SEGMENTATION CHARACTERISTICS OF LANLIAO FAULT IN NORTHERN HEZE UPLIFT AND ITS CONTROL ON KARST GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR
-
摘要:
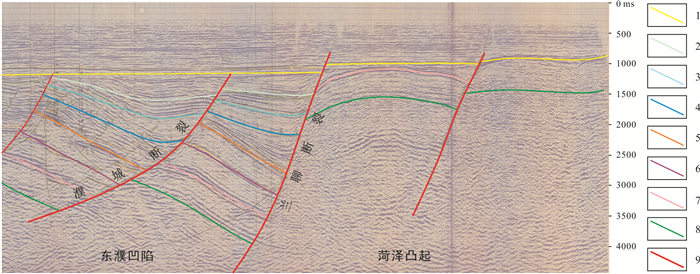
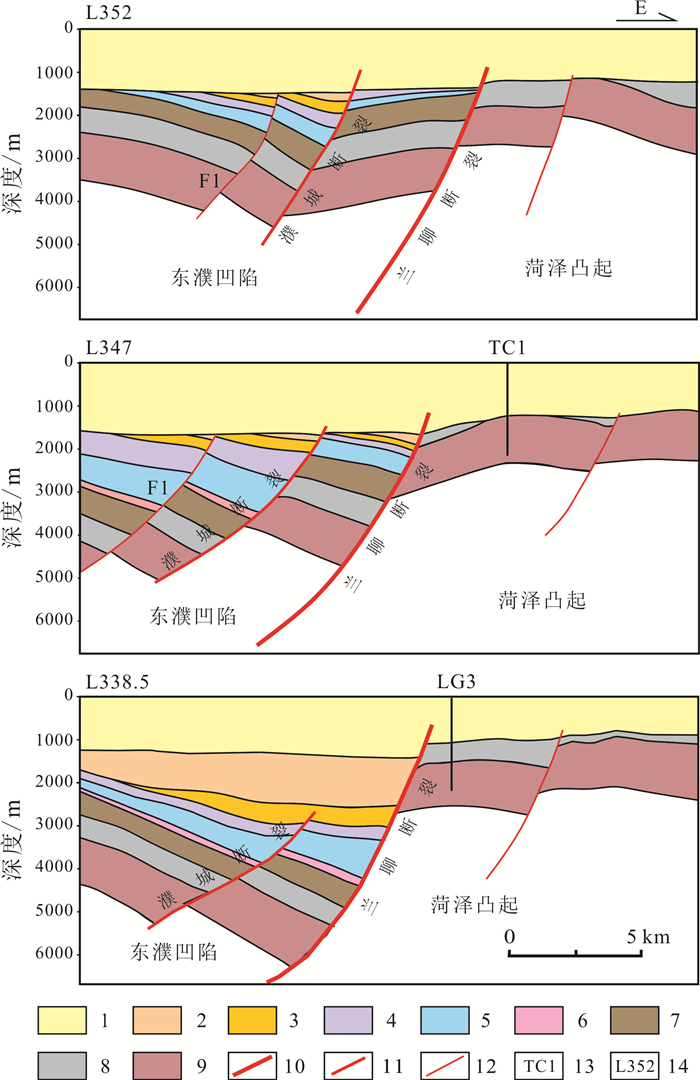
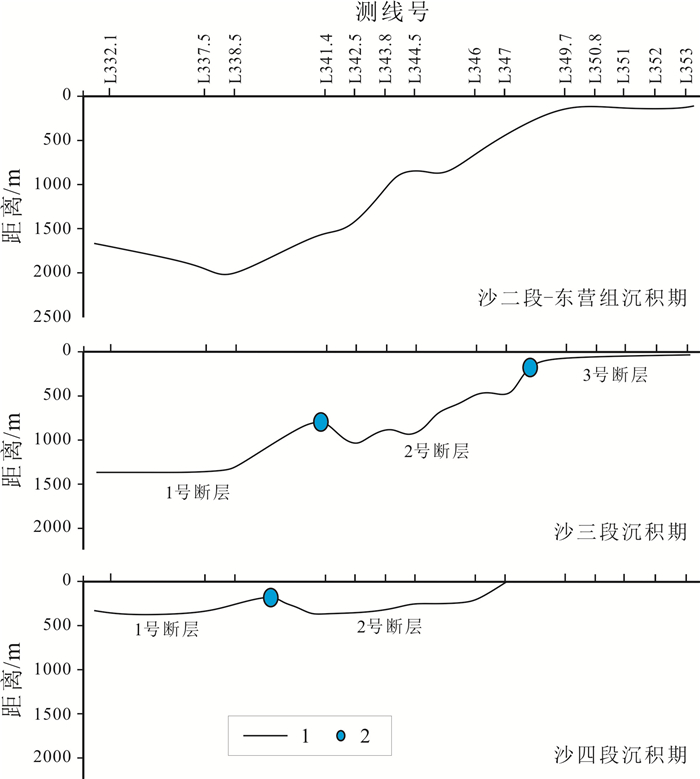
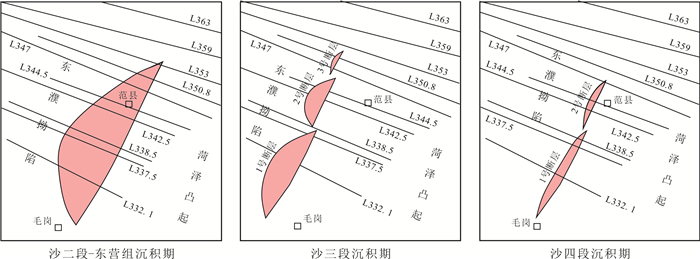
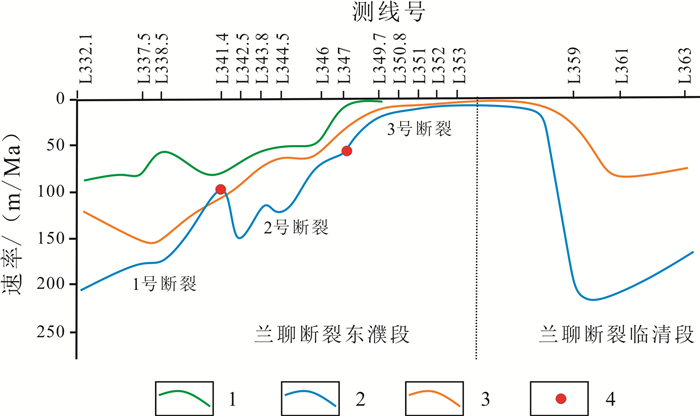
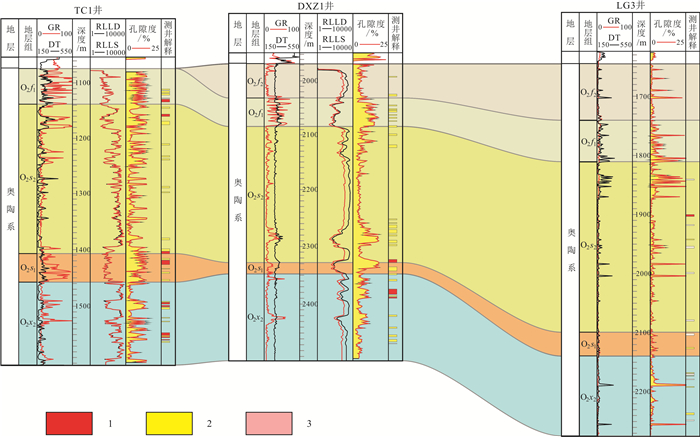
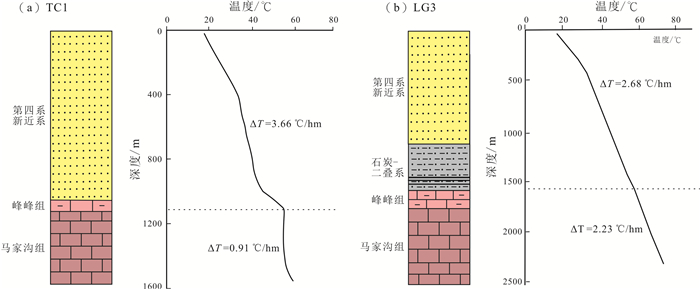
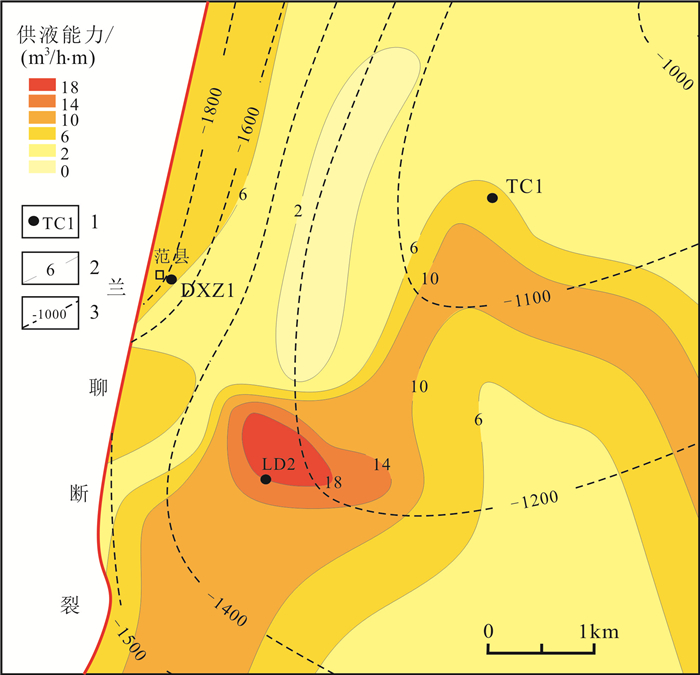
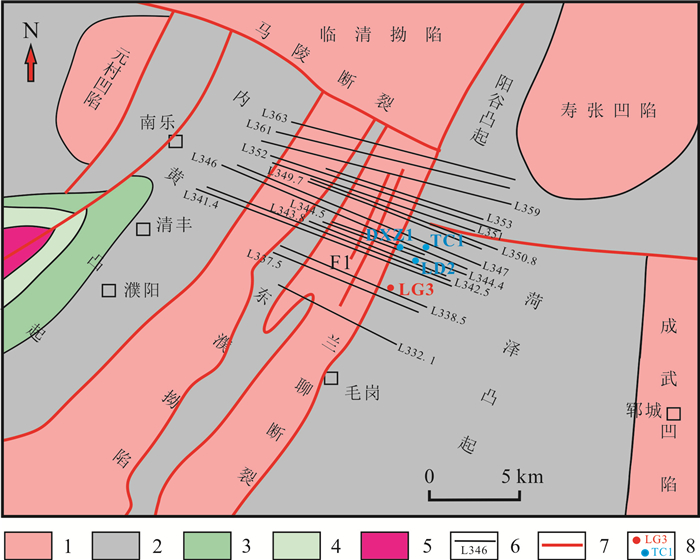
基于地震、钻测录井及其他生产测试资料,采用定性分析和定量研究相结合的方式对菏泽凸起北部兰聊断裂生长过程进行反演,并探讨其对岩溶热储的控制作用.研究表明,菏泽凸起北部兰聊断裂在演化过程中呈现三段式结构,具有早期分段-晚期连锁的特征.沙河街组沉积初期,断层分段特征初见雏形;到沙三段沉积期,各个断层分段明显,具有独立正断层位移分布特征;至沙二段—东营组沉积期,各个断层侧向生长最终连接为一条大断裂.断层分段特征的差异性对研究区岩溶热储的空间展布、热传递差异和产能具有重要的控制作用.断层演化过程中,中部2号断裂系总垂直位移相对于南部1号断裂系和北部3号断裂系更大,剖面上为顺向排列的滚动半地堑构造组合样式,菏泽凸起隆升更明显,局部基岩剥蚀严重.该部位岩溶热储具有埋藏浅、岩溶裂缝发育、盖层平均地温梯度高、产能较好的特点,是地热勘探开发的最有利区域.
Abstract:Based on the seismic, drill logging and other production test data, the qualitative analysis and quantitative study are used for inversion of the growth process of Lanliao fault in northern Heze uplift, as well as its control effect on karst geothermal reservoir. The results show that the evolution of Lanliao fault can be divided into three stages, characterized by segmentation in early stage and linkage in late stage. In the early sedimentary stage of Shahejie Formation, the fault segmentation began to appear. Through the depositional stage of Sha-3 Member, each fault segmentation was obvious with the displacement characteristics of independent normal fault. To the depositional stage of Sha-2 Member-Dongying Formation, the fault segmentations grew laterally and eventually connected as a large fault. The difference of fault segmentation characteristics is significant to control the spatial distribution, heat transfer and productivity of karst geothermal reservoir in the study area. During the evolution of the faults, the total vertical displacement of No. 2 fault system in the middle is larger than that of No. 1 fault system in the south and No. 3 fault system in the north, showing a rolling half-graben structure association pattern in a forward arrangement in the profile, and the rise of Heze uplift is more obvious with serious bedrock denudation partially. The karst geothermal reservoir in the area is characterized by shallow burial, developed karst fracture, high average geothermal gradient of cap rock and good productivity, which is the most favorable for geothermal exploration and development.
-
Key words:
- karst geothermal reservoir /
- geothermal exploration /
- fault segmentation /
- Lanliao fault /
- Heze uplift
-

-
[1] Cartwright J A, Trudgill B D, Mansfield C S. Fault growth by segment linkage: An explanation for scatter in maximum displacement and trace length data from the Canyonlands Grabens of SE Utah[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1995, 17(9): 1319–1326. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(95)00033-A
[2] Peacock D C P. Displacements and segment linkage in strike-slip fault zones[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1991, 13(9): 1025–1035. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(91)90054-M
[3] Davis K, Burbank D W, Fisher D, et al. Thrust-fault growth and segment linkage in the active Ostler fault zone, New Zealand[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2005, 27(8): 1528–1546. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2005.04.011
[4] 杜彦男, 吴孔友, 刘寅, 等. 断陷盆地边界断裂结构特征及物性差异定量评价: 以车镇凹陷埕南断裂为例[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(3): 405–417. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ202003009.htm
Du Y N, Wu K Y, Liu Y, et al. The development of fault zone architecture of deep buried boundary faults in the rift basin: A case from the Chengnan fault of the Chezhen depression[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science), 2020, 56(3): 405–417. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ202003009.htm
[5] Trudgill B, Cartwright J. Relay-ramp forms and normal-fault linkages, Canyonlands National Park, Utah[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1994, 106(9): 1143–1157. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1994)106<1143:RRFANF>2.3.CO;2
[6] 柏道远, 李彬, 李银敏, 等. 湖南常德-安仁断裂印支期构造运动分段性: 来自花岗岩的约束[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 173–187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202105019.htm
Bai D Y, Li B, Li Y M, et al. Segmentation of the movement in Indosinian of the Changde-Anren fault in Hunan: Constraints from granite[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40 (5): 173–187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202105019.htm
[7] 王海学, 吕延防, 付晓飞, 等. 裂陷盆地转换带形成演化及其控藏机理[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(4): 102–110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201304017.htm
Wang H X, Lü Y F, Fu X F, et al. Formation, evolution and reservoir-controlling mechanism of relay zone in rift basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(4): 102–110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201304017.htm
[8] Peacock D C P, Sanderson D J. Displacements, segment linkage and relay ramps in normal fault zones[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1991, 13(6): 721–733. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(91)90033-F
[9] 雷宝华. 生长断层活动强度定量研究的主要方法评述[J]. 地球科学进展, 2012, 27(9): 947–956. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201209005.htm
Lei B H. Review of methods with quantitative studies of activity intensity of the growth fault[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2012, 27 (9): 947–956. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201209005.htm
[10] 陈刚, 戴俊生, 叶兴树, 等. 生长指数与断层落差的对比研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报, 2007, 29(3): 20–23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY200703005.htm
Chen G, Dai J S, Ye X S, et al. A comparison of the fault growth index with fault throw[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University 2007, 29(3): 20–23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY200703005.htm
[11] Muraoka H, Kamata H. Displacement distribution along minor fault traces[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1983, 5(5): 483–495. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(83)90054-8
[12] 施发剑. 兰聊断裂带的形成与演化[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2012.
Shi F J. The formation and evolution of Lanliao fault zone[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2012.
[13] 余海波, 程秀申, 徐田武, 等. 东濮凹陷古近系构造特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2021, 28(3): 42–52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202103006.htm
Yu H B, Cheng X S, Xu T W, et al. Paleogene tectonic characteristics and their controlling effect on hydrocarbon accumulation in Dongpu Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2021, 28(3): 42–52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202103006.htm
[14] 张亚敏, 吕延仓, 徐林丽, 等. 东濮凹陷兰聊断裂带构造演化与油气勘探[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2000, 21(1): 57–60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200001014.htm
Zhang Y M, Lü Y C, Xu L L, et al. Structural evolution and hydrocarbon exploration of Lanliao fault belt in Dongpu depression [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2000, 21(1): 57–60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200001014.htm
[15] 孙思敏, 彭仕宓, 汪新文. 东濮凹陷兰聊断层的分段特征及其石油地质意义[J]. 石油学报, 2003, 24(4): 26–30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200304007.htm
Sun S M, Peng S M, Wang X W. Segmentation characteristics of Lanliao fault in Dongpu depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2003, 24(4): 26–30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200304007.htm
[16] 孙思敏, 彭仕宓, 汪新文, 等. 东濮凹陷长垣断层系中转换斜坡的特征与油气勘探[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(1): 22–24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200301007.htm
Sun S M, Peng S M, Wang X W, et al. The characteristic of relay ramps in fault system of the placanticline in Dongpu sag and their relevance to hydrocarbon exploration[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(1): 22–24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200301007.htm
[17] 孙思敏. 东濮凹陷调节构造特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2007, 14 (2): 38–41, 46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200702010.htm
Sun S M. Characteristics of accommodation structures in Dongpu sag [J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2007, 14(2): 38–41, 46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200702010.htm
[18] 孙思敏, 彭仕宓, 汪新文. 东濮凹陷长垣断层的生长特征与半地堑演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2003, 24(2): 123–125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200302004.htm
Sun S M, Peng S M, Wang X W. Growing characteristics of Changyuan fault and half-graben evolution in Dongpu depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2003, 24(2): 123–125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200302004.htm
[19] 尚墨翰. 东濮凹陷构造-沉积演化与油气成藏的关系[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2014, 21(4): 50–53, 57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201404012.htm
Shang M H. Relationship between structural-depositional evolution and oil-gas accumulation in Dongpu sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2014, 21(4): 50–53, 57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201404012.htm
[20] 杨询昌, 周世海, 王成明. 山东省深部岩溶热储埋藏分布及岩溶发育特征[J]. 山东国土资源, 2013. 29(4): 8–12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI201304005.htm
Yang X C, Zhou S H, Wang C M. Distribution of deep karst thermal reservoir and karst development characteristics in Shandong Province [J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2013, 29(4): 8–12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI201304005.htm
[21] 康凤新, 隋海波, 郑婷婷. 山前岩溶热储聚热与富水机理: 以济南北岩溶热储为例[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(5): 1606–1624. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202005018.htm
Kang F X, Sui H B, Zheng T T. Heat accumulation and water enrichment mechanism of piedmont karstic geothermal reservoirs: A case study of northern Jinan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94 (5): 1606–1624. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202005018.htm
[22] 刘树亮, 刘子勇, 高中显, 等. 山东地区基岩岩溶热储分布特征及资源潜力评价[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(6): 699–708. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201906002.htm
Liu S L, Liu Z Y, Gao Z X, et al. Distribution characteristics and resource potential of thermal bedrock karst reservoirs in Shandong[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(6): 699–708. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201906002.htm
[23] 刘金侠, 毛翔, 季汉成, 等. 东濮凹陷奥陶系岩溶型热储分布特征及成因研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(3): 180–189. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201703021.htm
Liu J X, Mao X, Ji H C, et al. Distribution and genesis of karstic thermal reservoir in Dongpu depression[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(3): 180–189. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201703021.htm
[24] 王贵玲, 张薇, 蔺文静, 等. 京津冀地区地热资源成藏模式与潜力研究[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(6): 1074–1085. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201706004.htm
Wang G L, Zhang W, Lin W J, et al. Research on formation mode and development potential of geothermal resources in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(6): 1074–1085. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201706004.htm
[25] 毛小平, 汪新伟, 李克文, 等. 地热田热量来源及形成主控因素[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(11): 4256–4266. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201811040.htm
Mao X P, Wang X W, Li K W, et al. Sources of heat and control factors in geothermal field[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(11): 4256–4266. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201811040.htm
[26] 郭飒飒, 朱传庆, 邱楠生, 等. 雄安新区深部地热资源形成条件与有利区预测[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7): 2026–2035. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202007011.htm
Guo S S, Zhu C Q, Qiu N S, et al. Formation conditions and favorable areas for the deep geothermal resources in Xiong'an New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7): 2026–2035. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202007011.htm
[27] 曹瑛倬, 鲍志东, 鲁锴, 等. 冀中坳陷雄县地热田主控因素及成因模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(4): 863–872. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202104006.htm
Cao Y Z, Bao Z D, Lu K, et al. Genetic model and main controlling factors of the Xiongxian geothermal field[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(4): 863–872. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202104006.htm
[28] 汪新伟, 郭世炎, 高楠安, 等. 雄安新区牛东断裂带碳酸盐岩热储探测及其对地热勘探的启示[J]. 地质通报, 2023, 42(1): 14–26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202301002.htm
Wang X W, Guo S Y, Gao N A, et al. Detection of carbonate geothermal reservoir in Niudong fault zone of Xiong'an New Area and its geothermal exploration significance[J]. Geology Bulletin of China, 2023, 42(1): 14–26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202301002.htm
[29] 梁富康. 东濮凹陷南部沙三段沉积体系展布及岩性圈闭区带预测[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2011.
Liang F K. Depositional system and lithologic traps in the third member of the Shahejie Formation, South of Dongpu sag[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2011.
[30] 高红灿, 郑荣才, 陈发亮, 等. 渤海湾盆地东濮凹陷古近系沙河街组层序地层[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(6): 839–850. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201106006.htm
Gao H C, Zheng R C, Chen F L, et al. Sequence stratigraphy of the Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Dongpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2011, 32(6): 839–850. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201106006.htm
[31] Su J B, Zhu W B, Wei J, et al. Fault growth and linkage: Implications for tectonosedimentary evolution in the Chezhen Basin of Bohai Bay, eastern China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2011, 95(1): 1–26.
[32] Anders M H, Schlische R W. Overlapping faults, intrabasin highs, and the growth of normal faults[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1994, 102(2): 165–179.
[33] Schlische R W. Geometry and origin of fault-related folds in extensional settings[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1995, 79(11): 1661–1678.
[34] Dawers N H, Anders M H. Displacement-length scaling and fault linkage[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1995, 17(5): 607–614.
[35] 赵勇, 戴俊生. 应用落差分析研究生长断层[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(3): 13–15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200303003.htm
Zhao Y, Dai J S. Identification of growth fault by fault fall analysis [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(3): 13–15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200303003.htm
[36] 王领法, 张尚坤, 谢寅骧, 等. 菏泽凸起地下热水资源成矿地质条件研究[J]. 菏泽师专学报, 2002, 24(2): 25–27, 35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZSB200202005.htm
Wang L F, Zhang S K, Xie Y X, et al. Study of the geological conditions of the underground hot-water resources of Heze salient[J]. Journal of Heze Teachers College, 2002, 24(2): 25–27, 35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZSB200202005.htm
[37] 赵迎冬, 甘华军, 时阳, 等. 北部湾盆地福山凹陷异常地温特征及其对油气藏的影响[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2016, 23(3): 40–46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201603007.htm
Zhao Y D, Gan H J, Shi Y, et al. Characteristics of geothermal anomaly and its effect on oil and gas reservoir in Fushan sag of Beibuwan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2016, 23(3): 40–46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201603007.htm
[38] 朱铁军. 东营凹陷中央隆起带地温场建立及地热系统发育模式[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2021, 28(2): 68–75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202102011.htm
Zhu T J. Establishment of geothermal field and development model of geothermal system in central uplift belt of Dongying Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2021, 28(2): 68–75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202102011.htm
[39] 王朱亭, 张超, 姜光政, 等. 雄安新区现今地温场特征及成因机制[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(11): 4313–4322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201911026.htm
Wang Z T, Zhang C, Jiang G Z, et al. Present-day geothermal field of Xiongan New Area and its heat source mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(11): 4313–4322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201911026.htm
[40] 宿宇驰, 毛小平, 张飞, 等. 沧县隆起北部地温场特征及其主控因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(2): 403–411. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202102010.htm
Su Y C, Mao X P, Zhang F, et al. Characteristics and major controlling factors of geothermal field of North Cangxian uplift[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(2): 403–411. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202102010.htm
[41] 王思琪, 张保建, 李燕燕, 等. 雄安新区高阳地热田东北部深部古潜山聚热机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 12–21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202103002.htm
Wang S Q, Zhang B J, Li Y Y, et al. Heat accumulation mechanism of deep ancient buried hill in the northeast of Gaoyang geothermal field, Xiong'an New Area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 12–21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202103002.htm
[42] 黄旭, 章惠, 汪新伟, 等. 渤海湾盆地南乐地热田特征及其成因分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 71–82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202105010.htm
Huang X, Zhang H, Wang X W, et al. Characteristics and mechanism analysis of geothermal field in Nanle sub-uplift, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 71–82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202105010.htm
[43] 汪新伟, 王婷灏, 张瑄, 等. 太原盆地西温庄地热田的成因机制[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(3): 1042–1056. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201903030.htm
Wang X W, Wang T H, Zhang X, et al. Genetic mechanism of Xiwenzhuang geothermal field in Taiyuan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(3): 1042–1056. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201903030.htm
-



 下载:
下载: