Comparative Study on Evaluation Performance of Different Units of Susceptibility of Accumulation Layer Landslide in Qinba Mountain Area at Town Scale
-
摘要:
秦巴山区堆积层滑坡数量多、分布广、密度大、频次高,所造成的危害十分严重,且具有孕灾条件复杂多样和部分灾害评价数据获取难度大等特征。笔者选取秦巴山区小岭镇作为研究区,在地质灾害野外调查基础上,结合堆积层滑坡区域特点,采取栅格、斜坡两种单元类型,因地制宜的提取了滑坡孕灾因子,分析其相关性,提选出坡度、坡高、坡面形态、斜坡结构类型、堆积层厚度、距道路、矿区、断裂的距离等8个因子作为堆积层滑坡特征因子,运用随机森林模型方法对该镇域进行了滑坡易发性评价;并通过评价结果频率比、ROC曲线、易发性概率均值与标准差,对栅格单元、斜坡单元两种单元类型的精度与准确性进行了验证,结果表明:两种评价单元的预测结果都有良好的表现,但斜坡单元作为评价单元总体预测性能高于栅格单元,栅格单元在灾害防治具体空间部署上有着更精细的参考。研究成果对秦巴山区镇域地质灾害风险评价工作有一定的理论和实践意义。
Abstract:The accumulation layer landslides in Qinba Mountain area are abundant, widely distributed and frequently, and the harm caused by them is very serious. Moreover, it is characterized by complex and diverse disaster pregnancy conditions and difficult to obtain some disaster evaluation data. Xiaoling Town, Qinba Mountain, was selected as the research area. The geological hazard field survey was taken as the basis. Combined with the regional characteristics of accumulation landslide, two element types, grid element and slope element, are adopted. The landslide hazard factors were selected according to local conditions, and their correlation was analyzed. Eight factors, including slope, slope height, slope morphology, slope structure type, accumulation layer thickness, distance from road, mining area and fault, are selected as the characteristic factors of accumulation layer landslide. The random forest model method was used to evaluate the landslide susceptibility of the town area. In addition, the accuracy and accuracy of grid element and slope element were verified by frequency ratio, ROC curve, mean value and standard deviation of susceptibility probability of evaluation results. The results show that both evaluation elements have good performance in the re-prediction results, but the overall prediction performance of slope element as evaluation element is higher than that of grid element. In the specific spatial deployment of disaster prevention and control, more detailed reference comes from grid element. The research results have certain theoretical and practical significance for the risk assessment of geological hazards in towns in Qinba Mountains.
-
Key words:
- susceptibility /
- landslide of accumulation layer /
- random forest /
- unit evaluation /
- Qinba Mountains
-

-
表 1 研究区滑坡规模分类
Table 1. Classification of landslide scale in study area
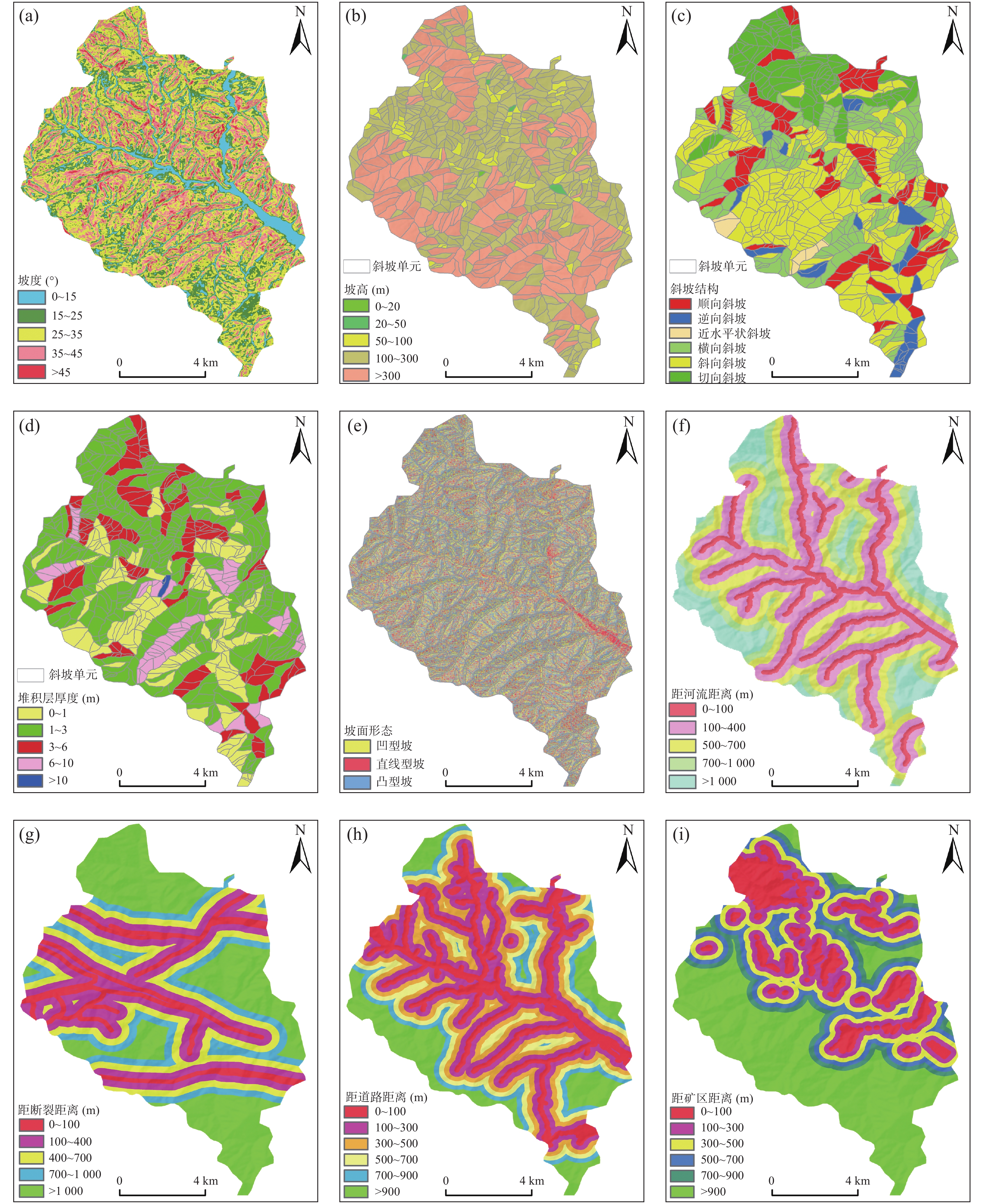
个数 规 模 比例(%) 大型(处) 比例(%) 中型(处) 比例(%) 小型(处) 比例(%) 堆积层滑坡 26 0 0 1 3.57 25 89.29 92.86 基岩滑坡 2 0 0 0 0 2 7.14 7.14 合 计 28 0 0 1 3.57 27 96.43 100.00 表 2 数据类型及用途
Table 2. Data types and uses
数据类型 比例尺/分辨率 数据用途 DEM 5 m 提取坡度、坡向、剖面曲率、河流水系等因子;提取评价单元。 地质图 1∶50000 提取断裂等因子 表 3 斜坡单元面积概况
Table 3. Overview of slope unit area
斜坡单元
面积类型最大面积
(km2)最小面积
(km2)平均面积
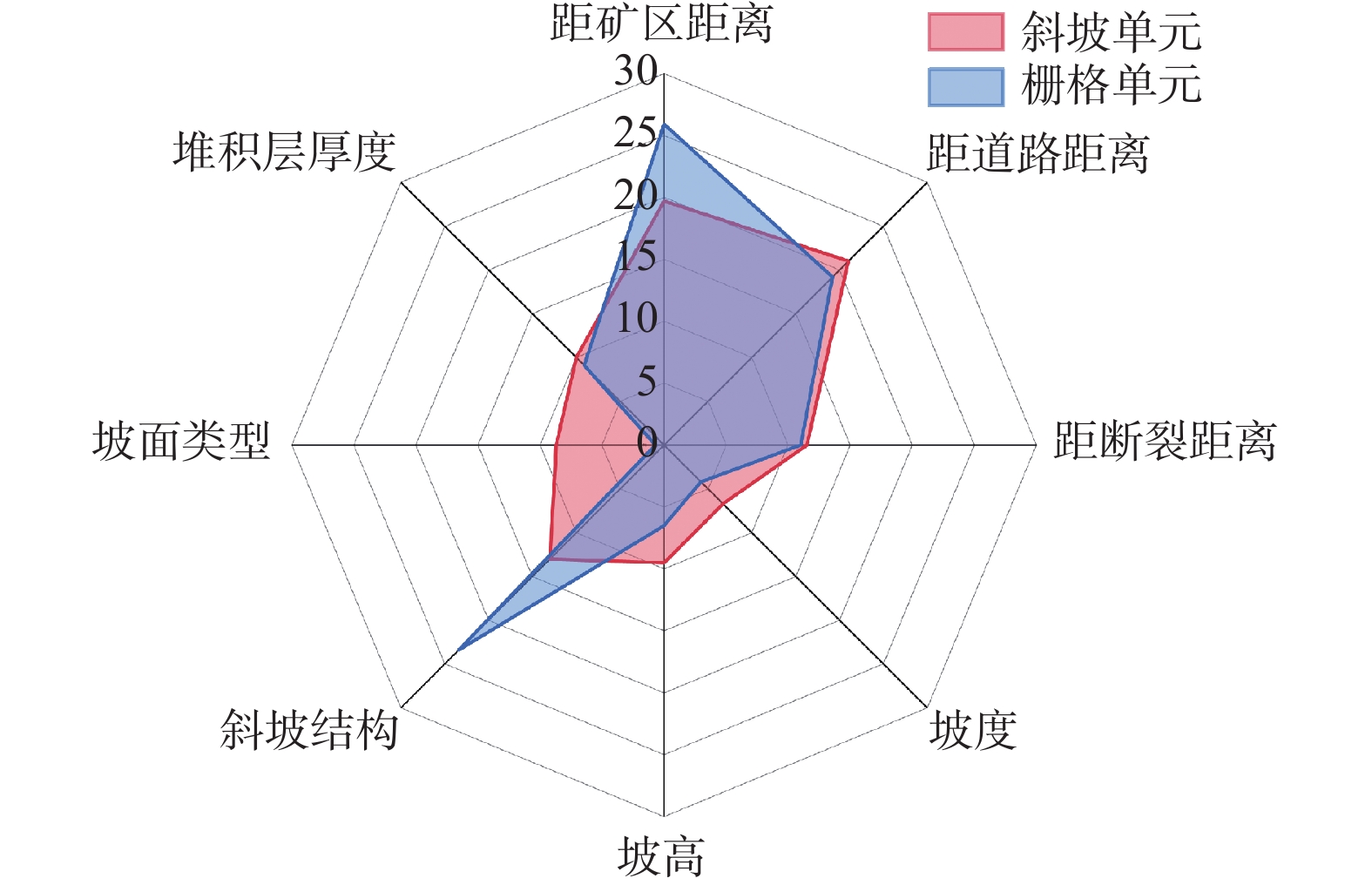
(km2)面积值 0.81 0.019 0.14 表 4 两种评价单元下各因子的滑坡发育优势空间
Table 4. Dominant space of landslide development of each factor under two evaluation units
特征
因子坡度
(°)坡高
(m)堆积层
厚度(m)坡面
形态斜坡
结构距河流
距离(m)距道路
距离(m)距矿区
距离(m)距断裂
距离(m)栅格单元 25~35 100~300 1~3 凹型坡 顺向斜坡 100~400 0~100 500~700 >1000 斜坡单元 25~35 100~300 1~3 凹型坡 顺向斜坡 100~400 0~100 >1000 >1000 表 5 特征因子数据正态性检验结果
Table 5. Characteristic factor data Normality test results
特征因子 K-S检验(栅格单元) S-W检验(斜坡单元) 坡高 (m) 0. 33(0. 000***) 0. 762(0. 000***) 距河流距离 (m) 0. 343(0. 000***) 0. 843(0. 000***) 距道路距离 (m) 0. 210(0. 000***) 0. 866(0. 000***) 距矿区距离 (m) 0. 361(0. 000***) 0. 869(0. 000***) 堆积层厚度 (m) 0. 268(0. 000***) 0. 841(0. 000***) 坡度(°) 0. 293(0. 000***) 0. 719(0. 000***) 坡面形态 0. 355(0. 000***) 0. 794(0. 000***) 斜坡结构 0. 439(0. 000***) 0. 849(0. 000***) 距断裂距离 (m) 0. 208(0. 000***) 0. 852(0. 000***) 注:***、**、*分别代表1%、5%、10%的显著性水平。 表 6 特征因子Kendall’s tau-b等级相关系数矩阵(栅格单元)
Table 6. Characteristic factor Kendall’s tau-b rank correlation coefficient matrix (grid units)
距矿区
距离(m)距道路
距离(m)坡面
类型坡度
(°)距断裂
距离(m)斜坡
结构坡高
(m)堆积层
厚度(m)距河流
距离(m)距矿区距离/(m) 1 距道路距离(m) 0.304 1 坡面类型 0.013 0.024 1 坡度(°) −0.01 0.087 0.023 1 距断裂距离(m) −0.001 0.118 0.005 −0.02 1 斜坡结构 −0.141 −0.057 0.006 −0.004 0.201 1 坡高(m) 0.214 0.203 0.009 0.06 0.002 −0.003 1 堆积层厚度(m) −0.053 −0.043 −0.003 −0.028 0.002 0.09 −0.024 1 距河流距离(m) 0.099 0.653 0.029 0.073 0.121 0.023 0.125 0.003 1 表 7 特征因子Kendall's tau-b等级相关系数矩阵(斜坡单元)
Table 7. Characteristic factor Kendall's tau-brank correlation coefficient matrix (slope units)
距矿区
距离(m)距道路
距离(m)坡面
类型坡度
(°)距断裂
距离(m)斜坡
结构坡高
(m)堆积层
厚度(m)距河流
距离(m)距矿区距离(m) 1 − 距道路距离(m) 0.246 1 坡面类型 0.059 0.124 1 坡度(°) −0.07 0.034 0.046 1 距断裂距离(m) 0.006 0.186 0.042 −0.018 1 斜坡结构 −0.112 −0.06 0.032 −0.083 0.199 1 坡高(m) 0.162 0.202 0.043 0.154 −0.011 −0.001 1 堆积层厚度(m) −0.039 −0.05 −0.043 −0.085 −0.002 0.093 −0.068 1 距河流距离(m) 0.02 0.606 0.122 0.004 0.138 0.011 0.125 −0.002 1 表 8 栅格单元与斜坡单元下评价结果频率比
Table 8. Frequency ratio of evaluation results under grid unit and slope unit
评价
单元易发
性滑坡
单元数
(个)滑坡
单元
比例(%)全区
单元
(个)全区
单元
比例(%)频率
比栅格
单元极低 0 0. 00 3055331 66.76 0. 00 低 27 0. 44 892435 19.50 0. 02 中 252 4.07 411435 8.99 0. 45 高 603 9.73 139129 3.04 3.20 极高 5310 85.76 78260 1.71 50.15 斜坡
单元极低 0 0. 00 451 35. 67 0. 00 低 0 0. 00 129 28. 53 0 中 1 3.57 79 18. 38 0. 19 高 1 3.57 38 12. 62 0.28 极高 26 92.86 32 4. 80 19.35 表 9 不同评价单元下易发性概率均值与标准差
Table 9. Mean and standard deviation of probability of Susceptibility under different evaluation units
评价单元 均值 标准差 栅格单元 0. 10 0. 13 斜坡单元 0. 13 0. 18 -
[1] 常志璐, 黄发明, 蒋水华等. 基于多尺度分割方法的斜坡单元划分及滑坡易发性预测[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2023, 55(01): 184-195
CHANG Zhilu, HUANG Faming, JIANG Shuihua et al, Slope Unit Extraction and Landslide Susceptibility Prediction Using Multi-scale Segmentation Method [J] Advanced EngineeringE Sciences, 2023, 55(01): 184-195
[2] 方匡南, 吴见彬, 朱建平等. 随机森林方法研究综述[J]. 统计与信息论坛, 2011, 26(03): 32-38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3116.2011.03.006
FANG Kuangnan, WU Jianbin, ZHU Jianping, et al. Review of random forest methods [J]. Statistics and Information Forum, 2011, 26 (03): 32-38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3116.2011.03.006
[3] 范立民, 何进军, 李存购. 秦巴山区滑坡发育规律研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2004(01): 47-51
FAN Limin, HE Jinjun, LI Cungou. Study on the development law of landslides in Qinba Mountains [J]. Chinese Journal of Geological Hazards and Prevention, 2004 (01): 47-51
[4] 郭芳芳, 杨农, 孟晖等. 地形起伏度和坡度分析在区域滑坡灾害评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质, 2008, 35(01): 131-143.
[5] 郭子正, 殷坤龙, 黄发明, 等. 基于滑坡分类和加权频率比模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019, 38(02): 287-300 doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.0838
GUO Zizheng, YIN Kunlong, HUANG Fa ming, et al. Landslide susceptibility evaluation based on landslide classification and weighted frequency ratio model [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(02): 287-300 doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.0838
[6] 黄发明, 胡松雁, 闫学涯, 等. 基于机器学习的滑坡易发性预测建模及其主控因子识别[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(02): 79-90
HUANG Fangming, HU Songyan, YAN Xueya, et al. . Landslide susceptibility prediction modeling and main control factor identification based on machine learning [J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 202, 41(02): 79-90.
[7] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, No.26(182): 433-454
HUANG Runqiu. Large-scale landslides and their mechanism in China since the 20th century [J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, No.26(182): 433-454
[8] 贾琳, 蔡静森, 晏鄂川等. 基于地质环境分区的南漳县城区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 人民长江, 2021, 52(05): 86-94
JIA Lin, CAI Jingsen, YAN Echuan, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility in Nanzhang County based on geological environment zoning [J]. People's Yangtze River, 2021, 52 (05): 86-94
[9] 谷天峰, 王家鼎, 付新平, 等. 基于斜坡单元的区域斜坡稳定性评价方法[J]. 地理科学. 2013, 33(11): 1400-1405
GU Tianfeng, WANG Jiading, FU Xinping, et al. Regional slope stability evaluation method based on slope unit [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2013, 33(11): 1400-1405
[10] 刘彬. 基于GIS与随机森林算法的斜坡单元类型划分方法[J]. 经纬天地, 2021(04): 82-86
LIU Bin. Classification method of slope unit types based on GIS and random forest algorithm. Jingwei Heavenand Earth, 2021(04): 82-86.
[11] 刘坚, 李树林, 陈涛, 等. 基于优化随机森林模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2018, 43(07): 1085-1091
LIU Jian, LL Shulin, CHEN Tao, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on optimized random forest model [J]. Geomatics andInformation Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(07): 1085-1091.
[12] 刘伟, 袁湘秦, 连海波, 等. 陕南地区堆积层滑坡发育规律研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(10): 194-197+224.
LIU Wei, YUAN Xiangqin, LIAN Haibo, et al. Research on the development law of accumulation landslide in southern Shaanxi [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(10): 194-197 224.
[13] 强菲, 赵法锁, 段钊, 等. 陕南秦巴山区地质灾害发育及空间分布规律[J]. 灾害学, 2015, 30(02): 193-198
QIANG Fei, ZHAO FaSuo, DUAN Zhao, et al. Developmentand spatialdistribution of geological disasters in Qinling-Data Mountains ofsouth Shaanxi [J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2015, 30 (2): 193-198.
[14] 陕西省自然资源厅. 陕西省城镇(乡镇)地质灾害风险调查评价技术要求(1: 10000)(试行)[R]. 西安: 陕西省自然资源厅, 2021
[15] 唐睿旋. 堆积层滑坡单体稳定性评估及区域易发性评价研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017
TANG Ruixuan .Study on stability assessment and regional vulnerability assessment of accumulative landslide[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2017
[16] 田述军, 张珊珊, 唐青松等. 基于不同评价单元的滑坡易发性评价对比研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2019, 28(06): 137-145
TIAN Shujun, ZHANG Shanshan, TANG Qingsong et al, Comparative study of landslide susceptibility assessment based on different evaluation units [J] Journal Of Natural Disasters, 2019, 28(06): 137-145
[17] 吴润泽, 胡旭东, 梅红波, 等. 基于随机森林的滑坡空间易发性评价: 以三峡库区湖北段为例[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(01): 321-330
WU Runze, HU Xudong, MEI Hongbo, et al. Spatial susceptibility assessment of landslides based on random forest: A case study in the Hubei section of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area [J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(01): 321-330.
[18] 邢林啸. 三峡库区典型堆积层滑坡成因机制与预测预报研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2012
XING Linxiao. Research on the genetic mechanism and prediction of typical accumulation landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2012
[19] 赵力行, 范文, 柴小庆, 等. 秦巴山区地质灾害发育规律研究——以镇巴县幅为例[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(02): 187-195 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.02.011
ZHAO lixing, FAN Wen, CHAI Xiaoqing, et al. A study on thedevelopment law of geological hazards in qinling-bashan mountainsーtaking the Zhenba Countyarea as an example [J]. Geology and resources, 2020, 29(02): 187-195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.02.011
[20] 张林梵, 王佳运, 张茂省等. 基于BP神经网络的区域滑坡易发性评价[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(02): 260-270
Zhang Linfan, Wang Jiayun, Zhang Maosheng et al. Evaluation of regional landslide susceptibility based on BP neural network [J]. Northwest Geology, 2022, 55 (02): 260-270.
[21] 段钊, 彭建兵, 陈伟等. 泾河下游黄土台塬区滑崩灾害空间分异研究[J]. 西北地质, 2018, 51(03): 214-222 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2018.03.020
Duan Zhao, Peng Jianbing, Chen Wei, et al. Spatial differentiation of landslide disasters in the loess plateau area of the lower reaches of the Jinghe River [J]. Northwest Geology, 2018, 51 (03): 214-222 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2018.03.020
[22] 张世林. 秦巴山区斜坡结构类型及变形破坏模式研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020
ZHANG Shilin. Study on slope structure type and deformation failure mode in qinling-bashan mountain area [D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2020
[23] 郑迎凯, 陈建国, 王成彬, 等. 确定性系数与随机森林模型在云南芒市滑坡易发性评价中的应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(06): 131-144
ZHENG Yingkai, CHEN Jianguo, WANG Chengbin, et al. Application of deterministic coefficient and random forest model in landslide susceptibility assessment in Mangshi City, Yunnan Province [J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(06): 131-144.
[24] Ahmed Mohamed Youssef, Hamid Reza Pourghasemi, Zohre Sadat P ourtaghi, et al.Landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest, boosted regression tree, classification and regression tree, and general linear models and comparison of their performance at WadiTayyah Basin, Asir Region, Saudi Arabia[J]. Landslides, 2016, 13: 839-856.
[25] Merghadi Abdelaziz, Abderrahmane Boumezbeur, Tien Bui Dieu, et al. Landslide Susceptibility Assessmentat Mila Basin (Algeria): A Comparative Assessment of Prediction Capability of Advanced Machine Learning Methods[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2018, 7(7). [9]
[26] Saro Lee, Joong-Sun Won, Seong Woo Jeon, InhyePark, Moung Jin Lee, et al. Spatial Landslide Hazard Prediction Using Rainfall Probability and a Logistic Regression Model[J]. Mathematical Geosciences, 2015, 47(5).
-




 下载:
下载: