Hydrocarbon Accumulation Characteristics and Future Exploration Direction in Senegal Basin, Northwest Africa
-
摘要:
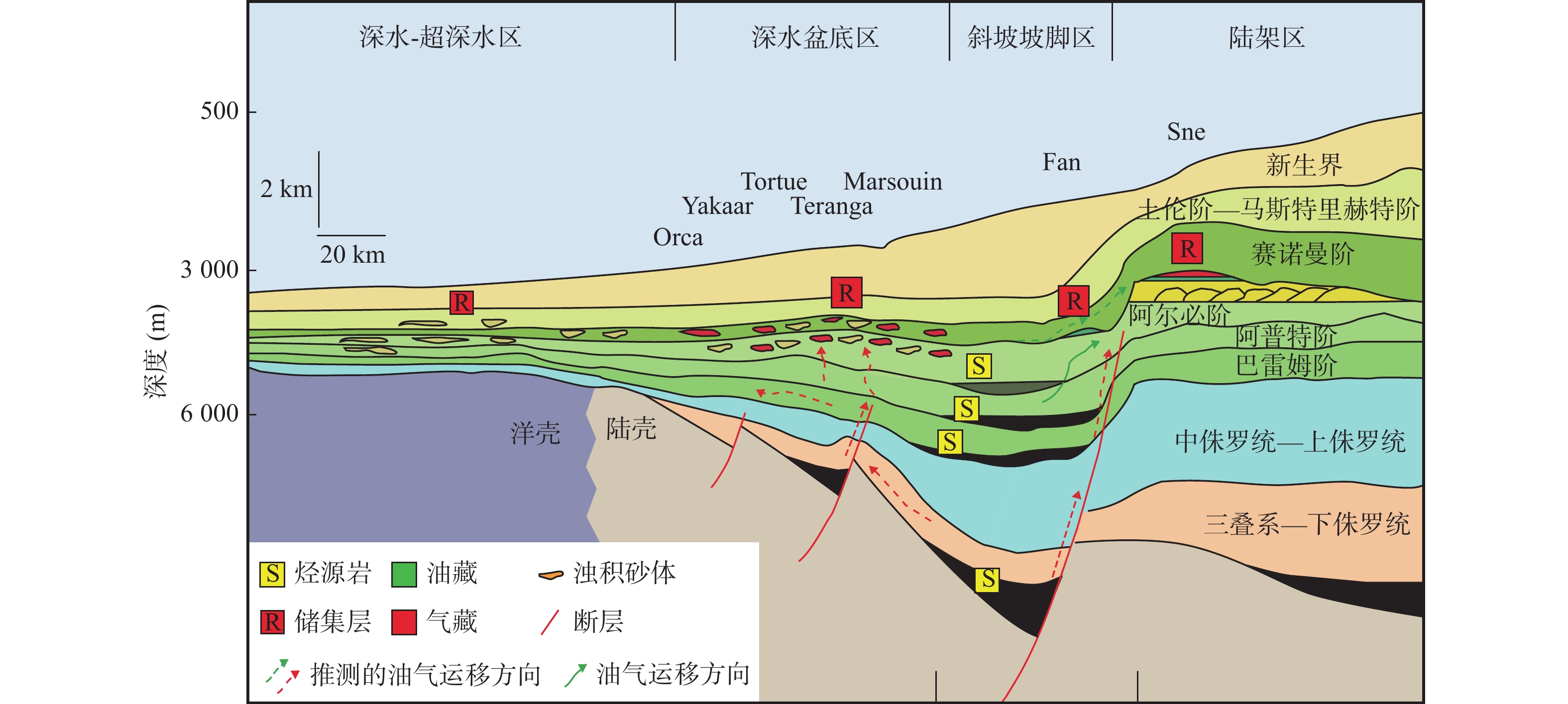
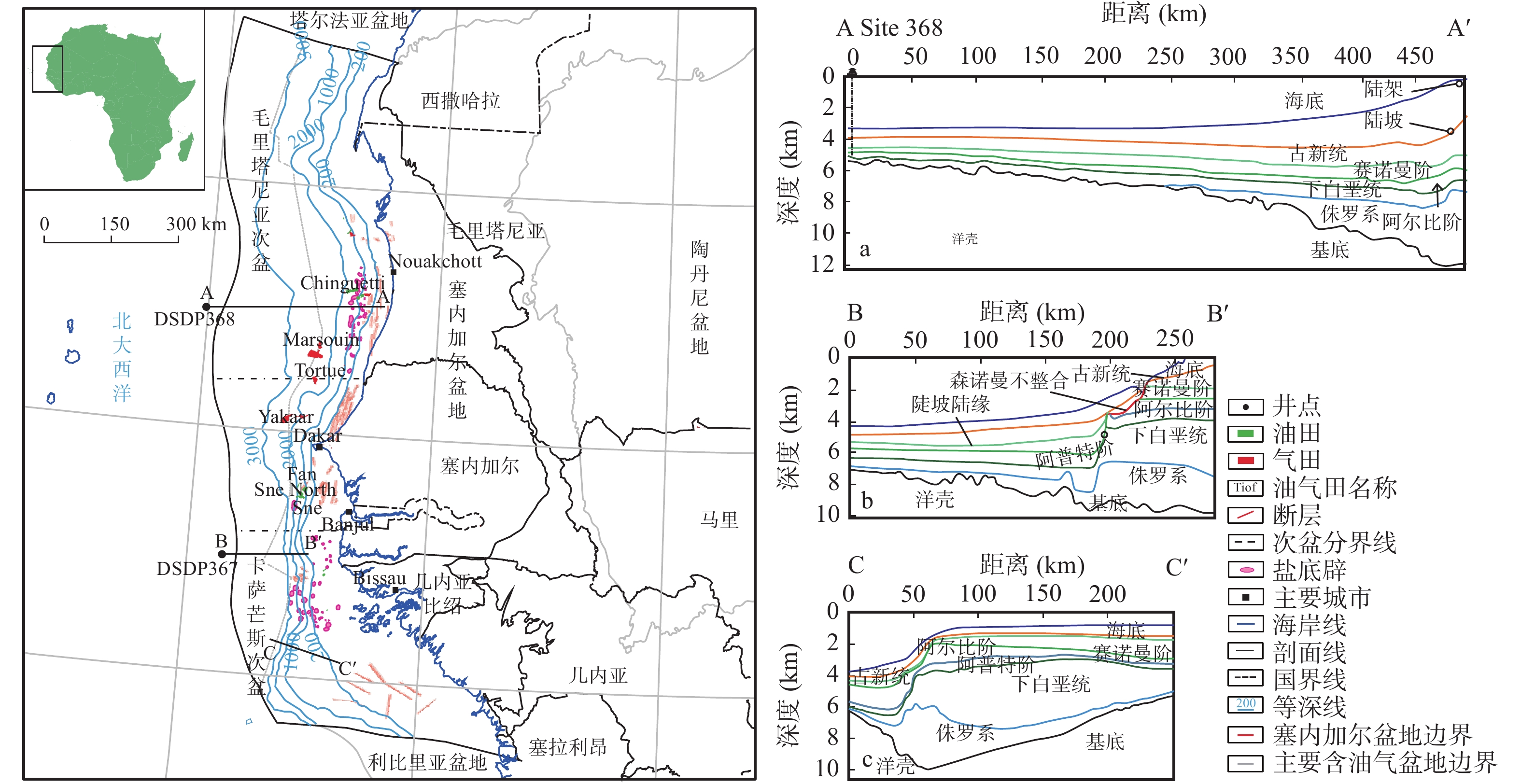
西非北部塞内加尔盆地是位于前寒武系—古生界结晶基底之上的巨型裂谷−被动陆缘叠合盆地。笔者基于地震、典型钻井、测井资料及国际油气商业数据库和勘探的最新成果,结合区域地质背景和盆地构造沉积演化特征,分析盆地油气成藏条件、成藏特征和富集规律,并预测未来勘探方向。研究表明,盆地经历前裂谷、同裂谷和被动陆缘3期构造演化阶段,盆地结构呈“北缓南陡”形态,具体表现为“北部窄陆架缓陆坡、南部宽陆架陡陆坡”特征。盆地发育裂陷期湖相和被动陆缘期海相两套烃源岩,裂陷期烃源岩对盆地深水区白垩系成藏具有重大贡献,被动陆缘期烃源岩在上覆地层较厚时才成熟。盆地可划分为3种油气成藏模式。①陆架区下生上储,断层沟通不整合,陆架三角洲前缘浊积砂岩成藏模式。②斜坡坡脚区下生上储、断砂配置输导、近源供烃成藏模式。③深水−超深水区下生上储,垂向运移,构造−地层型浊积砂岩成藏模式。陆架边缘三角洲前缘砂体、斜坡坡脚处的浊积水道和海底扇、深水区浊积水道和浊积扇是塞内加尔盆地重点勘探领域,深水区大型构造−地层圈闭为盆地最重要的勘探目标。
Abstract:The Senegal basin in Northwest Africa is a giant rift−passive margin superimposed basin floored by the Precambrian−Paleozoic crystalline basement. Based on combinations of seismic, drilling, well logging data and the latest international commercial petroleum databases and exploration results, along with understanding of regional geological history (tectono−sedimentary evolutions), this study was focused on hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and patterns and enrichment rules of hydrocarbons, and predicted the future direction of exploration in the Senegal basin. The study shows that the basin experienced three tectonic evolution stages: pre−rift, syn−rift, and passive margin. The current structure of the basin is characterized by “a gentle northern slope and a steep southern slope”, specifically, the narrow continental shelf and gentle continental slope in the north the wide shelf and steep slope in the south. The basin has lacustrine source rocks deposited during the rifting period and marine source rocks deposited in the passive margin period. The lacustrine source rocks have a more significant contribution to petroleum accumulations in the Cretaceous reservoirs in deepwater areas. Marine source rocks became mature until the thicker overlying sediments deposited. Three types of hydrocarbon accumulation models were recognized: ① lower−generation and upper−storage in the continental shelf area characterized by delta−front turbidite sandstones charged through unconformity and faults. ② lower−generation and upper−storage at the foot of the continental slope dominated by near−source fault−sandstones configuration. ③ lower−generation and upper upper−storage in deepwater and ultra−deepwater areas dominated by structural−stratigraphic turbidite trap through vertical migration. The shelf−margin delta−front sandstones, turbidite channels and submarine fan lobes at the slope foot, turbidite fan in the deepwater areas are favorable targets for exploration. Large structural−stratigraphic traps in deepwater areas are the most important exploration target in the Senegal basin.
-

-
图 3 塞内加尔盆地综合地质柱状图(据IHS,2023修改)
Figure 3.
图 4 塞内加尔盆地被动陆缘期海相烃源岩发育模式图(据孙涛等,2017a修改)
Figure 4.
图 5 西非晚白垩世古气候与古河流沉积位置图(据Macgregor,2010修改)
Figure 5.
图 7 塞内加尔盆陆缘沉积演化模式(据宫越等,2020修改)
Figure 7.
-
[1] 冯杨伟, 屈红军, 张功成, 等. 西非被动大陆边缘构造-沉积演化及其对生储盖的控制作用[J]. 海相油气地质, 2010, 15(3): 45-51
FENG Yangwei, QU Hongjun, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Toctonic-Sedimentary Evolution and its Control on Source-Reservior-Cap Rocks in Passive Continental Margin, West Africa[J]. Marine origin petroleum geology, 2010, 15(3): 45-51.
[2] 宫越, 冯志强, 邬长武, 等. 塞内加尔盆地白垩系陆源碎屑沉积体系及控制因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(6): 1244-1256.
GONG, Yue, FENG Zhiqiang, WU Changwu, et al. Sedimentary system of the Cretaceous terrigenous clastics and its controlling factors in Senegal Basin, northern West Africa [J]. Acta Petroleum Sinica, 2017, 38(10): 1099-1109.
[3] 刘延莉. 塞内加尔盆地油气地质特征及勘探潜力[J]. 地质与资源, 2014, 23(2): 197 − 201
LIU Yanli. The petroleum geology and prospective analysis of the Senegal Basin[J]. Geology and Resource, 2014, 23(2): 197 − 201.
[4] 孙涛, 王建新, 孙玉梅, 等. 西非塞内加尔盆地海相优质烃源岩控制因素讨论[J]. 海洋石油, 2017a, 37(4): 41-52
SUN Tao, WANG Jianxin, SUN Yumei, et al. Discussion on Controlling Factors of Excellent Marine Source Rocks in Senegal Basin, West Africa[J]. Offshore Oil, 2017, 37(4): 41-52.
[5] 孙涛, 王建新, 孙玉梅. 西非塞内加尔盆地深水区油气地球化学特征与油气成藏[J]. 沉积学报, 2017b, 35(6): 1284-1292
SUN Tao, WANG Jianxin, SUN Yumei. Petroleum Geochemical Characteristics and Accumulation in Offshore of Senegal Basin [J]. Acta Sedimentology Sinica, 2017, 35(6): 1284-1292.
[6] 王大鹏, 殷进垠, 田纳新, 等. 塞内加尔盆地成藏组合划分与资源潜力评价[J]. 现代地质, 2017(6): 1201-1213
WANG Dapeng, YIN Jinyin, TIAN Naxin, et al. Division and Resources Evaluation of Hydrocarbon Plays in the Senegal Basin, West Africa[J]. Geoscience, 2017(6): 1201-1213.
[7] 王宏语, 张峰, 蔡雨薇. 塞内加尔盆地北部次盆被动大陆边缘沉积演化特征与控制因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 10(4): 67-77
WANG Hongyu, ZHANG Feng, CAI Yuwei. Sedimentary evolution of the passive continental margin of the north sub-basin, Senegel Basin and its controlling factors[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 10(4): 67-77.
[8] 熊利平, 刘延莉, 霍红. 西非海岸南、北两段主要含油气盆地油气成藏特征对比[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2010, 31(4): 410-419
XIONG Liping, LIU Yanli, HUO Hong. Comparison of the hydrocarbon accumulation patterns of petroliferous basins between the north and south parts of the West African coast[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2010, 31(4): 410-419.
[9] 徐汉梁, 单玄龙, 高璇, 等. 西非塞内加尔盆地重油成藏条件及富集规律[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(16): 211-215
XU Hanliang, SHAN Xuanlong, GAO Xuan, et al. Heavy Oil Accumulation Condition and Enrichment Regularity of Senegal Basin in West Africa [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(16): 211-215.
[10] 朱伟林, 崔旱云, 吴培康, 等. 被动大陆边缘盆地油气勘探新进展与展望[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(10): 1099-1109
ZHU, Weilin, CUI Hanyun, WU Peikang, et al. New development and outlook for oil and gas exploration in passive continental margin basins[J]. Acta Petroleum Sinica, 2017, 38(10): 1099-1109.
[11] Bird D E, Hall S A, Burke K, et al. Early Central Atlantic Ocean seafloor spreading history[J]. Geosphere, 2007, 3(5): 282-298. doi: 10.1130/GES00047.1
[12] C&C Reserviors. Chinguetti Field Mauritanian Salt Basin, Mauritania, Field Evaluation Report[DB/OL]. [2022-05-10]. http://www.ccreservoirs.com/.
[13] Casson M, Calvès G, Redfern J, et al. Cretaceous continental margin evolution revealed using quantitative seismic geomorphology, offshore northwest Africa[J]. Basin Research, 2020, 20(4): 1-25.
[14] Davison I. Central Atlantic margin basins of North West Africa: Geology and hydrocarbon potential (Morocco to Guinea)[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2005, 43(1-3): 254-274. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2005.07.018
[15] Ellouz N, Patriat M, Gauier J P, et al. From rifting to Alpine inversion: Mesozoic and Cenozoic subsidence history of some Moroccan basins[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2003, 156: 185-212. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(02)00288-9
[16] Erlich N, Villamil T, Keens-Dumas J. Controls on the Deposition of Upper Cretaceous Organic Carbon–rich Rocks from Costa Rica to Suriname[J]. In: Bartolini C, Buffler R, and Blickwede J, ed. AAPG Studies in Geology No. 40: Paleogeography, Paleoclimate, and Source Rocks. Tulsa: The Circum-Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean: Hydrocarbon habitats, basin formation, and plate tectonics[C]. AAPG Memoir 79, 2003: 1−45.
[17] Golonka J. Late Triassic and Early Jurassic palaeogeography of the world[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2007, 244(1): 297-307.
[18] IHS Energy Group. International petroleum exploration and production database [DB/OL]. [2023-01-20]. http://www.ihs.com/products/oil-gas-information/data-access/geophysical-surveys/index.aspx.
[19] Kosmos Energy. Investor Presentation[DB/OL]. [2021-06-13]. http://www.kosmosenergy.com/.
[20] Kuhnt W, Wiedmann J. Cenomanian-Turonian Source Rocks: Paleobiogeographic and Paleoenvironmental Aspects[J]. In: Huc A Y, ed. AAPG Studies in Geology No. 40: Paleogeography, Paleoclimate, and Source Rocks. Tulsa[C]. The American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 1995: 213–231.
[21] Labails C, Olivet J, Aslanian D, et al. An alternative early opening scenario for the Central Atlantic Ocean[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 2010, 297: 355-368.
[22] Lüning S, Kolonic S, Belhadj E M, et al. Integrated depositional model for the Cenomanian–Turonian organic-rich strata in North Africa[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2004, 64(1-2): 51-117. doi: 10.1016/S0012-8252(03)00039-4
[23] Macgregor D. Understanding African and Brazilian Margin Climate, Topography and Drainage Systems, Implications for Predicting Deepwater Reservoirs and Source Rock Burial History: Search and Discovery Article#10270. 2010 [DB/OL]. [2021-05-23]. http://www.searchanddiscovery.com.
[24] Martin L, Effimoff I, Medou J, et al. Hydrocarbon Prospectivity of Offshore Senegal-Unlocking the Door to a New Deepwater Petroleum Province: Search and Discovery Article#10278. 2010 [DB/OL]. [2020-05-21]. http://www.searchanddiscovery.com.
[25] Moulin M, Aslanian D, Unternehr P. A new starting point for the South and Equatorial Atlantic Ocean[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2010, 98(1-2): 1-37. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2009.08.001
[26] Ndiaye M, Ngom P M, Gorin G, et al. A new interpretation of the deep-part of Senegal-Mauritanian Basin in the Diourbel-Thies area by integrating seismic, magnetic, gravimetric and borehole data: Implication for petroleum exploration[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2016, 121: 330-341. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2016.06.002
[27] Nzoussi-Mbassani P, Khamli N, Disnar J R, et al. Cenomanian–Turonian organic sedimentation in North-West Africa: A comparison between the Tarfaya (Morocco) and Senegal Basins. [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2005, 177(3-4): 271-295. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2005.03.008
[28] Rowan M G. Passive-margin salt basins: Hyperextension, evaporite deposition, and salt tectonics[J]. Basin Research, 2014, 26(1): 154-182. doi: 10.1111/bre.12043
[29] Sayers B, Cooke R. Seismic Foldout: MSGBC - Where is the next success?[J]. GeoExpro, 2018, 5(15): 20-24.
[30] Sebastien F, Carine L, Vanessa L. Paleoceanographic significance of cerium anomalies during the OAE 2 on the NW African margin[J]. Journal of Sedimentary research, 2018, 88: 1284-1299. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2018.66
[31] Villeneuve M, Fournier F, Cirilli S, et al. Structure of the Paleozoic basement in the Senegalo-Mauritanian basin (West Africa)[J]. Bulletin De La Societe Geologique De France, 2015, 186(2): 195-206.
[32] Withjack M O, Schlische R W, Olsen P E. Diachronous rifting, drifting, and inversion on the passive margin of central eastern North America: An analog for other passive margins[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1998, 82(2): 817-835.
[33] Yannick M, Calvès G, Clift P, et al. Seismic stratigraphy of Cretaceous eastern Central Atlantic Ocean: Basin evolution and palaeoceanographic implications[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2018, 499: 107-121. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2018.07.023
[34] Ye J, Chardon D, Rouby D, et al. Paleogeographic and structural evolution of northwestern Africa and its Atlantic margins since the early Mesozoic[J]. Geosphere, 2017, 13(4): 1254-1284.
[35] Zavala C, Arcuri M. Intrabasinal and extrabasinal turbidites: Origin and distinctive characteristics[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2017, 337: 36-54.
-



 下载:
下载: