Geological Characteristics and Genesis of Manganese Ore in Moshigou Area, Qinghai Province
-
摘要:
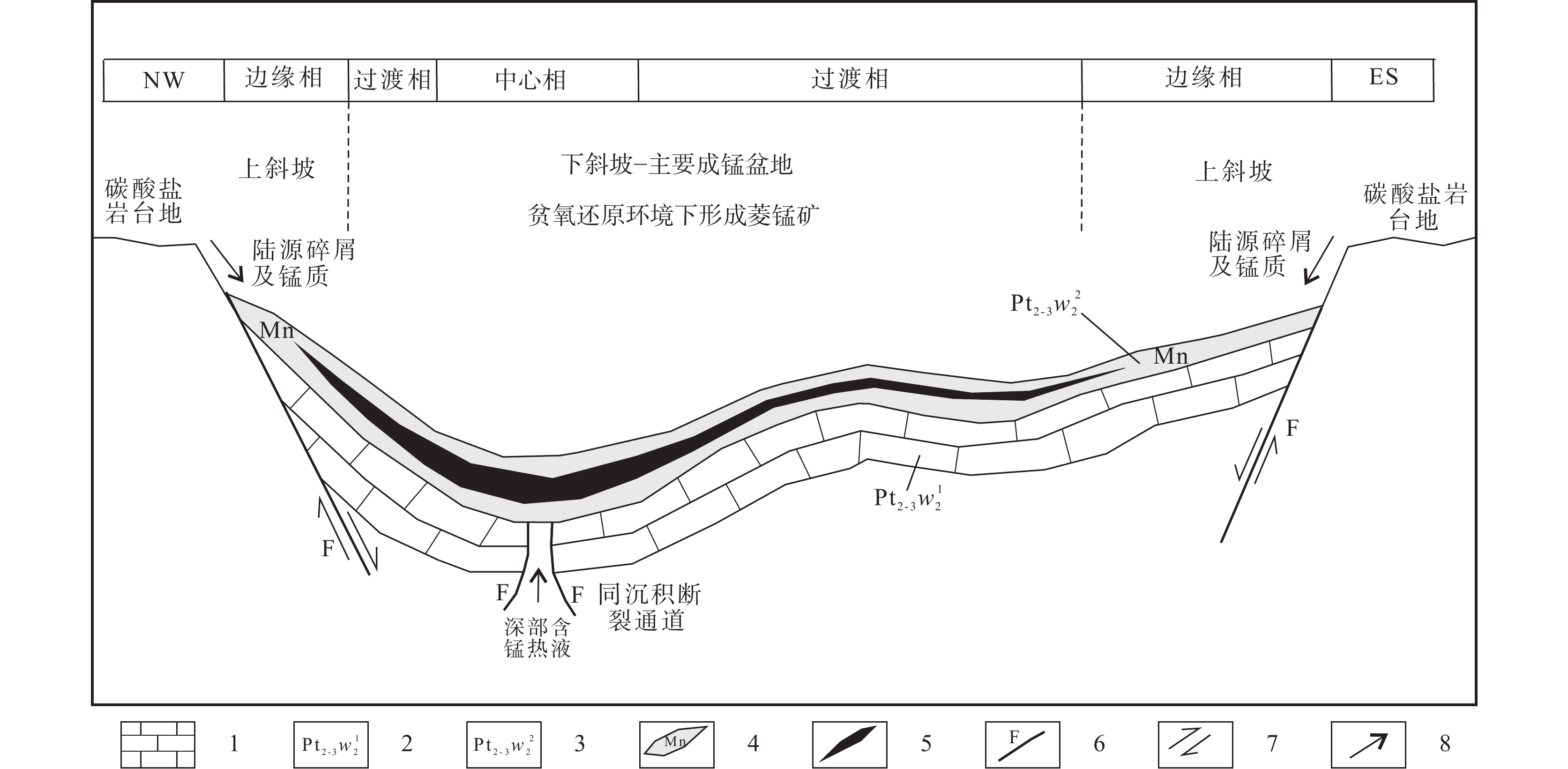
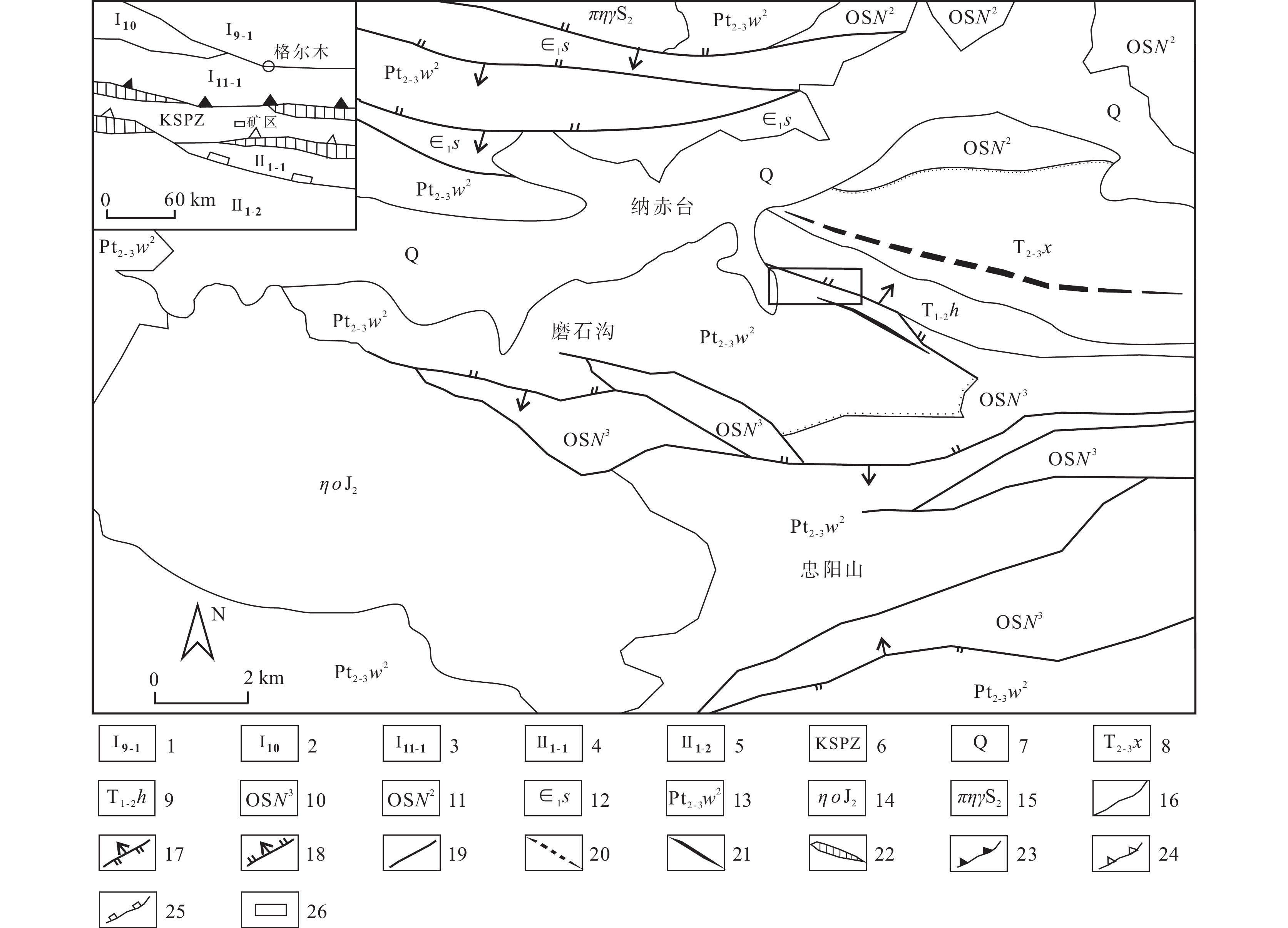
青海磨石沟锰矿是近年来东昆仑南坡地区新发现的台盆相沉积型碳酸锰矿,主要赋存于中新元古界万宝沟群碳酸盐岩组顶部。含锰岩系及锰矿体具有厚度大、延伸稳定、岩性组合简单及整体品位偏低但储量较大的特点,是青海省内少数具有良好前景的锰矿勘查基地之一。根据磨石沟锰矿区的最新勘查成果,从成矿地质背景、矿区地质特征、厚大的白云岩–碳质板岩含锰岩系、层状密集分布的锰矿体、矿石质量特征及主–微量元素特征等方面推断矿床成因与热水沉积关系密切,初步探究磨石沟地区热水沉积锰矿的成矿模式。通过综合分析,初步评价磨石沟锰矿区的找矿潜力,为类似沉积型锰矿勘查提供找矿借鉴。
Abstract:Moshigou manganese mining area in Qinghai is a platform basin sedimentary manganese carbonate deposit newly discovered in the south slope of East Kunlun in recent years, which mainly occurs at the top of the carbonate formation of Wanbaogou group in meso Neoproterozoic. Manganese bearing rock series and manganese orebody are characterized by large thickness, stable extension, simple lithologic combination, low overall grade but large reserves. They are one of the few manganese ore exploration bases with good prospects in Qinghai Province. According to the latest exploration results of Moshigou manganese mining area, it is inferred that the genesis of the deposit is closely related to hot water sedimentation from the aspects of metallogenic geological background, geological characteristics of the mining area, thick dolomite carbonaceous slate manganese bearing rock series, layered densely distributed manganese ore bodies, ore quality characteristics, main and trace element characteristics, etc., and the metallogenic model of hot water sedimentary manganese ore in Moshigou area is preliminarily explored. Through comprehensive analysis, the prospecting potential of Moshigou manganese mining area is preliminarily evaluated, so as to provide prospecting reference for similar sedimentary manganese ore exploration.
-

-
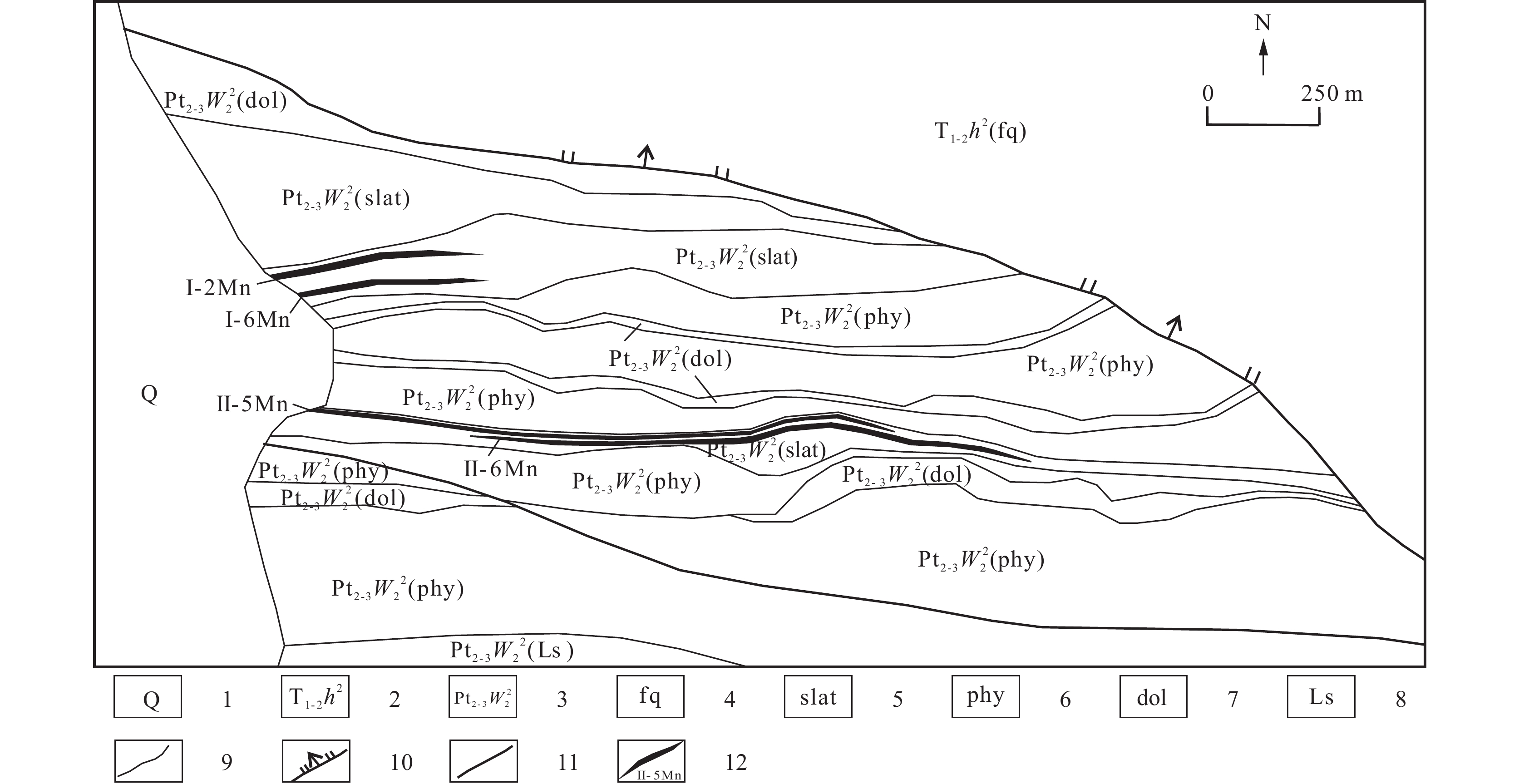
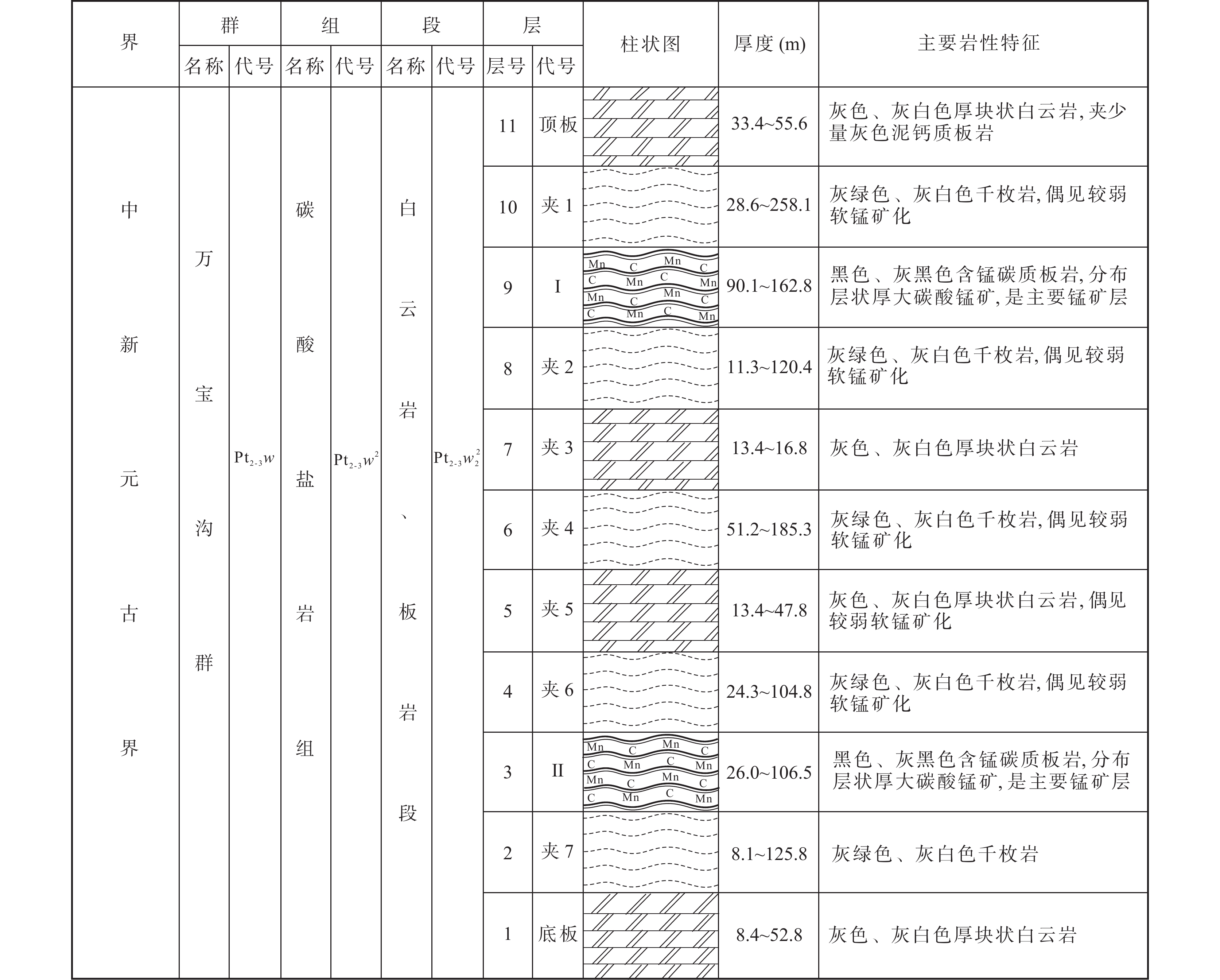
表 1 磨石沟锰矿区主矿体特征简表
Table 1. Characteristics of main ore body in Moshigou manganese mining area
主矿体 项目 厚度 Mn TFe P SiO2 CaO MgO Al2O3 Loss Mn/TFe P/Mn (CaO+MgO)/
(SiO2+Al2O3)(m) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) Ⅰ-2Mn 单工程 5.42 11.88 5.18 0.15 40.10 4.79 3.89 9.17 14.51 2.29 0.013 0.18 Ⅰ-6Mn 单工程 9.03 13.86 4.01 0.16 37.41 5.50 4.21 7.75 15.83 3.46 0.012 0.22 Ⅱ-5Mn 最小值 0.61 10.27 4.08 0.08 31.14 7.70 2.02 6.80 21.96 2.52 0.008 0.26 最大值 2.55 16.03 4.33 0.20 36.41 9.55 3.52 8.42 23.42 3.70 0.012 0.29 平均值 1.43 12.44 4.22 0.11 33.86 8.83 2.91 7.73 22.70 2.95 0.009 0.28 Ⅱ-6Mn 最小值 0.95 11.04 3.02 0.054 30.84 6.64 1.92 4.85 19.62 3.66 0.005 0.24 最大值 2.54 15.23 3.89 0.014 42.05 12.02 4.16 7.10 21.01 3.92 0.001 0.33 平均值 1.47 11.92 3.47 0.09 35.38 9.69 3.16 5.86 20.62 3.44 0.008 0.31 注:测试单位为青海省有色地质测试中心。采用光谱–化学分析法测试,仪器为ICAP-6300 ICP等离子体发射光谱仪A-7,检出限0.001×10−2,可靠性良好。 表 2 磨石沟锰矿区碳酸锰矿石化学成分及参数表
Table 2. Chemical composition and parameters of manganese carbonate ore in Moshigou manganese mining area
样品编号 Mn(%) Fe(%) Al2O3(%) SiO2(%) Al/(Al+Fe+Mn) SiO2/Al2O3 MS2021QZ01‐H12 10.90 3.50 5.62 33.26 0.17 5.92 MS2021QZ01‐H13 11.34 3.02 4.85 30.84 0.15 6.36 MS2021QZ01‐H18 10.88 4.08 6.80 35.06 0.19 5.16 MS2021QZ01‐H20 10.82 4.18 8.21 31.10 0.22 3.79 MS2021QZ01‐H41 10.98 5.40 8.24 42.30 0.21 5.13 MS2021TC01‐H19 22.63 4.41 7.38 30.59 0.13 4.14 MS2021TC01‐H32 11.62 5.17 10.97 48.70 0.26 4.44 MS2021TC01‐H34 26.46 3.72 6.01 33.65 0.10 5.60 MS2021TC01‐H55 12.30 5.79 8.44 34.82 0.20 4.13 MS2021TC01‐H56 16.06 6.26 8.01 30.99 0.16 3.87 MS2021TC01‐H57 16.17 3.48 5.51 29.06 0.13 5.27 MS2021TC01‐H58 12.69 4.26 6.38 32.30 0.17 5.06 MS2021TC01‐H60 17.76 3.76 6.96 33.80 0.15 4.86 MS2021TC01‐H61 14.80 4.40 8.50 39.36 0.19 4.63 MS2021TC01‐H62 15.80 6.20 7.94 34.52 0.16 4.35 MS2021TC01‐H63 15.13 4.22 5.96 28.34 0.14 4.76 MS2021TC01‐H64 15.28 4.51 6.94 31.68 0.16 4.56 MS2021TC02‐H46 13.66 4.50 7.55 42.62 0.18 5.65 MS2021TC02‐H47 19.59 2.98 4.74 28.56 0.10 6.03 MS2021TC02‐H48 18.54 2.85 4.58 30.43 0.10 6.64 MS2021TC02‐H49 15.72 2.98 4.81 27.90 0.12 5.80 MS2021TC02‐H50 12.02 4.42 9.14 40.96 0.23 4.48 MS2021TC02‐H52 15.57 4.42 8.82 41.45 0.19 4.70 MS2021TC02‐H53 11.21 4.65 10.39 45.37 0.26 4.37 MS2021TC02‐H54 12.62 3.02 4.90 27.71 0.14 5.66 MS2021TC02‐H55 12.16 3.00 5.30 27.88 0.16 5.26 MS2021TC02‐H118 12.1 5.36 13.04 45.79 0.28 3.51 MS2021TC02‐H121 12.91 3.81 6.16 28.95 0.16 4.70 MS2021TC02‐H122 14.76 4.84 7.96 36.44 0.18 4.58 MS2021TC02‐H125 14.35 4.70 4.50 34.96 0.11 7.77 注:测试单位:青海省有色地质测试中心。采用光谱–化学分析法测试,仪器为ICAP-6300 ICP等离子体发射光谱仪A-7,检出限0.001×10−2,可靠性良好。 表 3 磨石沟锰矿区碳酸锰矿石微量元素及参数表
Table 3. Table of trace elements and parameters of manganese carbonate ore in Moshigou manganese mining area
样品编号 岩性 V(%) Co(%) Ni(%) Ni/Co V/(V+Ni) QZ01‐H07 锰矿石 0.0240 0.0047 0.0046 0.98 0.84 QZ01‐H14 锰矿石 0.0048 0.004 0.0038 0.95 0.56 QZ01‐H18 锰矿石 0.0100 0.0046 0.0032 0.70 0.76 QZ01‐H103 锰矿石 0.0050 0.0048 0.0035 0.73 0.59 ZK0001‐H01 底板千枚岩 0.0170 0.0021 0.0038 1.81 0.82 ZK0001‐H32 锰矿石 0.0045 0.0037 0.0033 0.89 0.58 ZK0001‐H96 顶板白云岩 0.0100 0.0023 0.0042 1.83 0.7 注:测试单位:青海省有色地质测试中心。主要采用X荧光法(XRF)测试,仪器为日本理学公司Primus-Ⅱ型,检出限5.96×10−6,可靠性良好。 -
[1] 蔡雄飞, 魏启荣. 东昆仑万保沟岩群洋岛地层序列特征和构造古地理的恢复[J]. 地层学杂志, 2007(02): 117-126 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2007.02.003
CAI Xiongfei, WEI Qirong. Stratigraphic sequence of ocean islands and palinspastic reconstruction of the Wanbaogou group-complex in the Eastern Kunlun orogenic belt[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2007 (02): 117-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2007.02.003
[2] 查显锋, 计文化, 张海迪, 等. 青海中部昆南增生杂岩带变形分期及构造过程[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(12): 2015-2024 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.12.010
CHA Xianfeng, JI Wenhua, ZHANG Haidi, et al. A discussion on the deformation phases and tectonic process of the Southern Kunlun accretionary complex belt, in central Qinghai[J]. Geological Bulletin, 2012, 31 (12): 2015-2024. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.12.010
[3] 邓红斌, 姚波, 钟刚, 等. 青海省格尔木市格尔木河西地区J46E023018、J46E023019、J46E024018、J46E024019、I46E001019五幅1∶ 5万区域地质矿产调查[R]. 四川省地质矿产勘查开发局川西北地质队, 2017
[4] 高永宝, 滕家欣, 陈登辉, 等. 新疆西昆仑玛尔坎苏锰矿带成矿地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 西北地质, 2017, 50(01): 261-269 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2017.01.022
GAO Yongbao, TENG Jiaxin, CHEN Denghui, et al. Metallogenic geological characteristics and prospecting direction of markansu manganese ore belt in West Kunlun, Xinjiang [J] Northwestern Geology, 2017, 50 (01): 261-269. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2017.01.022
[5] 郭宪璞, 王乃文, 丁孝忠. 东昆仑格尔木南部纳赤台群和万宝沟群基质系统与外来系统地球化学差异[J]. 地质通报, 2004(12): 1188-1195 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.12.004
GUO Xianpu, WANG Naiwen, DING Xiaozhong. Geochemical divergence between the matrix system and exotic block system in the Naij Tal and Wanbaogou groups in the East Kunlun Mountains [J]. Geological Bulletin, 2004 (12): 1188-1195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.12.004
[6] 江沙, 周星, 黄一杰, 等. 广西忻城县里苗-塘岭锰矿床控矿因素及成矿模式[J]. 地质与勘探, 2019, 55(03): 723-735
JIANG Sha, ZHOU Xing, HUANG Yijie, et al. Ore-controlling factors and metallogenic model of LiMiao-tangling manganese deposit in Xincheng County of Guangxi [J]. Geology and Exploration, 2019, 55 (03): 723-735.
[7] 纪冬平, 王朋, 高政伟, 等. 陕西宁强县中坝锰矿床地球化学特征及成矿模式[J]. 矿床地质, 2022, 41(03): 469-488 doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2022.03.002
JI Dongping, WANG Peng, GAO Zhengwei, et al. Geochemical characteristics and metallogenic model of Zhongba manganese deposit in Ningqiang County, Shaanxi, China [J]. Geology of Mineral Deposits, 2022, 41 (03): 469-488. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2022.03.002
[8] 李宪栋. 青海省分水岭地区中新元古代火山岩特征及构造环境[J]. 工业技术创新, 2017, 04(06): 98-103
LI Xiandong. Characteristics and structural environment of middle Neoproterozoic volcanic rocks in the Watershed area of Qinghai Province [J]. Industrial Technology Innovation, 2017, 04 (06): 98-103.
[9] 李荣志, 蒋新红, 邹颖贵, 等. 广西东平锰矿床地质特征及成矿模式[J]. 中国锰业, 2021, 39(03): 18-28 doi: 10.14101/j.cnki.issn.1002-4336.2021.03.005
LI Rongzhi, JIANG Xinhong, ZOU Yinggui, et al. Geological characteristics and mineralization and metallogenic model of Dongping manganese deposit in Guangxi [J]. China Manganese Industry, 2021, 39 (03): 18-28. doi: 10.14101/j.cnki.issn.1002-4336.2021.03.005
[10] 刘虎, 李庆宏, 陈艳, 等. 湖南桃江响涛源锰矿地球化学特征及其成因意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2019, 55(03): 712-722
LIU Hu, LI Qinghong, CHEN Yan, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genetic significance of the Xiangtaoyuan manganese deposit in Taojiang, Hunan province [J]. Geology and Exploration, 2019, 55 (03): 712-722.
[11] 刘振, 马志鑫, 刘伟, 等. 重庆秀山小茶园地区南华纪大塘坡组沉积环境与锰矿产出规律[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(03): 515-524
LIU Zhen, MA Zhixin, LIU Wei, et al. Sedimentary environment and manganese ore deposits in the Nanhua period Datangpo formation in Xiaochayuan area, Xiushan, Chongqing [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39 (03): 515-524.
[12] 刘志臣, 王聪, 张远国, 等. 贵州遵义锰矿床地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 矿物学报, 2015, 35(04): 481-488
LIU Zhichen, WANG Cong, ZHANG Yuanguo, et al. Geochemistry and ore genesis of Zunyi Mn Deposit, Guizhou, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2015, 35 (04): 481-488.
[13] 马延虎, 蔡德华, 任晋祁, 等. 万保沟幅、没草沟幅、青办食宿站幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 青海省地质调查院区调六分队, 2004
[14] 潘彤. 青海成矿单元划分[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2017, 39(1): 19-24 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2017.01.002
PAN Tong. Classification of metallogenic units in Qinghai, China[J]. Journal of Earth Science and Environment, 2017, 39 (1): 19-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2017.01.002
[15] 祁生胜, 王秉璋, 王瑾, 等. 晋宁运动在东昆仑东段的表现及其意义[J]. 青海地质, 2001(S1): 17-21
QI Shengsheng, WANG Bingzhang, WANG Jin, et al. Manifestation of Jinning movement in the eastern sector of East Kunlun and its significance [J]. Qinghai Geology, 2001 (S1): 17-21.
[16] 祁生胜. 青海省大地构造单元划分与成矿作用特征[J]. 青海国土经略, 2013(05): 53-62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8704.2013.05.018
QI Shengsheng. Division of tectonic units and characteristics of mineralization in Qinghai Province [J]. Qinghai Land and Resources Strategy, 2013 (05): 53-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8704.2013.05.018
[17] 秦元奎, 张华成, 姚敬劬. 广西大新县下雷锰矿床的地球化学特征及其意义[J]. 地质论评, 2010, 56(05): 664-672 doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2010.05.014
QIN yuankui, ZHANG Huacheng, YAO Jingyu. Geochemical characteristics and geological implication of the Xialei manganese deposit, Daxin County, Guangxi [J]. Geological Review, 2010, 56 (05): 664-672. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2010.05.014
[18] 桑继镇, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑东段清水泉辉长岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(05): 700-710 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.05.007
SANG Jizhen, PEI Xianzhi, LI Ruibao, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and geochemical characteristics of gabbro in Qingshuiquan, east section of East Kunlun, and its tectionic significance[J]. Geological Bulletin, 2016, 35 (05): 700-710. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.05.007
[19] 沈红钱, 张遂, 曾飞, 等. 华南南华纪武陵锰矿成矿带松桃李家湾-高地-道坨地堑盆地研究新进展和潜力预测[J]. 贵州地质, 2021, 38(02): 129-138 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2021.02.003
SHEN Hongqian, ZHANG Sui, ZENG Fei, et al. New research progress and potential prediction of Lijiawan-Gaodi-Daotuo graben located in Songtao area, Wuling manganese ore belt in Nanhua period, South China [J]. Guizhou Geology, 2021, 38 (02): 129-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2021.02.003
[20] 石浩, 覃小锋, 王宗起, 等. 黔东松桃地区李家湾锰矿床地质、地球化学特征及成因信息[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(01): 109-122 doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2019.01.010
SHI Hao, QIN Xiaofeng, WANG Zongqi, et al. Geological, geochemical characteristics and genetic information of the Lijiawan manganese deposit in Songtao area, eastern Guizhou [J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(01): 109-122. doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2019.01.010
[21] 史连昌, 才航加, 许海全, 等. 东昆仑南坡俯冲增生杂岩楔中纳赤台群物质组成特征[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(Z1): 251-257 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.02.008
SHI Lianchang, CAI Hangjia, XU Haiquan, et al. Material composition characteristics of Naijtai group in subduction accretion complex on the southern slope of East Kunlun mountains [J]. Geological Bulletin, 2017, 36 (z1): 251-257. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.02.008
[22] 孙崇仁, 喇继德, 李璋荣, 等. 青海省岩石地层[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1997
SUN Chongren, LA Jide, LI Zhangrong, et al. Lithostratigraphy of Qinghai Province [M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1997.
[23] 王发明, 唐健, 蔡德华, 等. 水泥厂幅、忠阳山幅、黑刺沟幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 青海省地质调查院区调三分队, 2004.
[24] 王国灿, 魏启荣, 贾春兴, 等. 关于东昆仑地区前寒武纪地质的几点认识[J]. 地质通报, 2007(08): 929-937 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.08.003
WANG Guocan, WEI Qirong, JIA Chunxing, et al. Some ideas of Precambrian geology in the East Kunlun, China [J]. Geological bulletin, 2007 (08): 929-937. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.08.003
[25] 吴佳昌, 赵品忠, 黄宗添, 等. 滇东南地区石炭系锰矿找矿新发现[J]. 地质与勘探, 2019, 55(S1): 306-313
WU Jiachang, ZHAO Pinzhong, HUANG Zongtian, et al. New discovery of prospecting for manganese ore in Carboniferous of Southeast Yunnan province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2019, 55 (S1): 306-313.
[26] 谢成良, 叶高峰, 魏文博, 等. 藏北高原主要断裂带电性结构特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(12): 3991-4002 doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.011
XIE Chengliang, YE Gaofeng, WEI Wenbo, et al. Electrical features of the main faults beneath northern Xizang Plateau[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 2012, 55 (12): 3991-4002. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.011
[27] 谢升浪, 郑才贤, 贾波, 等. 东昆仑菜园子沟地区锰矿地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 中国锰业, 2021, 39(2): 24-27 doi: 10.14101/j.cnki.issn.1002-4336.2021.02.005
XIE Shenglang, ZHENG Caixian, JIA Bo, et al. The geological characteristics and prospecting criteria of manganese deposits in Caiyuanzigou area, East Kunlun [J]. China Manganese Industry, 2021, 39 (2): 24-27. doi: 10.14101/j.cnki.issn.1002-4336.2021.02.005
[28] 解玉月. 昆中断裂东段不同时代蛇绿岩特征及形成环境[J]. 青海地质, 1998(01): 27-36
XIE Yuyue. Features of Ophiolites with different period in the eastern sector of middle Kunlun fault and its original environment[J]. Qinghai geology, 1998 (01): 27-36.
[29] 许鑫, 宋述光, 苏犁. 东昆仑中段万宝沟群玄武岩的形成时代和构造意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2016, 35(06): 965-980 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2016.06.004
XU Xin, SONG Shuguang, SU Li. Formation age and tectonic significance of Wanbaogou basalt in the middle East Kunlun orogenic belt [J]. Journal of Rock Mineralogy, 2016, 35 (06): 965-980. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2016.06.004
[30] 薛友智, 姚敬劬, 黄金水, 等. 再论锰的“内源外生”成矿说[J]. 地质与勘探, 2019, 55(04): 891-898
XUE Youzhi, YAO Jingyu, hUANG Jinshui, et al. A review of the metallogenic theory of endogenous origin and exogenous mineralization of manganese ores[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2019, 55 (04): 891-898.
[31] 姚远, 赖健清, 唐一昂, 等. 广西东平沉积锰矿地球化学特征及成矿物质来源研究[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2016, 31(04): 506-514 doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2016.04.005
YAO yuan, LAI Jianqing, TANG Yiang, et al. Geochemistry characteristics and the ore material source of Dongping sedimentary manganese deposits in Guangxi [J]. On geological prospecting, 2016, 31 (04): 506-514. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2016.04.005
[32] 伊帆, 伊海生. 桂西南地区下三叠统北泗组含锰岩系地球化学特征及意义[J]. 地球化学, 2017, 46(01): 46-65 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.01.005
YI Fan, YI Haisheng. Geochemical characteristics of the Beisi formation manganese-bearing rocks of the Lower Triassic series in the Tiandeng area, Southwest Guangxi and their implications[J]. Geochemistry, 2017, 46 (01): 46-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.01.005
[33] 尹青. 桂西南地区下三叠统锰矿沉积特征与成因机理研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2015.
YIN Qing. Research on depositional feature and mineralization mechanism of manganese deposit of the lower triassic in Southwest Guangxi area[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2015.
[34] 张雪亭, 杨生德, 王秉璋. 青海省板块构造研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007
ZHANG Xueting, YANG Shengde, WANG Bingzhang. Study on plate tectonics in Qinghai Province [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007.
[35] 朱坤贺. 东昆仑造山带的俯冲与增生构造[J]. 江西科学, 2022, 40(02): 318-322 doi: 10.13990/j.issn1001-3679.2022.02.022
ZHU Kunhe. Subduction and accretionary tectonics of the East Kunlun orogen[J]. Jiangxi Science and Technology, 2022, 40 (02): 318-322. doi: 10.13990/j.issn1001-3679.2022.02.022
[36] Adachi M, Yamamoto K, Sugiski R. Hydrothermal chert and associated siliceous rocks from the northern Pacific: Their geological significance as indication of ridge activity[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1986, 47: 125-148. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(86)90075-8
[37] Bostom K, Peterson M N A. Origin of aluminum poor ferromanganoan sediments in areas of high heat flow on the East Pacific rise[J]. Marine Geology, 1969, 7: 427-447. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(69)90016-4
[38] Bostrom K, Kraemer T, Gartner S. Provenance and accumulation rates of opaling silica, Al, Ti, Fe, Mn, Cu, Ni and Co in Pacific pelagic sedimen-ts [J]. Chemical Geology, 1973, 11(2): 123-148. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(73)90049-1
[39] Crerar D A, Namson J, Chyi M S. Manganiferous cherts of the Franciscan Assemblage. I. General geology, ancient and modern analogues, and implications for hydrothermal convection at oceanic spreading centers[J]. Deep Sea Research Part B, Oceanograghic Literature Review, 1982, 29(12): 771.
[40] Jones B, Manning D A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1): 111-129.
[41] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1985.
[42] Tribovillard N, Thomas J A, Lyons T. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 232(1): 12-32.
[43] Tyson P D. Climatic change in Southern Africa : Past and present conditions and possible future scenarios[J]. Climatic change, 1991, 18: 241-258. doi: 10.1007/BF00139000
-



 下载:
下载: