Research Progress of Microwave Heating in Rare Earth Metallurgy and New Material Synthesis
-
摘要:
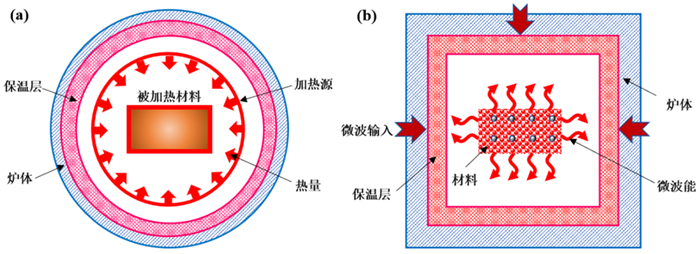
综述了微波加热技术在稀土冶金和稀土新材料合成领域的国内外研究与应用现状,发现微波加热通过物料能量耗散,对介质直接加热,具有加热效率高、能量利用率高、明显改善产品性能等优势。微波加热作为一种新型的冶金技术越来越受到关注,随着研究的深入,其在稀土冶金与稀土新材料合成领域必将发挥重要的作用,具有广阔的发展前景。
Abstract:The development and current applications of microwave heating in the field of rare earth metallurgy and new material synthesis are reviewed. It is found that microwave heating directly heats the materials through material energy dissipation, and has the advantages of high heating efficiency, high energy utilization, significantly improving product performance, and so on. As a new heating mode, microwave heating is attracted more and more attention, with the development of research, it would play an important role in the fields of rare earth metallurgy and new material synthesis, and has wide application prospects.
-
Key words:
- rare earth metallurgy /
- material synthesis /
- microwave heating
-

-
[1] SADRI F, NAZARI AM, GHAHREMAN A. A review on the cracking, baking and leaching processes of rare earth element concentrates[J]. Rare Earth, 2017, 35(8):739-752.
[2] 陶春.中国稀土资源战略研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学, 2011.
[3] LI M, LI JF, ZHANG DL, et al. Decomposition of Mixed Rare Earth Concentrate by NaOH Roasting and Kinetics of Hydrochloric Acid Leaching Process[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2019, 38(9):1019-1029.
[4] WYSOCKA I. Determination of rare earth elements concentrations in natural waters-a review of ICP-MS measurement approaches[J]. Talanta, 2020, 221:121636.
[5] LI DQ. Development course of separating rare earths with acid phosphorus extractants:A critical review[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2019, 37(5):468-486.
[6] WANG XB, YAO MT, LI JS, et al. Global Embodied Rare Earths Flows and the Outflow Paths of China's Embodied Rare Earths:Combining Multi-Regional Input-Output Analysis with the Complex Network Approach[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 216:435-445.
[7] 刘海力, 马晓茜, 郭平生, 等.餐厨垃圾的微波干燥特性及动力学模型[J].科学通报, 2014, 59(10):936-942.
[8] 丁泽智, 杨晚生.微波加热技术的现状与发展分析[J].南方农机, 2019, 50(5):152.
[9] 王永洪, 陈旭国, 赵海波, 等.微波技术在橡胶加工中的应用研究进展[J].热带农业科学, 2007, 27(6):59-63.
[10] 刘书祯, 白燕, 程艳明, 等.微波技术在冶金中的应用[J].湿法冶金, 2011, 30(2):91-94.
[11] LI SC, YUE XH. Application of Microwave in Mineral processing[J]. Metal Mine, 2006, 156(4):155-162.
[12] 金钦汉, 戴树珊, 黄卡玛.微波化学[M].北京:科学出版社, 1999.
[13] 王彪.微波加热过程中热点效应的试验与模拟研究[D].山东: 山东大学, 2017.
[14] JONES DA, LELYVELD TP, MAVROFLDIS SD, et al. Microwave heating applications in environmental engineering-a review[J]. Resources Conservation & Recycling, 2002, 32(4):75-90.
[15] 邓秀文.吸波材料研究进展[J].化工时刊, 2007, 21(8):58-65.
[16] 杨瑾.微波加热与传统加热方式的异同[J].工程机械与维修, 2006(4):89-90.
[17] 刘晨辉.基于冶金物料介电特性的微波加热应用新工艺研究[D].昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2014.
[18] ZHONG CB, XU CL, LYU RL, et al. Enhancing mineral liberation of a Canadian rare earth ore with microwave pretreatment[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2018, 36(2):215-224.
[19] HUANG YK, ZHANG TA, LIU J, et al. Decomposition of the mixed rare earth concentrate by microwave-assisted method[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2016, 34(5):529-535.
[20] 许延辉, 马升峰, 郭文亮, 等.微波场中氟碳铈矿和独居石混合稀土精矿的升温特性研究[J].冶金工程, 2019, 6(2):89-97.
[21] 李解, 李成元, 李保卫, 等.微波加热低品位稀土精矿酸浸实验研究[J].稀有金属, 2014, 38(5):839-845.
[22] SHUKLA N, DHAWAN N. Rapid microwave processing of discarded tubular lights for extraction of rare earth values[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 142:238-249.
[23] HUANG YK, ZHANG TA, DOU ZH, et al. Influence of microwave heating on the extractions of fluorine and Rare Earth elements from mixed rare earth concentrate[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2016, 162:104-110.
[24] LIE J, ISMADJI S, LIU JC. Microwave-assisted leaching of rare earth elements (Y and Eu) from waste cathode ray tube phosphor[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2019, 94(12):3859-3865.
[25] 彭金辉, 夏洪应.微波冶金[M].北京:科学出版社, 2016:102-108.
[26] 尹少华, 林国, 彭金辉, 等.响应曲面法优化微波干燥碳酸稀土的实验研究[J].稀有金属, 2016, 40(4):350-355.
[27] 黎峰, 卢铁城, 马奔原, 等.微波干燥对YAG纳米粉体分散性和粒径的影响[J].四川大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 49(2):413.
[28] 李解, 王少炳, 李保卫, 等.微波辅助硫酸低温焙烧稀土精矿试验研究[J].稀土, 2013, 34(6):45-50.
[29] 王少炳.微波辅助浓硫酸低温焙烧稀土精矿的实验研究[D].包头: 内蒙古科技大学, 2013.
[30] CHEN KH, PENG JH, SRINIVASAKANNAN C, et al. Effect of Temperature on the Preparation of Yttrium Oxide in Microwave Field[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 742:13-19.
[31] CHEN KH, GUO SH, ZENG YQ, et al. Facile preparation and characterization of lanthanum oxide powders by the calcination of lanthanum carbonate hydrate in microwave field[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(1):165-170.
[32] 欧阳成, 周蓉, 荆旭冬.微波-超声波协同作用下氧化铈的制备与表征[J].湿法冶金, 2014, 33(4):305-308.
[33] 曾青云, 郭守金, 薛丽燕, 等.外场辅助制备低氯氧化镧前驱体[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2018, 9(5):7-13.
[34] YIN SH, CHEN KH, SRINIVASAKANNAN C, et al. Enhancing recovery of ammonia from rare earth wastewater by air stripping combination of microwave heating and high gravity technology[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 337:515-521.
[35] LAN X, GAO JT, DU Y, et al. Effect of super gravity on successive precipitation and separation behaviors of rare earths in multi-components rare-earth system[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 228.
[36] 江静华, 方峰, 谈淑泳, 等.稀土元素及稀土新材料[J].2000(3): 45-48.
[37] COEY JMD. Perspective and Prospects for Rare Earth Permanent Magnets[J]. Engineering, 2020, 6(2):42-68.
[38] 刘博林.稀土发光材料的研究进展[D].吉林: 东北师范大学, 2008.
[39] BI JW, SUN LX, WEI QM, et al. Rapid ultrasonic-microwave assisted synthesis of Eu3+ doped Y2O3 nanophosphors with enhanced luminescence properties[J]. Nanotechnology Weekly, 2020, 9(5):9523-9530.
[40] CHANDEKAR KV, KHAN A, ALSHAHRANI T, et al. Novel rare earth Dy doping impact on physical properties of PbI2 nanostructures synthesized by microwave route for optoelectronics[J]. Materials Characterization, 2020:110688.
[41] 李娴, 叶旭, 张洪强.稀土掺杂钨酸盐发光材料的微波固相合成及发光性能研究[J].广东化工, 2015, 42(17):18-19, 35.
[42] 韩英.稀土离子掺杂的钼酸钙基发光材料的微波合成及其性能研究[D].河北: 河北大学, 2017.
[43] 周先波, 崔晴, 沈海峰, 等.氧化锌/铈纳米材料的微波合成及其光催化性能研究[J].化工新型材料, 2019, 47(8):148-152, 157.
[44] 陈洪亮.稀土氧化物纳米材料的超声(微波)合成及其催化性能研究[D].南京: 南京大学, 2006.
[45] ALKETBI M, POLYEHRONOPOULOU K, ZEDAN AF, et al. Tuning the activity of Cu-containing rare earth oxide catalysts for CO oxidation reaction:Cooling while heating paradigm in microwave-assisted synthesis[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2018, 108:142-150.
[46] CHENG J, SONG LY, WU R, et al. Promoting effect of microwave irradiation on CeO2-TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2020, 38(1):59-69.
[47] 杨建利, 晏志军, 张润兰, 等.加入柠檬酸微波合成超微分子筛[J].应用化工, 2010, 39(12):1868-1870.
[48] 彭森, 盛安妮.微波加热技术在烧结陶瓷材料中的应用分析[J].环球市场, 2019(27):386.
[49] 丁明桐, 杜先智, 陈凡, 等.Y-ZrO2稀土增韧陶瓷的微波烧结[J].安徽师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2000(4):344-347.
[50] TANG Z, HUANG ZY, HAN W, et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of uranium doped Y2Zr2O7 transparent ceramics as potential near-infrared optical lens[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2020, 178:90-93.
[51] AHMAD S, MAHMOUD MM, SEIFERT HJ. Crystallization of two rare-earth aluminosilicate glass-ceramics using conventional and microwave heat-treatments[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 797:45-57.
[52] 杨玉梅.稀土永磁材料的研究与应用[J].中国粉体工业, 2020(2):27-30.
[53] 葛海.微波磁场烧结NdFeB磁体的工艺与性能研究[D].武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2004.
[54] 李丽娅, 易健宏, 彭元东.钐钴基稀土永磁材料的微波时效处理方法: CN104233138A[P].2014-12-24.
[55] 殷毅.稀土超磁致伸缩材料及其应用研究现状[J].磁性材料及器件, 2018, 49(3):57-60.
[56] BHONGALE SR, INGAWALE HR, SHINDE TJ, et al. Effect of Nd3+ substitution on structural and magnetic properties of Mg-Cd ferrites synthesized by microwave sintering technique[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2018, 36(4):390-397.
-



 下载:
下载: