APPLICATION OF MICROSEISMIC MONITORING TECHNOLOGY IN HYDRAULIC FRACTURING OF THE SHALE OIL IN NORTHERN SONGLIAO BASIN
-
摘要:
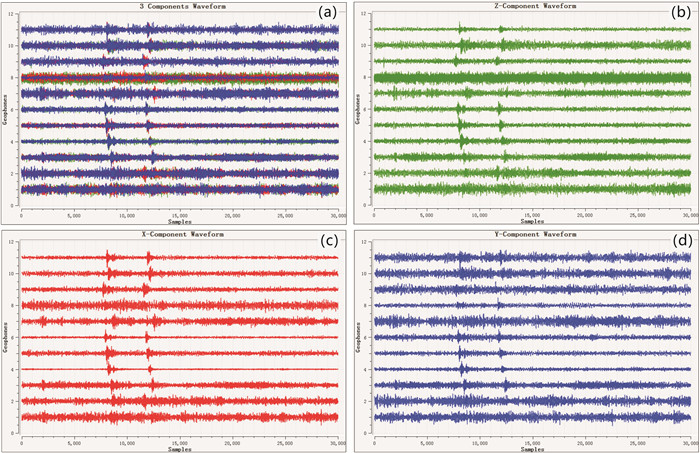
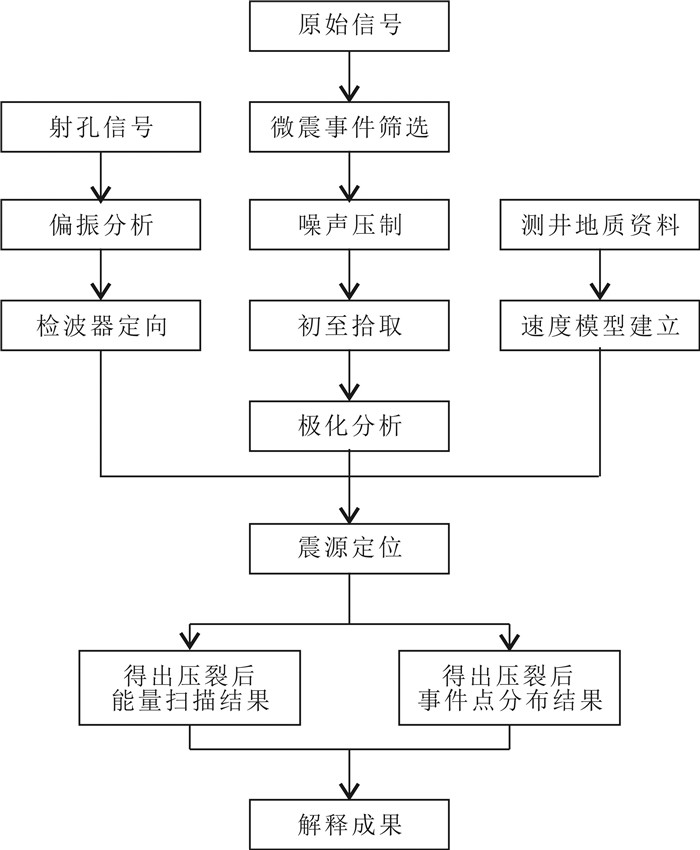
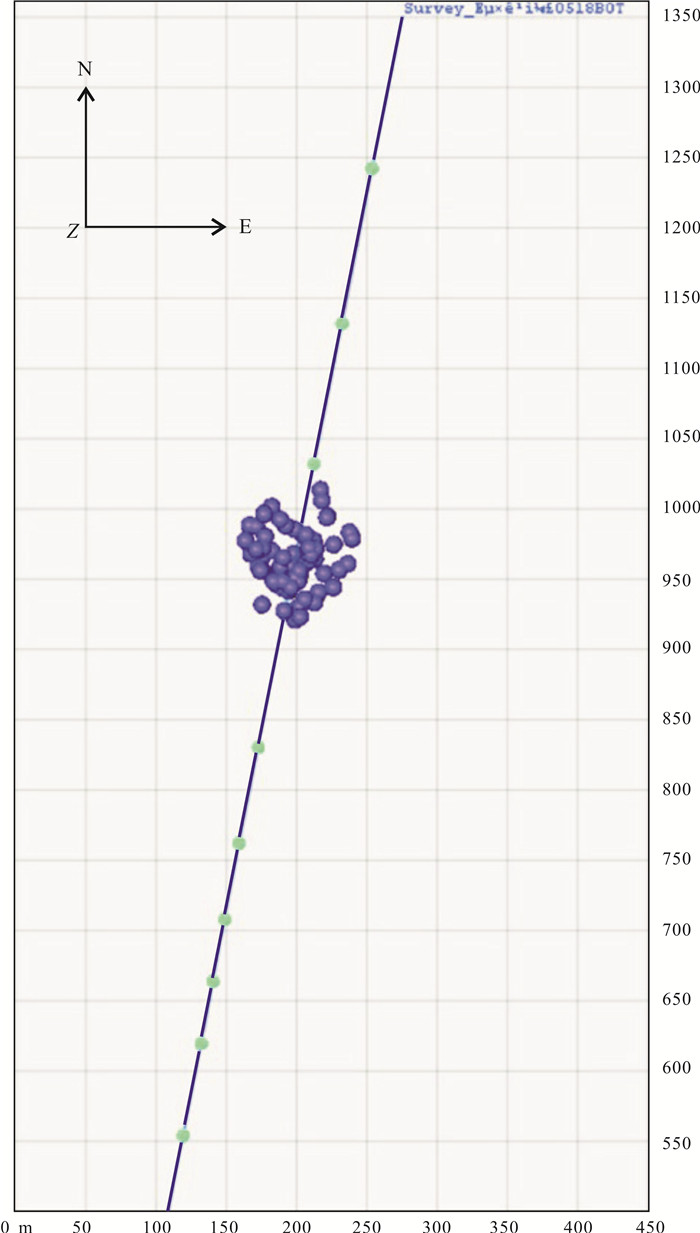
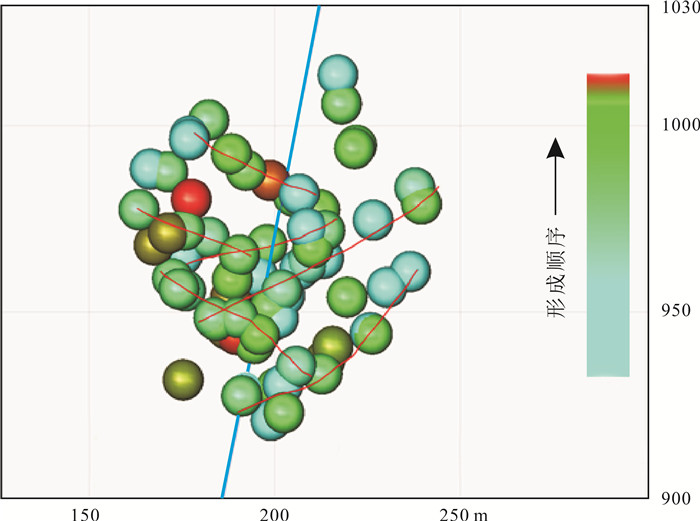
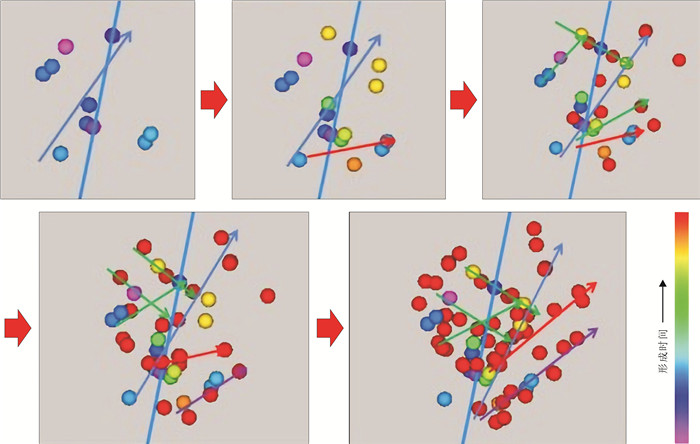
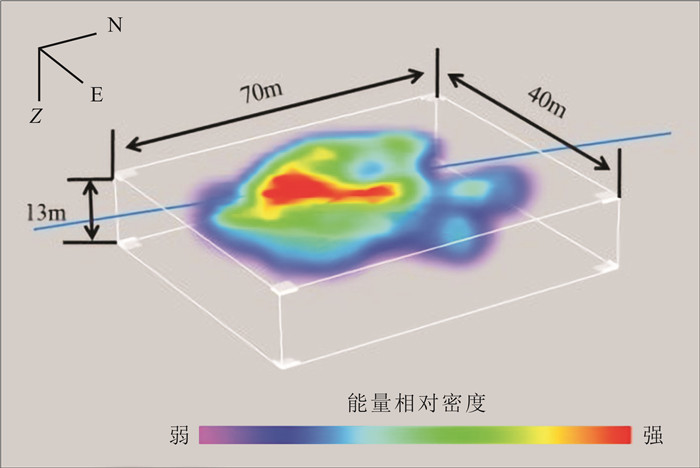
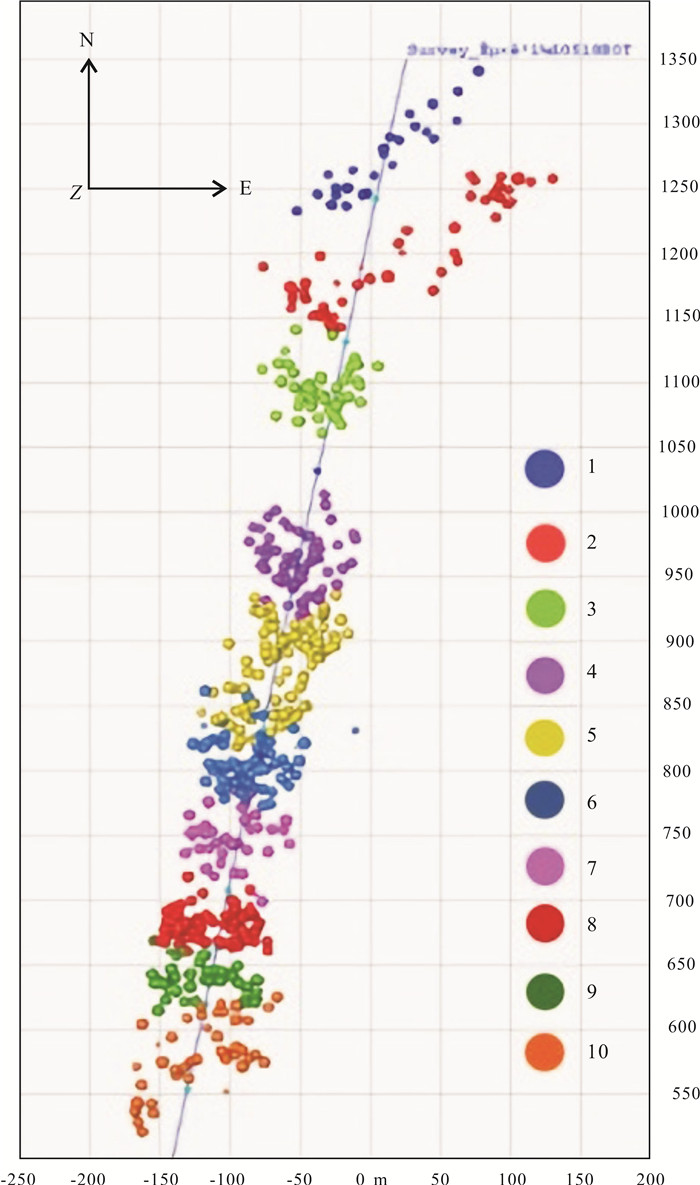
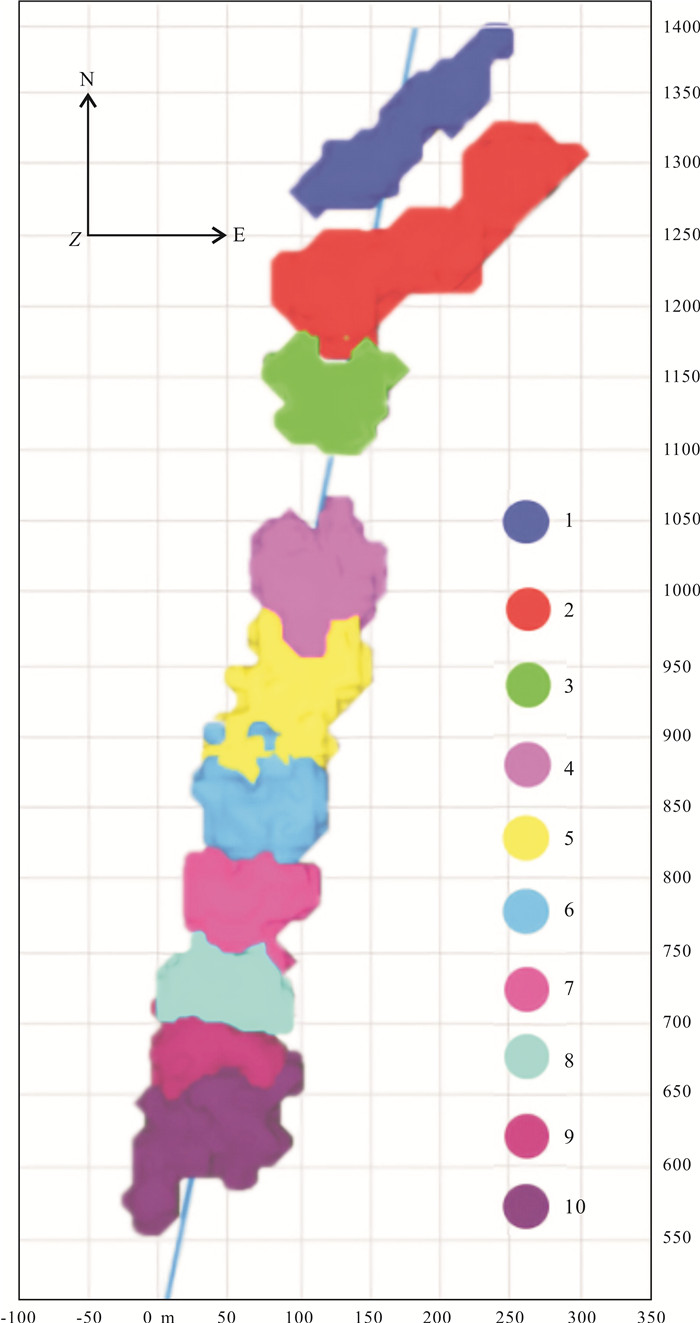
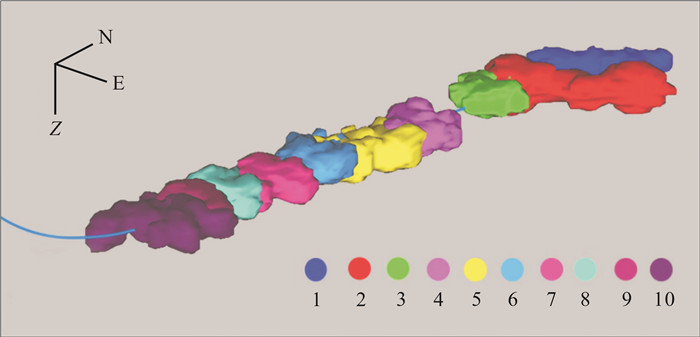
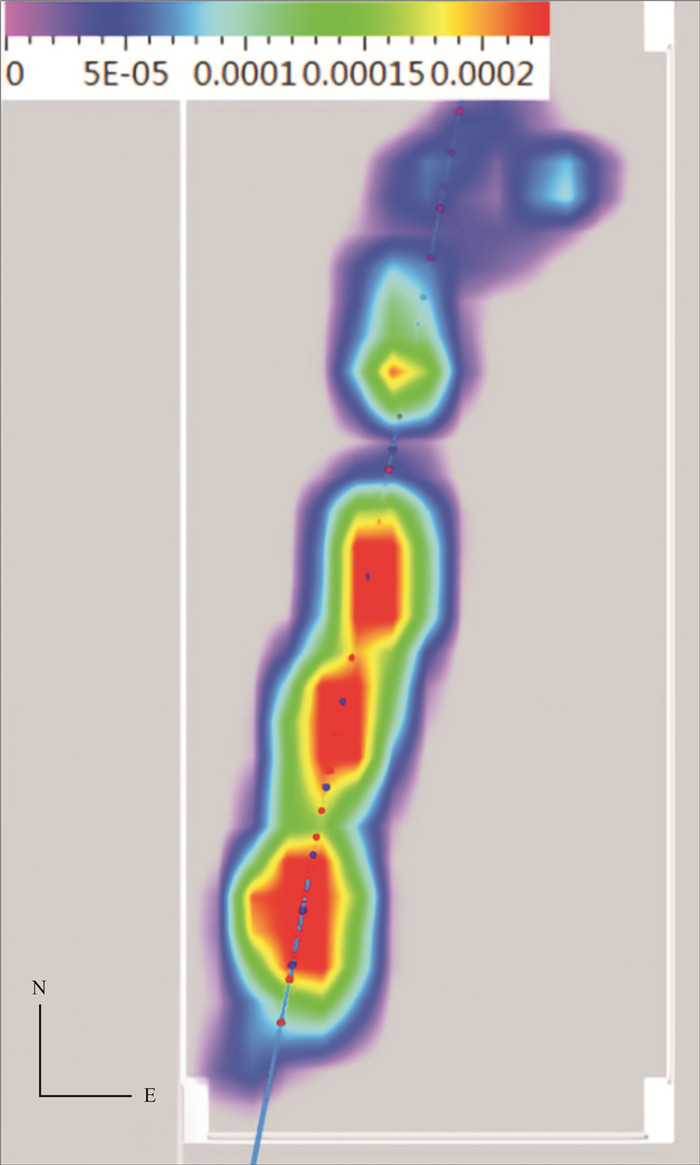
松辽盆地页岩油储量丰富,是重要的油气资源接替领域.页岩油是一种重要的非常规油气类型,但是其形成和埋藏的地质条件复杂,储层物性差.页岩油的勘探、开发都需要进行水力压裂,微地震监测是压裂效果需要评价的重要技术.根据松页油1HF井的地表、地下的地震地质条件和水平段展布特征,设计较为规则的矩形观测系统实施地面微地震监测,保证全方位均匀地覆盖目标区.通过保证检波器和地表良好耦合的系列措施,对埋深2 000 m以下的页岩油目标,采集到肉眼可识别的压裂微地震信号,采用层析成像技术进行压裂破裂范围计算和微地震事件反演定位.成像结果表明,各段压裂后造缝效果较为明显,有效沟通了储层与井眼的流体通道.微地震监测的实践初步证明,合理的压裂参数设计和工程施工,可获得页岩油压裂的良好效果,形成的微地震监测技术是评价压裂效果的重要而有效的手段,为页岩油的勘探开发提供技术支撑.
Abstract:Songliao Basin is rich in shale oil reserves, and serves as a significant oil-gas resources replacing field. Shale oil is an important unconventional oil-gas type. Due to complex geological conditions of formation and burial, and poor reservoir physical property, its exploration and development requires hydraulic fracturing, and microseismic monitoring is an essential technology to evaluate fracturing effect. According to the surface and underground seismic geological conditions and distribution characteristics of horizontal stages in SYY-1HF well, a regular rectangular observation system is designed for ground microseismic monitoring to ensure uniform coverage of the target area in all directions. For shale oil buried below 2000 m, the fracturing microseismic signals visible to naked eyes are collected through good coupling of geophone and ground, and tomography technique is used for calculation of fracture range and inversion positioning of microseismic events. The imaging results show that the fracture formation effect is obvious after fracturing in each stage, which effectively links the fluid channel between reservoir and wellbore. The practice of microseismic monitoring has initially proved that reasonable fracturing parameter design and engineering construction can achieve good fracturing effect of shale oil; the microseismic monitoring technology is a significant and effective means to evaluate fracturing effect and provide technical support for exploration and development of shale oil.
-
Key words:
- Songliao Basin /
- shale oil /
- microseismic monitoring /
- hydraulic fracturing
-

-
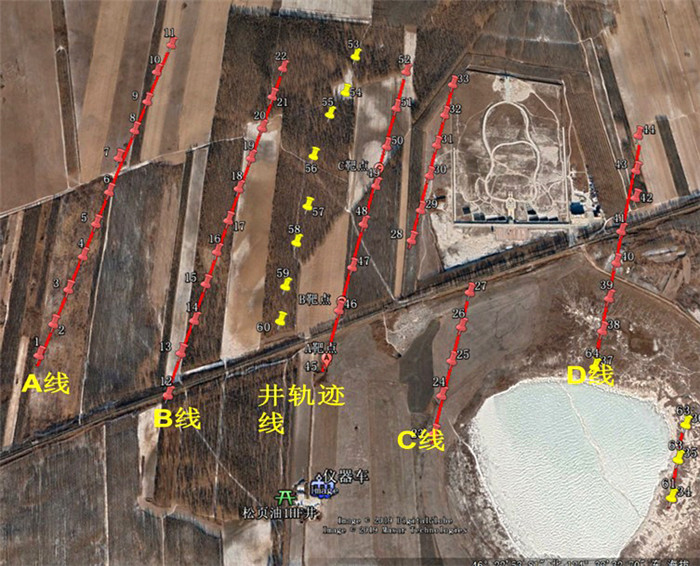
表 1 松页油1HF井简况
Table 1. Profile of SYY-1HF well
压裂井号 松页油1HF井(SYY-1HF) 井别/井型 参数井/开窗侧钻水平井 构造位置 松辽盆地中央拗陷区齐家凹陷南部 地理位置 黑龙江省大庆市大同区大榆山村西1.9 km 压裂层位 上白垩统青山口组一段(K2qn1) 压裂井段 2 765~3 418 m 井口坐标 X:5138828.0 Y:21620127.0 A靶坐标 X:5139333.98 Y:21620225.38,垂深:2 432.31 m B靶坐标 X:5139554.40 Y:21620268.20,垂深:2 434.18 m C靶坐标 X:5140120.23 Y:21620379.25,垂深:2 444.39 m 监测站点 三分量站点52个,低频台站12个,有效站点63个 -
[1] 杨海波, 杨建国, 郭庆霞.大庆探区非常规油气资源潜力及勘探开发对策分析[J].地质与资源, 2015, 24(3):242-247, 183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2015.03.013 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8736.shtml
Yang H B, Yang J G, Guo Q X. Resources prospects and development strategy of unconventional oil and gas in Daqing exploratory area[J]. Geology and Resources, 2015, 24(03):242-247+183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2015.03.013 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8736.shtml
[2] 杨建国, 李士超, 姚玉来, 等.松辽盆地北部陆相页岩油调查取得重大突破[J].地质与资源, 2020, 29(3):300. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.03.015 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10208.shtml
Yang J G, Li S C, Yao Y L, et al. Significant breakthrough in the continental shale oil survey in northern Songliao Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(3):300. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.03.015 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10208.shtml
[3] 贾利春, 陈勉, 金衍.国外页岩气井水力压裂裂缝监测技术进展[J].天然气与石油, 2012(1):44-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5539.2012.01.014
Jia L C, Chen M, Jin Y. Technical progress in overseas hydraulic fracture monitoring techniques for shale gas well[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2012, 30(1):44-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5539.2012.01.014
[4] 李振春, 盛冠群, 王维波, 等.井地联合观测多分量微地震逆时干涉定位[J].石油地球物理勘探, 2014, 49(4):661-666, 671. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ201404006.htm
Li Z C, Sheng G Q, Wang W B, et al. Time-reverse microseismic hypocenter location with interferometric imaging condition based on surface and downhole multi-components[J]. Petroleum Geophysical Exploration, 2014, 49(4):661-666, 671. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ201404006.htm
[5] 张晟瑞, 任朝发, 李星缘, 等.地面微地震资料噪声压制方法[J].地球物理学进展, 2018, 33(6):2522-2527. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201806043.htm
Zhang S R, Ren C F, Li X Y, et al. Denoising method of surface microseismic data[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018, 33(6):2522-2527. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201806043.htm
[6] Stevenson P R. Microearthquakes at Flathead Lake, Montana:A study using automatic earthquake processing[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1976, 66(1):61-80.
[7] Allen R. Automatic earthquake recognition and timing from single traces[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1978, 68:1521-1532. http://gji.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/ijlink?linkType=ABST&journalCode=ssabull&resid=68/5/1521
[8] Baer M, Kradolfer U. An automatic phase picker for local and teleseismic events[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1987, 77:1437-1445.
[9] Ross Z E, Ben-Zion Y. An earthquake detection algorithm with pseudo-probabilities of multiple indicators[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2014, 197:458-463. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt516
[10] Vaezi Y, Baan M V D. Comparison of the STA/LTA and power spectral density methods for microseismic event detection[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2015, 203(3):1896-1908. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggv419
[11] Akram J, Peter D, Eaton D. A k-mean characteristic function for optimizing STA/LTA based detection of microseismic events[J]. Geophysics, GEO-2018-0484.R1.
[12] 吕世超, 郭晓中, 贾立坤.水力压裂井中微地震监测资料处理与解释[J].油气藏评价与开发, 2013, 3(6):37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1426.2013.06.009
Lv S C, Guo X Z, Jia L K. Microseismic monitoring data processing and interpretation of horizontal fracturing wells[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2013, 3(6):37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1426.2013.06.009
[13] 田峰.地面微地震压裂监测技术在煤层气开发中的应用[J].中国煤炭地质, 2018, 30(8):75-78, 90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2018.08.14
Tian F. Application of surface microseismic fracturing monitoring technology in CBM exploitation[J]. Coal Geology in China, 2018, 30(8):75-78, 90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2018.08.14
[14] 周新国.油层水力压裂原理的探讨与技术应用[J].科技致富向导, 2009(20):94-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJZF200920098.htm
Zhou X G. Discussion on hydraulic fracturing principle of oil reservoir and its technical application[J]. Guide of Sci-tech Magazine, 2009(20):94-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJZF200920098.htm
[15] Duncan P M. Microseismic monitoring: Technology state of play[C]. 2010, SPE 131777.
[16] 张山, 刘清林, 赵群, 等.微地震监测技术在油田开发中的应用[J].石油物探, 2002, 41(2):226-231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2002.02.021
Zhang S, Liu Q L, Zhao Q, et al. Application of microseismic monitoring technology in development of oil field[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2002, 2002, 41(2):226-231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2002.02.021
[17] 任朝发, 赵海波, 陈百军, 等.地面微地震监测采集观测系统定位精度的影响因素分析——以大庆SZ探区为例[J].石油物探, 2018, 57(5):668-677. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2018.05.005
Ren C F, Zhao H B, Chen B J, et al. Analysis of location precision factors in surface microseismic monitoring acquisition geometry:A case study of an SZ exploration area in Daqing, China[J]. Petroleum Geophysical Prospecting, 2018, 57(5):668-677. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2018.05.005
[18] 李红梅.微地震监测技术在非常规油气藏压裂效果综合评估中的应用[J].油气地质与采收率, 2015, 22(3):129-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2015.03.024
Li H M. Application of micro-seismic monitoring technology to unconventional hydrocarbon reservoir fracturing evaluation[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2015, 22(3):129-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2015.03.024
[19] 芮拥军.地面微地震水力压裂监测可行性分析[J].物探与化探, 2015, 3(2):341-345. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201502021.htm
Rui Y J. Feasibility analysis of surface micro-seismic hydraulic fracturing monitoring[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 3(2):341-345. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201502021.htm
[20] 张伟, 王海, 李洪臣, 等.用变换时窗统计能量比法拾取地震初至波[J].物探与化探, 2009, 33(2):178-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200902016.htm
Zhang W, Wang H, Li H C, et al. The application of statist energy ratio of transform time windows to the pickup of seismic first arrival wave[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(2):178-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200902016.htm
[21] 王程, 王维红.基于背景噪声和特征值下降比的微地震SVD去噪改进方法[J].东北石油大学学报, 2020, 44(5):1-12, 124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY202005001.htm
Wang C, Wang W H. Optimal method of SVD for micro-seismic data based on background noise and wigenvalue ratio of reduction[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2020, 44(5):1-12, 124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY202005001.htm
[22] Julian B R, Foulger G R. Time-dependent seismic tomography[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2010, 182(3):1327-1338. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04668.x
[23] 杨瑞召, 李德伟, 庞海玲, 等.页岩气压裂微地震监测中的裂缝成像方法[J].天然气工业, 2017, 37(5):31-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201705006.htm
Yang R Z, Li D W, Pang H L, et al. Fracture imaging of the surface based microseismic monitoring in shale gas fracking:Methods and application[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(05):31-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201705006.htm
[24] 吴建光, 张平, 吕昊, 等.基于震幅叠加的微地震事件定位在地面监测中的应用[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(1):255-264. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201701025.htm
Wu J G, Zhang P, Lv H, et al. Application of microseismic event location using amplitude summation in surface monitoring[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2017, 47(1):255-264. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201701025.htm
-



 下载:
下载: