DISTRIBUTION CHARACTERISTICS OF HEAVY METALS IN THE WATER AND SUSPENDED SUBSTANCE OF NENJIANG RIVER BASIN: Environmental Implication
-
摘要:
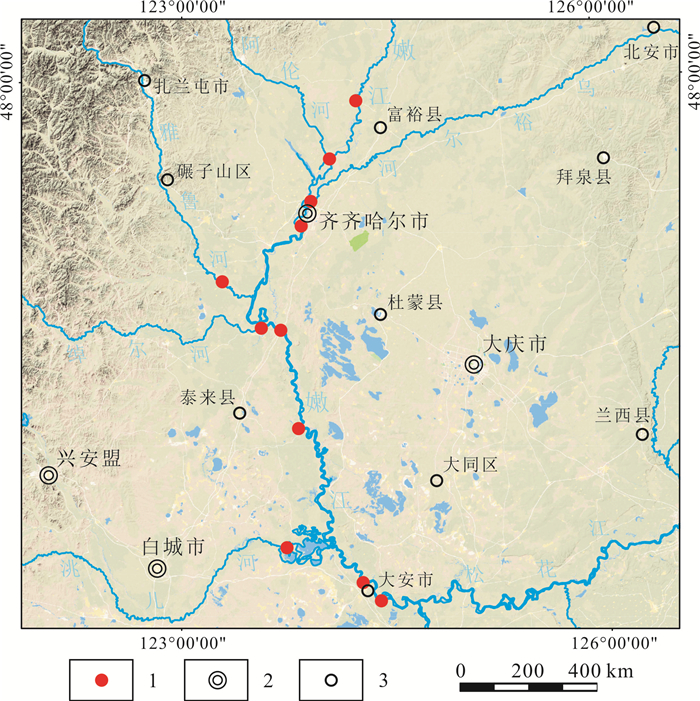
水和悬浮物是河流重金属元素迁移的主要载体.对嫩江中下游悬浮物及滤后水重金属元素分布特征进行了较系统的研究,结果表明:丰水期是嫩江流域内悬浮物迁移的主要季节,支流的汇入会影响嫩江干流悬浮物浓度,大安市生产生活对水体悬浮物浓度产生明显影响;齐齐哈尔市的生产生活对嫩江水体悬浮物重金属含量影响不大,而对水中Cr、Cu、Pb、Ni、Zn元素产生明显影响;雅鲁河是向嫩江输入重金属Cr、Ni最多的支流,年输入嫩江通量分别为1223、100.46 t;阿伦河是向嫩江输入重金属Cd、Cu、Pb最多的支流,年输入嫩江通量分别为0.08、10.93、9.96 t;嫩江向松花江年输入重金属As、Hg、Cd、Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn、Ni通量分别为113.7、0.32、0.79、438、164、152、440、224 t.
Abstract:Water and suspended substance are the main carriers for the migration of heavy metal elements in rivers. The paper systematically studies the distribution characteristics of heavy metals in suspended substance and filtered water from the middle and lower reaches of Nenjiang River. The results show that the migration of suspended substance mainly occurs in wet season, and the inflow of tributaries may affect the concentration of suspended matter in the main stream. The industrial and domestic activities in Da'an City have obvious influence on the concentration of suspended matter; while those in Qiqihar have little influence on the heavy metal contents in suspended substance, but significant influence on Cr, Cu, Pb, Ni, and Zn in water. Yalu River brings the most heavy metals Cr and Ni to Nenjiang River, with the annual flux of 1223 and 100.46 t, respectively. Arun River inputs the most heavy metals Cd, Cu and Pb, with the annual flux of 0.08, 10.93 and 9.96 t, respectively. The annual fluxes of heavy metals such as As, Hg, Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn and Ni from Nenjiang River to Songhua River are 113.7, 0.32, 0.79, 438, 164, 152, 440 and 224 t, respectively.
-
Key words:
- Nenjiang River /
- suspended substance in water /
- filtered water /
- heavy metal
-

-
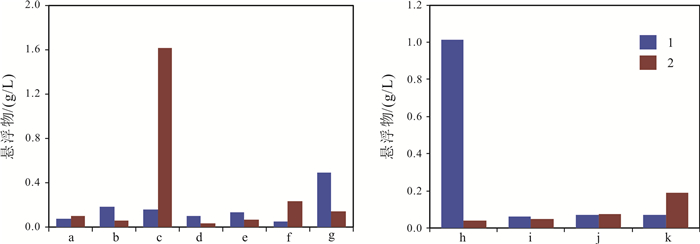
表 1 嫩江干流及其主要支流悬浮物含量统计
Table 1. Contents of suspended solids in the main stream and tributaries of Nenjiang River
干流 丰水期 枯水期 支流 丰水期 枯水期 富裕段 0.074 0.098 阿伦河 1.015 0.039 齐齐哈尔上游段 0.184 0.060 雅鲁河 0.064 0.049 齐齐哈尔下游段 0.158 1.612 绰尔河 0.072 0.074 泰来上游 0.101 0.037 洮儿河 0.071 0.193 泰来下游 0.137 0.070 大安上游 0.050 0.232 大安下游 0.489 0.145 平均 0.173 0.107 平均 0.305 0.089 含量单位:g/L. 表 2 嫩江干流及主要支流滤后水重金属元素含量
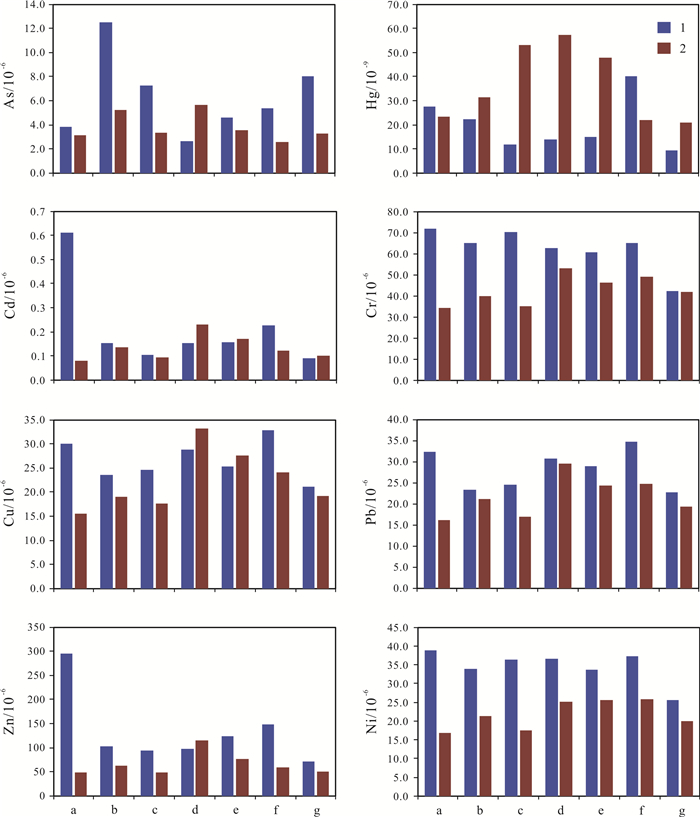
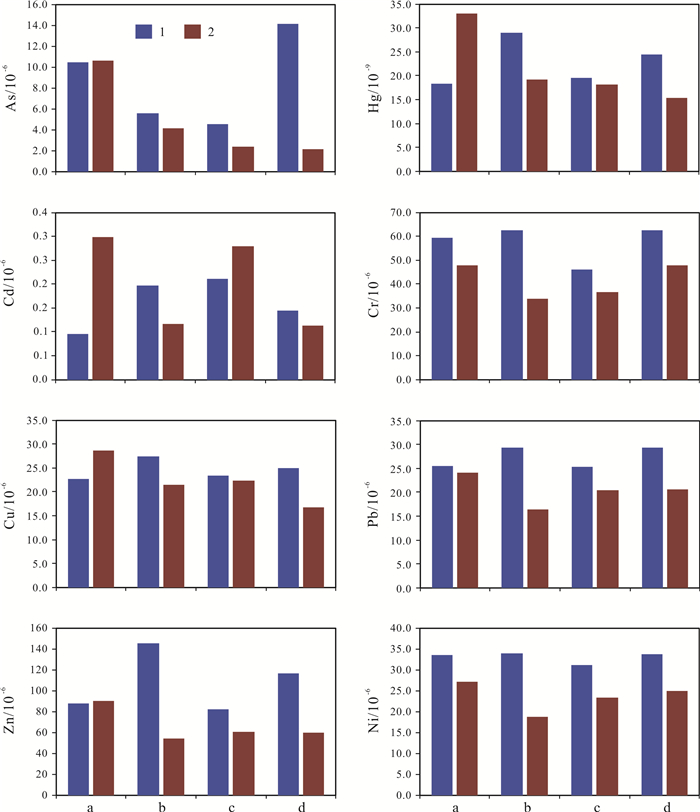
Table 2. Heavy metal contents in the filtered water of Nenjiang River and main tributaries
河流段 米样时间 As Hg Cd Cr Cu Pb Ni Zn 富裕县段 丰水期 2.40 0.060 0.076 4.79 1.55 0.68 1.38 5.36 枯水期 3.30 0.074 0.005 3.42 0.93 0.04 0.62 1.35 齐齐哈尔上游段 丰水期 2.55 0.010 0.011 13.02 1.43 0.81 1.61 7.21 枯水期 3.00 0.028 0.003 4.69 0.80 0.10 0.73 0.69 齐齐哈尔下游段 丰水期 1.50 0.011 0.010 14.18 3.53 1.31 1.90 9.78 枯水期 3.45 0.008 0.003 3.34 0.76 0.02 0.72 0.85 泰来县上游段 丰水期 3.30 0.009 0.015 47.16 1.44 1.01 10.26 7.95 枯水期 4.05 0.014 0.012 5.34 3.45 0.35 1.34 3.76 泰来县下游段 丰水期 2.70 0.010 0.009 15.05 1.51 0.92 1.83 6.59 枯水期 4.20 0.006 0.003 3.97 1.27 0.01 0.72 0.06 大安上游段 丰水期 3.90 0.011 0.010 10.22 1.54 0.70 1.44 3.74 枯水期 4.20 0.006 0.008 3.35 1.47 0.06 0.90 1.07 大安下游段 丰水期 2.40 0.014 0.007 10.00 1.47 0.69 1.38 5.32 枯水期 4.50 0.006 0.005 3.88 0.98 0.04 0.76 0.99 阿伦河段 丰水期 3.60 0.016 0.022 6.84 2.14 1.71 3.16 34.96 枯水期 4.80 0.016 0.008 3.00 1.55 0.16 0.89 0.67 雅鲁河段 丰水期 3.45 0.010 0.009 1312.30 1.16 0.93 4.86 96.88 枯水期 4.50 0.006 0.001 4.39 0.65 0.10 0.34 8.76 绰尔河 丰水期 1.95 0.008 0.012 118.69 1.61 0.82 33.32 17.82 枯水期 4.80 0.011 0.003 4.54 1.10 0.12 0.57 1.79 洮儿河 丰水期 10.05 0.009 0.015 19.16 1.72 0.65 2.18 5.80 枯水期 7.50 0.008 0.020 5.61 1.75 0.05 2.37 0.06 含量单位:mg/mL. 表 3 嫩江及主要支流多年年均径流量统计
Table 3. Average annual runoff of Nenjiang River and main tributaries
河流段 嫩江 阿伦河 雅鲁河 绰尔河 洮儿河 径流量/(108m3/a) 216.12 7.12 18.5 20.6 17.4 悬浮物总量/t 6 852 965 375 190.8 104 552.8 151 168 229 233 表 4 嫩江及主要支流输出重金属通量
Table 4. Output flux of heavy metals from Nenjiang River and main tributaries
元素 介质 嫩江 阿伦河 雅鲁河 绰尔河 洮儿河 As 悬浮物 38.61 3.96 0.51 0.52 1.86 水 74.56 2.99 7.35 6.95 15.27 Hg 悬浮物 0.103 0.010 0.003 0.003 0.005 水 0.216 0.011 0.015 0.020 0.015 Cd 悬浮物 0.66 0.07 0.02 0.04 0.03 水 0.13 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.03 Cr 悬浮物 288.23 20.08 5.03 6.25 12.65 水 149.99 3.50 1217.94 126.93 21.55 Cu 悬浮物 138.01 9.61 2.56 3.45 4.79 水 26.47 1.31 1.67 2.79 3.02 Pb 悬浮物 144.46 9.29 2.39 3.46 5.72 水 7.89 0.67 0.95 0.97 0.61 Zn 悬浮物 416.79 33.43 10.44 10.82 20.23 水 23.12 1.44 4.81 34.91 3.96 Ni 悬浮物 156.09 11.41 2.75 4.12 6.73 水 68.19 12.68 97.72 20.20 5.10 单位:t. -
[1] 屈翠辉, 郑建勋, 杨绍晋, 等. 黄河、长江、珠江下游控制站悬浮物的化学成份及其制约因素的研究[J]. 科学通报, 1984, 29(17): 1063-1066. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198417012.htm
Qu C H, Zheng J Z, Yang S J, et al. Chemical composition of suspended matter and its restriction factors in control stations of the lower reaches of the Yellow River, the Yangtze River and the Pearl River[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1984, 29(17): 1063-1066. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198417012.htm
[2] 刘文, 徐士进, 杨杰东, 等. 金沙江河流悬浮物与沉积物的矿物学特征及其表生地球化学意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2007, 26(2): 164-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200702011.htm
Liu W, Xu S J, Yang J D, et al. Mineralogical characteristics of suspended matters and sediments in the Jinshajiang River and their superficial geochemical significance[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2007, 26(2): 164-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200702011.htm
[3] Zhou D M, Chen H M, Zheng C R. Heavy metals in water bodies purified by suspended substrate of rivers[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2002, 14(1): 44-48. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jes-e200201008
[4] Woitke P, Wellmitz J, Helm D, et al. Analysis and assessment of heavy metal pollution in suspended solids and sediments of the river Danube[J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 51(8): 633-642. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00217-0
[5] 王文正, 张经. 欧洲罗纳河和中国几条主要河流悬浮物的矿物学组成分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1994, 25(3): 319-327. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1994.03.014
Wang W Z, Zhang J. Analysis on the mineral compositions of suspended matter from Rhone and some main Chinese rivers[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1994, 25(3): 319-327. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1994.03.014
[6] 何江, 王新伟, 李朝生, 等. 黄河包头段水-沉积物系统中重金属的污染特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 2003, 23(1): 53-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX200301010.htm
He J, Wang X W, Li C S, et al. Pollution character of heavy metals in the water-sediment system from Baotou section of the Yellow River[J]. Acta scientiae Circumstantiae, 2003, 23(1): 53-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX200301010.htm
[7] 张敏, 王德淑. 长江铜陵段表层水中重金属含量及存在形态分布研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2003, 3(6): 61-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ200306017.htm
Zhang M, Wang D S. Investigation on heavy metal elements distribution on surface water of Tongling section along the Yangtse River[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2003, 3(6): 61-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ200306017.htm
[8] 王中波, 杨守业, 李萍, 等. 长江水系沉积物碎屑矿物组成及其示踪意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 24(4): 570-578. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200604014.htm
Wang Z B, Yang S Y, Li P, et al. Detrital mineral compositions of the Changjiang River sediments and their tracing implications[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(4): 570-578. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200604014.htm
[9] Yang S Y, Jung H S, Choi M S, et al. The rare earth element compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtze) and Huanghe (Yellow) river sediments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 201(2): 407-419.
[10] Zhang C S, Wang L J, Zhang S, et al. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in the mainstream of the Yangtze River, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 1998, 13(4): 451-462.
[11] Dupré B, Gaillardet J, Rousseau D, et al. Major and trace elements of river-borne material: the Congo Basin[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(8): 1301-1321. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(96)00043-9
[12] Gaillardet J, Dupré B, Allègre C J. A global geochemical mass budget applied to the Congo basin rivers: erosion rates and continental crust composition[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(17): 3469-3485.
[13] Roy S, Gaillardet J, Allègre C J. Geochemistry of dissolved and suspended loads of the Seine River, France: anthropogenic impact, carbonate and silicate weathering[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(9): 1277-1292. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S001670379900099X
[14] Singh P, Rajamani V. REE geochemistry of recent clastic sediments from the Kaveri floodplains, southern India: implication to source area weathering and sedimentary processes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(18): 3093-3108. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016703701006366
[15] Sharma A, Rajamani V. Weathering of charnockites and sediment production in the catchment area of the Cauvery River, southern India[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2001, 143(1/2): 169-184. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0037073801001026
[16] Vital H, Stattegger K. Major and trace elements of stream sediments from the lowermost Amazon River[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 168(1/2): 151-168. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254100001911
[17] 高建飞, 丁悌平, 田世洪, 等. 黄河水及其悬浮物硅同位素组成的变化特征及其地质环境意义[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(10): 1613-1628. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201110007.htm
Gao J F, Ding D P, Tian S H, et al. Silicon isotope compositions of suspended matter in the Yellow River, China, and its significance in geological environment[J]. Acta geologicasinica, 2011, 85(10): 1613-1628. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201110007.htm
[18] 刘飞, 成杭新, 杨柯, 等. 广州市土壤-大气界面Hg交换通量研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(2): 331-338. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201402022.htm
Liu F, Cheng H X, Yang K, et al. Research of mercury exchange flux between soil and air in Guangzhou City[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(2): 331-338. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201402022.htm
[19] 齐齐哈尔市志编审委员会. 齐齐哈尔市志[M]. 合肥: 黄山书社, 1998: 171-173.
Editorial Committee of Chronicle of Qiqihar City. Chronicle of Qiqihar City[M]. Hefei: Huangshan Publishing House, 1998: 171-173. (in Chinese)
[20] 何宏平. 粘土矿物与金属离子作用研究[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2001: 237-239.
He H P. Study on the interaction between clay minerals and metal ions[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2001: 237-239.
[21] 何文光. 甘南县志[M]. 合肥: 黄山书社, 1992: 189-190.
He W G. Chronicle of Gannan County[M]. Hefei: Huangshan Publishing House, 1992: 189-190. (in Chinese)
[22] 金耀东. 兴安盟志[M]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古人民出版社, 1997: 145-147.
Jin Y D. Chronicle of Xing'an League[M]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia People's Publishing House, 1997: 145-147. (in Chinese)
[23] 吉林省地方志编纂委员会. 吉林省志·自然地理志[M]. 长春: 吉林人民出版社, 1992: 321-323.
Jilin Provincial Local Chronicles Compilation Committee. Chronicle of Jilin Province: Physical geography[M]. Changchun Jilin People's Publishing House, 1996: 321-323. (in Chinese)
[24] 肇源县地方志编审委员会办公室. 肇源县志[M]. 肇源: 肇源县地方志编审委员会办公室, 1996: 165-167.
Zhaoyuan County Local Chronicles Compilation Committee. Chronicles of Zhaoyuan County[M]. Zhaoyuan: Zhaoyuan County Local Chronicles Compilation Office, 1998: 165-167. (in Chinese)
[25] 吴敦敖, 鲁文毓. 铬在土壤-地下水系统中的污染研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 1991, 11(3): 276-283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX199103003.htm
Wu D A, Lu W Y. Study on the pollution of chromium in soil-groundwater system[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 1991, 11(3): 26-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX199103003.htm
-



 下载:
下载: