GEOHERITAGE CHARACTERISTICS OF NYENCHENTHANGLHA MOUNTAINS AND FEASIBILITY ANALYSIS ON THE ESTABLISHMENT OF UNESCO GLOBAL GEOPARK
-
摘要:
西藏念青唐古拉山东段地处西藏腹地的拉萨市西北部当雄县,发育了丰富、典型、类型多样的地质遗迹资源. 在野外系统调查的基础上,将念青唐古拉山地质遗迹资源划分为纳木错、羊八井地热田和念青唐古拉山冰川地貌为代表的3大类7类11亚类. 它们沿该区特有的盆-山构造体系聚集展布,具有极高的科学价值、美学价值和开发利用价值,在全球范围具有典型性、稀有性、完整性和国际对比意义. 这些丰富的地质遗迹与佛教建筑融合的文化遗产、高原腹地的生态系统相生相成,全面展示了青藏高原人与自然和谐共生的体系. 基于此,从自然文化、范围边界、管理机构、可持续发展经济政策和利益相关者需求等方面分析认为,念青唐古拉山世界地质公园创建优势显著、切实可行、意义重大,进一步提出采用“以地热田为主题的念青唐古拉山世界地质公园”建园方案,采取政府支持、借鉴经验、普及理念、科研保护、旅游产业和社区发展等多维对策,对利用区域绿色地质遗迹资源,促进地方生态文明建设与经济可持续发展具有理论与实践双重意义.
Abstract:The eastern section of Nyenchenthanglha Mountains, located in Dangxiong County of northwestern Lhasa City, the hinterland of, is rich in typical and diverse geoheritage resources represented by Namtso Lake, Yambajan geothermal field and glacier landform of Nyenchenthanglha Mountains. The geoheritages can be divided into 3 categories, 7 class and 11 subclasses based on systematic field survey. Clustered and distributed along the basin-mountain tectonic system in the area, the geoheritages are of high scientific, aesthetic and development values, with typicality, rarity, integrity and international comparison significance globally. These rich geological relics complement each other with the cultural heritage of Buddhist architecture and ecosystem in the hinterland of Qinghai- Plateau, comprehensively demonstrating the most mysterious system of harmony between man and nature on the plateau. It is concluded that the establishment of Nyenchenthanglha Global Geopark is feasible and of great significance with obvious advantages in terms of natural culture, scope boundary, management organization, sustainable economic policy and stakeholder needs. The construction plan of geothermal field-themed Nyenchenthanglha Global Geopark is further proposed with multidimensional countermeasures such as government support, others' experiences, concept popularization, scientific research protection, tourism and community development, which provides theoretical and practical basis for utilization of regional green geoheritages and promotion of local eco-civilization construction and economic sustainable development.
-
Key words:
- Nyenchenthanglha Mountains /
- Namtso Lake /
- Yambajan geothermal field /
- geoheritage /
- global geopark /
- Xizang
-

-
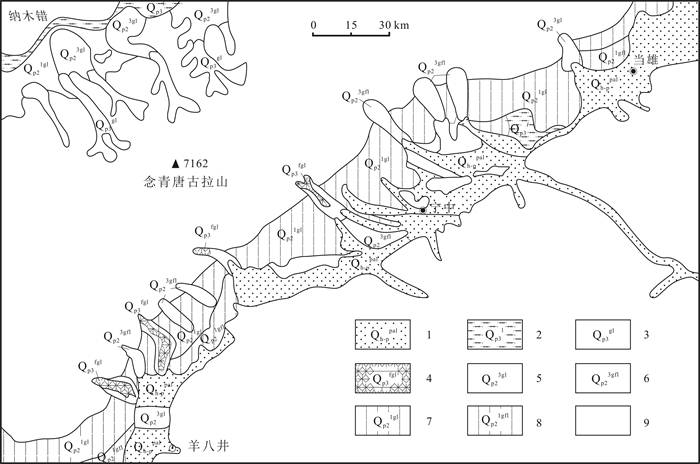
图 1 念青唐古拉山地质图(据文献[7]修改)
Figure 1.
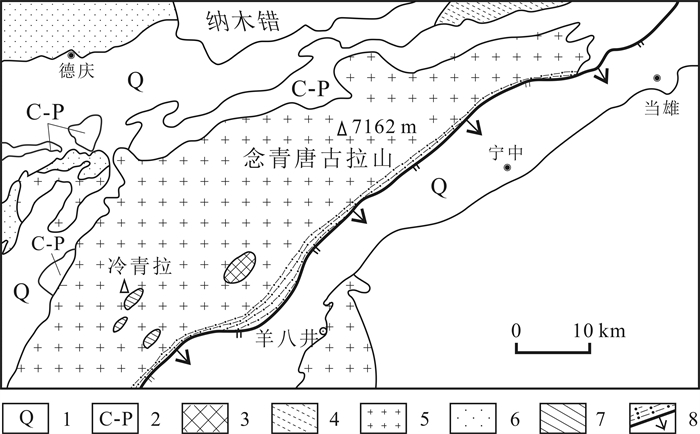
图 2 念青唐古拉东南麓更新世冰川沉积物分布图 (据文献[11]修改)
Figure 2.
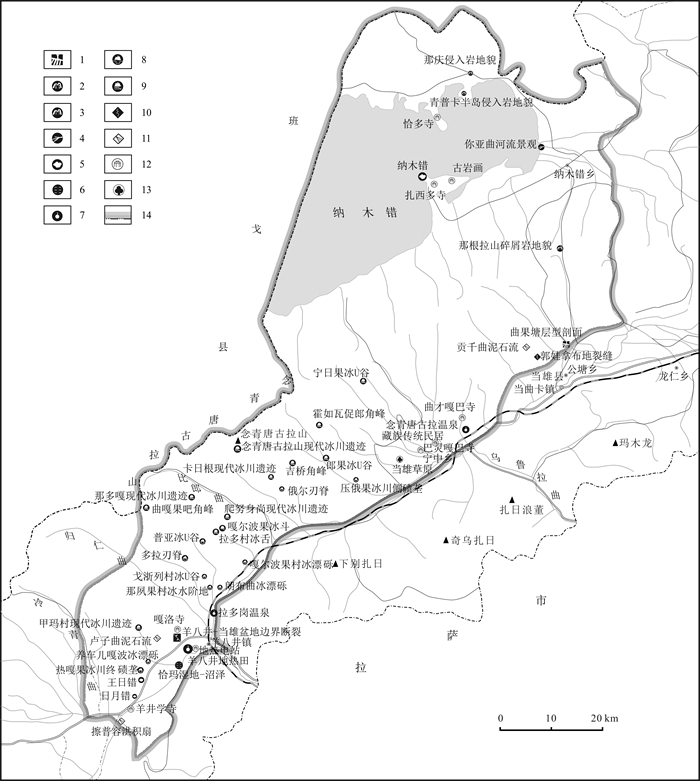
表 1 念青唐古拉山主要地质遗迹资源分类表
Table 1. Classification of major geoheritage resources in Nyenchentanglha Mountains
大类 类 亚类 主要地质遗迹名称 基础地质 地层剖面 层型(典型)剖面 曲果塘层型(典型)剖面 构造剖面 断裂 羊八井-当雄盆地边界断裂 地貌景观 岩土体地貌 侵入岩地貌 青普卡半岛侵入岩地貌、那庆侵入岩地貌 碎屑岩地貌 那根拉山口碎屑岩地貌 水体地貌 河流(景观带) 你亚曲河流(景观带) 湖泊、潭 日月错、王日错、纳木错 泉 羊八井地热田、念青唐古拉温泉、拉多岗温泉 冰川地貌 古冰川遗迹 热嘎果古冰川遗迹(终碛垄)、养车儿嘎波古冰川遗迹(冰漂砾)、那夙果村古冰川遗迹(冰水阶地)、戈浙列村古冰川遗迹(U型谷)、朗布曲古冰川遗迹(冰漂砾)、嘎尔波果村古冰川遗迹(冰漂砾)、压俄果古冰川遗迹(侧碛垄)、俄尔古冰川遗迹(刃脊)、多拉古冰川遗迹(刃脊)、普亚古冰川遗迹(U型谷) 现代冰川遗迹 念青唐古拉山现代冰川遗迹、嘎尔波果现代冰川遗迹(冰斗)、宁日果现代冰川遗迹(U型谷)、霍如瓦促郎现代冰川遗迹(角峰)、郎果现代冰川遗迹(U型谷)、吉桥现代冰川遗迹(角峰)、甲玛村现代冰川遗迹、卡日根现代冰川遗迹、曲嘎果吧现代冰川遗迹(角峰)、爬努身尚现代冰川遗迹、那多嘎现代冰川遗迹、拉多村现代冰川遗迹(冰舌) 地质灾害 地震遗迹 地裂缝 郭娃拿布地裂缝 地质灾害遗迹 泥石流 擦普容泥石流(洪积扇)、卢子曲泥石流、贡千曲泥石流 表 2 纳木错水质物理性质检测表
Table 2. Physical property test results of water quality in Namtso Lake
检测项目 检测结果 标准限值 pH值 7.95 6.5~8.5 气味 无 无异臭 口味 无 无异味 色度 <5 15 浑浊度 <1 3 肉眼可见物 无 无 表 3 纳木错水质阴、阳离子及重金属检测表
Table 3. Anion, cation and heavy metal test results of water from Namtso Lake
检测项目 检测结果/(mg/L) 标准限值/(mg/L) K+ 38.51 - Na+ 315.6 200 Ca2+ 10.12 - Mg2+ 88.79 - Fe2++Fe3+ < 0.1 0.3 NH4+ < 0.03 - Al3+ - 0.2 ∑阳离子 453.0 - Cl- 64.47 250 SO42- 196.7 250 HCO3- 645.2 - CO32- 150.3 - OH- 0.00 - NO3- 0.51 10 NO2- < 0.001 10 PO43- - - F- 4.23 1.0 ∑阴离子 1061 - Cu - 1.0 Pb - 0.01 Zn - 1.0 Cd - 0.005 Mn - 0.1 Co - - Ni - 0.02 As - 0.01 Hg - 0.001 Se - 0.01 表 4 纳木错水质硬度、酸碱度及其他物质检测表
Table 4. Water hardness, pH value and other substances test results of Namtso Lake
检测项目 检测结果/(mg/L) 标准限值/(mg/L) 总硬度 390.9 450 永久硬度 - - 暂时硬度 - - 负硬度 - - 总碱度 1031 - 总酸度 - - Cr6+ - 0.05 I- - - 酚类 - 0.002 氰化物 - 0.05 阴合剂 - 0.3 游离CO2 0.00 - 偏磷酸HPO3 - - CODMn 0.33 5 可溶性SiO2 - - 偏硅酸H2SiO3 0.38 - 溶解总固体 986.5 1000 电导率/(μs/cm) - - 表 5 羊八井地热田地质特征
Table 5. Geological features of Yambajan geothermal field
项目 地质特征 地热基本类型 岩浆活动型中的近期岩浆型 成因 水源 大气降水为主 热源 近期岩浆侵入 物质成分来源 溶滤作用及热力变质作用 地热地质特征 控制性构造 新生代构造作用 盖层 各种火山岩、沉积岩或矿物沉淀及水热蚀变发生自封闭 热储 各种火山岩、沉积岩或松散沉积 火山作用 上新世以来岩浆作用 水文地质特征 含水层类型补、径、排条件 承压水系现代补给充足,垂直上升运动为主,以沸泉、喷泉等形式排泄强烈 地热特征 地表显示 沸泉、喷泉、喷气孔、水热爆炸、泉华及蚀变带 水汽最高温度/℃ 150~200 地热梯度/(℃/100 m) 10~30以上 矿化特征 水质类型 氯化型为主 矿化度/(g/L) <5 特殊组分 HBO2、SiO2、F等 气体成分 H2S、CO2及N2-CO2 伴生矿床及现代成矿 汞矿、硫磺矿、黄铁矿及辉锑矿 -
[1] 姜建军, 王文. 地质遗产可持续利用探讨[J]. 国土资源科技管理, 2001, 18(4): 6-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKG200104002.htm
Jiang J J, Wang W. A discussion on sustainable utilization of geological legacy[J]. Management Geological Science and Technology, 2001, 18 (4): 6-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKG200104002.htm
[2] 赵鸿燕, 张天义, 曹希强. 地质遗迹资源属性浅析[J]. 地质与资源, 2007, 16(1): 78-80. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract9428.shtml
Zhao H Y, Zhang T Y, Cao X Q. A preliminary study on the attribute of geological relic resources[J]. Geology and Resources, 2007, 16 (1): 78-80. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract9428.shtml
[3] 赵逊, 赵汀. 从地质遗迹的保护到世界地质公园的建立[J]. 地质论评, 2003, 49(4): 389-399. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2003.04.009
Zhao X, Zhao T. The process from the geoheritage conservation to the construction of world geoparks[J]. Geological Review, 2003, 49(4): 389-399. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2003.04.009
[4] 姜建军. 国家地质公园——地质圣地共同财富[J]. 国土资源科技管理, 2002, 19(1): 41-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKG200201010.htm
Jiang J J. National geoparks: Sacred places of geology and common wealth of China[J]. Management Geological Science and Technology, 2002, 19(1): 41-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKG200201010.htm
[5] 章秉辰, 雷正化. 西藏羊八井国家地质公园地质遗迹资源特征及建设方案策划[J]. 科技和产业, 2012, 12(7): 127-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYYK201207031.htm
Zhang B C, Lei Z H. Features of Xizang Yangbajing National Geopark and construction scheme design[J]. Science Technology and Industry, 2012, 12(7): 127-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYYK201207031.htm
[6] 王根厚, 周详, 曾庆高, 等. 西藏中部念青唐古拉山链中生代以来构造演化[J]. 现代地质, 1997, 11(3): 298-304.
Wang G H, Zhou X, Zeng Q G, et al. Tectonic evolution of Nyainqentanghla chain since Mesozoic in Xizang[J]. Geoscience - Journal of Graduate School, China University of Geosciences, 1997, 11(3): 298-304.
[7] 胡道功, 吴珍汉, 叶培盛, 等. 西藏念青唐古拉山闪长质片麻岩锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 地质通报, 2003, 22(11/12): 936-940. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2003Z1016.htm
Hu D G, Wu Z H, Ye P S, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb ages of zircons from dioritic gneiss in the Nyainqêntanglha Mountains, Xizang[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2003, 22(11/12): 936-940. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2003Z1016.htm
[8] 赵希涛, 朱大岗, 严富华, 等. 西藏纳木错末次间冰期以来的气候变迁与湖面变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2003, 23(1): 41-52.
Zhao X T, Zhu D G, Yan F H, et al. Climatic change and lake-level variation of Nam Co, Xizang since the last interglacial stage[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2003, 23(1): 41-52.
[9] 杨期隆, 辛奎德. 西藏羊八井地热田简介[J]. 地质论评, 1991, 37 (3): 283-287. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199103010.htm
Yang Q L, Xin K D. A brief introduction to the geothermal system of the Yangbajain geothermal field[J]. Geological Review, 1991, 37 (3): 283-287. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199103010.htm
[10] 吴中海, 赵希涛, 朱大岗, 等. 念青唐古拉山西布冰川区的冰碛层[J]. 地球学报, 2002, 23(4): 343-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200204009.htm
Wu Z H, Zhao X T, Zhu D G, et al. The moraines of Xibu glacier area in the Nyainqentanglha Range[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2002, 23(4): 343-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200204009.htm
[11] 吴中海, 赵希涛, 江万, 等. 念青唐古拉山东南麓更新世冰川沉积物年龄测定[J]. 冰川冻土, 2003, 25(3): 272-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT200303006.htm
Wu Z H, Zhao X T, Jiang W, et al. Dating Result of the Pleistocene glacial deposits on the southeast foot of Nyaiqentanglha Mountains[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2003, 25(3): 272-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT200303006.htm
[12] 王鑫, 张洁. 念青唐古拉——当神山遇见冰川[J]. 中国西部, 2015 (19): 58-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBZG201519014.htm
Wang X, Zhang J. Nyaiqentanglha Mountains: When the sacred mountain meets the glacier[J]. Western China, 2015(19): 58-65. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBZG201519014.htm
[13] 吴中海, 赵希涛, 吴珍汉, 等. 西藏当雄-羊八井盆地的第四纪地质与断裂活动研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2006, 12(3): 305-316. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX200603003.htm
Wu Z H, Zhao X T, Wu Z H, et al. Quaternary geology and faulting in the Damxung-Yangbajain Basin, southern Xizang[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2006, 12(3): 305-316. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX200603003.htm
[14] 唐升贵, 刘发祥, 赵振远. 西藏念青唐古拉山东段冰湖的时空分布特征及其影响因素探讨[J]. 科技资讯, 2014, 12(16): 35-36, 38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXLJ201416025.htm
Tang S G, Liu F X, Zhao Z Y. Discuss on the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and impact factors of the eastern Nyainqentanglha Mountain glacier lakes in Xizang[J]. Science & Technology Information, 2014, 12(16): 35-36, 38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXLJ201416025.htm
[15] 曲广鹏, 参木友, 赵景学, 等. 念青唐古拉山东南坡植被群落数量生态分析及群落多样性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(10): 1618- 1624. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201510005.htm
Qu G P, Can M Y, Zhao J X, et al. Quantitative ecology and species diversity of the vegetation in southeast slope of the Nyenchentanglha Mountain[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(10): 1618-1624. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201510005.htm
[16] 张建平. 解析联合国教科文组织世界地质公园标准[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(4): 874-880. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202004008.htm
Zhang J P. Interpretation of the criteria of UNESCO global geopark [J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(4): 874-880. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202004008.htm
[17] 陈斌, 杨更, 向贵府, 等. 地质公园规划功能分区相关问题及其优化[J]. 地质论评, 2019, 65(2): 438-444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201902016.htm
Chen B, Yang G, Xiang G F, et al. Relevant problems in function division planning of geoparks and optimization measures[J]. Geological Review, 2019, 65(2): 438-444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201902016.htm
[18] 段丽萍. 西藏地质旅游资源概况及开发建议[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(1/2): 302-307. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2006Z1047.htm
Duan L P. Geological tourism resources in Xizang, China, and suggestions of their exploitation[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(1/2): 302-307. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2006Z1047.htm
[19] 吴学成, 李江风, 方世明, 等. 地质遗迹保护视角下的地质公园旅游开发构想——以克什克腾世界地质公园阿斯哈图石林园区为例[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2014, 28(4): 187-193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201404032.htm
Wu X C, Li J F, Fang S M, et al. On the development conception of geopark from the perspective of geological relics protection: A case of Asihatu Stone Forest scenic spot in Hexigten Global Geopark[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2014, 28(4): 187-193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201404032.htm
[20] 李倩, 田飞, 田明中. 内蒙古翁牛特地质公园地质遗迹分布及其保护意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2016, 25(1): 97-100. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8610.shtml
Li Q, Tian F, Tian M Z. Distribution and conservation of the geoheritages in Ongniud Geopark, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Resources, 2016, 25(1): 97-100. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8610.shtml
[21] 闫远方, 武法东, 韩晋芳, 等. 创建沂蒙山世界地质公园的可行性分析[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2016, 26(S2): 296-299. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGRZ2016S2071.htm
Yan Y F, Wu F D, Han J F, et al. Feasibility analysis of construction of Mount Yimengshan UNESCO global geopark[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2016, 26(S2): 296-299. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGRZ2016S2071.htm
[22] 汪冰, 余振国, 李闽. 地质公园矿山公园建设助推脱贫攻坚效益评估[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 2018, 31(11): 21-25, 31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDKJ201811006.htm
Wang B, Yu Z G, Li M. Benefit evaluation on the construction of geo-park and mine park promotes poverty alleviation[J]. Natural Resource Economics of China, 2018, 31(11): 21-25, 31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDKJ201811006.htm
-



 下载:
下载: