MAIN CONTROLLING FACTORS AND RESERVOIR DEVELOPMENT MODEL OF LOWER PALEOZOIC CARBONATE ROCKS IN BURIED HILL Z OILFIELD
-
摘要:
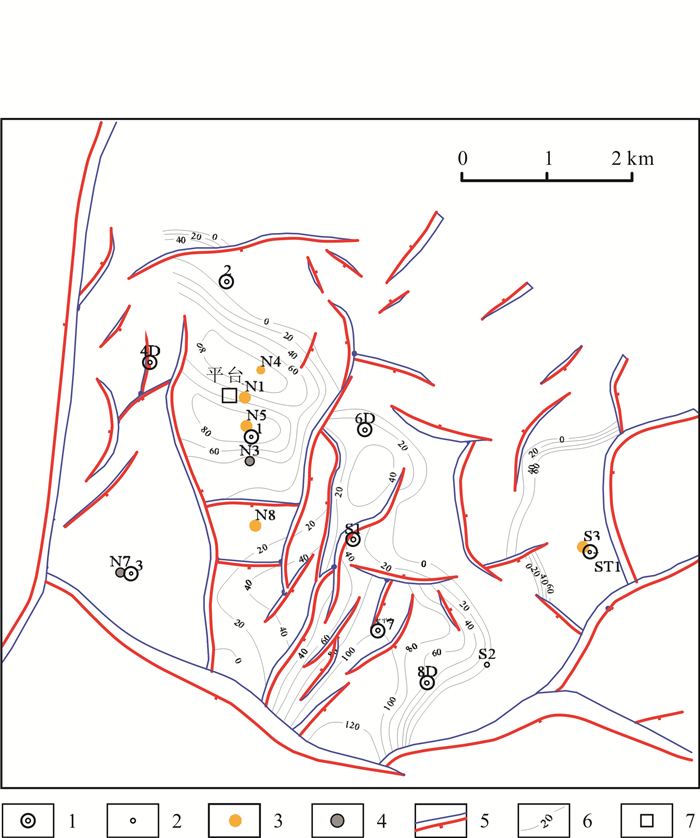
碳酸盐岩潜山是渤海重要的油气藏类型之一. 以渤海区域重点开发目标Z油田为例, 应用钻测井、岩心、微观薄片及地震等基础资料, 对碳酸盐岩储层特征、形成机制及地质发育模式进行综合分析. 明确了碳酸盐岩潜山储层岩性以白云岩为主, 储集空间为晶间孔、裂缝和溶蚀孔隙. 碳酸盐岩潜山储层主要受沉积、成岩及构造因素控制. 结合单井特征及垂向岩溶分带性, 将潜山纵向分为表层风化带、垂直渗流带和顺层溶蚀带. 受成岩、构造等多因素影响, 上油组较下油组储层发育, 上油组储层全区发育, 下油组储层局限发育. 明确了岩溶分带及储层展布地质模式, 为油田的下步调整和挖潜方向提供依据.
Abstract:Carbonate rock buried hill is one of the important oil-gas reservoirs in Bohai Sea. Taking Z Oilfield, the key development target in Bohai Sea area as an example, the characteristics, formation mechanism and geological development model of carbonate rock reservoir are comprehensively analyzed by using basic data such as drilling and logging, cores, microscopic thin sections and seismic data. The results show that the lithology of carbonate rock buried hill reservoir is mainly dolomite, with the reservoir spaces of intergranular pore, fracture and dissolution pore. Carbonate rock buried hill reservoir is mainly controlled by sedimentary, diagenetic and structural factors. Combined with the characteristics of single well and vertical karst zonation, the buried hill can be divided into surface weathering zone, vertical seepage zone and bedding dissolution zone. Under the influence of multiple factors such as diagenesis and structure, the reservoir in the upper oil formation is more developed than that in the lower, with full-region development for the former and limited development for the latter. The karst zoning and geological model of reservoir distribution provide the basis for next adjustment and potential tapping direction.
-
Key words:
- carbonate rock /
- buried hill /
- oil-gas field /
- karst zoning /
- reservoir model /
- Bohai Bay Basin
-

-
表 1 Z油田碳酸盐岩储集空间类型表
Table 1. Types of reservoir space for carbonate rocks in Z Oilfield
储集空间 孔隙类型 发育主要岩石 特征及识别标志 原生孔隙 粒间孔 灰岩、白云质灰岩 孔隙形态主要与生物形态一致,其次为不规则形,孔径大小不一 粒内孔 生屑灰岩、白云质生屑灰岩 多呈不规则状、伸长状 次生孔隙 晶间孔 白云岩、白云质灰岩 在晶粒粗大的白云石晶体间常见,孔隙边界平直,构成折线型孔隙 粒间溶孔 碎屑角砾岩、泥晶角砾岩 边界不规则或呈锯齿状 粒内溶孔 生屑灰岩、白云质生屑灰岩 孔径大小不一,孔壁多不规则或呈港湾状,部分孔壁见残留沥青 残余孔 灰岩、白云质灰岩、白云岩及灰质白云岩 孔隙边部、中部的残留孔隙,长形、多边形,边缘为棱角状、不规则状 裂缝 构造缝 白云岩、灰质白云岩、灰岩及白云质灰岩 呈网状、根须状分布或沿层面延伸 成岩缝 角砾岩、灰岩、白云岩 裂面弯曲,形状极不规则 溶缝、溶沟 各类岩石 溶缝、溶沟壁不规则,宽度变化大,延伸不远或呈尖灭状 表 2 沉积环境与物性关系统计表
Table 2. Relationship between sedimentary environment and physical properties
岩性 厚度/m 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 灰岩 145 1.5 160 白云质灰岩 135 2.0 210 鲕粒灰岩 516 2.2 168 泥晶灰岩 132 1.8 230 生屑灰岩 69 1.1 124 白云岩 784 4.7 377 灰质白云岩 157 2.7 378 泥质白云岩 99 2.0 230 泥岩 83 0.9 103 -
[1] 赵澄林, 朱筱敏. 沉积岩石学[M]. 3版. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2001: 20-25.
Zhao C L, Zhu X M. Sedimentary petrology[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2001: 20-25. (in Chinese)
[2] 孙钰, 钟建华, 袁向春, 等. 国内湖相碳酸盐岩研究的回顾与展望[J]. 特种油气藏, 2008, 15(5): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2008.05.001
Sun Y, Zhong J H, Yuan X C, et al. Review and prospect of the study on domestic lacustrine carbonate rocks[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2008, 15(5): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2008.05.001
[3] 张德军, 赵洪伟, 陈树旺, 等. 阜新盆地辽阜地2井下白垩统岩石地层特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2021, 30(3): 325-332. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2021.03.014 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10301.shtml
Zhang D J, Zhao H W, Chen S W, et al. Lithostratigraphic characteristics of LFD-2 well in Fuxin Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2021, 30(3): 325-332. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2021.03.014 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10301.shtml
[4] 刘希瑶, 王德力, 刘驰. 大兴安岭北部中生代花岗岩类地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(3): 207-211, 281. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.03.001 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10194.shtml
Liu X Y, Wang D L, Liu C. Geochemistry of Mesozoic granitoids in northern Daxinganling Mountains: Geologicalimplication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(3): 207-211, 281. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.03.001 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10194.shtml
[5] 高福亮, 江洋, 张国仁, 等. 辽宁大连骆驼山地区第四纪溶洞形成条件分析[J]. 地质与资源, 2021, 30(4): 425-430. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2021.04.003 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10312.shtml
Gao F L, Jiang Y, Zhang G R, et al. Forming conditions of the Quaternary karst caves in Luotuo Mountainof Dalian City, Liaoning Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2021, 30(4): 425-430. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2021.04.003 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10312.shtml
[6] Mount J F. 浅海陆架环境中硅质碎屑和碳酸盐沉积物的混合[J]. 海洋地质译丛, 1985(2): 44-48 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY198502009.htm
Mount J F. Mixing of siliceous debris and carbonate sediments in shallow shelf environment[J]. Offshore Oil, 1985(2): 44-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY198502009.htm
[7] 何治亮, 魏修武, 钱一雄, 等. 海相碳酸盐岩优质储层形成机理与分布预测[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(4): 489-498. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201104004.htm
He Z L, Wei X C, Qian Y X, et al. Forming mechanism and distribution prediction of quality marine carbonate reservoirs[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2011, 32(4): 489-498. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201104004.htm
[8] 赵贤正, 王权, 金凤鸣, 等. 冀中坳陷隐蔽型潜山油气藏主控因素与勘探实践[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(S1): 71-79. doi: 10.7623/syxb2012S1009
Zhao X Z, Wang Q, Jin F M, et al. Main controlling factors and exploration practice of subtle buried-hill hydrocarbon reservoir in Jizhongdepression[J]. ActaPetroleiSinica, 2012, 33(S1): 71-79. doi: 10.7623/syxb2012S1009
[9] 李欣, 闫伟鹏, 崔周旗, 等. 渤海湾盆地潜山油气藏勘探潜力与方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 2012, 34(2): 140-144, 152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201202009.htm
Li X, Yan W P, Cui Z Q, et al. Prospecting potential and targets of buried-hill oil and gas reservoirs in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. PetroleumGeology & Experiment, 2012, 34(2): 140-144, 152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201202009.htm
[10] 吕丁友, 侯东梅, 杨庆红, 等. 渤南低凸起西段构造成因机制与油气成藏规律研究[J]. 中国海上油气, 2011, 21(4): 229-233. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201104003.htm
Lü D Y, Hou D M, Yang Q H, et al. A study on structure origins and hydrocarbon accumulation pattern in the west part of Bonanlower-uplift [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2011, 21(4): 229-233. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201104003.htm
[11] 邓运华. 试论辽东湾坳陷沙河街组碳酸盐岩形成环境及其特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1991, 18(6): 32-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK199106005.htm
Deng Y H. A discussion on the environment of formation and the characteristics of the carbonate rock in the Shahejie group in the Liaodong Bay basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1991, 18(6): 32-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK199106005.htm
[12] 董艳蕾, 朱筱敏, 滑双君, 等. 黄骅坳陷沙河街组一段下亚段混合沉积成因类型及演化模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(1): 98-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201101014.htm
Dong Y L, Zhu X M, Hua S J, et al. Genetic types and evolutionary model of mixed clastic-carbonate deposits in the lower part of the Sha-1 Formation, the Huanghua Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2011, 32(1): 98-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201101014.htm
[13] 金振奎, 邹元荣, 张响响, 等. 黄骅坳陷古近系沙河街组湖泊碳酸盐沉积相[J]. 古地理学报, 2002, 4(3): 11-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200203001.htm
Jin Z K, Zou Y R, Zhang XX, et al. Lacustrine carbonate sedimentary facies of the Shahejie Formation of Paleogene in Huanghua depression [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2002, 4(3): 11-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200203001.htm
[14] 林会喜. 济阳坳陷桩西埕岛地区下古生界潜山储层岩溶作用[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 31(5): 490-497. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200405009.htm
Lin H X. Karstification of Lower Paleozoic reservoir in Zhuangxi-Chengdao area, Jiyang sag, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition), 2004, 31(5): 490-497. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200405009.htm
[15] 鄢圣武, 白宪洲, 秦宇龙, 等. 四川昭觉-美姑地区峨眉山玄武岩古火山机构的发现及其喷发旋回的确定[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48 (2): 536-548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202102014.htm
Yan S W, Bai X Z, Qin Y L, et al. Discovery of Paleo-volcanic edifice and determination of its eruptive circles ofEmeishan basalt in Zhaojue-Meigu area, Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(2): 536-548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202102014.htm
[16] 李崴崴, 陈井胜, 高忠晖, 等. 赤峰哈拉道口早石炭世花岗闪长岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(3): 212-223. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10195.shtml
Li W W, Chen J S, Gao Z H, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Early Carboniferous granodiorites in Haladaokou area of Chifeng City: Geological implication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29 (3): 212-223. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10195.shtml
[17] 刘亮, 韩洪明, 杨鹏涛, 等. 四川龙门山地区阳新组灰岩地质特征及用途[J]. 地质与资源, 2019, 28(5): 448-453. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8419.shtml
Liu L, Han H M, Yang P T, et al. Geology and utilization of Yangxin Formation limestone in Longmenshan area, Sichuan Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2019, 28(5): 448-453. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8419.shtml
[18] 王慧, 张欢, 潘志龙, 等. 内蒙古北山地区哈日阿玛岛弧花岗岩地球化学、年代学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2021, 30(2): 103-117. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10274.shtml
Wang H, Zhang H, Pan Z L, et al. Geochemistry and geochronology ofHariama island arc granitoids in Beishan area of Inner Mongolia: Geological implication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2021, 30(2): 103-117. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10274.shtml
[19] 汤良杰, 万桂梅, 周心怀, 等. 渤海盆地新生代构造演化特征[J]. 高校地质学报, 2008, 14(2): 191-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200802008.htm
Tang L J, Wan G M, Zhou X H, et al. Cenozoicgeotectonic evolution of the BohaiBasin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2008, 14(2): 191-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200802008.htm
[20] 马宝军, 漆家福, 刘阳, 等. 渤南地区新生代构造演化与油气成藏[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2006, 33(5): 572-575. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200605011.htm
Ma B J, Qi J F, Liu Y, et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation in Bonanregion[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2006, 33(5): 572-575. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200605011.htm
[21] 马立驰, 王永诗, 姜在兴, 等. 断陷盆地碳酸盐岩潜山储层模式——以渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2006, 28 (1): 21-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD200601003.htm
Ma L C, Wang Y S, Jiang Z X, et al. Reservoir model of carbonate buried-hill in rifted basin-taking the Jiyang depression as an example [J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2006, 28(1): 21-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD200601003.htm
[22] 杜韫华. 渤海湾地区下第三系湖相碳酸盐岩及沉积模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1990, 11(4): 376-392. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT199004004.htm
Du Y H. Eocene lacustrinecarbonate rocks and sedimentary model in BohaiBay region[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1990, 11(4): 376-392. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT199004004.htm
[23] 王拥军, 张宝民, 王政军, 等. 渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷奥陶系潜山油气地质特征与成藏主控因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2012, 23(1): 51-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201201009.htm
Wang Y J, Zhang B M, Wang Z J, et al. Geological Characteristics of Ordovician Buried Hill and Main factors of oil/gas accumulation in NanpuSag, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2012, 23(1): 51-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201201009.htm
[24] 张奎华, 马立权. 济阳坳陷下古生界碳酸盐岩潜山内幕储层再研究[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2007, 14(4): 26-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200704006.htm
Zhang K H, Ma L Q. Restudy of tamerreservoir of buried hill of Low-Paleozoic carbonate rocks in JiyangDepression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2007, 14(4): 26-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200704006.htm
-




 下载:
下载: