet in the Cape Granite Suite[J]. Lithos, 2009, 112: 217–235. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.02.011
Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited: temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1983,64:295-304.
Whalen J B, Currie K L and Chappell B W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics discrimination and petrogeneisis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95: 407–419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
Wilson M. Igneous Petrogenesis[M]. London: Springer, 1989: 295–323.
Xia R, Deng J, Qing M, et al. Zircon U–Pb dating, geochemistry and Sr–Nd–Pb–Hf–O isotopes for the Nan'getan granodiorites and mafic microgranular enclaves in the East Kunlun Orogen: Record of closure of the Paleo-Tethys[J]. Lithos, 2015, 234–235: 47–70.
Xia R, Deng J, Qing M, et al. Petrogenesis of ca 240 Ma intermediate and felsic intrusions in the Nan’getan: Implications for crust–mantle interaction and geodynamic process of the East Kunlun Orogen[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 90: 1099–1119. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.04.002
Xin W, Sun F Y, Zhang Y T, et al. Mafic-intermediate igneous rocks in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt. , northwestern China: Petrogenesis and implications for regional geodynamic evolution during the Triassic[J]. Lithos, 2019, 346–347: 105159.
Xion F H, Ma C Q, Jiang H G, et al. Petrogenetic and tectonic significance of Permian calcalkaline lamprophyres, East Kunlun orogenic belt, Northern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. International Geology Review, 2013, 55(14): 1817–81834. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2013.804683
Xiong F H, Ma C Q, Zhang J Y, et al. Reworking of old continental lithosphere: An important crustal evolution mechanism in orogenic belts, as evidenced by Triassic I-type granitoids in the East Kunlun orogen, Northern Xizang Plateau[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2014, 171(6): 847–863. doi: 10.1144/jgs2013-038
Xiong F H, Ma C Q, Chen B, et al. Intermediate-mafic dikes in the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Xizang Plateau: A window into paleo-arc magma feeding system[J]. Lithos, 2019: 340–341: 152–165.
Yu M, Dick M, Feng C Y, Li B, et al. The tectonic evolution of the East Kunlun Orogen, northern Xizang Plateau: A critical review with an integrated geodynamic model[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 191(2): 104168.
Zhao X, Wei J H, Fu L B, et al. Multi-stage crustal melting from Late Permian back-arc extension through Middle Triassic continental collision to Late Triassic post-collisional extension in the East Kunlun Orogen[J]. Lithos, 2020, 360–361: 105446.
Zheng Y F. Subduction zone geochemistry[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2019, 10: 1223–1254. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2019.02.003
Zhou H Z, Zhang D H, Wei J H, et al. Petrogenesis of Late Triassic mafic enclaves and host granodiorite in the Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, China: Implications for the reworking of juvenile crust by delamination-induced asthenosphere upwelling[J]. Gondwana Research, 2020, 84: 52–70. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2020.02.012
-




 下载:
下载: