ANALYSIS ON THE SPATIOTEMPORAL VARIATION OF SOIL pH IN XINGKAI LAKE PLAIN, HEILONGJIANG PROVINCE
-
摘要:
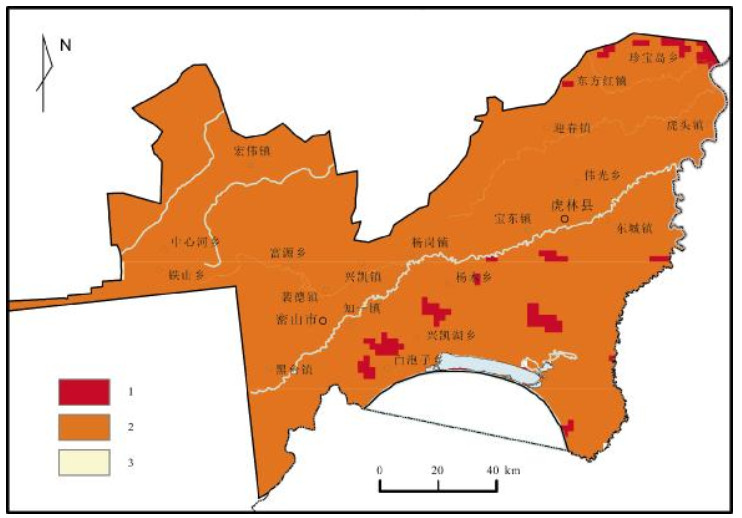
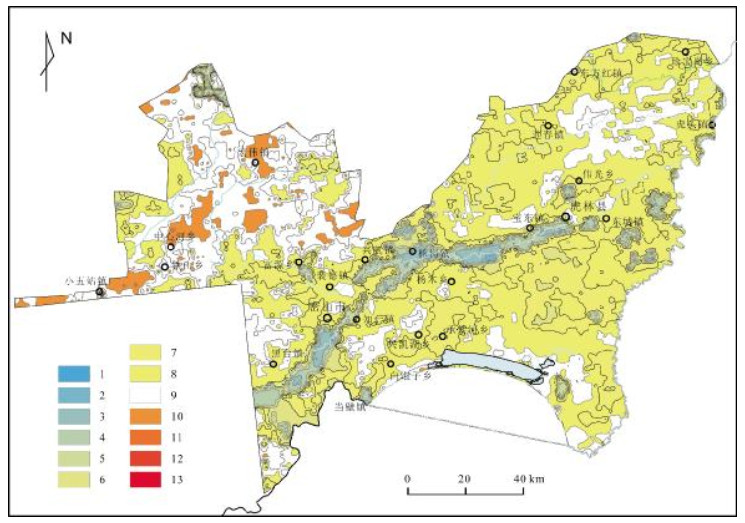
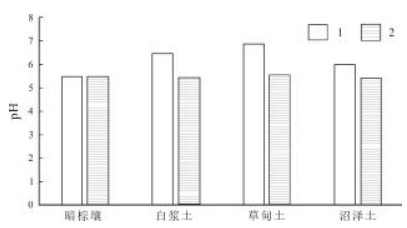
土壤酸碱度是影响土壤化学和生物学性质的一个重要因素,会对土地生产力产生重要影响.为掌握兴凯湖平原土壤pH值近年来变化状况,采用空间统计方法,基于全国第二次土壤普查及2019年土壤pH值数据,对工作区近30年土壤pH值时空变化特征进行了分析.结果表明:兴凯湖平原土壤pH值总体呈下降趋势,但整体上土壤pH值变幅不大,主要集中在±0.5~±1区间.从土地利用类型上来看,兴凯湖平原耕地区土壤pH值均呈下降趋势,西部的林地区pH值整体保持不变或略有上升.在兴凯湖平原4种主要土壤类型中,除暗棕壤外,其他3类土壤在近30年间pH平均值均呈下降趋势.因此需要对工作区土壤pH值变化的原因进行多因素、定量分析,以进一步明确具体原因.
Abstract:Soil pH is an important factor affecting the chemical and biological properties of soil. It also has an important impact on land productivity. To learn about the variation of soil pH in Xingkai Lake Plain in recent years, on the basis of the second national soil survey and soil pH data of 2019, the spatial statistics is used to analyze the spatiotemporal variation characteristics of soil pH in the study area over the past 30 years. The results show that the soil pH is generally declining, but does not vary greatly(±0.5 to ±1). In terms of land use types, the soil pH of cultivated land show a downward trend, while that in the western forest area remains unchanged or increases slightly. Among the 4 main soil types in Xingkai Lake Plain, except for dark brown soil, the other three are all falling in average pH values during the past 30 years. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct multi-factor and quantitative analysis to further clarify the specific causes of soil pH variation in the study area.
-
Key words:
- soil /
- pH /
- spatiotemporal variation /
- Xingkai Lake Plain /
- Heilongjiang Province
-

-
表 1 1980年和2019年土壤采样点pH值统计
Table 1. Soil pH statistics of the sampling sites in 1980 and 2019
年份 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 中位数 标准偏差 方差 偏度 峰度 1980 4152 4.70 8.80 6.22 6.20 0.91 0.824 1.192 2.019 2019 4152 4.27 7.10 5.47 5.46 0.34 0.114 0.307 0.735 表 2 不同土壤pH级别面积变化情况
Table 2. Variation of area and percentage by soil pH values
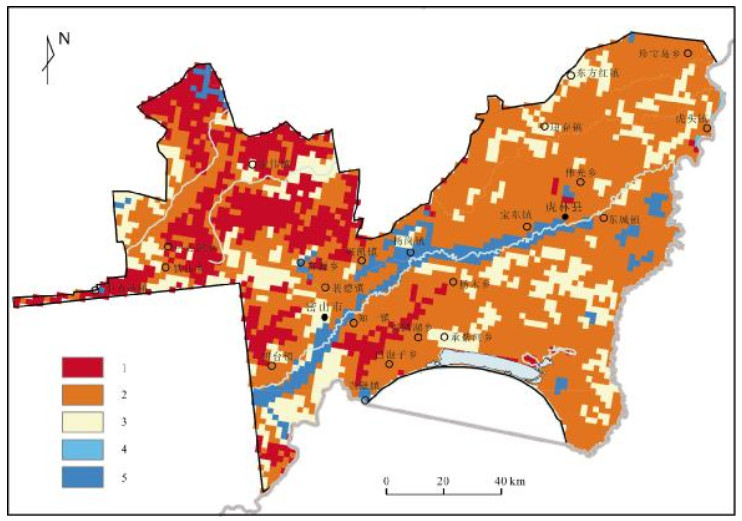
pH值级别 面积/km2 比例/% 备注 -4.5~-4.0 8 0.05 下降总比例61.02% -4.0~-3.5 300 1.81 -3.5~-3.0 616 3.71 -3.0~-2.5 208 1.25 -2.5~-2.0 68 0.41 -2.0~-1.5 956 5.76 -1.5~-1.0 3316 19.97 -1.0~-0.5 4660 28.06 -0.5~0 3140 18.91 不变比例30.25% 0~0.5 1884 11.34 0.5~1.0 1236 7.44 上升总比例8.73% 1.0~1.5 192 1.16 1.5~2.0 20 0.12 2.0~2.5 4 0.02 -
[1] Brady N C, Weil R R.土壤学与生活(原书第十四版)[M].李保国, 徐建明, 译.北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 340.
[2] 熊毅, 李庆逵.中国土壤[M]. 2版.北京:科学出版社, 1987:433-463.
[3] 徐仁扣, Coventry D R.某些农业措施对土壤酸化的影响[J].农业环境保护, 2002, 21(5):385-388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200205000.htm
[4] 王志刚, 赵永存, 廖启林, 等.近20年来江苏省土壤pH值时空变化及其驱动力[J].生态学报, 2008, 28(2):720-727. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.02.033
[5] 徐仁扣.酸化红壤的修复原理与技术[M].北京:科学出版社, 2013.
[6] Mok J S, Yoo H D, Kim P H, et al. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in oysters from the southern coast of Korea:Assessment of potential risk to human health[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2015, 94(6):749-755. doi: 10.1007/s00128-015-1534-4
[7] Zhu H H, Chen C, Xu C, et al. Effects of soil acidification and liming on the phytoavailability of cadmium in paddy soils of central subtropical China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 219:99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.043
[8] 杨劲松.土壤盐渍化研究展望[J].土壤, 1995(1):23-27. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.1995.01.008
[9] 胡敏, 向永生, 张智, 等.恩施州耕地土壤pH近30年变化特征[J].应用生态学报, 2017, 28(4):1289-1297. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB201704028.htm
[10] 刘丽, 张玉龙, 虞娜, 等.基于GIS的辽宁北部地区土壤酸化特征及其原因分析——以昌图县为例[J].沈阳农业大学学报, 2012, 43(2):173-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYNY201202011.htm
[11] 朱小琴, 孙维侠, 黄标, 等.长江三角洲城乡交错区农业土壤pH特征及影响因素探讨——以江苏省无锡市为例[J].土壤学报, 2009, 46(4):594-602. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2009.04.005
[12] 郭治兴, 王静, 柴敏, 等.近30年来广东省土壤pH值的时空变化[J].应用生态学报, 2011, 22(2):425-430. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB201102024.htm
[13] 佀国涵, 王瑞, 袁家富, 等.鄂西南山区土壤酸化趋势研究——以恩施州宣恩县为例[J].中国农学通报, 2014, 30(12):151-155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201412027.htm
[14] 张驭航, 李玲, 王秀丽, 等.河南省土壤pH值时空变化特征分析[J].土壤通报, 2019, 50(5):1091-1100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201905012.htm
[15] Hicks W K, Kuylenstierna J C I, Owen A, et al. Soil sensitivity to acidification in Asia:Status and prospects[J]. AMBIO A Journal of the Human Environment, 2008, 37(4):295-303. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447(2008)37[295:SSTAIA]2.0.CO;2
[16] 李帅, 刘丹, 于成龙, 等. 1991-2012年黑龙江省酸雨变化特征[J].气象与环境学报, 2015, 31(5):105-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNQX201505015.htm
[17] Guo J H, Liu X J, Zhang Y, et al. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands[J]. Science, 2010, 327(5968):1008-1010. doi: 10.1126/science.1182570
[18] Lilienfein J, Wilcke W, Vilela L, et al. Effect of no-tillage and conventional tillage systems on the chemical composition of soil solid phase and soil solution of Brazilian Savanna Oxisols[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2000, 163(4):411-419. doi: 10.1002/1522-2624(200008)163:4<411::AID-JPLN411>3.0.CO;2-V
[19] 邵明娜.虎林市耕地地力调查与平衡施肥调研[J].农民致富之友, 2016(23):124-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NMZF201623123.htm
[20] 虎林市统计局.虎林市2017年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[R].虎林: 虎林市统计局, 2018.
-



 下载:
下载: