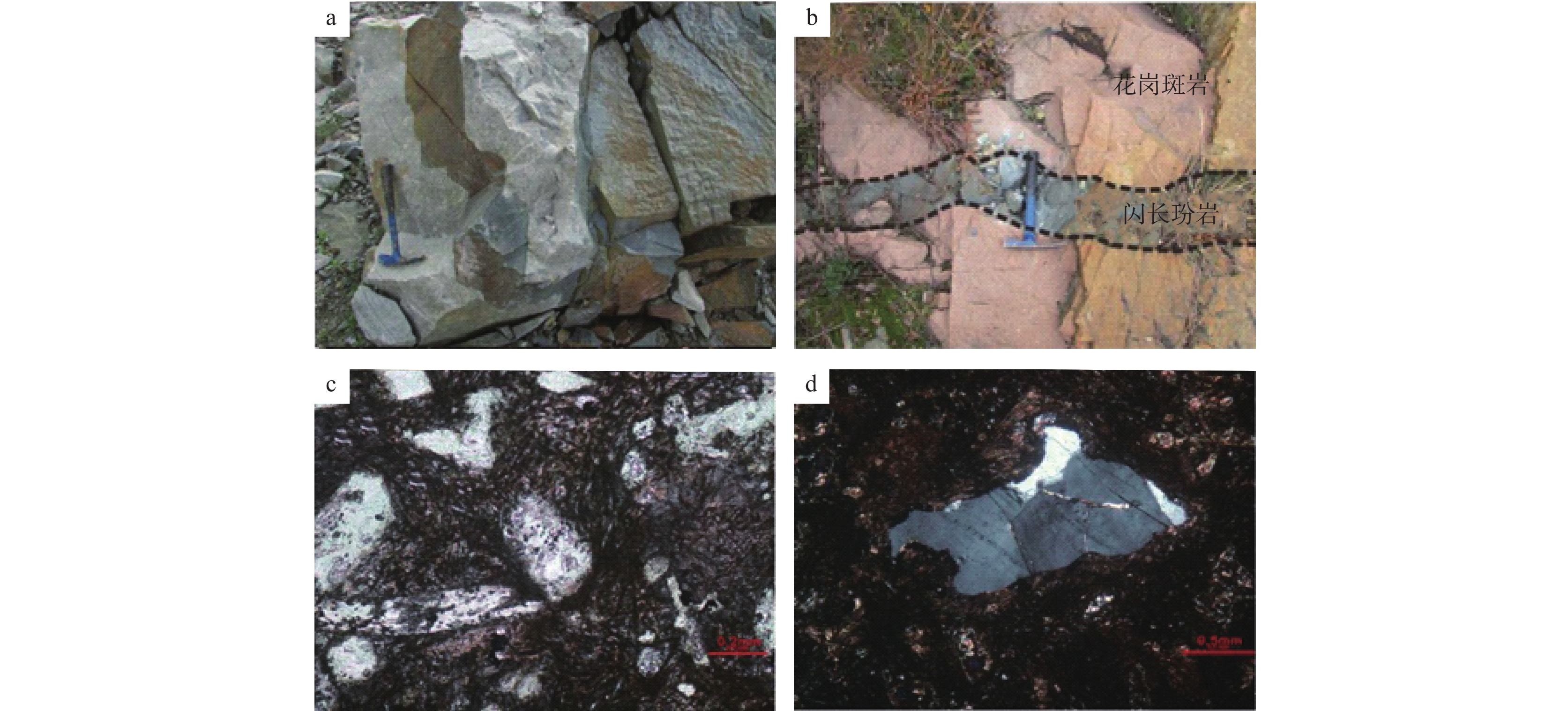
Geochemical Characteristics of Diorite Porphyrite in Dawu Area, Western Dabie and Its Tectonic Significance
-
摘要:
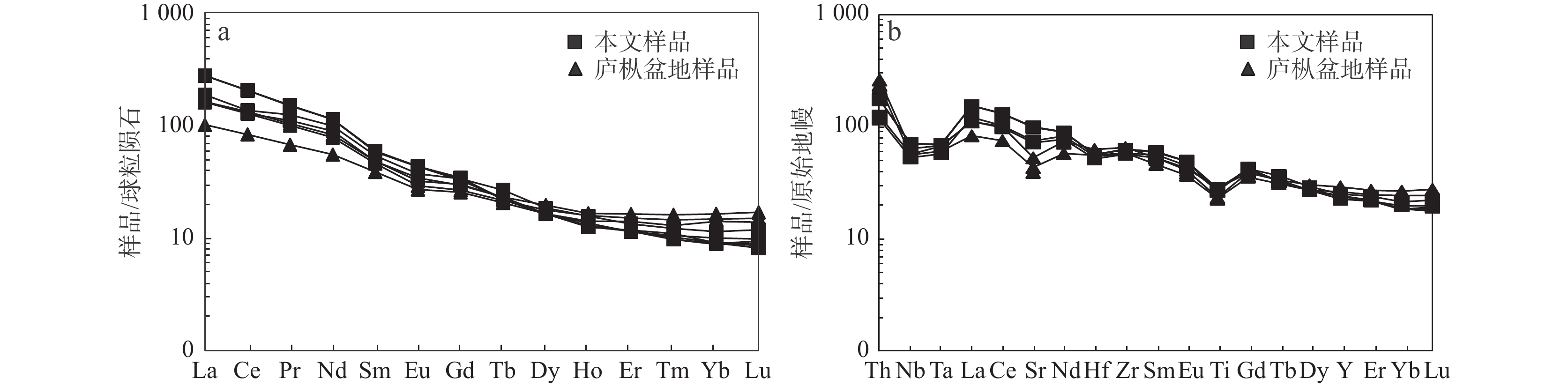
基性岩浆能反映地幔源区性质、成因环境和形成演化过程。通过野外地质调查,结合岩石地球化学分析,探讨区域岩浆源区性质、成因及构造环境。全岩地球化学分析结果显示,闪长玢岩样品SiO2含量为49.97%~55.01%,属中−基性岩系列,MgO含量为4.63%~5.49%,Mg#为60.17~90.19, Nb/Ta值为13.06~18.47, Zr/Hf值为40.09~44.05,暗示该岩浆源区可能源自于富集地幔。LREE/HREE值为9.45~13.97,整体表现为较陡右倾型,且亏损高场强元素(Nb、Ta、Hf、Ti)亏损,富集大离子亲石元素Sr,表明岩浆形成过程中可能受到俯冲板片流体交代作用的影响。闪长玢岩脉穿切花岗斑岩脉,花岗斑岩结晶时代为(130.8±1.8)Ma,闪长玢岩的侵位时间可能为早白垩世。在Zr−Ti构造环境判别图解中,闪长玢岩样品落于板内玄武岩区,结合区域构造背景,笔者认为闪长玢岩应形成于造山后伸展−拉张环境。
Abstract:Basic magmas can reflect the nature of mantle source region, genetic environment and formation and evolution process. Through the detailed field geological survey and rock geochemical analysis, we discuss the nature, genesis and tectonic environment of the magma source area of regional diorite porphyrite. The geochemical analysis of the whole rock shows that the SiO2 content of the diorite porphyrite samples is 49.97%~55.01%, belonging to the medium−basic rock series, the MgO content is 4.63%~5.49%, and the Mg# content is 60.17~90.19, the Nb/Ta value of the sample is 13.06~18.47, and the Zr/Hf value is 40.09~44.05, indicating that the magma source area of the diorite porphyrate may be from the enriched mantle. In addition, The LREE/HREE ratio is 9.45~13.97, and the diorite porphyrite samples show a steep−right diorite, and they are enriched in high field strength elements (Nb, Ta, Hf, Ti) and rich in large ion lithophile elements Sr. It is suggested that porphyrite may have been influenced by fluid metasomatism of subducted plates during the formation process. The field outcrops show that diorite porphyrite dikes intrude into granitic porphyry dikes (forming age is 130.8±1.8 Ma), so the emplacement time of dikes may be early Cretaceous. In the discrimination diagram of Zr−Ti tectonic environment, the diorite porphyrite samples fall in the intraplate basalt area. Combined with the regional tectonic background, we believe that the diorite porphyrite should be formed in the post−orogenic extension environment.
-
Key words:
- Xidabie /
- Dawu area /
- diorite porphyrite /
- basite /
- extension−tension tectonic environment
-

-
图 1 大别山地区构造简图(据索书田等,1993修改)
Figure 1.
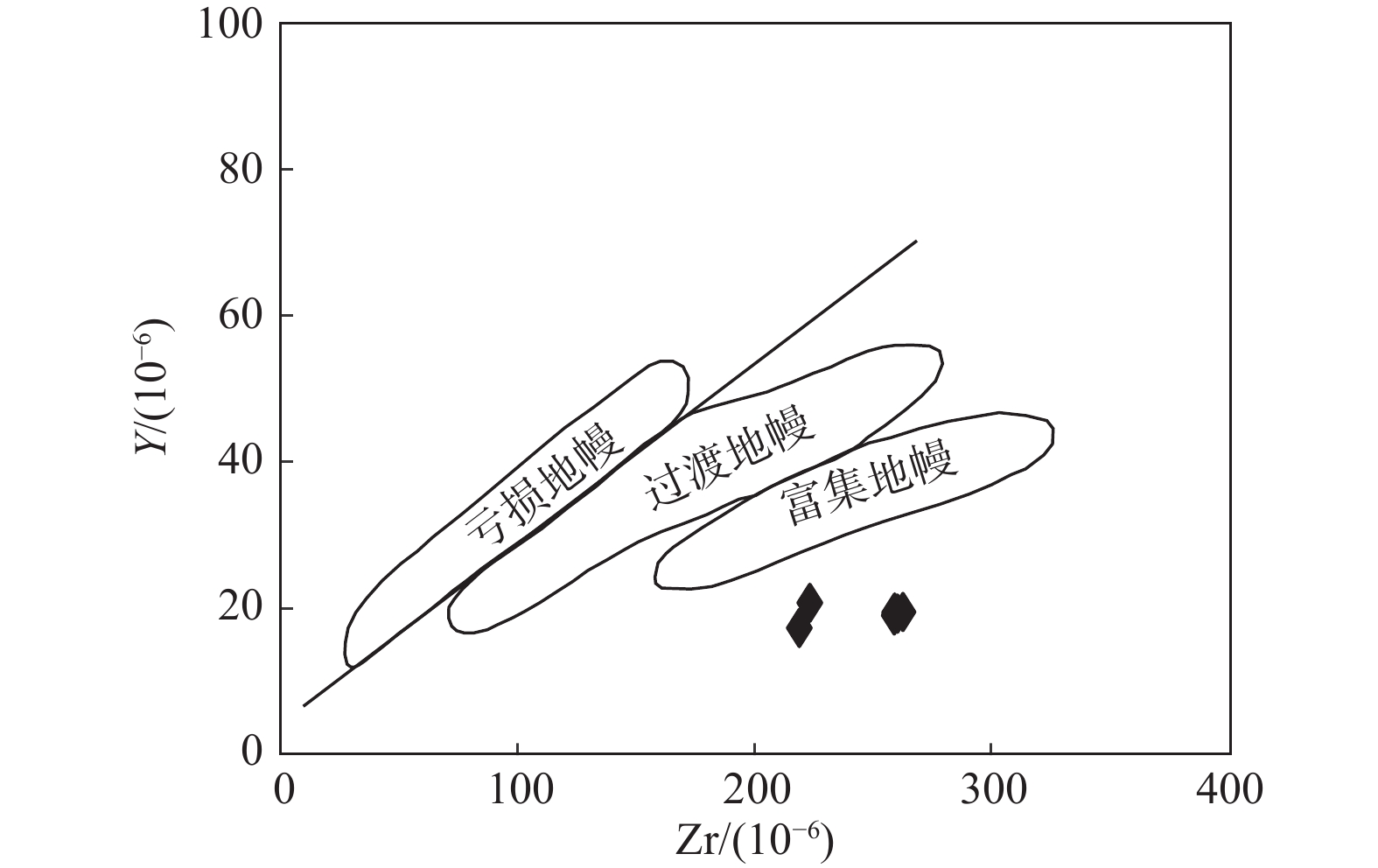
图 4 闪长玢岩Zr−Y判别图解(据Maitre et al.,1989)
Figure 4.
图 5 TiO2−K2O−P2O5判别图解(a)(Pearce,1975); TiO2−Zr(P2O5×10000)判别图解(b)(Winchester et al.,1976);Ti−Zr判别图解(c)(Pearce et al.,1973);Th/Hf−Ta/Hf判别图解(d)(据汪云亮等,2001)
Figure 5.
表 1 闪长玢岩主量元素、微量元素、稀土元素分析结果表
Table 1. Analysis results of major elements, trace elements and rare earth elements of diorite porphyrite
样号 D2073/1 D2073/2 D2073/3 D2073/4 D2073/5 D4078/4 BZK21-02 BZK21-03 BZK21-04 岩性 闪长玢岩 Na2O 1.82 3.78 3.86 2.12 3.57 1.92 4.41 4.6 3.21 MgO 5.38 4.81 4.63 5.16 4.78 5.49 2.24 2.7 3.39 Al2O3 14.04 14.47 14.65 14.11 14.52 14.01 15.18 15.23 17.05 SiO2 49.97 54.64 55.01 52.23 52.06 50.04 52.12 53.24 56.12 P2O5 0.52 0.79 0.8 0.58 0.61 0.54 0.35 0.59 0.51 K2O 4.39 3.41 3.69 3.49 3.52 4.26 3.1 2.93 4.73 CaO 5.93 4.7 5.06 4.65 4.91 6.17 3.33 4.72 1.86 TiO2 1.23 1.15 1.14 1.09 1.12 1.22 0.82 0.84 0.87 MnO 0.15 0.1 0.1 0.11 0.13 0.16 0.32 0.38 0.17 Fe2O3 2.28 0.93 0.93 0.91 0.96 2.37 9.31 6.64 7.45 FeO 5.4 0.79 0.79 0.81 0.8 5.25 4.22 3.9 5.24 H2O+ 3.14 0.28 0.16 0.19 0.25 3.28 CO2 5.25 4.28 LOST 7.83 4.68 3.62 4.57 3.91 7.55 8.27 7.56 4.53 Th 6.72 12.1 12.09 12.05 12.11 5.98 21 19.96 25 Nb 13.94 20.73 20.12 20.69 20.41 12.25 14.6 13.63 17.1 Ta 1.07 1.14 1.14 1.12 1.15 0.81 0.92 0.89 1.1 Sr 625.32 1102.02 1112.55 1107.05 1109.42 670.4 213 254.17 363 Zr 218.8 262.66 258.98 259.13 260.32 223.3 241 229.39 280 Hf 5.09 5.96 5.93 5.95 5.91 5.57 6 5.81 7.17 Eu 1.96 2.53 2.52 2.55 2.57 2.15 1.65 1.52 1.83 Yb 1.46 1.32 1.27 1.31 1.29 1.69 2.23 2.12 2.5 La 45.68 81.43 81.61 81.47 81.58 53.09 44.9 27.19 45.4 Ce 91.52 151.97 153.01 152.03 152.86 97.71 90.9 56.98 95.2 Pr 11.72 16.39 16.31 16.47 16.53 13.37 10.5 6.85 11 Nd 45.71 59.27 59.76 59.35 59.61 51.32 39.6 27.05 42.2 Sm 7.57 9.54 9.31 9.42 9.51 8.57 7.2 5.98 7.6 Eu 1.96 2.53 2.52 2.55 2.53 2.15 1.65 1.52 1.83 Gd 5.89 6.6 6.92 6.83 6.97 6.81 5.28 5.03 5.98 Tb 0.82 0.79 0.78 0.79 0.77 0.96 0.76 0.72 0.82 Dy 3.87 3.88 3.87 3.86 3.89 4.4 4.21 3.86 4.69 Ho 0.7 0.65 0.66 0.64 0.66 0.82 0.83 0.73 0.87 Er 1.69 1.71 1.71 1.75 1.73 2.01 2.29 2.13 2.51 Tm 0.24 0.23 0.22 0.25 0.22 0.28 0.34 0.3 0.38 Yb 1.46 1.32 1.27 1.31 1.29 1.69 2.23 2.12 2.5 Lu 0.22 0.19 0.2 0.18 0.21 0.27 0.35 0.32 0.4 Y 17.3 19.48 19.02 19.43 19.29 20.79 24.7 22.45 26.9 总和 236.35 355.98 357.17 356.33 357.65 264.24 235.74 163.23 248.28 LREE/HREE 9.45 13.62 13.97 13.64 13.79 8.75 6.34 4.48 6.06 (La/Yb)N 21.09 21.18 41.59 43.32 41.93 42.64 13.57 8.65 12.24 δEu 0.87 0.84 0.91 0.93 0.92 0.93 0.81 0.87 0.89 注:主量元素含量%,稀土与微量元素含量10−6 。 -
[1] 曹正琦. 湖北大悟地区晚中生代脉岩及控矿构造研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2016, 1−147
CAO Zhengqi. Study on Late Mesozoic dike rocks and ore-controlling structures in Dawu area, Hubei Province [D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2016, 1-147.
[2] 范裕, 周涛发, 袁峰等. 宁芜盆地闪长玢岩的形成时代及对成矿的指示意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(9): 2715-2728
FAN Yu, ZHOU Taofa, YUAN Feng, et al. Geochronology of the diorite porphyrites in Ning-Wu basin and their metallogenic significances[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(9): 2715-2728.
[3] 葛宁洁, 侯振辉, 李惠民, 等. 大别造山带岳西沙村镁铁超镁铁岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 科学通报, 1999, 44(19): 2110-2114 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.19.020
GE Ningjie, HOU Zhenghui, LI Huiming, et al. Zircon U-Pb age of mafic ultramafic granites in Yuexisha village, Dabie orogenic belt [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44 (19): 2110-2114. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.19.020
[4] 黄丹峰, 罗照华, 卢欣祥. 大别山北缘金刚台火山岩SHRIMP锆石U- P b年龄及构造意[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(1): 1-9
HUANG Danfeng, LUO Zhaohua, LU Xinxiang. Zircon U-Pb Dating of the Linglong Volcanic Deposit in the Northern Dabie Mountains [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17 (1): 1-9.
[5] 刘清泉, 邵拥军, 张智慧, 等. 大别山姚冲花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素及地质意义[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25 (2): 479-491 doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2015.02.027
LIU Qingquan, SHAO Yongjun, ZHANG Zhihui, et al. Zircon U-Pb Age, Hf Isotope and Geochronology Significance of the Yaochong Granite in the Dazhuangzi Gold Deposit, Shandong Province [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25 (2): 479-491. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2015.02.027
[6] 刘福来, 薛怀民, 许志琴, 等. 大别超高压变质带的进变质, 超高压和退变质时代的准确限定: 以双河大理岩中榴辉岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(7): 1761-1778 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2006.07.002
LIU Fulai, XUE Huaiming, XU Zhiqing, et al. Precise restriction of progressive metamorphic, ultra-high pressure and retrograde metamorphic ages in the Dabie UHP metamorphic belt: A case study of SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of eclogites in Shuanghe marble [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(7): 1761-1778. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2006.07.002
[7] 刘军, 息朝庄, 黄波, 等. 柴达木西北缘大通沟南山北闪长岩年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(2): 93−105.
LIU Jun, XI Chaozhuang, HUANG Bo, et al. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Geological Significance of Thediorite in Datonggou Nanshanbei, Northwestern Qaidam Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(2): 93−105.
[8] 李曙光, 洪吉安, 李惠民, 等. 大别山辉石岩—辉长岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 1999, (3): 351-355
LI Shuguang, HONG Jiean, LI Huiming, et al. Zircon U-Pb age of pyroxenite-gabbro pluton in Dabie mountain and its geological significance[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 1999, (3): 351-355.
[9] 李曙光, 李秋立, 侯振辉, 等. 大别山超高压变质岩的冷却史及折返机制[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(04): 91-98
LI Shuguang, LI Qiuli, HOU Zhenghui, et al. Cooling-history and reentrant mechanism of ultra-high pressure metamorphic rocks in Dabie Mountains [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2005,21 (04): 91-98.
[10] 马昌前, 杨坤光, 明厚利, 等. 大别山中生代地壳从挤压转向伸展的时间: 花岗岩的证据[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2003, 33(9): 811-827.
[11] 穆可斌, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 南秦岭白龙江群中花岗岩脉群年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(3): 111-135. doi: 10.19751/j. cnki. 61-1149/p. 2019.03. 010
MU Kebin, PEI Xianzhi, LI Ruibao, et al. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Geological Significance of the Granite Veins in the Bailongjiang Group, South Qinling[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(3): 111-135. doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2019.03.010
[12] 彭松柏, 刘松峰, 林木森, 等. 华夏早古生代俯冲作用(Ⅱ): 大爽高镁-镁质安山岩新证据[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(6): 931-947
PENG Songbo, LIU Songfeng, LIN Mushen, et al. Early Paleozoic subduction in the Cathaysia (Ⅱ): New evidence for Dashuang high magnesium and magnesitic andesite [J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41 (6): 931-947.
[13] 戚学祥, 旷宏伟, 陈培良, 等. 长江中下游燕山期侵入岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 资源调查与环境, 2002, 23(1): 8
QI Xuexiang, KUANG Hongwei, CHEN Peiliang, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of Yanshanian intrusive rocks in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Resources Survey and Environment, 2002, 23(1): 8.
[14] 任志, 周涛发, 袁峰, 等. 安徽沙坪沟钥矿区中酸性侵入岩期次研究—年代学及岩石化学约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30 (4): 1097-1116
REN Zhi, ZHOU Taofa, YUAN Feng, et al. Geochronology and Geochemical Constraints of the Xilaokou Gold Deposit, Shandong Province [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30 (4): 1097-1116.
[15] 索书田, 桑隆康, 韩郁箐, 等. 大别山前寒武纪变质地体岩石学与构造学[M].武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1993
SUO Shutian, SANG Longkang, HAN Yuqing, et al. Petrology and Tectonics of Precambrian Metamorphic Terrane in Dabie Mountains[M].Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1993.
[16] 孙书勤, 汪云亮, 张成江. 玄武岩类岩石大地构造环境的Th、Nb、Zr判别[J]. 地质论评, 2003, (01): 40-47 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2003.01.006
SUN Shuqing, WANG Yunliang, ZHANG Chengjiang. Discrimination of Th, Nb, Zr in tectonic setting of basaltic rocks [J]. Geological Review, 2003, (01): 40-47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2003.01.006
[17] 汪云亮, 张成江, 修淑芝. 玄武岩类形成的大地构造环境的Th/Hf-Ta/Hf图解判别[J]. 岩石学报, 2001, 17(3): 413-421
WANG Yunliang, ZHANG Chengjiang, XIU Shuzi. Th/Hf-Ta/Hf identification of tectonic setting of basalts[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2001, 17(3): 413-421.
[18] 王世明, 马昌前, 王琳燕, 等. 大别山早白垩世基性脉岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年、地球化学特征及成因[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2010, (04): 572-584
WANG Shiming, MA Changqian, WANG Lingyan, et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating and geochemical characteristics of the Early Cretaceous basic dike rocks in the Dabie Mountains, Shandong Province [J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010, (04): 572-584.
[19] 汪晶, 吴明安, 李小东, 等. 庐枞盆地早白垩世闪长玢岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其成矿指示意义[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(4): 547-561
WANG Jing, WU Mingan, LI Xiaodong, et al. Zircon U-Pb Dating, Geochemical Characteristics of Early-Cretaceous Diorite-Porphyrites in Luzhong Basin and Their Implications for Mineralization[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(4): 547-561.
[20] 吴开彬, 邓新, 杨坤光. 北大别白垩纪花岗岩多期侵位与造山带演化的关系[J]. 地球科学, 2013, (S1): 43-52
WU Kaining, DENG Xin, YANG Kunguang. Relationship between multi-stage emplacement of Cretaceous granites and evolution of orogenic belt in Beibei [J]. Earth Science, 2013, (S1): 43-52.
[21] 吴元保, 陈道公, E. DELOULE, 等. 北大别片麻岩的锆石U-Pb年龄离子探针测定及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 2001, 47(3): 239-244 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2001.03.004
WU Yuanbao, CHEN Ddaogong, E. Deloule, et al. Zircon U-Pb Dating and Ion Probe Determination of Gneiss in Dazhuangzi Gold Deposit, Shandong Province and Its Geological Significance [J]. Geological Review, 2001, 47(3): 239-244. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2001.03.004
[22] 袁峰, 周涛发, 范裕, 等. 庐枞盆地中生代火山岩的起源、演化及形成背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(8): ;1691-1702
YUAN Feng, ZHOU Taofa, FAN Yu, et al. Source, Evolution and Tectonic Setting of Mesozoic Volcanic Rocks in Luzong Basin, Anhui Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(8);1691-1702.
[23] 赵子福, 郑永飞, 魏春生, 等. 大别山沙村和椒子岩基性-超基性岩锆石Il-Pb定年、元素和碳氧同位素地球化学研究北大别片麻岩的锆石U-Pb年龄离子探针测定及其地质意义[J]. 高校地质学, 2003, 9: 139-162
ZHAO Zifu, ZHENG Yongfei, WEI Chunsheng, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating, element and carbon and oxygen isotopic geochemistry of shacun hejiaozi basic-ultrabasic rocks in Dabie Mountains and its geological significance [J]. Geology of Universities, 2003, 9: 139-162.
[24] 赵子福, 郑永飞, 魏春生, 等. 大别山中生代中酸性岩浆岩锆石U-Pb定年、元素和氧同位素地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20(5): 1151-1174 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2004.05.012
ZHAO Zifu, ZHENG Yongfei, WEI Chunsheng, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating and oxygen isotopic geochemistry of the Mesozoic magmatic rocks in the Dabie Mountains, Shandong Province [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2004, 20(5): 1151-1174. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2004.05.012
[25] 俞胜, 赵斌斌, 贾轩, 等.北山造山带南缘一条山北闪长岩地球化学、年代学特征及其构造意义[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(4): 267−279.
YU Sheng, ZHAO Binbin, JIA Xuan, et al. Geochemistry,Geochronology Characteristics and Tectonic Significance of Yitiaoshan Diorite in the Southern Margin of Beishan Orogenic Belt[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(4): 267−279.
[26] 张凯, 王居里, 汪佩佩, 等. 南秦岭太平沟铜(金)矿相关花岗岩体锆石U-Pb年代学及岩石成因[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(4): 73-85. doi: 10.19751/j.cnki. 61-1149/p. 2020.04. 007.
ZHANG Kai, WANG Juli, WANG Peipei, et al. Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Petrogenesis of Taipinggou Copper (Gold)-related Granites, South Qinling[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(4): 73-85. doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2020.04.007.
[27] Chen B, Jahn B M, Wei C J. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids in the Dabie UHP complex, Central China: trace element and Nd-Sr iso-tope evidence[J]. Lithos, 2002, 60: 67-88. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(01)00077-9
[28] David A F, Carl S, Mark F, et al. Relationships between crustal partial melting, plutonism, orogeny, and exhumation: Idaho–Bitterroot batholith - ScienceDirect.[J]. Tectonophysics, 2001, 342(3-4): 313-350. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(01)00169-X
[29] Fernandez A N and Barbarin B. Relative rheology of coeval mafic and felsic magmas: Nature of resulting interaction processes. Shape and mineral fabrics of mafic microgranular enclaves. In: Didier J, Barbarin B (eds. ) [J]. Enclaves and Granite Petrology, Amsterdam-Oxford-New York-Tokyo: Elsevier. 1991, 263−275.
[30] Gibson I L, Kirkpatrick R J, Emmerman R, et al. The trace element composition of the lavas and dikes from a 3-km vertical section through the lava pile of eastern Iceland[J]. Journal of Geoph-ysical Research, 1982, 87: 6532-6546. doi: 10.1029/JB087iB08p06532
[31] Gill J. Orogenic andesites and plate tectonics[M]. Springer-Verlag, 1981.
[32] Green T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3-4): 347-359. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)00145-X
[33] Halls H c. The importance and potential of mafic dyke swarms in studies of geodynamic processes[J]. geoscience Canada, 1982, 9(3): 145-154.
[34] Hacker B R, Ratschbacher L, Webb L, et al. U/Pb zircon ages constrain the architecture of the ultrahigh-pressure Qinling-Dabie Orogen, China[J]. Earth Planet. sci. lett, 1998, 161(1-4): 215-230. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00152-6
[35] Hacker B R and Wang Q C. Ar/Ar geochronology of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism in central China[J]. Tectonics, 1995, 14: 994-1006. doi: 10.1029/95TC00932
[36] Hofmann P F. United Plates of America, the birth of a craton: Early Proterozoic assembly and growth of Laurentia[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1988, 16(1): 543-603. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.16.050188.002551
[37] Jahn B M, Wu F Y, Lo C H, et al, Crust-mantle interaction induced by deep subduction of the continental crust: Geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence from post-collisional mafic -Ultramafic intrusion of the northern Dabie complex, central china[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 157(1−2): 119−146. doi:10.1016/s0009-2541(98)00197-1.
[38] Leech M L. Arrested orogenic development: eclogitization, delamination, and tectonic collapse[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 185(1-2): 149-159.
[39] Maitre RW L, Bateman P, Dudek A, et al. A Classification of Igneous Rocks and Glossary of Terms[M]. Oxford: Blackwell, 1989, 1−193.
[40] Mcculloch M T, Gamble J A, McCulloch, M. T. & Gamble, J. A. Geochemical and geodynamical constraints on subduction zone magmatism. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 102, 358-374[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 102(3-4): 358-374. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(91)90029-H
[41] Mcdonough W F, Sun S S. The composition of the Earth[M]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3−4): 223−253.
[42] Ma C Q, Li Z C, Ehlers C, Yang KC and Wang RI. A post-collisional magmatic pluming system; Mesozoic granitoid plutons from the Dabieshan high-pressure and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic zone, east-central China[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45: 431-456. doi:10. 1016/S0024-4937(98):00043-7
[43] Pearce J A, Peate D W. Tectonic Implication of the composition of volcanic ARC magmas[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1995, 23(1): 251-285. doi:10.1146/annurev.ea.23.050195.001343.
[44] Pearce T H. The TiO2 - K2O – P diagram : A method of discriminating between oceanic and nonoceanic basalt. [J]. Earth Planet. sci. lett, 1975, 24(3): 419-426. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(75)90149-1
[45] Pearce J A, Cann J R. Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analyses[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1973, 19(2): 290-300.
[46] Poland M p, Fink J H, Tauxe L. Patteens of magma flow in segmented silicic dikes at summer coon volcano, Colorado[J]. AMS and Thin Section Analysis. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 219(1-2): 155-169. doi:10.1016/s0012-821x(03)00706-4.
[47] Li S, Xiao Y, Liou D, et al. Collision of the North China and Yangtse Blocks and formation of coesite-bearing eclogites: Timing and processes[J]. Chemical Geology, 1993, 109(1-4): 89-111. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(93)90063-O
[48] Rapp RP and Watson E B. Dehydration melting of meta-basalt at 8-32kbar: Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4): 891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
[49] Rudnik R, Gao S. Composition of the continental crust. In: rudnik, R., ed., The crust Treatise on geochemistry [J]. Elservior, Amsterdam, 2003, 3-164,doi:10.1016/B0-08-043751-6/03016-4.
[50] Taylor S R. Mclennan S M. The continental crust: its composition and evolution[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1985, 94(4): 57-72.
[51] Whitney D L, Teyssier C, Fayon A K, et al. Tectonic controls on metamorphism, partial melting, and intrusion: timing and duration of regional metamorphism and magmatism in the Nide Massif, Turkey[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 376(1-2): 37-60. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2003.08.009
[52] Westerman D S, Dini A, Innocenti F, et al. When and where did hybridization occur ?the case of the monte capanne pluton, italy[J]. Atlantic Geology, 2003, 39(2): 147-162,doi:10.4138/1177.
[53] Winchester J A, Floyd P A. Geochemical magma type discrimination: application to altered and metamorphosed basic igneous rocks[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1976, 28(3): 459-469. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(76)90207-7
[54] Xu haijin, Ma Chanqian, Ye Kai. Early Cretaceous granitiod and their implications for Collapse of the Dabie orogen, eastern China: SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating and geochemistry [J]. Chem Geol., 2007, 240(3/4): 238-272.
[55] Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, Wei C S, et al. Zircon U- Pb Age, Element and C-O isotope geochemistry of Post-collisional Mafic-Ultramafic Rocks from the Dabie Orogen in East-central China[J]. Lithos, 2005, 83(1-2): 1-28. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.12.014
-




 下载:
下载: