Study on Sand Bodies Controlled by Growth Faults in Xiaermen Area of Biyang Sag
-
摘要:
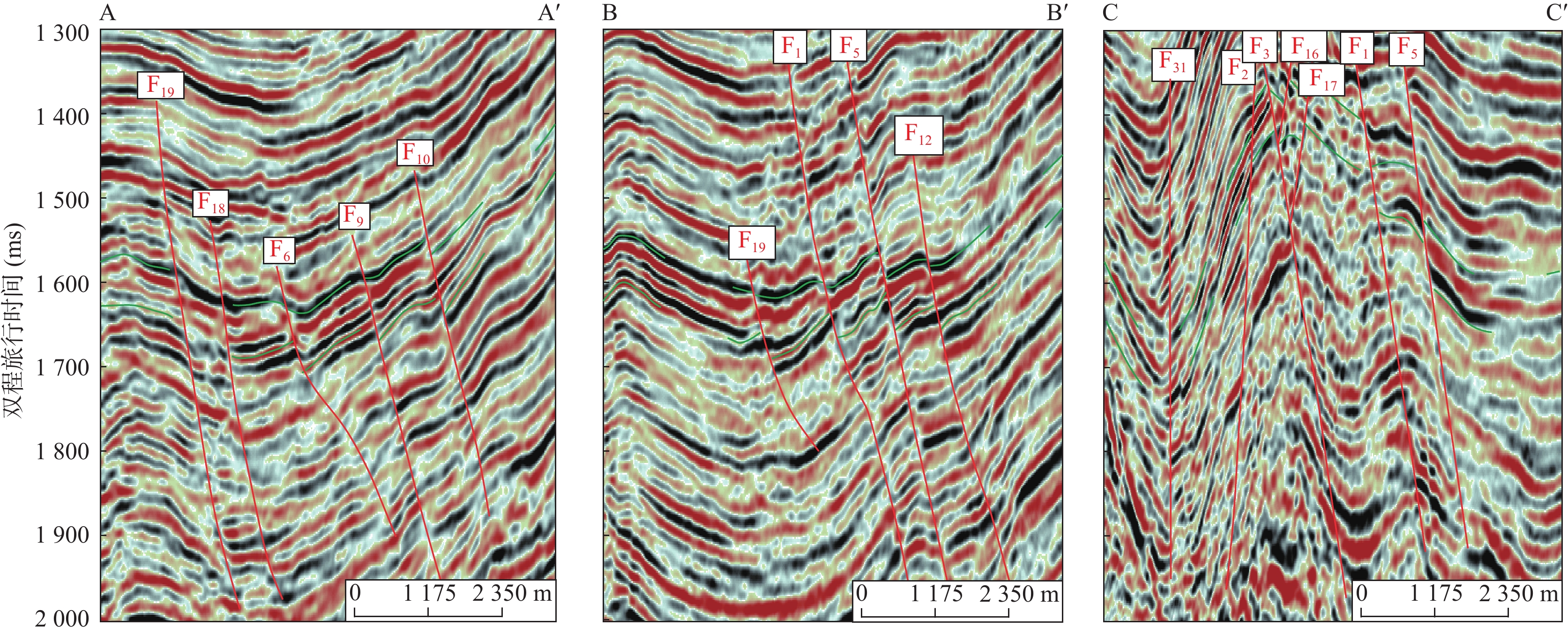
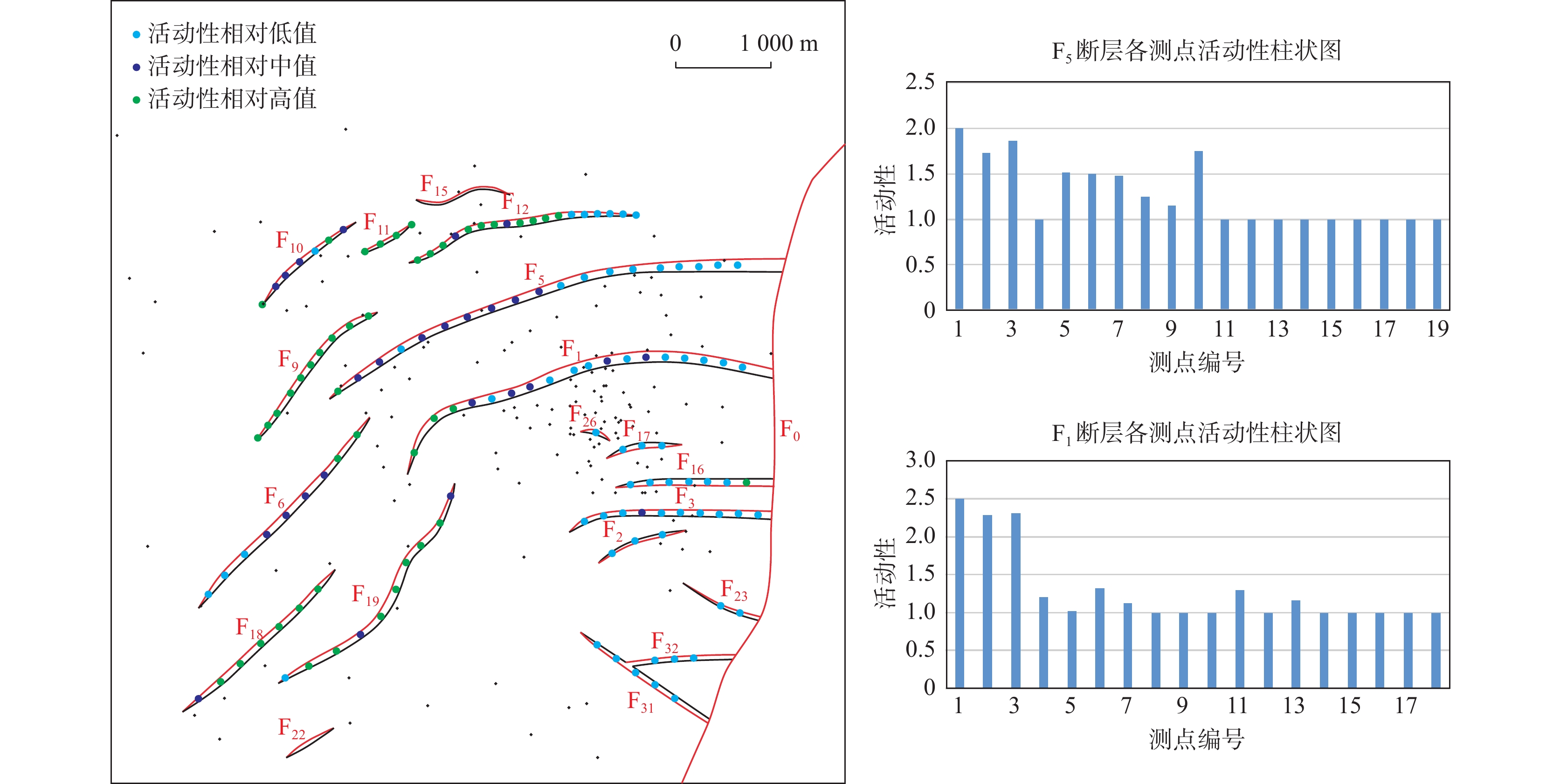
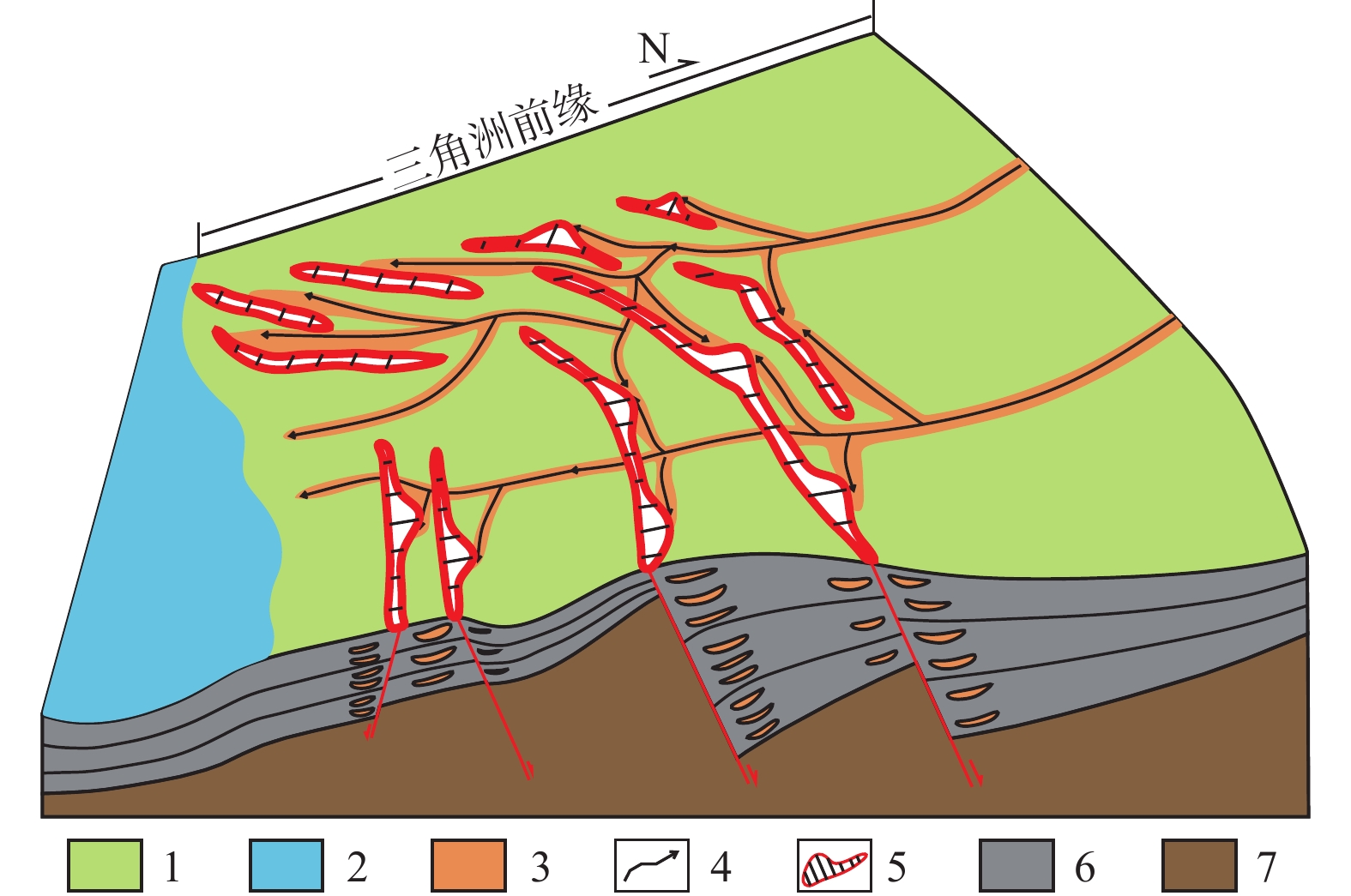
泌阳凹陷下二门地区油气资源丰富,油藏类型以断层-岩性油气藏为主,断裂特征与砂体展布的配置关系是该区油气勘探的主控因素。笔者综合3D地震、钻测井、岩心资料,以古近系核桃园组三段Ⅳ油组1小层(Eh3Ⅳ1)为例,通过精细构造解析、断层活动性定量分析和砂体展布特征刻画,从构造活动−沉积响应的角度分析生长断层对辫状河三角洲砂体展布的控制作用。结果表明,下二门地区主要发育一系列SW−NE转近E−W走向的北倾生长正断层,剖面形态呈阶梯状断层组合,各条断层沿走向活动性差异明显。研究区主要发育侯庄辫状河三角洲前缘亚相和前三角洲亚相,平面上来自北部的水下分流河道砂体在断层转换带或同一断层活动性较弱部位易通过,而在活动性较强部位受到限制或转向。垂向上,通过活动性较弱区域砂体垂向连续叠置、加厚发育,通过活动性较强区域砂体垂向间歇分散、减薄发育。该研究可为东部断陷盆地低序级生长断层发育区砂体展布规律认识和断层−岩性油气藏勘探开发提供一定借鉴。
Abstract:Xiaermen area of Biyang sag is rich in oil and gas resources. The reservoir type is mainly fault-lithologic reservoir. The configuration relationship between fault characteristics and sand body distribution is the main controlling factor of oil and gas exploration in this area. Based on 3D seismic, drilling, logging and core data, taking the Small layer 1 of Ⅳ oil formation in the third member of Paleogene Hetaoyuan Formation (Eh3Ⅳ1) as an example, through structure analysis, quantitative analysis of fault activity and characterization of sand body distribution characteristics, this paper analyzes the distribution characteristics of Braided River Delta sand body controlled by growth fault from the perspective of tectonic activity sedimentary response. The results show that a series of North dipping growth normal faults with SW-NE turning to E-W strike are mainly developed in Xiaermen area. The profile forms a stepped fault combination, and the activity of each fault is obviously different along the strike. The study area mainly develops Houzhuang braided river delta front subfacies and pre delta subfacies. The underwater distributary channel sand body from the north is easy to pass through the fault transition zone or the weak part of the same fault activity, but is limited or turned in the strong part. Vertically, sand bodies in areas with weak activity are vertically continuously superimposed and thickened, while sand bodies in areas with strong activity are vertically intermittently dispersed and thinned. This study can provide some reference for the understanding of sand body distribution law and exploration & development in the low order growth fault development area of the eastern fault basin.
-
Key words:
- Biyang sag /
- Xiaermen Area /
- Hetaoyuan formation /
- growth faults /
- sand body distribution
-

-
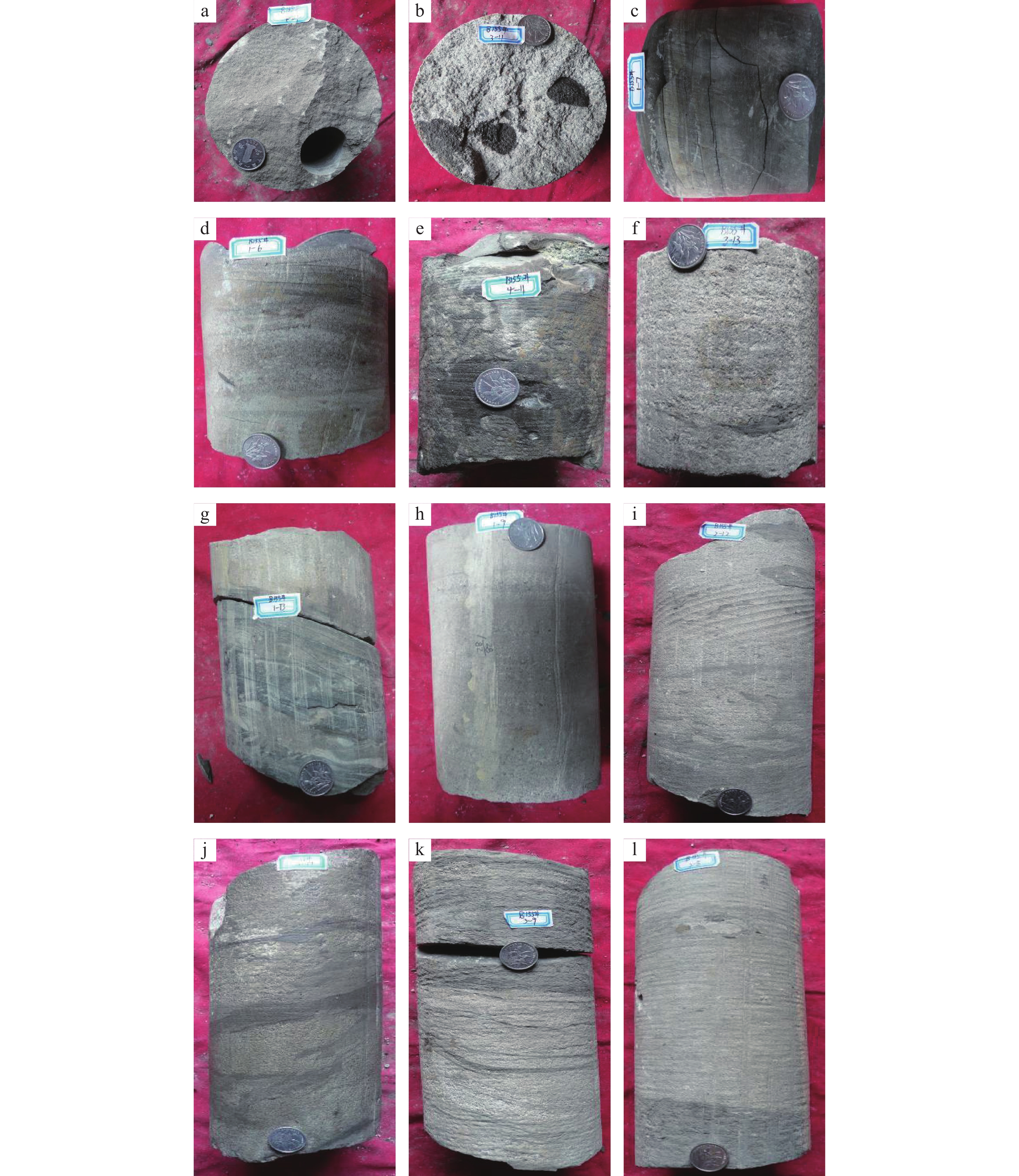
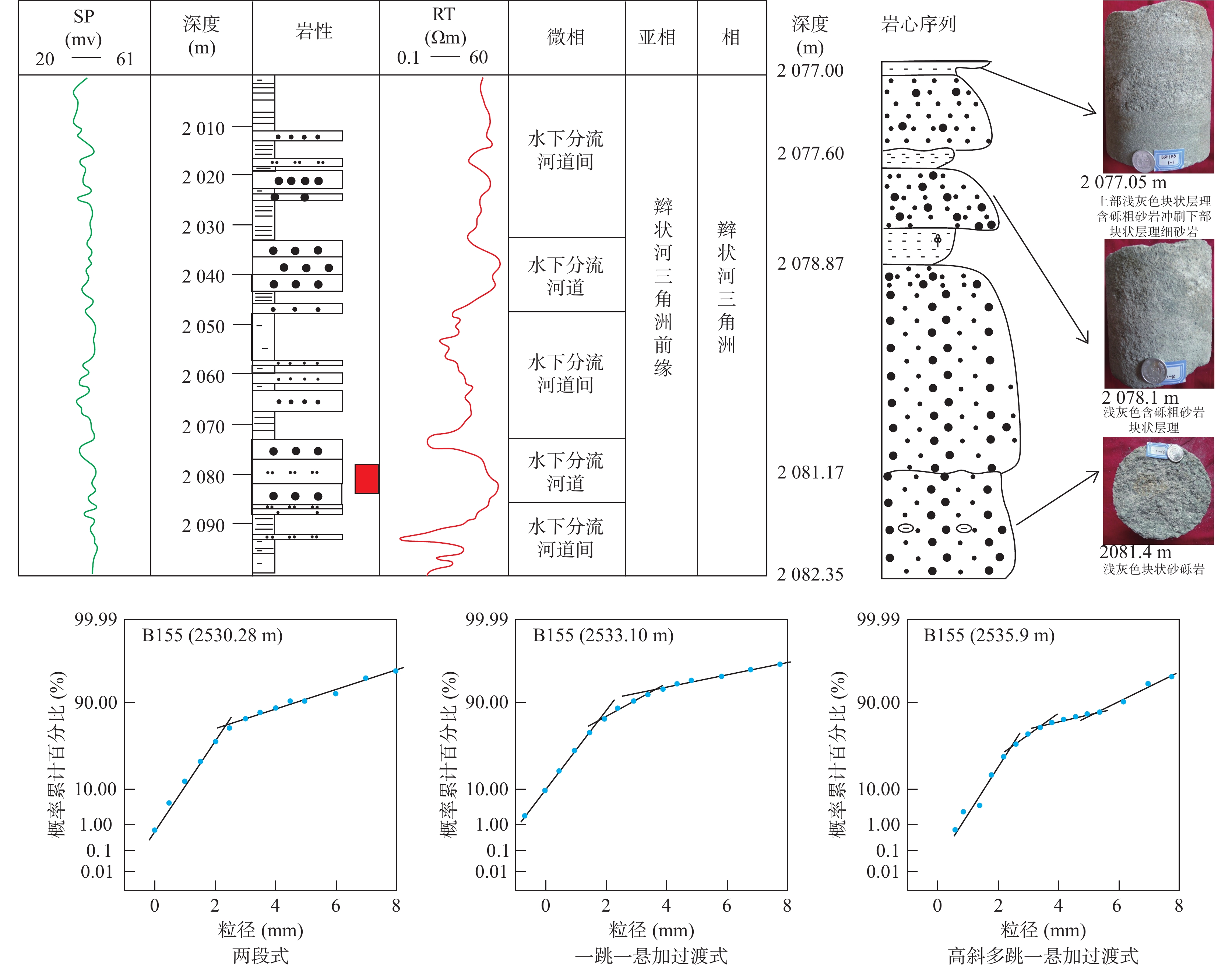
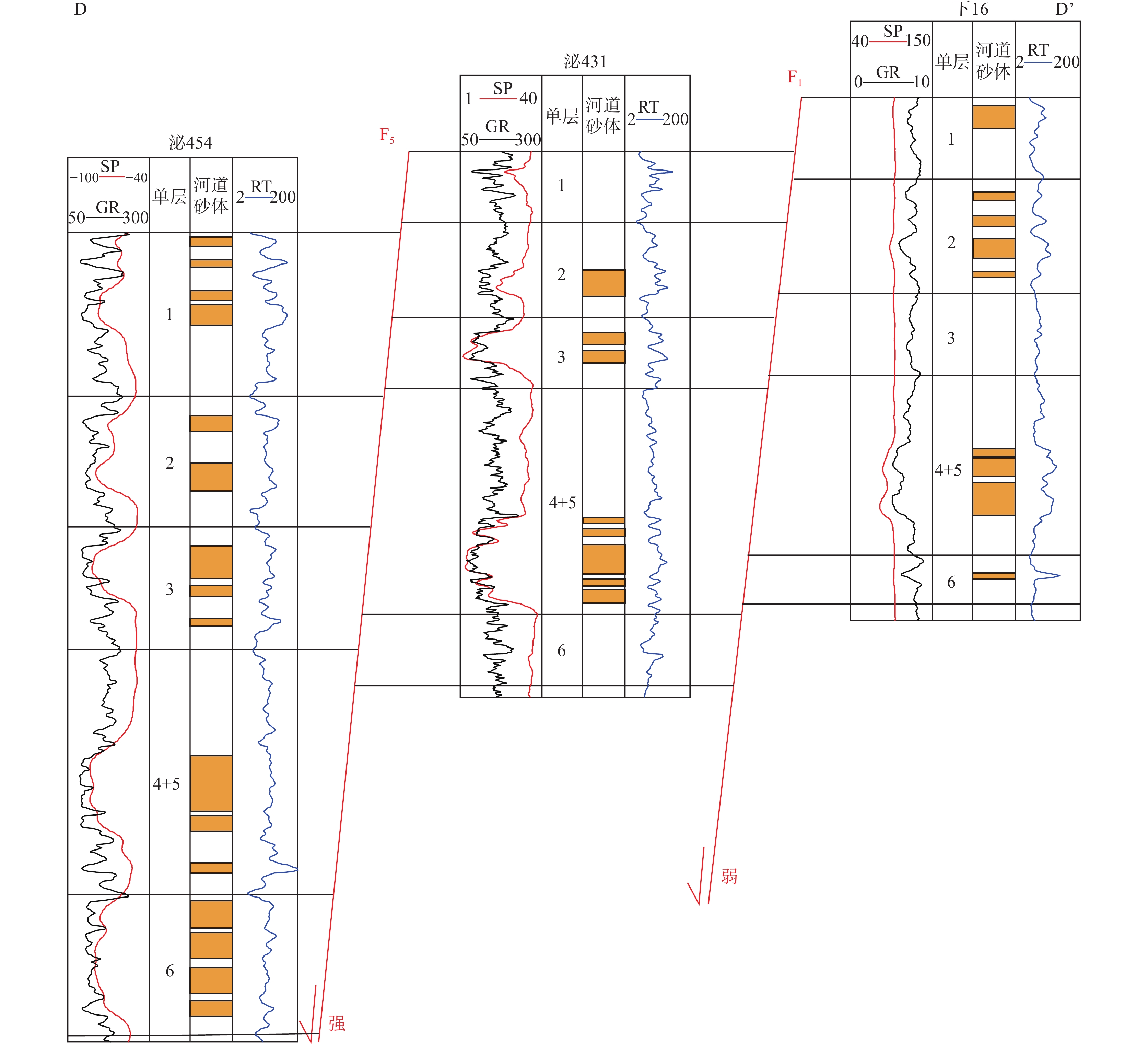
图 7 下二门地区单井相图及水下分流河道砂体粒度曲线图(据廖纪佳等,2012修改)
Figure 7.
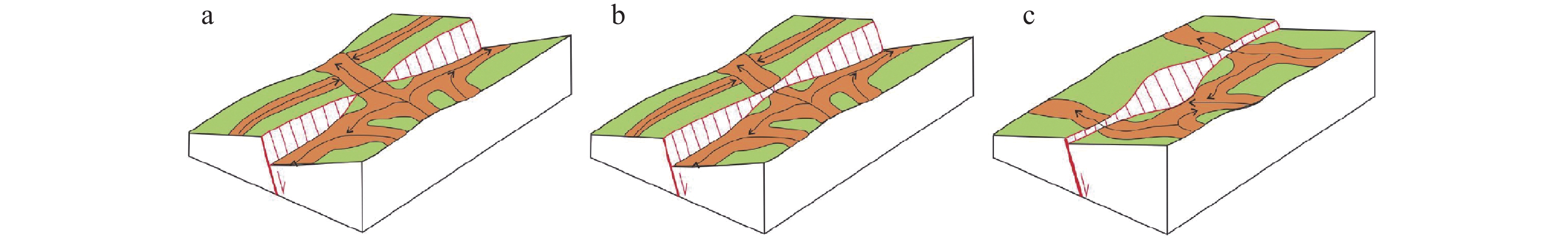
图 11 下二门地区河道砂体过生长断层前后样式图(据窦鲁星等,2020修改)
Figure 11.
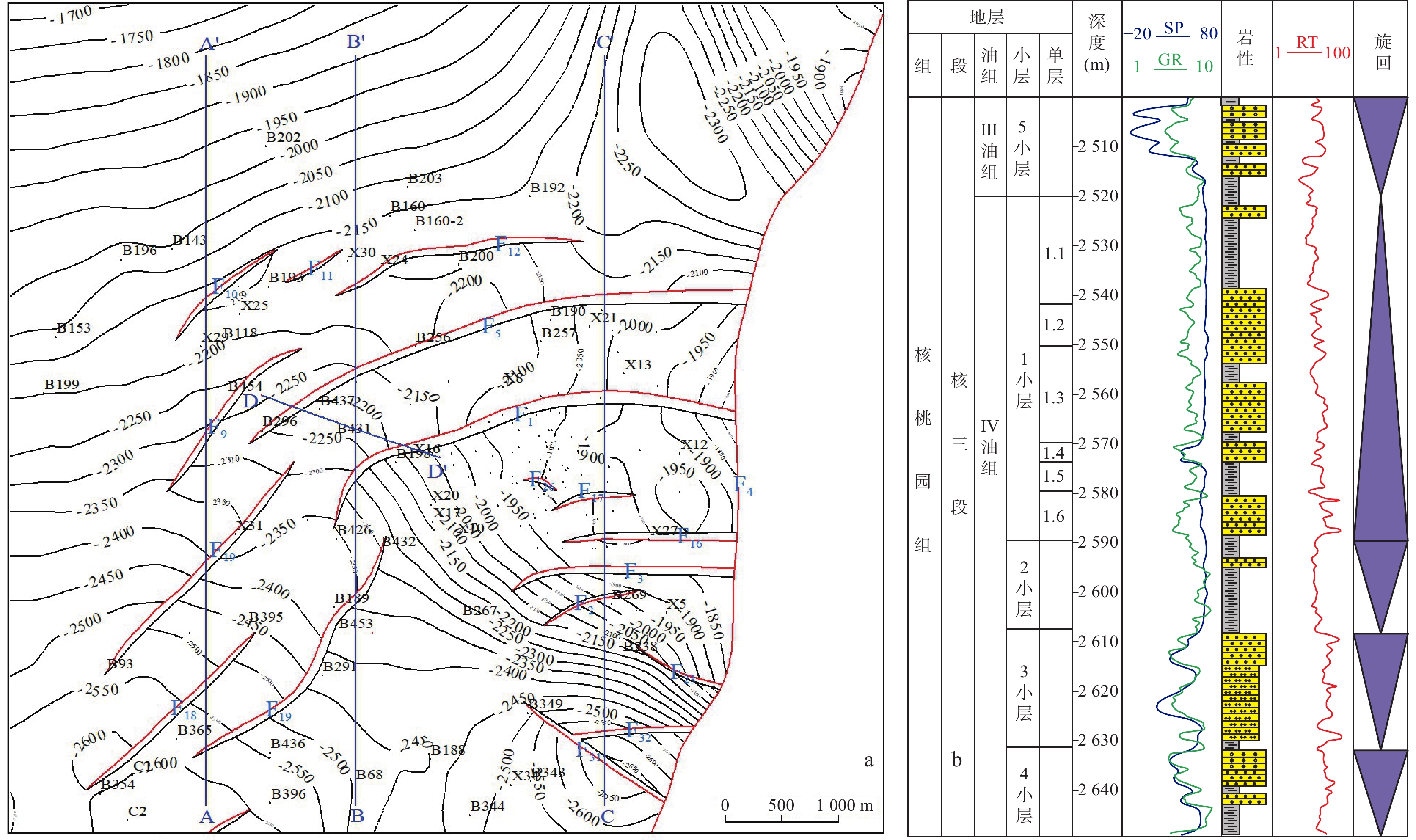
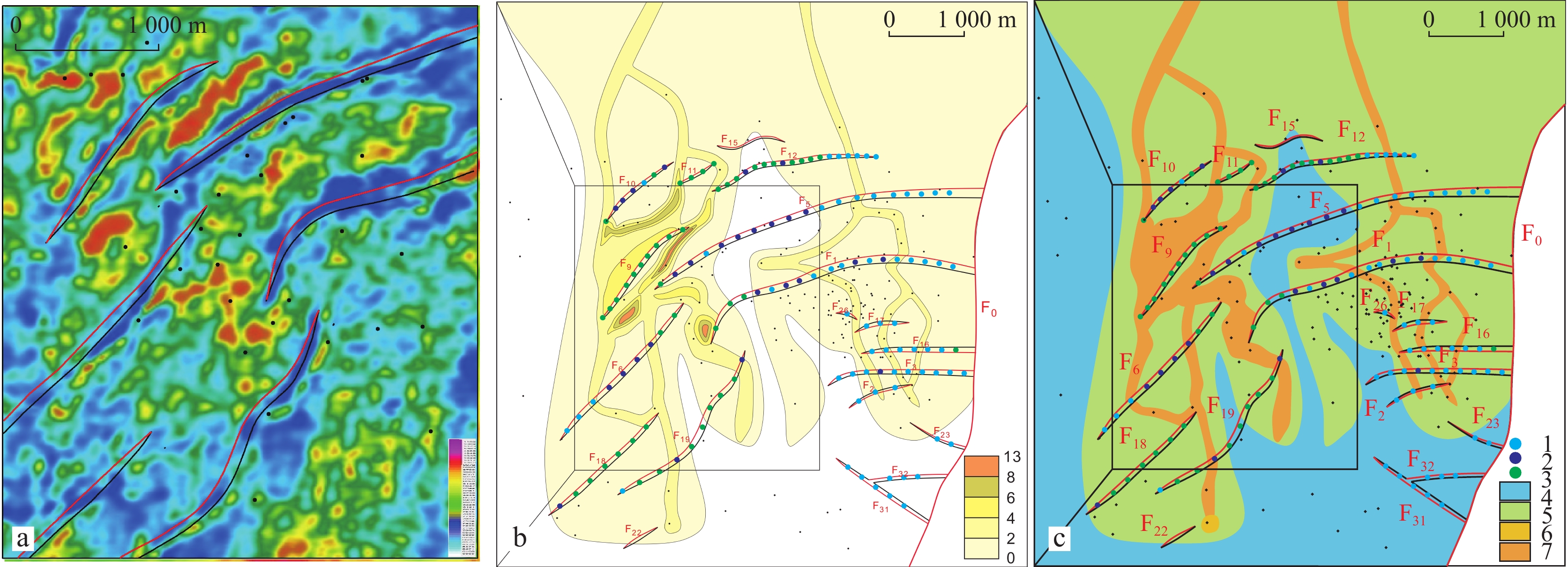
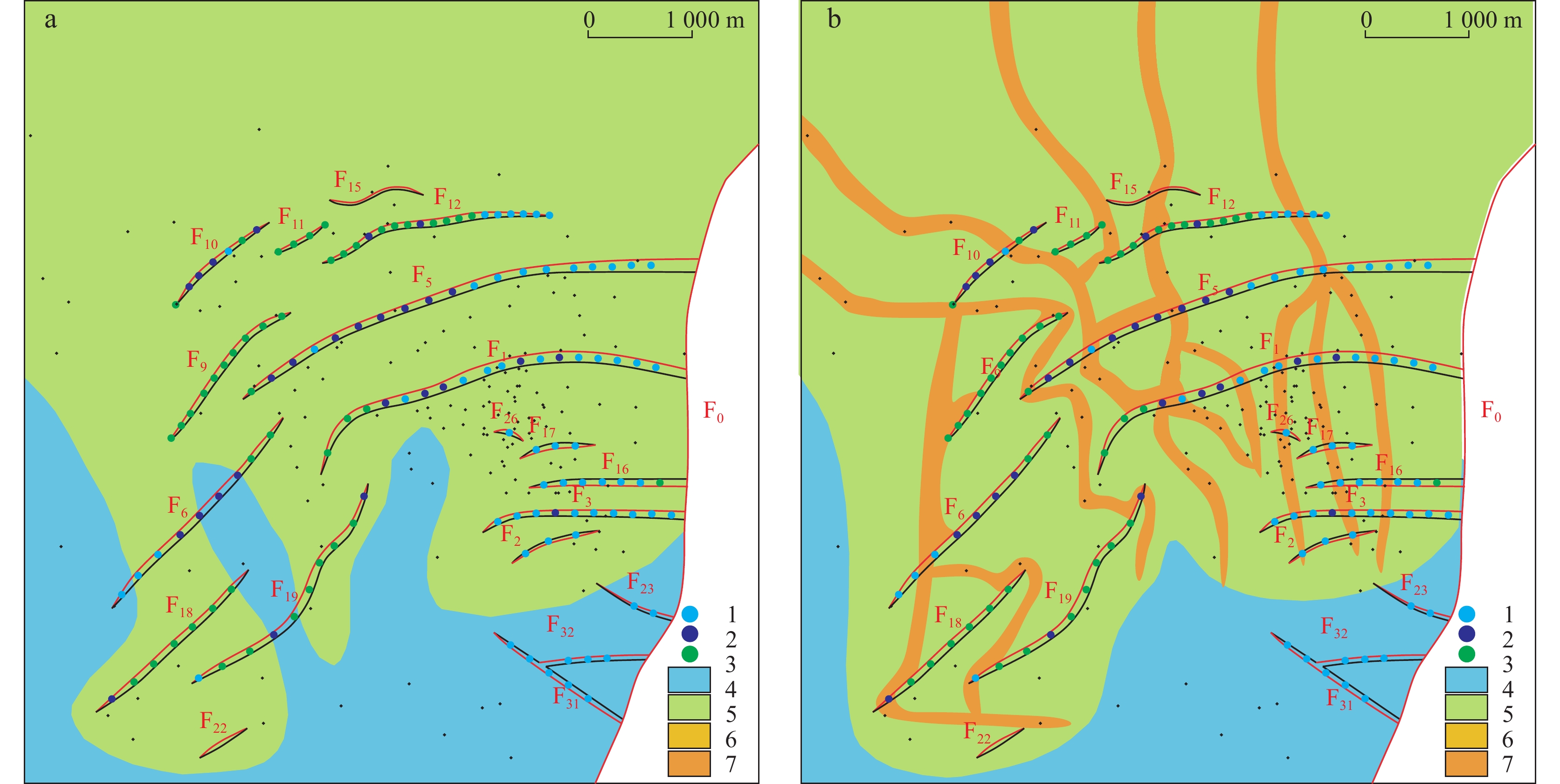
表 1 下二门地区Eh3Ⅳ油组生长断层要素统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of growth fault elements of Eh3Ⅳ in Xiaermen area
序号 断层编号 走向 倾向 延伸长度(km) 古落差(m) 断层级别 1 F1 NEE−SWW NNW 4.4 10~140 Ⅲ 2 F5 NEE−SWW NNW 4.9 10~120 Ⅲ 3 F6 NE−SW NW 2.7 10~80 Ⅳ 4 F9 NE−SW NW 2.5 10~60 Ⅳ 5 F10 NE−SW NW 1.8 10~40 Ⅳ 6 F11 NE−SW NW 0.9 10~20 Ⅴ 7 F12 NEE−SWW NNW 2.9 10~50 Ⅳ 8 F18 NE−SW NW 4.3 10~60 Ⅳ 9 F19 NE−SW NW 2.8 10~20 Ⅳ -
[1] 蔡佳, 罗家群, 甘华军, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷隐蔽油气藏模式与富集规律[J]. 石油实验地质, 2009, 31(3): 244-248 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.03.007
CAI Jia, LUO Jiaqun, GAN Huajun, et al. Accumulation pattern and enrichment laws of subtle hydrocarbon reservoirs in Biiyang Sag, Nanxiang Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2009, 31(3): 244-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.03.007
[2] 陈亮, 王华, 韩晋阳, 等. 泌阳凹陷下二门地区南部核三上亚段层序地层特征及地层-岩性圈闭预测[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2006, (1): 26-31 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.01.006
CHEN Liang, WANG Hua, HAN Jinyang, et al. Sequence stratigraphy and stratum-lithology trap prediction of the Eh3 upper member of Hetaoyuan Formation in south Xia’ermen Oilfield, Biyang Sag[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2006, (1): 26-31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.01.006
[3] 陈哲, 张昌民, 侯国伟, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组断层组合样式及其控砂机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 31(2): 824-837 doi: 10.11743/ogg20200415
CHEN Zhe, ZHANG Changmin, HOU Guowei, et al. Fault distribution patterns and their control on sand bodies in Pinghu Formation of Xihu Sag in East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 31(2): 824-837. doi: 10.11743/ogg20200415
[4] 董进, 张世红, 姜永彪. 正断层位移长度关系及其研究意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(4): 575-584 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.04.024
DONG Jin, ZHANG Shihong, JIANG Yongbiao. The displacement-length relationship of faults and its significance[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(4): 575-584. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.04.024
[5] 董艳蕾, 朱筱敏, 耿晓洁, 等. 泌阳凹陷东南部核桃园组近岸水下扇与扇三角洲沉积特征比较及控制因素分析[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(2): 271-279 doi: 10.11743/ogg20150212
DONG Yanlei, ZHU Xiaomin, GENG Xiaojie, et al. Sedimentary characteristics comparison and controlling factors analyses of nearshore subaqueous fan and fan delta in the Hetaoyuan Formation of southeastern Biyang Sag[J]. Oil&Gas Geology, 2015, 36(2): 271-279. doi: 10.11743/ogg20150212
[6] 窦鲁星, 候加根, 张莉, 等. 断陷湖盆同生断层发育区三角洲砂体分布模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(3): 534-546 doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.03.09
DOU Luxing, HOU Jiagen, ZHANG Li, et al. Distribution pattern of deltaic sand bodies controlled by syn-depositional faults in a rift lacustrine basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(3): 534-546. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.03.09
[7] 李勤英, 罗凤芝, 苗翠芝. 断层活动速率研究方法及应用探讨[J]. 断块油气田, 2000, 7(2): 15-17
LI Qinying, LUO Fengzhi, MIAO Cuizhi. Research on fault activity ratio and its application[J]. Fault-block Oil&Gas Field, 2000, 7(2): 15-17.
[8] 李占东, 刘秋宏, 李丽, 等. 同生断裂传递带控砂研究—以海拉尔盆地乌尔逊-贝尔凹陷为例[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2016, 31(2): 537-544
LI Zhandong, LIU Qiuhong, LI Li, et al. Study of the syngenetic fracture transfer zone sand control—take Urxun-Beir depression in Hailar basin for example[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2016, 31(2): 537-544.
[9] 李智, 岳欣欣, 杨云飞, 等. 泌阳凹陷栗园地区基岩油藏石油地质特征[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(5): 343−350.
LI Zhi, YUE Xinxin, YANG Yunfei, et al. Petroleum Geological Characteristics of Base Rock Pools in Liyuan Area, Biyang Depression[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(5): 343−350.
[10] 李智, 张志业, 何登发, 等. 南阳凹陷边界断层三维几何学及运动学特征[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2020a, 42(5): 48-62
LI Zhi, ZHANG Zhiye, HE Dengfa, et al. 3D Geometrical and Kinematic Characteristics of the Boundary Fault in Nanyang Depression[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science&Technology Edition), 2020a, 42(5): 48-62.
[11] 李智, 张志业, 何登发, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷与南阳凹陷油气地质特征类比及勘探启示[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020b, 39(2): 74-84
LI Zhi, ZHANG Zhiye, HE Dengfa, et al. Comparison in petroleum geology between Biyang Depression and Nanyang Depression in Nanxiang Basin and its exploration significance[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020b, 39(2): 74-84.
[12] 李智, 张志业, 何登发, 等. 唐河-栗园-泌阳断层的几何学和运动学特征—兼论桐柏造山带与泌阳凹陷的盆-山关系[J]. 地质科学, 2020c, 55(3): 921-938
LI Zhi, ZHANG Zhiye, HE Dengfa, et al. Geometry and kinematics of the Tanghe-Liyuan-Biyang fault and its implication on the relationship between Tongbai orogenic belt and Biyang Depression[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2020c, 55(3): 921-938.
[13] 李智, 张志业, 李双建, 等. 南襄盆地地质结构与形成演化[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(2): 116-127
LI Zhi, ZHANG Zhiye, LI Shuangjian, et al. Geological Architecture and Tectonic Evolution of Nanxiang Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(2): 116-127.
[14] 廖纪佳, 朱筱敏, 董艳蕾, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷深凹区核三段沉积特征及演化[J]. 地球学报, 2012, 33(2): 167-175
LIAO Jijia, ZHU Xiaomin, DONG Yanlei, et al. Sedimentary Characteristics and Evolution of He-3 Formation in Deep Area of Biyang Sag, Nanxiang Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 167-175.
[15] 刘玉虎, 曹春辉, 李瑞磊, 等. 边界断裂时空差异演化对断陷盆地的控制作用—以松辽盆地南部伏龙泉断陷为例[J]. 地球科学进展, 2020, 35(1): 79-87 doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2020.009
LIU Yuhu, CAO Chunhui, LI Ruilei, et al. The control of the spatial and temporal differential evolution of boundary faults on faulted basins—Taking the Fulongquan fault depression in the Southern Songliao Basin as an example[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2020, 35(1): 79-87. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2020.009
[16] 卢异, 王书香, 陈松, 等. 一种断裂活动强度计算方法及其应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2010, 21(4): 612-616
LU Yi, WANG Shuxiang, CHEN Song, et al. Computing method about idtensity of fault activity and its application[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2010, 21(4): 612-616.
[17] 王苗, 黄传炎, 左宗鑫, 等. 同沉积生长断层的控砂作用研究—以北部湾福山凹陷永安-白莲地区流沙港组一段为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(2): 194-205 doi: 10.11781/sysydz201402194
WANG Miao, HUANG Chuanyan, ZUO Zongxin, et al. Controls of synsedimentary faults on sedimentary filling of 1st member of Liushagang Formation in Yongan-Bailian areas in Fushan Sag, Beibuwan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2014, 36(2): 194-205. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201402194
[18] 王燮培, 费琪, 张家骅. 石油勘探构造分析[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1990: 68-78
WANG Xiepei, FEI Qi, ZHANG Jiahua. Structural analysis of petroleum exploration[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1990: 68-78.
[19] 谢通, 黄传炎, 张宏伟, 等. 霸县凹陷断坳转换期同沉积断裂的特征及对砂体的控制作用[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 30(6): 1-9.
XIE Tong, HUANG Chuanyan, ZHANG Hongwei, et al. Characteristics of syndepositional faults in Baxian Sag and control effects of them on sand bodies in the fault-depression transition period[J]. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition), 2015, 30(6): 1-9.
[20] 杨晓利, 张自力, 孙明, 等. 同沉积断层控砂模式—以南堡凹陷南部地区Es1段为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(4): 526-533 doi: 10.11743/ogg20140412
YANG Xiaoli, ZHANG Zili, SUN Ming, et al. Models of contemporaneous fault controlling sandstone deposition: a case study of Es1in southern Nanpu Sag[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(4): 526-533. doi: 10.11743/ogg20140412
[21] 张建光, 姚光庆, 陈亚兵, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷深水湖底扇厘定及碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学物源追踪[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2011, 36(6): 1105-1118
ZHANG Jianguang, YAO Guangqing, CHEN Yabing, et al. Sub-Lacustrine Fan of Chengdian and Zircon U-Pb Ages and Constraint on Its Provenance in Biyang Depression, Nanxiang Basin, China[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geoscience, 2011, 36(6): 1105-1118.
[22] 赵勇, 戴俊生. 应用落差分析研究生长断层[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(3): 13-15 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2003.03.004
ZHAO Yong, DAI Junsheng. Identification of growth fault by fault fall analysis[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(3): 13-15. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2003.03.004
[23] 朱筱敏, 董艳蕾, 胡廷惠, 等. 精细层序地层格架与地震沉积学研究—以泌阳凹陷核桃园组为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(4): 615-624 doi: 10.11743/ogg20110416
ZHU Xiaomin, DONG Yanlei, HU Tinghui, et al. Seismic sedimentology study of fine sequence stratigraphic framework: a case study of the Hetaoyuan Formation in the Biyang Sag[J]. Oil&Gas Geology, 2011, 32(4): 615-624. doi: 10.11743/ogg20110416
[24] DUFFY O B, BELL R E, JACKSON C A L, et al. Fault growth and interactions in a multiphase rift fault network: Horda Platform, Norwegian North Sea[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2015, 80: 99-119. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2015.08.015
[25] HARDIN F R, HARDIN G C. Contemporaneous normal faults of gulf coast and their relation to flexures[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1961, 45(2): 238-248.
[26] MULROONEY M J, RISMYHR B, YENWONGFAI H D, et al. Impacts of small-scale faults on continental to coastal plain deposition: Evidence from the Realgrunnen Subgroup in the Goliat field, southwest Barents Sea, Norway[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 95: 276-302. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.04.023
-




 下载:
下载: