PALEOGEOGRAPHIC DISTRIBUTION AND TAPHONOMY CHARACTERISTICS OF Naraoia FROM CAMBRIAN BALANG FORMATION IN GUIZHOU PROVINCE
-
摘要:
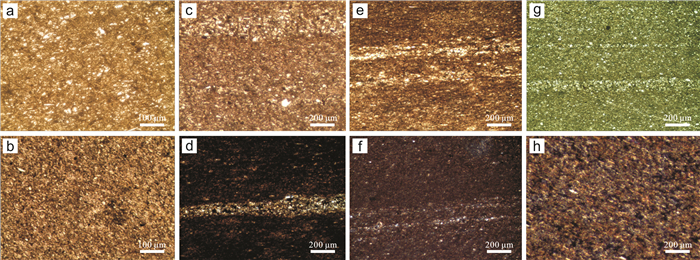
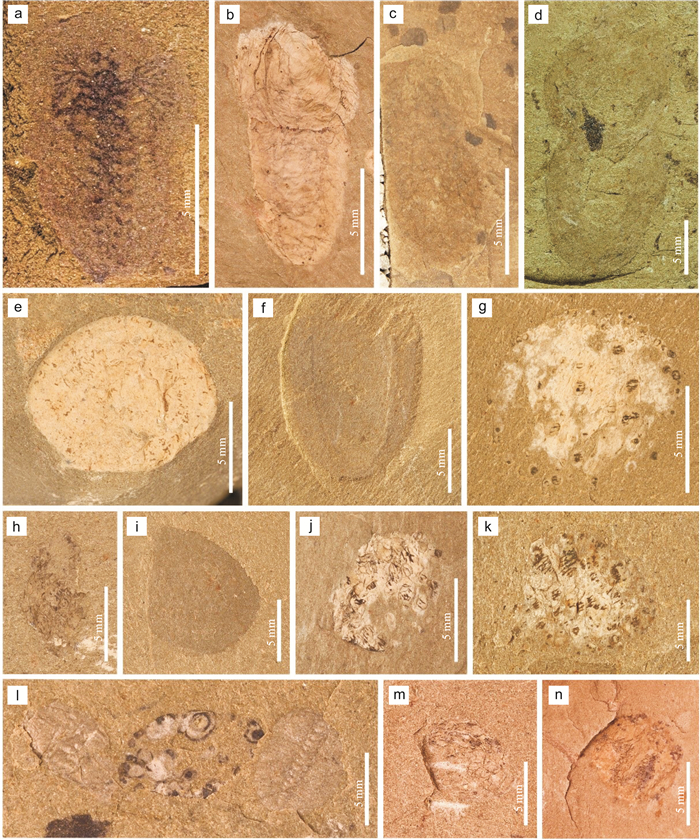
纳罗虫属作为一类已经灭绝的节肢动物,主要分布在寒武纪地层中. 其中,黔东南寒武系杷榔生物群的纳罗虫保存在江南斜坡沉积相区,目前在台江革一和剑河辣子寨地区杷榔组中发现了大量纳罗虫标本. 本次研究基于采自剑河辣子寨剖面的213块标本,鉴定为Naraoia taijiangensis,化石主要保存在该剖面3个化石富集层中. 结合这3个化石层的岩性特征、沉积环境及化石保存状态,对N. taijiangensis的埋藏特征进行分析,发现化石保存与快速的沉积事件相关,以印痕化石保存为特征,局部有矿化现象;完整的化石个体出现在较厚的快速沉积层中;不完整的化石则多保存在相对较薄的快速沉积层中. 这一发现为揭示斜坡相区杷榔生物群的埋藏特征提供了依据.
Abstract:Naraoia, an extinct genus of arthropod, is mainly preserved in Cambrian strata. In eastern Guizhou, the Naraoia from Cambrian Balang Biota are distributed in the sedimentary facies of Jiangnan slope, where lots of Naraoia fossils have been found in the Balang Formation in Taijiang and Jianhe areas. Based on the 213 specimens collected from Lazizhai section in Jianhe County, the fossils are identified to be Naraoia taijiangensis, which are accumulated mainly in three fossil enrichment layers. By analyzing the lithologicl characteristics, sedimentary environment and fossil preserved situation of the three fossil layers, it is confirmed that the fossil preservation is related to a rapid sedimentation event. The preservation is characterized by fossil impression, with local mineralization. The intact individuals of N. taijiangensis are found at the bottom of thick rapid sedimentary layer, while the fragmentary fossils are preserved in thinner layer. This discovery provides a basis for the burial characteristics of the Balang Biota in the slope facies area.
-
Key words:
- Naraoia /
- paleogeography /
- taphonomy /
- Balang Formation /
- Cambrian /
- Guizhou Province
-

-
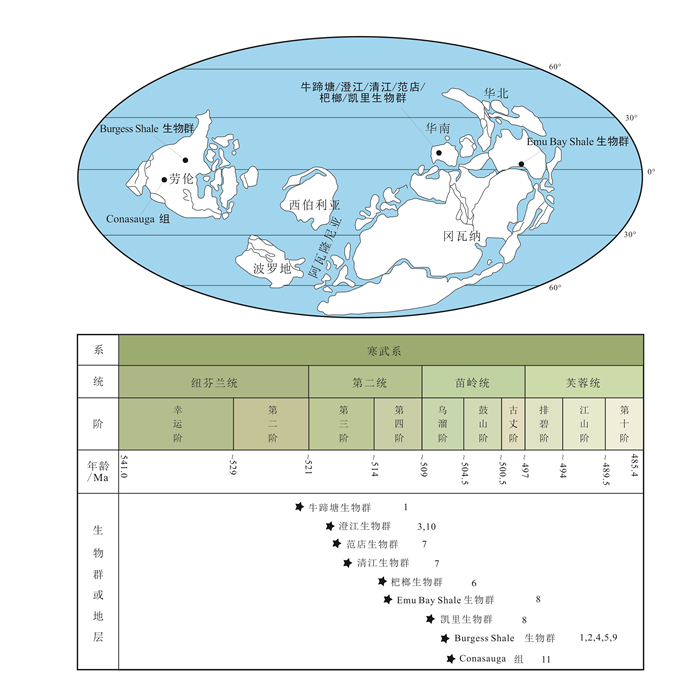
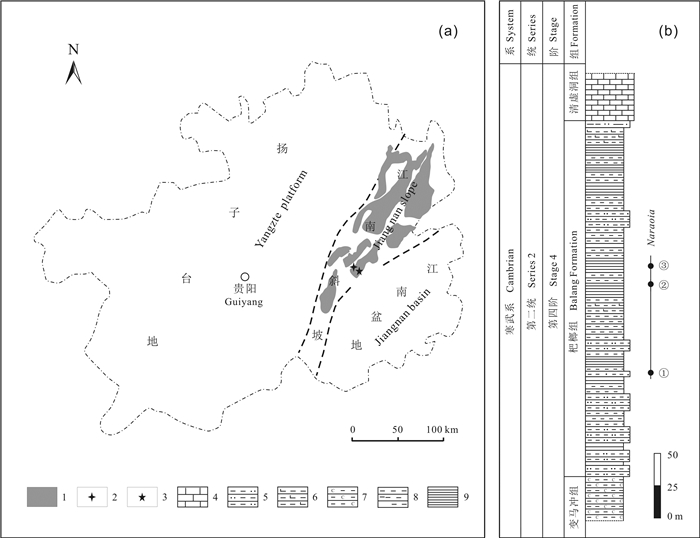
图 2 寒武纪Naraoia和Misszhouia的古地理分布图(据文献[23]修改)
Figure 2.
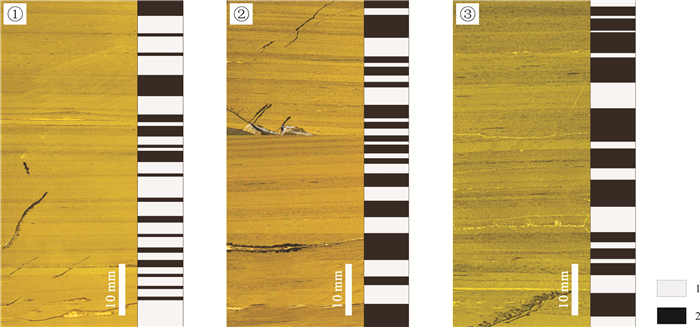
表 1 剑河辣子寨杷榔组3个采集层中N. taijiangensis化石保存类型数量统计
Table 1. Fossil numbers by preserved types of N. taijiangensis from Balang Formation in Laizizhai area
化石层位 Ⅰ类 Ⅱ类 Ⅲ类 总计 ①号层位 4 14 146 164 ②号层位 3 9 30 42 ③号层位 2 0 5 7 -
[1] Vannier J, Chen J Y. Digestive system and feeding mode in Cambrian naraoiid arthropods[J]. Lethaia, 2002, 35(2): 107-120. doi: 10.1111/j.1502-3931.2002.tb00072.x
[2] Zhang X L, Shu D G, Erwin D H. Cambrian naraoiids (arthropoda): Morphology, ontogeny, systematics, and evolutionary relationships[J]. Journal of Paleontology, 2007, 68(S68): 1-52.
[3] Zhai D Y, Edgecombe G D, Bond A D, et al. Fine-scale appendage structure of the Cambrian trilobitomorph Naraoia spinosa and its ontogenetic and ecological implications[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2019, 286(1916): 20192371. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2019.2371
[4] 张文堂, 侯先光. Naraoia在亚洲大陆的发现[J]. 古生物学报, 1985, 24(6): 591-595. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX198506000.htm
Zhang W T, Hou X G. Preliminary notes on the occurrence of the unusual trilobite Naraoia in Asia[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 1985, 24(6): 591-595. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX198506000.htm
[5] Steiner M, Zhu M Y, Zhao Y L, et al. Lower Cambrian burgess shale-type fossil associations of South China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2005, 220(1/2): 129-152.
[6] Caron J B, Rudkin D M, Milliken S. A new Late Silurian (Pridolian) naraoiid (Euarthropoda: Nektaspida) from the Bertie Formation of southern Ontario, Canada Delayed fallout from the Cambrian explosion[J]. Journal of Paleontology, 2004, 78(6): 1138-1145. doi: 10.1666/0022-3360(2004)078<1138:ANLSPN>2.0.CO;2
[7] Walcott C. Cambrian geology and paleontology Ⅱ. Middle Cambrian branchiopoda, malacostraca, trilobita and merostomata[J]. Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections, 1912, 57(6): 145-288.
[8] 赵元龙, 袁金良, 朱茂炎, 等. 贵州中寒武世早期凯里生物群研究的新进展[J]. 古生物学报, 1999, 38(S1): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX1999S1000.htm
Zhao Y L, Yuan J L, Zhu M Y, et al. A progress report on research on the early Middle Cambrian Kaili Biota, Guizhou, PRC [J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 1999, 38(S1): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX1999S1000.htm
[9] Peng J, Zhao Y L, Sun H J. Discovery and significance of Naraoia from the Qiandongian (Lower Cambrian) Balang Formation, Eastern Guizhou, South China[J]. Bulletin of Geosciences, 2012, 87(1): 143-150.
[10] Mayers B, Aria C, Caron J B. Three new naraoiid species from the Burgess shale, with a morphometric and phylogenetic reinvestigation of Naraoiidae[J]. Palaeontology, 2019, 62(1): 19-50. doi: 10.1111/pala.12383
[11] Peng J, Zhao Y L, Wu Y S, et al. The Balang Fauna: A new Early Cambrian fauna from Kaili City, Guizhou Province[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(11): 1159-1162. doi: 10.1360/982005-183
[12] Peng J, Feng H Z, Fu X P, et al. New Bradoriid arthropods from the Early Cambrian Balang Formation of eastern Guizhou, South China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 2010, 84 (1): 56-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2010.00170.x
[13] Peng J, Sun H J, Zhao Y L, et al. The Jiaobang section: The Balang Formation and the Balang Fauna (Cambrian Series 2 Stage 4) near Jiaobang villiage, Jianhe County, Guizhou Province, China[J]. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Science), 2012, 29(S1): 125-132.
[14] Peng J, Sun H J, Zhao Y L, et al. The fossiliferous Geyi section of the Balang Formation (Cambrian Series 2, Stage 4) near Taijiang County, Guizhou Province, South China[J]. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Science), 2012, 29(S1): 89-97.
[15] 马海涛, 彭进, 赵元龙, 等. 贵州岑巩羊桥罗家塘杷榔动物群的发现及其后生动物早期演化的意义[J]. 地质论评, 2011, 57 (5): 743-748. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201105016.htm
Ma H T, Peng J, Zhao Y L, et al. Discovery of the Balang Fauna at Luojiatang, Yangqiao, Cengong, Guizhou, and its significance to the early evolution of the Metazoa[J]. Geological Review, 2011, 57(5): 743-748. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201105016.htm
[16] 达扬, 彭进, 赵元龙, 等. 贵州台江革一黔东统杷榔组沉积环境初探[J]. 地质论评, 2011, 57(4): 574-582. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201104014.htm
Da Y, Peng J, Zhao Y L, et al. Preliminary investigation on sedimentary environment of the Balang Formation in Geyi, Taijiang, Eastern Guizhou, China[J]. Geological Review, 2011, 57(4): 574-582. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201104014.htm
[17] 赵元龙, 彭进, 伍孟银, 等. 贵州麻江下司寒武系杷榔组棘皮动物始海百合新类型化石[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(2): 249-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201502005.htm
Zhao Y L, Peng J, Wu M Y, et al. A new type eocrinoids of echinoderms from the Balang Formation in Cambrian at Xiasi Town, Majiang County, Guizhou Province, China[J]. Earth Science — Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(2): 249-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201502005.htm
[18] 申震, 彭进, 文荣琴, 等. 寒武纪似节头虫Arthricocephalites及其地层意义[J]. 古生物学报, 2016, 55(1): 9-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX201601002.htm
Shen Z, Peng J, Wen R Q, et al. Arthricocephalites (Trilobite) from the Cambrian and its stratigraphic significance[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2016, 55(1): 9-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX201601002.htm
[19] 刘帅, 文荣琴, 彭进, 等. 贵州寒武系杷榔组杷榔化石库埋藏学初步研究——以剑河辣子寨剖面为例[J]. 古生物学报, 2017, 56(3): 282-300. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX201703003.htm
Liu S, Wen R Q, Peng J, et al. A preliminary study on taphonomy of the Balang Lagerstätte from the Cambrian (Stage 4), Balang Formation at Jianhe, Guizhou, China: Example for Lazizhai section of the Balang Formation[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2017, 56(3): 282-300. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX201703003.htm
[20] 王秋军, 彭进, 文荣琴, 等. 贵州剑河寒武纪杷榔动物群中的海绵化石组合[J]. 古生物学报, 2018, 57(3): 312-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX201803005.htm
Wang Q J, Peng J, Wen R Q, et al. The sponge assemblage from the Cambrian Balang Fauna of Jianhe, Guizhou[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2018, 57(3): 312-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX201803005.htm
[21] 邵云彬, 彭进, 王秋军, 等. 贵州寒武纪杷榔组古蠕虫类埋藏特征及意义[J]. 古生物学报, 2021, 60(4): 483-498. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX202104001.htm
Shao Y B, Peng J, Wang Q J, et al. Taphonomic characteristics and significance of the palaeoscolecids from the Cambrian Balang Formation in Jianhe County, Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2021, 60(4): 483-498. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX202104001.htm
[22] Liu S, Peng J, Wen R Q, et al. New data for Isoxys of the Balang Fauna (Cambrian Stage 4), South China[J]. Bulletin of Geosciences, 2018, 93(2): 147-162.
[23] Wen R Q, Babcock L E, Peng J, et al. The bivalved arthropod Tuzoia from the Balang Formation (Cambrian Stage 4) of Guizhou, China, and new observations on comparative species[J]. Papers in Palaeontology, 2019, 5(4): 719-742. doi: 10.1002/spp2.1262
[24] 周志毅, 袁金良, 张正华, 等. 贵州及其邻近地区寒武纪生物地理分区[J]. 地层学杂志, 1979, 3(4): 258-271. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ197904003.htm
Zhou Z Y, Yuan J L, Zhang Z H, et al. Cambrian biogeographical province of Guizhou and the neighbouring areas[J]. Acta Stratigraphica Sinica, 1979, 3(4): 258-271. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ197904003.htm
[25] 尹恭正. 寒武系[C]//贵州省地质矿产局. 中华人民共和国地质矿产部地质专报(一)区域地质(第7号): 贵州省区域地质志. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987: 49-96.
Yin G Z. Cambrian system[C]//Guizhou Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources, People's Republic of China: Geological Memoirs (Series 1 No. 7): Regional Geology of Guizhou Province. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1987: 49-96.
[26] Peng S C, Babcock L E. Cambrian of the Hunan-Guizhou region, South China[C]//Peng S C, Babcock L E, Zhu M Y. Cambrian System of South China. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2001: 3-51.
[27] 周志毅, 袁金良, 张正华, 等. 贵州寒武纪地层的分类和对比[J]. 地层学杂志, 1980, 4(4): 273-281. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ198004003.htm
Zhou Z Y, Yuan J L, Zhang Z H, et al. Classification and correlation of Cambrian strata in Guizhou Province, China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 1980, 4(4): 273-281. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ198004003.htm
[28] 袁金良, 赵元龙, 李越, 等. 黔东南早、中寒武世凯里组三叶虫动物群[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2002: 1-423.
Yuan J L, Zhao Y L, Li Y, et al. Trilobite fauna of the Kaili Formation, Lower-Middle Cambrian, from Southeastern Guizhou, South China[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 2002: 1-423. (in Chinese)
[29] 秦琴, 彭进, 傅晓平, 等. 贵州黔东世(早寒武世)杷榔组Changaspis Lee in Chien, 1961的再研究[J]. 古生物学报, 2010, 49(2): 220-230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX201002006.htm
Qin Q, Peng J, Fu X P, et al. Restudy of Changaspis (Lee), 1961 From Qiandongian (Early Cambrian) Balang Formation near eastern Guizhou, South China[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2010, 49(2): 220-230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX201002006.htm
[30] 闫巧洁, 彭进, 赵元龙, 等. 贵州剑河寒武系黔东统杷榔组沉积环境及生物地层再研究——以剑河交榜剖面为例[J]. 地质论评, 2014, 60(4): 893-902. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201404022.htm
Yan Q J, Peng J, Zhao Y L, et al. Restudy of sedimentary and biostratigraphy of the Qiandongian (Cambrian) Balang Formation at Jianhe, Guizhou, China: Example for Jiaobang Section of the Balang Formation[J]. Geological Review, 2014, 60(4): 893-902. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201404022.htm
[31] Walcott C D. Addenda to descriptions of Burgess shale fossils (with 23 plates)[J]. Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections, 1931, 85: 1-46.
[32] Nedin C. The Emu Bay shale, a Lower Cambrian fossil lagerstätte, Kangaroo Island, South Australia[J]. Memoirs of the Association of Australasian Palaeontologists, 1995, 18: 31-40.
[33] Schwimmer D R, Montante W M. Exceptional fossil preservation in the Conasauga Formation, Cambrian, northwestern Georgia, USA[J]. Palaios, 2007, 22(4): 360-372.
[34] Fu D J, Tong G H, Dai T, et al. The Qingjiang biota: A Burgess shale-type fossil Lagerstätte from the Early Cambrian of South China[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6433): 1338-1342.
[35] Du K S, Ortega-Hernández J, Yang J, et al. A new Early Cambrian Konservat-Lagerstätte expands the occurrence of Burgess shale-type deposits on the Yangtze Platform[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 211: 103409.
[36] 赵元龙, 朱茂炎, Babcock L E, 等. 凯里生物群——5.08亿年前的海洋生物[M]. 贵阳: 贵州科技出版社, 2011: 1-251.
Zhao Y L, Zhu M Y, Babcock L E, et al. The Kaili Biota: Marine organisms from 508 million years ago[M]. Guiyang: Guizhou Science and Technology Publishing House, 2011: 1-251.
[37] 赵方臣, 朱茂炎. 云南早寒武世澄江化石库中两种埋藏相的化石定量分析[J]. 古生物学报, 2007, 46(1): 75-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX200701004.htm
Zhao F C, Zhu M Y. Quantitative comparison of the fossil assemblages between the event and background mudstones from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang Lagerstätte, Yunnan[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2007, 46(1): 75-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX200701004.htm
[38] 赵方臣. 云南寒武纪澄江生物群埋藏学和定量古生态学研究[D]. 南京: 中国科学院南京地质古生物研究所, 2009: 1-164.
Zhao F C. Quantitative analysis of taphonomy and palaeoecology of the Early Cambrian Chengjiang Lagerstätte, Yunnan[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2009: 1-164.
[39] Babcock L E, Chang W T. Comparative taphonomy of two nonmineralized arthropods: Naraoia (Nektaspida; Early Cambrian, Chengjiang Biota, China) and Limulus (Xiphosurida; Holocene, Atlantic Ocean)[J]. Bulletin of the National Museum of Natural Science, 1997, 10: 233-250.
[40] 刘玉娟. 黔东寒武系第4阶至乌溜阶腕足动物研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2020: 1-161.
Liu Y J. Brachiopoda from Cambrian Stage 4 to the Wuliuan Stage in eastern Guizhou[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2020: 1-161.
[41] 刘帅. 贵州寒武纪杷榔动物群埋藏学研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2018: 1-125.
Liu S. Study on taphonomy of the Balang Fauna Lagerstätte from the Cambrian (Stage 4) of Guizhou, China[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2018: 1-125.
[42] 文荣琴. 贵州寒武纪杷榔组大型双瓣壳节肢动物系统古生物学和古生态学研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2019: 1-157.
Wen R Q. Systematics and paleoecology of large bivalved arthropods from the Balang Formation (Cambrian), Guizhou, China[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2019: 1-157.
[43] 赵方臣, 朱茂炎, 胡世学. 不同生活方式的物种对快速沉积埋藏事件的反应——来自寒武纪早期澄江生物群中的证据[J]. 古生物学报, 2012, 51(3): 265-280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX201203002.htm
Zhao F C, Zhu M Y, Hu S X. Diverse responses of Cambrian organisms to sedimentary events: Evidence from the Chengjiang Lagerstätte of eastern Yunnan[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2012, 51(3): 265-280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX201203002.htm
[44] Lin J P. Taphonomy of naraoiids (arthropoda) from the Middle Cambrian Kaili Biota, Guizhou Province, South China[J]. Palaios, 2006, 21(1): 15-25.
[45] Daley A C, Drage H B. The fossil record of ecdysis, and trends in the moulting behaviour of trilobites[J]. Arthropod Structure & Development, 2016, 45(2): 71-96.
[46] 朱茂炎. 云南澄江化石群埋藏学[D]. 南京: 中国科学院南京地质古生物研究所, 1992: 1-111.
Zhu M Y. Taphonomy of the Chengjiang Lagerstätte of Yunnan, China[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1992: 1-111.
[47] 张兴亮, 舒德干. 试论动物非矿化组织的保存[J]. 沉积学报, 2001, 19(1): 13-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200101002.htm
Zhang X L, Shu D G. Preservation mechanisms of non-mineralized animal tissues[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2001, 19(1): 13-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200101002.htm
[48] Zhu M Y, Babcock L E, Steiner M. Fossilization modes in the Chengjiang Lagerstätte (Cambrian of China): Testing the roles of organic preservation and diagenetic alteration in exceptional preservation[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2005, 220(1/2): 31-46.
[49] Butterfield N J. Organic preservation of non-mineralizing organisms and the taphonomy of the Burgess shale[J]. Paleobiology, 1990, 16(3): 272-286.
[50] Martin D, Briggs D E G, Parkes R J. Experimental mineralization of invertebrate eggs and the preservation of Neoproterozoic embryos [J]. Geology, 2003, 31(1): 39-42.
[51] 陈蕾, 张洪霞, 李莹, 等. 微生物在地球化学铁循环过程中的作用[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2016, 46(9): 1069-1078. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCXK201609003.htm
Chen L, Zhang H X, Li Y, et al. The role of microorganisms in the geochemical iron cycle[J]. Science China Vitae, 2016, 46 (9): 1069-1078. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCXK201609003.htm
[52] 邵丽鸥. 小小洞天——微生物世界[M]. 长春: 吉林美术出版社, 2014: 48-49.
Shao L O. Microbial world[M]. Changchun: Jilin Fine Arts Publishing House, 2014: 48-49. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: