Geochronology, Isotopic Geochemistry of Diorite Porphyrite in Tianming Gold Deposit, Hunan
-
摘要:
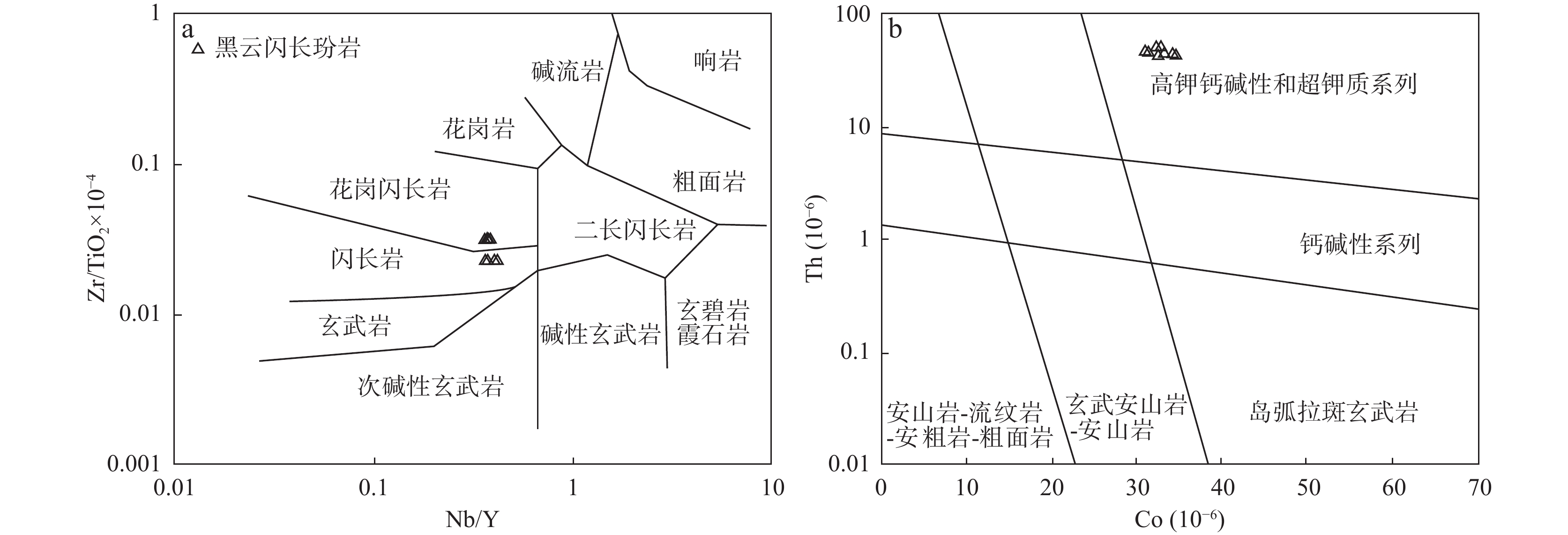
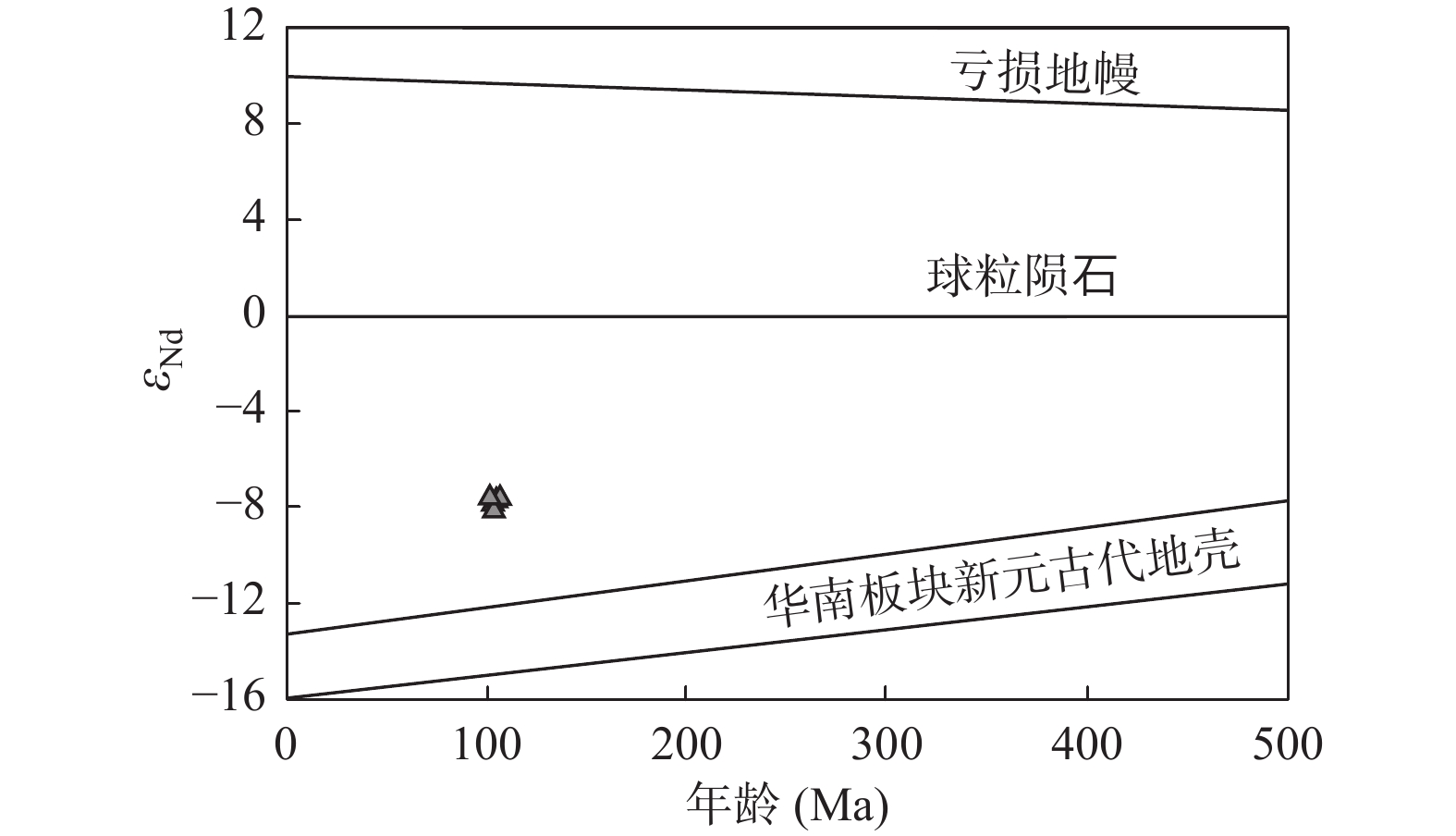
湖南安化天明金矿区的勘查工作中,岩芯揭露隐伏云斜煌斑岩。为探讨脉岩与成矿关系,对云斜煌斑岩开展岩石学、LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb年代学、全岩主微量元素和Sr−Nd同位素组成研究。结果显示,云斜煌斑岩遭受强烈的碳酸盐化蚀变;成岩时代不早于104 Ma,可能是晚燕山期华南构造–岩浆事件的响应;(418.79±1.57)Ma与(2506±14)Ma两组谐和年龄分别记录了志留纪扬子地块华夏诸岛弧陆弧碰撞以及太古宙地壳初始大规模增生,表明基底物质来源于上述2次地质事件。云斜煌斑岩属高钾钙碱性系列,轻稀土元素(LREE)富集、重稀土元素(HREE)亏损,具有明显的Eu负异常和Ce正异常;大离子亲石元素和高场强元素亏损,相容元素含量高;全岩εNd(t)=−8.28~−7.61表明壳幔混源;认为云斜煌斑岩由地幔岩浆在源区残留角闪石、钛铁矿和/或金红石,经历以斜长石为主的分离结晶,并受地壳混染,最终在近EW向断裂中侵位形成。对比湘中地区脉岩,赋矿地层,地壳Au、Sb含量,暗示脉岩与锑可能具有深部同源性,天明矿床具有锑成矿潜力。
Abstract:The exploration in the Tianming Mining Area, Anhua, Hunan, has uncovered the concealed mica−plagioclase lamprophyre. In order to study the relationship between the dike and mineralization, we conducted various studies including petrographic, LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Pb chronology, whole−rock major and trace elements and Sr−Nd isotope composition analyses on the mica-plagioclase lamprophyre. The results indicate that the mica−plagioclase lamprophyre underwent significant carbonate alteration. The diagenesis age is estimated to be no earlier than 104 Ma and may be a response to the Late Yanshanian tectonic−magmatic events in South China Block. The concordant ages of (418.79±1.57) Ma and (2506±14 )Ma document the events of Silurian arc−crust collision of the Yangtze plate and the Cathaysia island arc, and Archaean crustal accretion, respectively, indicating the crystal basement material source. The mica−plagioclase lamprophyre belongs to a high−K calcium−alkaline series with an enriched light rare−earth element (LREE) and depleted heavy rare−earth element (HREE), with Eu negative anomalies and Ce positive anomalies. The rock also has large ionic lithophile and high−field strength elements depleted and high compatible element content. Whole−rock εNd(t) values ranging from −8.28 to −7.61 suggest crust−mantle mixing. Our findings suggest that the mica−plagioclase lamprophyre was formed by mantle magma in the source area with residual hornblende, ilmenite, and/or rutile. It underwent fractional crystallization dominant of plagioclase, was mixed by crust, and finally intruded in near−EW faulting tectonics. Comparison of the Au and Sb contents of dikes in central Hunan, ore−bearing formation, and crust, implies that the dikes and antimony may have deep homology. These findings suggest that the Tianming deposit has antimony mineralization potential. Overall, the study highlights the complex geological processes that lead to the formation of mineral deposits. By using a multidisciplinary approach, it is able to unravel the complex history of the mica−plagioclase lamprophyre and its association with mineralization. These findings can provide valuable insights for future exploration activities in the region.
-

-
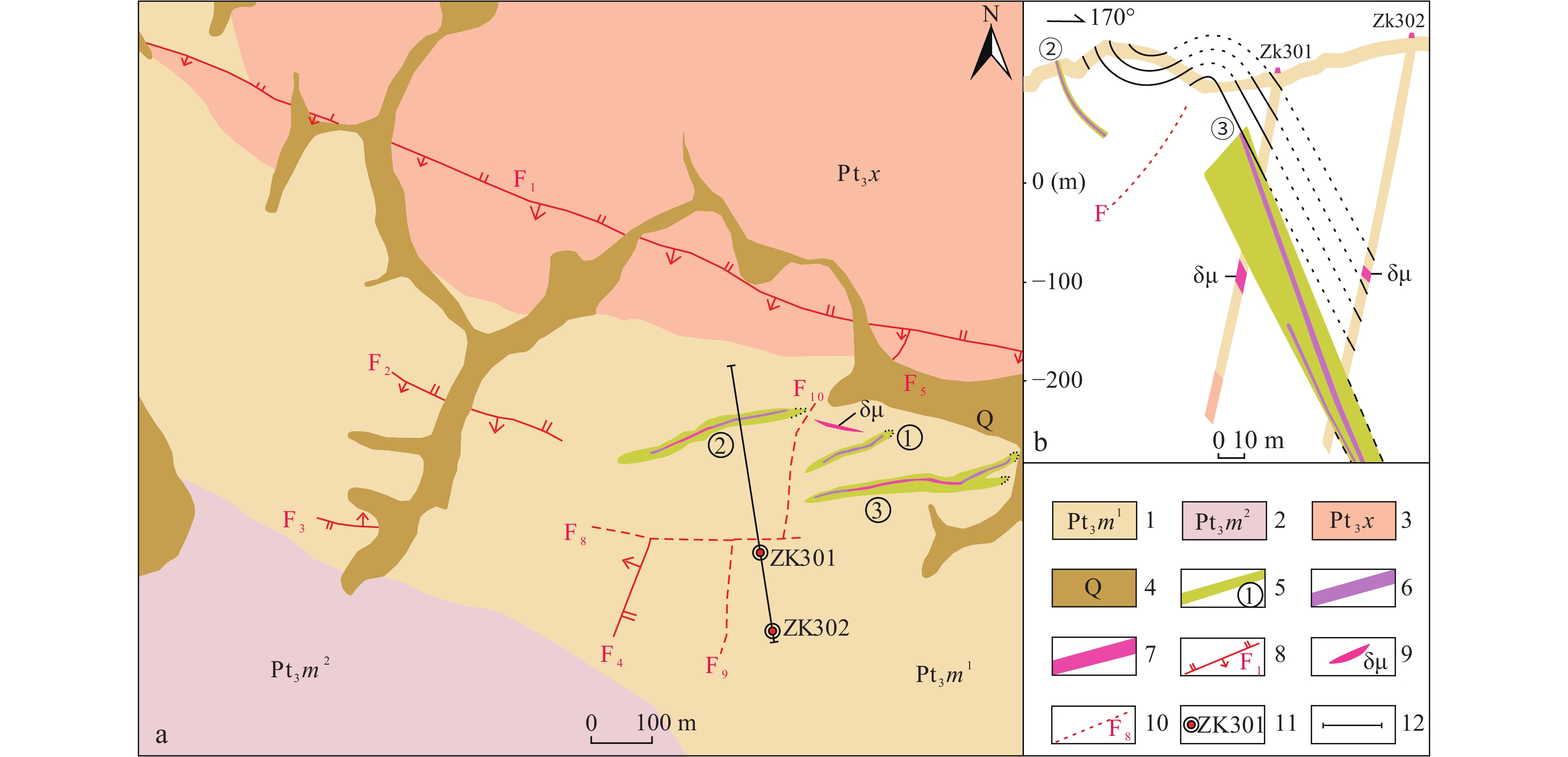
图 1 大地构造位置图(a)(Chen et al.,1998)及雪峰弧形构造带地质简图(b)(权正钰等,1997)
Figure 1.
图 6 湖南天明金矿区云斜煌斑岩原始地幔标准化微量元素标准化蛛网图(a)及球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图(b)(标准化数据来自Sun et al.,1989)
Figure 6.
图 7 湖南天明金矿区云斜煌斑岩(La/Yb)N–δEu(a)及La/Sm–La二元图解(b)(Davidson et al.,2007)
Figure 7.
图 8 湖南天明金矿区云斜煌斑岩εNd(t)–年龄(Ma)判别图解(Zindler et al.,1986)
Figure 8.
表 1 湖南天明金矿区云斜煌斑岩锆石U−Pb同位素数据表
Table 1. Zircon U−Pb isotopic datas of the mica−plogioclase lamprophyre in Tianming gold deposit, Hunan
编号 质量分数(10−6) Th/U 同位素比值 年龄 (Ma) 谐和 Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ TM21 1 106 533 404 1.32 0.1800 0.0052 3.7899 0.1342 0.1489 0.0013 2654 47 1591 28 895 7 43% 2 193 2244 3797 0.59 0.3190 0.0057 1.0642 0.0153 0.0242 0.0003 3565 28 736 8 154 2 −31% 3 8 274 214 1.28 0.0499 0.0030 0.1759 0.0086 0.0257 0.0006 191 143 165 7 163 4 99% 4 41 2406 1353 1.78 0.0488 0.0011 0.1314 0.0031 0.0195 0.0002 139 54 125 3 124 2 99% 5 103 28 274 0.10 0.1127 0.0022 5.2517 0.1000 0.3370 0.0050 1843 37 1861 16 1872 24 99% 6 18 981 780 1.26 0.0485 0.0015 0.1084 0.0033 0.0162 0.0002 120 69 104 3 104 1 99% 7 88 581 1035 0.56 0.0560 0.0007 0.5449 0.0064 0.0704 0.0006 454 23 442 4 439 3 99% 8 9 241 277 0.87 0.1029 0.0026 0.3063 0.0078 0.0215 0.0003 1677 45 271 6 137 2 34% 9 250 242 468 0.52 0.1423 0.0015 8.3904 0.0960 0.4265 0.0042 2255 17 2274 10 2290 19 99% 10 80 795 875 0.91 0.0993 0.0031 0.8707 0.0272 0.0633 0.0005 1613 62 636 15 395 3 53% 11 92 91 421 0.22 0.1856 0.0041 3.6580 0.0866 0.1420 0.0013 2706 3 1562 19 856 7 41% 12 88 122 123 0.99 0.1780 0.0039 12.2904 0.2084 0.4985 0.0064 2635 37 2627 16 2607 27 99% 13 47 150 220 0.68 0.0744 0.0013 1.7906 0.0262 0.1741 0.0016 1052 35 1042 10 1035 9 99% 14 234 65 882 0.07 0.1225 0.0015 3.9590 0.0637 0.2337 0.0038 1994 23 1626 13 1354 20 81% 15 20 391 385 1.02 0.0509 0.0015 0.2724 0.0076 0.0387 0.0005 239 69 245 6 245 3 99% 16 104 390 769 0.51 0.2121 0.0069 2.2918 0.0916 0.0774 0.0009 2922 53 1210 28 481 5 13% 17 12 273 261 1.05 0.0500 0.0021 0.2327 0.0094 0.0337 0.0005 198 101 212 8 213 3 99% 18 28 297 515 0.58 0.0894 0.0018 0.5082 0.0100 0.0410 0.0004 1413 37 417 7 259 2 53% 19 22 1 0 23.02 0.8456 0.0181 7994.8204 817.3634 70.2138 7.1622 – – 9125 104 27498 649 −1% 20 92 1750 1740 1.01 0.0704 0.0011 0.3662 0.0059 0.0378 0.0005 943 31 317 4 239 3 72% 21 43 1319 727 1.81 0.0986 0.0036 0.4829 0.0210 0.0347 0.0003 1598 68 400 14 220 2 41% 22 59 176 106 1.67 0.1251 0.0019 6.3110 0.0902 0.3639 0.0030 2031 26 2020 13 2001 14 99% 23 294 126 541 0.23 0.1563 0.0017 9.8478 0.1103 0.4542 0.0042 2417 19 2421 10 2414 19 99% 24 77 296 1737 0.17 0.0696 0.0013 0.3756 0.0066 0.0389 0.0003 917 38 324 5 246 2 72% 25 38 92 158 0.58 0.0796 0.0016 2.1954 0.0450 0.1993 0.0024 1187 41 1180 14 1172 13 99% 26 195 130 334 0.39 0.1657 0.0024 10.8713 0.1651 0.4736 0.0060 2515 24 2512 14 2499 26 99% 27 237 56 421 0.13 0.1640 0.0016 10.7716 0.1076 0.4740 0.0037 2498 16 2504 9 2501 16 99% 28 100 66 169 0.39 0.1629 0.0019 10.7176 0.1190 0.4760 0.0050 2487 19 2499 10 2510 22 99% 29 109 160 164 0.98 0.1588 0.0019 10.4792 0.1097 0.4762 0.0042 2444 16 2478 10 2511 18 98% 30 64 95 96 0.99 0.1616 0.0020 10.6353 0.1282 0.4754 0.0041 2473 21 2492 11 2507 18 99% 31 202 259 315 0.82 0.1593 0.0021 10.4939 0.1208 0.4759 0.0044 2448 22 2479 11 2509 19 98% 32 5 55 81 0.69 0.0530 0.0039 0.3625 0.0248 0.0502 0.0012 328 165 314 18 316 8 99% 33 82 87 132 0.66 0.1647 0.0020 10.8166 0.1372 0.4745 0.0046 2506 20 2507 12 2503 20 99% 34 67 448 441 1.02 0.0614 0.0007 0.9597 0.0139 0.1126 0.0011 654 26 683 7 688 6 99% 35 57 130 220 0.59 0.1311 0.0028 3.2645 0.1028 0.1762 0.0028 2113 37 1473 24 1046 15 66% 36 4 59 60 0.98 0.0925 0.0048 0.5158 0.0259 0.0409 0.0008 1480 98 422 17 259 5 51% 续表1 编号 质量分数(10-6) Th/U 同位素比值 年龄 (Ma) 谐和 Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 37 4 48 63 0.76 0.0523 0.0045 0.3246 0.0271 0.0453 0.0011 298 196 285 21 286 7 99% 38 3 41 47 0.88 0.0900 0.0052 0.5158 0.0298 0.0419 0.0008 1426 105 422 20 264 5 54% 39 2 58 65 0.88 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0207 0.0043 – – – – 132 27 – 40 3 37 38 0.97 0.1566 0.0100 1.1008 0.0553 0.0523 0.0015 2419 109 754 27 329 9 21% 41 3 46 56 0.82 0.0409 0.0081 0.2857 0.0617 0.0408 0.0008 – – 255 49 258 5 99% 42 15 147 180 0.82 0.0751 0.0030 0.6367 0.0247 0.0614 0.0005 1072 80 500 15 384 3 73% 43 4 56 63 0.88 0.0541 0.0025 0.3209 0.0134 0.0440 0.0007 376 73 283 10 277 4 98% 44 4 55 64 0.86 0.0552 0.0058 0.3235 0.0315 0.0433 0.0021 420 235 285 24 273 13 95% 45 207 179 367 0.49 0.1489 0.0015 8.9746 0.1285 0.4357 0.0048 2333 17 2335 13 2332 22 99% 46 23 460 500 0.92 0.0509 0.0010 0.2433 0.0054 0.0346 0.0004 239 44 221 4 219 3 99% 47 51 313 633 0.49 0.0568 0.0012 0.5228 0.0130 0.0664 0.0009 483 44 427 9 414 5 97% 48 29 287 303 0.95 0.0900 0.0029 0.8106 0.0277 0.0650 0.0008 1428 61 603 16 406 5 60% 49 42 137 473 0.29 0.1089 0.0025 0.9740 0.0229 0.0645 0.0005 1781 41 691 12 403 3 47% 50 37 108 512 0.21 0.0535 0.0010 0.5045 0.0151 0.0680 0.0016 350 43 415 10 424 9 97% 51 51 311 592 0.53 0.0696 0.0012 0.6536 0.0118 0.0680 0.0011 917 37 511 7 424 6 81% 52 41 174 512 0.34 0.0612 0.0011 0.5675 0.0101 0.0670 0.0007 656 39 456 7 418 4 91% 53 72 684 746 0.92 0.0735 0.0012 0.7183 0.0197 0.0700 0.0012 1028 33 550 12 436 7 76% 54 34 270 398 0.68 0.0557 0.0008 0.5147 0.0074 0.0668 0.0005 439 31 422 5 417 3 98% 55 82 459 1023 0.45 0.0550 0.0008 0.5114 0.0094 0.0671 0.0008 409 33 419 6 419 5 99% 56 28 119 354 0.34 0.0551 0.0009 0.5155 0.0085 0.0676 0.0006 417 32 422 6 421 4 99% 57 33 305 349 0.87 0.0558 0.0009 0.5210 0.0085 0.0674 0.0006 443 35 426 6 420 4 98% 58 92 413 1187 0.35 0.0557 0.0007 0.5309 0.0080 0.0689 0.0008 443 32 432 5 429 5 99% 表 2 湖南天明金矿区云斜煌斑岩全岩地球化学数据表
Table 2. Whole−rock geochemical data of the mica−plogioclase lamprophyre in Tianming gold deposit, Hunan
样品号 TM2102 TM2103 TM2104 TM2105 TM2106 TM2107 TM2108 TM2109 SiO2 43.31 43.27 46.31 46.23 47.67 47.65 44.05 44.11 主量元素 TiO2 0.84 0.81 0.84 0.84 0.84 0.87 0.72 0.74 Al2O3 12.76 12.74 11.9 11.89 11.58 11.59 10.88 10.9 Fe2O3 0.27 0.28 0.32 0.28 0.56 0.54 0.62 0.54 FeO 6.59 6.51 5.83 5.86 5.43 5.37 5.78 5.81 MnO 0.12 0.12 0.11 0.11 0.11 0.11 0.13 0.13 MgO 7.4 7.38 7.03 7.05 7.1 7.1 7.55 7.53 CaO 6.64 6.64 6.8 6.8 6.26 6.27 7.91 7.91 Na2O 1.03 1.03 0.84 0.83 2.04 2.12 0.98 0.97 K2O 1.09 1.1 1.01 0.99 0.79 0.8 1.35 1.35 P2O5 0.4 0.41 0.39 0.38 0.39 0.39 0.4 0.4 LOI 18.92 18.94 17.98 18.08 16.62 16.59 18.99 18.98 Total 99.37 99.23 99.36 99.34 99.39 99.4 99.36 99.37 微量元素 Cr 354 354 532 524 711 701 618 640 Co 32.7 33.7 31.8 31.1 33.8 33.3 34.4 34.8 Ni 130 133 129 129 194 196 163 163 V 151 153 152 147 135 132 145 147 Rb 57.3 62.5 105.2 92.7 118.5 124.3 86.5 96.2 Sr 645 660 746 753 890 865 722 734 Ba 227 234 501 507 395 390 3030 3070 Nb 8.08 8 7.92 7.84 7.06 6.94 6.67 6.95 Ta 0.59 0.58 0.56 0.55 0.52 0.49 0.52 0.48 Zr 224 228 206 209 199 197 190 195 Hf 6.35 6.39 5.9 5.96 5.85 5.76 5.5 5.64 U 5.75 5.87 5.4 5.39 4.85 4.78 5.11 5.13 Th 58 59.2 52.4 52.7 51.4 50.5 49.7 50.2 La 132 134 116 119 118 115 112 113 Ce 328 328 287 289 289 281 279 283 Pr 29.6 30.1 25.8 26.5 26.4 25.6 25.7 26.1 Nd 102 104 89.7 91.4 92 90.5 89.9 90.8 Sm 13.4 13.5 11.7 12 11.9 11.5 11.6 11.7 Eu 2.42 2.46 2.24 2.25 2.16 2.1 3.12 3.06 Gd 11.1 11.1 10.1 10.1 9.99 9.66 11.2 11.1 Tb 1.16 1.17 1.04 1.03 1.02 1.01 1.01 1.02 Dy 4.57 4.71 4.29 4.26 4.09 3.99 3.99 4.07 Ho 0.8 0.81 0.74 0.75 0.73 0.69 0.69 0.69 Er 2.36 2.42 2.2 2.2 2.11 2.08 2.1 2.11 Tm 0.31 0.3 0.27 0.28 0.28 0.27 0.26 0.27 Yb 1.93 1.96 1.78 1.79 1.79 1.69 1.69 1.7 Lu 0.28 0.28 0.26 0.26 0.25 0.25 0.24 0.24 Y 21 21.6 19.3 19.5 18.6 18.5 18.3 18.5 F 724 759 872 904 1210 1150 948 928 Ag 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.03 Sb 40.1 40.9 46.3 45.3 10.4 10.3 24.2 25.2 Cu 48.7 48.2 51.1 49.1 52.6 52.2 41.1 42.5 Pb 19.3 19.1 19.7 19.9 23.5 22.9 19.6 20.2 Zn 71 72.7 70 72.4 60.6 59.8 69.4 70.7 W 6.1 6.24 5.9 5.98 3.37 3.37 9.35 9.22 Sn 2.56 2.51 2.21 2.3 2.36 2.13 2.37 2.11 Mo 0.17 0.13 0.4 0.52 0.54 0.46 0.54 0.53 Bi 0.17 0.15 0.18 0.17 0.3 0.3 0.14 0.14 Au(10−9) 1.7 1.21 1.17 1.35 1.04 1.26 2.02 1.75 注:主量元素含量为%;微量元素含量为10−6;LOI=烧失量;ΣREE=稀土元素总量(不含Y);ΣLREE=轻稀土元素(La~Eu)总和;ΣHREE=重稀土元素(Gd~Lu)总和,下标N表示球粒陨石标准化;δEu= 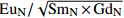 ;Mg#=Mg2+/(Mg2++Fe2+)×100;SiO2归一化=SiO2/(Tot-LOI)×100。
;Mg#=Mg2+/(Mg2++Fe2+)×100;SiO2归一化=SiO2/(Tot-LOI)×100。表 3 湖南天明金矿区云斜煌斑岩Sr–Nd同位素组成表
Table 3. Nb–Sr isotopic compositions of the mica–plogioclase lamprophyre in Tianming gold mining zone, Hunan
样品 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr ±σ ISr 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd INd ±σ εNd(t) TDM(Ga) TM2102 0.2572 0.738758 9 0.73838 0.0794 0.512158 0.512104 3 −7.81 1.13 TM2104 0.4083 0.740174 5 0.73957 0.0789 0.512168 0.512114 9 −7.61 1.11 TM2106 0.3855 0.731196 3 0.73063 0.0782 0.512151 0.512098 4 −7.93 1.12 TM2108 0.3469 0.737261 7 0.73675 0.078 0.512133 0.51208 7 −8.28 1.14 TM2109 0.3795 0.737287 7 0.73673 0.0779 0.512162 0.512109 3 −7.71 1.11 注:表中以t=104 Ma使用Geokit软件计算(路远发,2004),参数含义、计算方法及公式详见路远发等(2021)。 -
[1] 柏道远, 贾宝华, 钟响, 等. 湘中南晋宁期和加里东期构造线走向变化成因[J]. 地质力学学报, 2012, 18: 165-177 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2012.02.007
BAI Daoyuan, JIA Baohua, ZHONG Xiang, et al. Potential genesis of the trending changes of Jinning period and caledonian structural lineamens in middle-Southern Hunan[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2012, 18: 165-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2012.02.007
[2] 柏道远, 李银敏, 钟响, 等. 湖南NW向常德-安仁断裂的地质特征、活动历史及构造性质[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 43: 2496-2517
BAI Daoyuan, LI Yinmin, ZHONG Xiang, et al. Geological features, activity history and tectonic attribute of NW-trending Changde-Anren fault in Hunan[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 43: 2496-2517.
[3] 柏道远, 熊雄, 杨俊, 等. 雪峰造山带中段地质构造特征[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41: 399-418 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.02.008
BAI Daoyuan;XIONG Xiong;YANG Jun, et al. Geological structure characteristics of the middle segment of the Xuefeng orogen[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41: 399-418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.02.008
[4] 陈卫锋, 陈培荣, 黄宏业, 等. 湖南白马山岩体花岗岩及其包体的年代学和地球化学研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2007, 37(7): 873−893.
[5] 胡楚南 . 桃江县板溪锑矿床地质特征及成矿构造分析[J]. 湖南地质, 1991, 10(4): 317−320+288.
[6] 胡瑞忠, 毕献武, 苏文超, 等. 华南白垩—第三纪地壳拉张与铀成矿的关系[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 153-160
HU Ruizhong, BI Xianwu, SU Wenchao, et al. The relationship between uranium metallogenesis and crustal extension during the cretaceous—tertiary in South China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 153-160.
[7] 黄建中, 孙骥, 周超, 等. 江南造山带(湖南段)金矿成矿规律与资源潜力[J]. 地球学报, 2020 1-22.
HUANG Jianzhong, SUN Ji, ZHOU Chao, et al. Metallogenic regularity and resource potential of gold deposits of Hunan area in the Jiangnan orogenic belt, South China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2020, 1-22.
[8] 柯昌辉, 王晓霞, 杨阳, 等. 西秦岭地区脉岩成因与金成矿关系——来自李坝金矿年代学、地球化学及Nd-Hf-S同位素的约束[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39: 42-62.
KE Changhui, WANG Xiaoxia, YANG Yang, et al. Petrogenesis of dykes and its relationship to gold mineralization in the western Qinling belt: Constraints from zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and Nd-Hf-S isotopes of Liba gold deposit[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2020, 39: 42-62.
[9] 李建华, 张岳桥, 董树文, 等.华南大陆白垩纪构造-岩浆演化与动力学过程[C].中国地球科学联合学术年会, 2014, 2−5.
[10] 李献华, 赵振华, 桂训唐, 等. 华南前寒武纪地壳形成时代的Sm-Nd和锆石U-Pb同位素制约[J]. 地球化学, 1991, (3): 255−264
LI Xianhua, ZHAO Zhenhua, GUI Xuntang, et al. Sm-Nd isotopic and zircon U-Pb constraints on the age of formation of the precambrian crust in Southeast China[J]. Geochimica, 1991, (3): 255−264.
[11] 李献华. 华南白垩纪岩浆活动与岩石圈伸展———地质年代学与地球化学限制[J]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999: 264−275.
[12] 李艳广, 靳梦琪, 汪双双, 等. LA–ICP–MS U–Pb定年技术相关问题探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(4): 274−282.
LI Yanguang, JIN Mengqi, WANG Shuangshuang, LÜ Pengrui. Exploration of Issues Related to the LA–ICP–MS U–Pb Dating Technique[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(4): 274−282.
[13] 李智明. 锡矿山锑矿成矿机理的探讨[J]. 矿产与地质, 1993, 7(2): 88−93.
[14] 刘继顺. 湘中地区长英质脉岩与锑(金)成矿关系[J]. 有色金属矿产与勘查, 1996, 2-7
LIU Jishun. Relationship between felsic dikes and antimony-gold mineralization in central Hunan[J]. Mineral Exploration, 1996, 2-7.
[15] 卢作祥, 佘宏全. 国内外层控改造型金锑钨综合矿床的成矿特征与成矿机理[J]. 地质科技情报, 1989, 59-65
LU Zuoxiang, XU Hongquan. Minerogenetic features and genetic mechanism of strata-bound Au-Sb-W multiple ore deposits home and abroad[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1989, 59-65.
[16] 路远发, 李文霞. Pb-Sr-Nd-Hf同位素参数计算及程序设计[J]. 华南地质, 2021, 37: 233-245
LU Yuanfa, LI Wenxia. Calculation and Program Design for Pb-Sr-Nd-Hf Isotopic Parameters[J]. South China Geology, 2021, 37: 233-245.
[17] 路远发. GeoKit: 一个用VBA构建的地球化学工具软件包[J]. 地球化学, 2004, 459-464
LU Yuanfa. GeoKit——A geochemical toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. GEOCHIMICA, 2004, 459-464.
[18] 毛景文, 谢桂青, 李晓峰, 等. 华南地区中生代大规模成矿作用与岩石圈多阶段伸展[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 45-55
MAO Jingwen, XIE Guiqing, LI Xiaofeng, et al. Mesozoic large scale mineralization and multiple lithospheric extension in South China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 45-55.
[19] 潘灿军, 鲍振襄, 包觉敏. 湘西符竹溪金矿地质特征及成矿作用[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2015, 30: 53-59 doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2015.01.007
PAN Chanjun, BAO Zhenxiang, BAO Juemin. Geological characteristics and metallogenesis of Fuahuxi gold deposit in the West Hunan province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2015, 30: 53-59. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2015.01.007
[20] 潘桂棠, 陆松年, 肖庆辉, 等. 中国大地构造阶段划分和演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23: 1-23
PAN Guichang, LU Songnian, XIAO Qinghui, et al. Division of tectonic stages and tectonic evolution in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23: 1-23.
[21] 彭渤, 陈广浩. 湖南锑金矿成矿大爆发: 现象与机制[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2000, 24(4): 357−364.
[22] 彭建堂. 湖南雪峰地区金成矿演化机理探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 1999, 3-5
PENG Jiantang. Gold mineralization and its evolution in the Xuefeng district, Hunan[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 1999, 3-5.
[23] 权正钰, 王甫仁, 胡能勇, 等. 雪峰弧形构造带与金锑矿成矿关系[R]. 长沙: 湖南省地质研究所, 1997
[24] 任纪舜, 李崇. 华夏古陆及相关问题——中国南部前泥盆纪大地构造[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90: 607-614 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.04.001
REN Jishun, LI Chong. Cathaysia old land and relevant problems: pre-devonian tectonics of southern China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90: 607-614. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.04.001
[25] 舒良树. 华南构造演化的基本特征[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31: 1035-1053 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.07.003
SHU Liangshu. An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2012, 31: 1035-1053. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.07.003
[26] 王川, 彭建堂, 徐接标, 等. 湘中白马山复式岩体成因及其成矿效应[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37: 805-829
WANG Chuan, PENG Jiantang, XU Jiebiao, et al. Petrogenesis and metallogenic effect of the Baimashan granitic complex in central Hunan, South China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37: 805-829.
[27] 王孝磊, 周金城, 陈昕, 等. 江南造山带的形成与演化[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2017, 36: 714-735+696 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2017.05.003
WANG Xiaolei, ZHOU Jincheng, CHEN Xin, et al. Formation and evolution of the Jiangnan orogen[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2017, 36: 714-735+696. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2017.05.003
[28] 王梓桐, 王根厚, 张维杰, 等. 阿拉善地块南缘志留纪花岗闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 49(5): 586−600.
WANG Zitong, WANG Genghou, ZHANG Weijie, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and geochemical characteristics of the Silurian granodiorite in the southern margin of Alxa Block, China [J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2022, 49(5): 586−600.
[29] 文志林, 邓腾, 董国军, 等. 湘东北万古金矿床控矿构造特征与控矿规律研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2016, 40: 281-294
WEN Zhilin, DENG Teng, DONG Guojun, et al. Characteristics of ore-controlling structures of Wangu gold deposit in Northeastern Hunan Province[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2016, 40: 281-294.
[30] 吴良士, 胡雄伟. 湖南锡矿山地区云斜煌斑岩及其花岗岩包体的意义[J]. 地质地球化学, 2000, 51-55
WU Liangshi, HU Xiongwei. Xikuangshan mica-plagioclase lamprophyre and its granite inclusions, Hunan Province[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 2000, 51-55.
[31] 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16):1589−1604.
[32] 徐耀明, 蒋少涌, 朱志勇, 等. 九瑞矿集区山上湾矿区石英闪长玢岩和花岗闪长斑岩的年代学、地球化学及成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28: 3306-3324
XU Yaoming, JIANG Shaoyong, ZHU Zhiyong, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry and mineralization of the quartz diorite-porphyrite and granodiorite porphyry in the Shanshangwan area of the Jiurui ore district, Jiangxi Privince[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28: 3306-3324.
[33] 姚振凯, 朱蓉斌. 湖南符竹溪金矿床地质特征和成矿预测[J]. 铀矿地质, 1995,11(6): 344−349+356.
[34] 张国震, 张永, 辛后田, 等. 内蒙古北山老硐沟金多金属矿床闪长玢岩年代学、地球化学及其成矿意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2021, 40: 555-573
ZHANG Guozhen, ZHANG Yong, XIN Houtian, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of diorite porphyrite from Laodonggou gold-polymetallic deposit, Beishan, Inner Mongolia, and its metallogenic significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2021, 40: 555-573.
[35] 张培烈, 王根厚, 冯翼鹏, 等. 古特提斯洋闭合时限: 来自南羌塘唐古拉岩浆带查吾拉岩体的证据[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 49(3): 311−323.
ZHANG Peilie, WANG Genghou, FENG Jipeng, et al. Closure time of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean: Evidence from the southern Qiangtang Tanggula magmatic belt, Xizang, China [J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2022, 49(3): 311−323.
[36] 张岳桥, 徐先兵, 贾东, 等. 华南早中生代从印支期碰撞构造体系向燕山期俯冲构造体系转换的形变记录[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 16: 234-247 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.02.022
ZHANG Yueqiao, XU Xianbin, JIA Dong, et al. Deformation record of the change from Indosinian collision-related tectonic system to Yanshanian subduction-related tectonic system in South China during the Early Mesozoic[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 16: 234-247. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.02.022
[37] 张志远, 谢桂青, 李惠纯, 等. 湖南龙山锑金矿床白云母~(40)Ar-~(39)Ar年代学及其意义初探[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34: 2535-2547
ZHANG Zhiyuan, XIE Guiqing, LI Huichun, et al. Preliminary study on muscovite 40Ar-39Ar geochronology and its significance of the Longshan Sb-Au deposit in Hunan Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34: 2535-2547.
[38] 赵军红, 彭建堂, 胡瑞忠, 等. 湖南板溪脉岩的年代学、岩石学、地球化学及其构造环境[J]. 地球学报, 2005, 525-534
ZHAO Junhong, PENG Jiantang, HU Ruizhong, et al. Chronology, petrology, geochemistry and tectonic environment of Banxi quartz porphyry dikes, Hunan Province[J]. Acta Geocientica Sinica, 2005, 525-534.
[39] 赵玉锁, 杨立强, 陈永福, 等. 黑龙江金厂铜金矿床闪长玢岩地球化学及锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28: 451-467
ZHAO Yusuo, YANG Liqiang, CHEN Yongfu, et al. Geochemisry and zircon U-Pb geochronology of the diorite porphyry associated with the Jinchang Cu-Au deposit, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28: 451-467.
[40] 曾昊, 吴绍安, 陈澍民, 等. 雪峰弧金锑矿资源勘查年度进展报告[R]. 长沙: 中国地质调查局长沙自然资源综合调查中心, 2020.
[41] CHEN J, Jahn B-M. Crustal evolution of southeastern China: Nd and Sr isotopic evidence[J]. Tectonophysics, 1998, 284: 101-133. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00186-8
[42] CHEN S-M, ZHOU Y-X, LI B, et al. Genesis of Chaxi Gold Deposit in Southwestern Hunan Province, Jiangnan Orogen (South China): Constraints from Fluid Inclusions, H-O-S-Pb Isotopes, and Pyrite Trace Element Concentrations[J]. Minerals, 2022, 12: 867.
[43] Compston W, Williams I, Kirschvink J, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages for the Early Cambrian time-scale[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1992, 149: 171-184. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.149.2.0171
[44] Creaser R A, Erdmer P, Stevens R A, et al. . Tectonic affinity of Nisutlin and Anvil assemblage strata from the Teslin tectonic zone, northern Canadian Cordillera: Constraints from neodymium isotope and geochemical evidence[J]. Tectonics, 1997, 16: 107-121. doi: 10.1029/96TC03317
[45] Davidson J, Turner S, Handley H, et al. Amphibole “sponge” in arc crust? [J] Geology, 2007, 35: 787-790.
[46] DENG J, QING F-W. Gold mineralization in China: Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 36: 219-274.
[47] FENG Y, ZHANG Y, XIE Y, et al. Ore-forming mechanism and physicochemical evolution of Gutaishan Au deposit, South China: Perspective from quartz geochemistry and fluid inclusions[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 119: 103382. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103382
[48] Goldfarb R J, Groves D I, Gardoll S. Orogenic gold and geologic time: a global synthesis [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2001 18: 1-75. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(01)00016-6
[49] Hastie A R, Kerr A C, Pearce J A, et al. Classification of altered volcanic island arc rocks using immobile trace elements: development of the Th–Co discrimination diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2007, 48: 2341-2357. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egm062
[50] Hoskin P, Black L. Metamorphic zircon formation by solid‐state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon[J]. Journal of metamorphic Geology, 2000, 18: 423-439. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1314.2000.00266.x
[51] Kay R W, Mahlburg-Kay S. Creation and destruction of lower continental crust[J]. Geologische Rundschau, 1991, 80: 259-278. doi: 10.1007/BF01829365
[52] LI W, XIE G-Q, MAO J-W, et al. Muscovite 40Ar/39Ar and in situ sulfur isotope analyses of the slate-hosted Gutaishan Au–Sb deposit, South China: Implications for possible Late Triassic magmatic-hydrothermal mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 101: 839-853. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.08.006
[53] LI X-H. Cretaceous magmatism and lithospheric extension in Southeast China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2000, 18: 293-305. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00060-7
[54] LIU W-G, WEI S, ZHANG J, et al. An improved separation scheme for Sr through fluoride coprecipitation combined with a cation-exchange resin from geological samples with high Rb/Sr ratios for high-precision determination of Sr isotope ratios[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2020, 35: 953-960. doi: 10.1039/D0JA00035C
[55] LIU Y, HU Z, ZONG K, et al. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55: 1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
[56] Ludwig R. Isoplot a plotting and regression program for radiogenic-isotope data, version 2.57[R]. U.S . Geologic Survey, 1992, 40.
[57] Mcdonough W F, SUN S-S. The composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120: 223-253. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)00140-4
[58] Rollinson H R. Using geochemical data: evaluation, presentation, interpretation London Longman Scientific and Technical[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1994, 58: 523-523.
[59] Schmidberger S S, Simonetti A, Heaman L M, et al. Lu–Hf, in-situ Sr and Pb isotope and trace element systematics for mantle eclogites from the Diavik diamond mine: Evidence for Paleoproterozoic subduction beneath the Slave craton, Canada[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 254: 55-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2006.11.020
[60] SUN S-S, Mcdonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42: 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[61] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The continental crust, its composition and evolution: an examination of the geochemical record preserved in sedimentary rocks[M]. Blackwell Scientific Publishinq, Oxford,1985: 12−29.
[62] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust[J]. Reviews of geophysics, 1995, 33: 241-265. doi: 10.1029/95RG00262
[63] Unterschutz J L, Creaser R A, Erdmer P, et al. North American margin origin of Quesnel terrane strata in the southern Canadian Cordillera: Inferences from geochemical and Nd isotopic characteristics of Triassic metasedimentary rocks[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2002, 114: 462-475. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2002)114<0462:NAMOOQ>2.0.CO;2
[64] Vermeesch P. IsoplotR: A free and open toolbox for geochronology[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2018, 9: 1479-1493.
[65] Wasserburg G J, Jacobsen S B, Depaolo D J, et al. Precise determination of SmNd ratios, Sm and Nd isotopic abundances in standard solutions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1981, 45: 2311-2323.
[66] Winchester J A, Floyd P A. Geochemical magma type discrimination: application to altered and metamorphosed basic igneous rocks[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1976, 28: 459-469. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(76)90207-7
[67] Winchester J A, Floyd P A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J]. Chemical Geology, 1977, 20: 325-343. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(77)90057-2
[68] XIAO J, PENG J, HU A, et al. Characteristics of fluid inclusions of the Xingfengshan Gold Deposit, central Hunan, and its genetic implications[J]. GEOLOGICAL REVIEW, 2020, 66: 1376.
[69] XU D, DENG T, CHI G, et al. Gold mineralization in the Jiangnan Orogenic Belt of South China: Geological, geochemical and geochronological characteristics, ore deposit-type and geodynamic setting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 88: 565-618. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.004
[70] ZHANG L, YANG L-Q, Groves D I, et al. An overview of timing and structural geometry of gold, gold-antimony and antimony mineralization in the Jiangnan Orogen, southern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 115: 103173. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103173
[71] ZHANG S-B, ZHENG Y-F. Formation and evolution of Precambrian continental lithosphere in South China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23: 1241-1260. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.09.005
[72] ZHAO G. Jiangnan Orogen in South China: Developing from divergent double subduction[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 27: 1173-1180. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.09.004
[73] ZHENG Y-F, ZHAO Z-F, WU Y-B, et al. . Zircon U–Pb age, Hf and O isotope constraints on protolith origin of ultrahigh-pressure eclogite and gneiss in the Dabie orogen[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 231: 135-158. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.01.005
[74] Zindler A, Hart S. Chemical geodynamics[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1986, 14: 493-571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.14.050186.002425
-




 下载:
下载: