Research on Electrochemical Action to Promote Slime Water Settlement Based on EDLVO Theory
-
摘要:
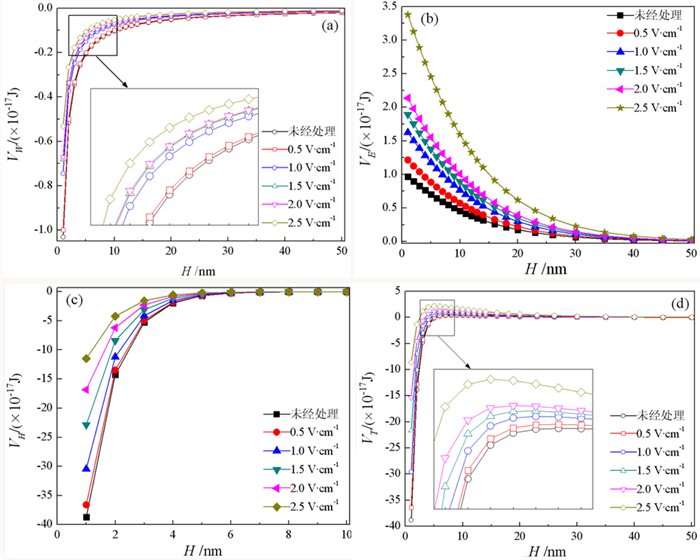
以褐煤煤泥、纯褐煤、伊利石、纯褐煤与伊利石体系为研究对象,探索了不同电位梯度条件下褐煤煤泥水和由纯矿物配制的悬浮液的沉降性能,借助EDLVO理论及扫描电镜分析了电化学作用强化褐煤煤泥水沉降的作用机理。沉降试验结果表明:电化学作用使纯褐煤悬浮液的沉降效果恶化,使伊利石、褐煤煤泥和纯褐煤与伊利石悬浮液的沉降效果改善。EDLVO计算结果表明:电化学作用下,纯褐煤颗粒间总作用能增大,表现为吸引能减弱;伊利石、纯褐煤与伊利石颗粒间总作用能减小,表现为排斥能减弱;且三种悬浮液体系都是极性吸引能起主导作用。当电位梯度为2 V/cm时,纯褐煤与伊利石颗粒间的总作用能达到最小值,沉降效果最好。本文为实现褐煤的煤泥水高效处理提供了新思路。
Abstract:In order to explore the interaction between particles in coal slime water under electrochemical action and its influence on condensation and settlement effect, first, under the condition of different potential gradient sedimentation experiment was carried out on the original coal slime and suspension, and then by coal, illite, coal and illite system as the research object, through the determination and calculation different electrochemical conditions of the coal and illite Debye length, zeta potential and surface energy parameters, with the aid of EDLVO theory for calculation, interaction energy between particles and scanning electron microscope before and after electrochemical treatment on coal and illite surface microstructure observation, the study and analysis of electrochemical mechanism. The settlement test results showed that the electrochemical action worsened the settlement effect of coal suspension and improved the settlement effect of clay suspension. The settlement effect was the best when the potential gradient was 2 V/cm for the original coal slime, coal and clay suspension, and the curve variation trend was basically the same. The results of EDLVO showed that under electrochemical action, the total interaction energy between coal particles increases, and the attraction energy decreases. The total interaction energy between illite, coal and illite particles decreased, and the repulsion energy decreased. And the three suspension systems are polar attraction can play a dominant role. The electrochemical action can obviously reduce the "energy barrier" of the total interaction energy between particles. When the potential gradient is 2 V/cm, the total interaction between coal and illite particles can reach the minimum value. The theoretical calculation results are consistent with the settlement test results, and the action mechanism of electrochemical action to promote the coalesce and settlement of lignite slime water is analyzed.
-
Key words:
- coal slime water /
- electrochemical action /
- settlement /
- interaction /
- EDLOV theory
-

-
表 1 煤泥的工业分析
Table 1. Industrial analysis of slime
/% 项目 Mad Ad Vdaf FCdaf 数值 13.36 65.14 52.32 47.68 注:Mad——空气干燥基水分;Ad——干燥基灰分;Vdaf——干燥无灰基挥发分;FCdaf——干燥无灰基固定碳。 表 3 电化学处理后样品的ζ电位
Table 3. Electrochemical treatment of the ζ potential of the sample
/mV 电位梯度/(V·cm-1) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 纯褐煤 -18.3 -20.5 -23.7 -25.6 -27.2 -34.2 伊利石 -52.0 -19 -14.2 -11.8 -5.6 -9.6 表 4 三种液体的表面能参数
Table 4. Surface energy parameters of three liquids
/(mJ·m-2) 介质名称 γ γLW γ+ γ- 水 72.8 21.8 25.5 25.5 丙三醇 64 34 3.92 57.4 甲醛 58 39 2.28 39.6 表 5 电化学处理后纯褐煤和伊利石的接触角
Table 5. Contact angle of coal and illite after electrochemical treatment
/(°) 电位梯度/(V·cm-1) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 煤 水 61.3 60.3 58.0 55.0 52.3 49.5 丙三醇 49.5 48.0 44.5 42.5 40.8 37.5 甲醛 32.5 30.8 28.0 26.0 23.8 20.5 伊利石 水 20.0 22.5 27.0 36.5 41.5 39.0 丙三醇 26.0 27.5 30.8 38.0 43.0 41.3 甲醛 21.3 23.3 28.3 37.0 42.0 40.0 表 6 电化学处理后纯褐煤和伊利石的表面能参数
Table 6. Surface energy parameters of coal and illite after electrochemical treatment
/(mJ·m-2) 电位梯度/(V·cm-1) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 煤 γ 55.4 55.6 54.1 54.2 54.8 54.8 γLW 51.8 51.2 46.5 45.2 45.0 42.1 γ+ 0.3 0.4 1.0 1.2 1.3 2.0 γ- 12.3 12.7 13.7 16.1 18.3 20.1 伊利石 γ 58.3 57.7 56.3 52.4 49.0 52.2 γLW 21.6 21.1 18.7 15.5 14.8 16.4 γ+ 6.7 6.8 7.4 7.9 7.2 7.4 γ- 50.4 49.3 47.8 43.0 40.5 43.3 表 7 电化学处理后纯褐煤和伊利石颗粒在水中相互作用能的Lewis分量
Table 7. Lewis components of the interaction energy between coal and illite particles in water after electrochemical treatment
/(mJ·m-2) 电位梯度/(V/cm) ΔG131AB ΔG232AB ΔG132AB ΔG131 ΔG232 ΔG132 0 -27.78 20.18 10.86 -40.56 20.18 15.96 0.5 -26.26 19.26 10.16 -38.62 19.25 15.28 1 -21.84 17.37 8.82 -31.09 17.13 13.80 1.5 -16.41 13.50 7.28 -24.84 12.43 12.85 2 -12.07 12.44 6.62 -20.39 11.09 12.34 2.5 -8.24 14.26 8.49 -14.86 13.49 13.37 注:1—纯褐煤,2—伊利石,3—水。 表 8 电化学处理后纯褐煤和伊利石颗粒在真空和水中Hamaker常数
Table 8. Electrochemical treatment of coal and illite particles in vacuum and water after the Hamaker constant
/(10-20 J) 电位梯度/(V·cm-1) A11 A22 A131 A232 A132 0 9.74 4.06 1.201 3 0.000 1 -0.010 9 0.5 9.63 3.97 1.162 9 0.00 1 -0.034 9 1 8.74 3.52 0.867 7 0.022 1 -0.138 5 1.5 8.5 2.91 0.793 2 0.101 7 -0.284 1 2 8.46 2.78 0.781 0.127 8 -0.316 0 2.5 7.91 3.08 0.620 4 0.072 8 -0.212 5 注:1—纯褐煤,2—伊利石,3—水;A33为4.10。 -
[1] 张明青, 刘颀, 宋灿灿. 从黏土行为视角认识煤泥水沉降性能[J]. 选煤技术, 2021(1): 44-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XMJS202101005.htm
[2] 张志军, 庄丽, 刘炯天. 选煤水化学——水化学性质对颗粒间相互作用的影响[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(5): 1685-1693. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202105030.htm
[3] 张志军, 孟齐, 刘炯天. 选煤水化学——循环煤泥水系统的水化学性质[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(2): 614-623. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202102025.htm
[4] 李敏恒, 王先鹏, 李凌月, 等. 选煤厂煤泥水沉降效果试验研究[J]. 煤炭加工与综合利用, 2021(4): 13-16. . https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTJG202104004.htm
[5] 刘莉君, 于伟, 李毅红, 等. 超声波辅助煤泥脱水的研究[J]. 选煤技术, 2021(1): 111-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XMJS202101015.htm
[6] ZHAO S, GUO B, PENG Y, et al. An impedance spectroscopy study on the mitigation of clay slime coatings on chalcocite by electrolytes[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2017, 101(9): 40-46.
[7] SHINOHARA Y, TSUBOUCHI N. Effect of the electronic state on low-rank coals with Ca2+ ion exchange[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2020, 1218(5): 128544.
[8] 王浩, 樊攀峰, 郑剑平, 等. 超声电化学协同处理难沉降煤泥水的试验研究[J]. 煤炭工程, 2015, 47(5): 118-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MKSJ201505039.htm
[9] ZHAO W, XU W, ZHONG S, et al. Desulfurization of coal by an electrochemical-reduction flotation technique[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2008, 18(4): 571-574. doi: 10.1016/S1006-1266(08)60296-5
[10] MOUSSOUT H, AHLAFI H, AAZZA M, et al. Interfacial electrochemical properties of natural moroccan ghassoul (stevensite) clay in aqueous suspension[J]. Heliyon, 2020, 6(3): e03634. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03634
[11] 贺斌, 董宪姝, 樊玉萍, 等. 基于EDLVO理论的煤泥水沉降机理的研究[J]. 煤炭技术, 2014, 33(4): 249-251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTJS201404098.htm
[12] LIAO Y, HAO X, AN M, et al. Enhancing low-rank coal flotation using mixed collector of dodecane and oleic acid: effect of droplet dispersion and its interaction with coal particle[J]. Fuel, 2020, 280(7): 118634.
[13] 李明明, 徐硕, 卢冀伟, 等. 电化学作用对伊利石颗粒凝聚沉降性能的影响[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2017(1): 125-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCZL201701029.htm
[14] LIU Z, ZHOU L C, LIU F D, et al. Impact of Al-based coagulants on the formation of aerobic granules: comparison between poly aluminum chloride(PAC) and aluminum sulfate(AS) [J]. The Science of the total environment, 2019, 48(10): 74-84.
[15] CHEN J, MIN F, LIU L. The interactions between fine particles of coal and kaolinite in aqueous, insights from experiments and molecular simulations[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 467(2): 12-21.
[16] YU Y, MA L, XU H, et al. DLVO theoretical analyses between montmorillonite and fine coal under different pH and divalent cations[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 330(7): 147-151.
[17] PIÑERES J, BARRAZA J. Energy barrier of aggregates coal particle-bubble through the extended DLVO theory[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2011, 100(1/2): 14-20.
[18] 张明青, 刘炯天, 王永田. 水质硬度对煤泥水中煤和高岭石颗粒分散行为的影响[J]. 煤炭学报, 2008(9): 1058-1062. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB200809025.htm
[19] GUO B, ZHOU W, LIU S, et al. Effect of γ-ray irradiation on the structure and electrochemical liquefaction of Shenhua coal[J]. Fuel, 2015, 143(3): 236-243.
[20] GUI X, CAO Y, XING Y, et al. A two-stage process for fine coal flotation intensification[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 313(3): 361-368.
[21] DUBE R, HONAKER R. Improving the flotation performance of an oxidized bituminous coal source[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 142(8): 105937.
[22] 程万里, 张秀梅, 邓政斌, 等. 基于EDLVO理论的浮选药剂对煤泥颗粒间的相互作用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(10): 3563-3572. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202010022.htm
[23] 印万忠, 王纪镇. 粒度大小和颗粒间相互作用对白钨矿浮选的影响(英文)[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(11): 3682-3687. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYSY201411033.htm
[24] WANG B, PENG Y. The interaction of clay minerals and saline water in coarse coal flotation[J]. Fuel, 2014, 134(6): 326-332.
[25] LIANG Z, HAN B, LIU H. Optimum conditions to treat high-concentration microparticle slime water with bioflocculants[J]. Mining Science and Technology (China), 2010, 20(3): 478-484.
-



 下载:
下载: